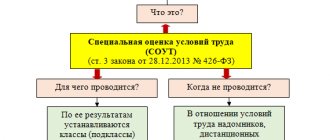
What is occupational safety training?
The procedure for conducting labor safety briefings is a mandatory condition of labor relations, which is regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The employer is obliged to familiarize all employees of the organization with the safety requirements that they must comply with while performing their job duties. Labor safety briefings are carried out:
- in order to familiarize workers with the requirements of local and regulatory legal acts on labor protection;
- with working conditions in the workplace;
- with methods of safe work performance when performing their job duties;
- with existing hazardous and harmful production factors in the workplace.
In other words, during the briefing, the employee is given an explanation of what dangerous factors he will have to face during his work, what labor safety requirements apply in this organization and in what documents this information is recorded.
Who should be trained
According to clause 2.1.1 of the Procedure, all persons hired for work must undergo training. It is also mandatory for employees who are transferred to another job.
REFERENCE
Is safety training necessary for a person who is not on the company’s staff, but performs work or provides services under a civil contract? The answer depends on the terms of the contract. If it states that the customer pays insurance premiums “for injuries” for the contractor (performer), then training should be carried out. This opinion was expressed by the Ministry of Labor in letter No. PG/02487-6-1 dated February 21, 2020 (see “Labor safety: is it necessary to instruct workers with whom GPC agreements have been concluded?”).
Types of labor safety briefings
The types of briefings, the procedure and requirements for organizing them by the employer are established by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation dated January 13, 2003 N 1/29 “On approval of the Procedure for training in labor protection and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements for employees of organizations.”
Resolution 1/29 defines five types of briefings on labor protection: introductory, primary, repeated, unscheduled and targeted. Let's look at each type of instruction in more detail.
Introductory training on labor protection is carried out with all employees of the organization, without exception, upon hiring.
At its core, the introductory briefing is a story about what safety requirements must be observed while on the territory of the organization as a whole.
Introductory training is carried out according to a program approved by the employer, developed on the basis of regulations governing labor safety issues, taking into account the specifics of the organization's activities.
Conducting introductory training on labor protection is mandatory for absolutely all employees.
Introductory briefing, as a rule, is carried out by a specialist (engineer) in labor protection, or, in the absence of one (in organizations with a staff of less than 50 people), responsibility for carrying out this procedure is assigned to another official by order of the head of the organization. In small organizations, the responsibility for conducting induction training is most often assigned to the director.
The following types of briefings fall into the category of briefings that are given to an employee directly at his workplace. The carrying out of these briefings is assigned by order to the immediate supervisor of the work (head of the site, head of the unit, head of the department, etc.).
Made according to changes from 03/01/2022
Initial briefing on labor protection - is carried out after the introductory briefing to all employees of the organization upon hiring, but before they begin their job duties.
Conducting initial training includes familiarizing the employee with existing dangerous or harmful production factors, studying the labor protection requirements contained in the organization’s local regulations, labor safety instructions, technical and operational documentation, as well as the use of safe methods and techniques for performing work.
Instruction is carried out according to approved programs developed separately for each position/profession and types of work. The initial training program is developed by the immediate supervisor of the work with the methodological support of a labor protection specialist.
Initial training can be carried out either individually with each employee or with a group of people who service the same type of equipment within a common workplace.
The employer may exempt from initial training employees whose duties are not related to the use, operation, maintenance, testing, adjustment and repair of equipment, the use of electrified or other mechanized hand tools, the storage and use of raw materials. To do this, the organization must approve a list of positions and professions of employees exempt from undergoing on-the-job training.
Repeated instruction on labor protection is carried out in order to consolidate the knowledge acquired by the employee on labor protection, at least once every 6 months.
Repeated training on labor protection is carried out with the same employees who have already undergone initial training, according to the same programs and instructions as the initial training in the workplace.
During repeated briefing, the employee is reminded of the labor protection rules for the given specialty and workplace.
Recommendation: in order not to be confused about the frequency of repeated briefings, you should set specific dates for it by order of the organization, for example: from January 10 to January 20 and from July 10 to July 20.
When establishing the frequency of repeated briefings, it should be taken into account that some industry rules on labor protection require repeated briefings to be carried out at least once every 3 months.
As a rule, these requirements apply to work associated with increased danger.
Unscheduled safety briefings are provided to employees in order to inform them about important changes that may affect their work due to:
- the occurrence of an emergency or a situation that poses a threat to safety;
- launch of new equipment;
- resuming the work process after a long period of inactivity;
- updates of regulations.
Also, unscheduled training on labor protection can be carried out at the request of supervisory authorities.
Unscheduled briefings have no set deadlines or frequency. The manager can assign it to individuals, departments and all personnel as a whole.
Unscheduled training should be carried out using either ready-made programs that are developed and approved by the organization, or labor protection instructions for a specific workplace/type of work. If an unscheduled briefing concerns changes in legislation, the texts of these documents must be used.
If at the time of repeated or unscheduled briefing the employee is absent from work (vacation, sick leave, business trip), he is instructed individually on the day he returns to work.
Targeted training on labor protection is carried out with employees when:
- performing one-time work not related to direct job responsibilities (cleaning work, loading and unloading work, etc.);
- performing work related to eliminating the consequences of accidents, natural disasters and catastrophes;
- carrying out work for which a permit is issued;
- conducting excursions and public events in the organization.
Targeted briefing, like unscheduled briefing, does not have established deadlines or frequency.
Targeted briefing programs do not have a clear structure and list of issues that need to be addressed. They are developed taking into account the profession or type of work performed by the employee on the basis of safety requirements set out in regulations on labor protection and operational documentation of equipment manufacturers.
Instruction options
The essence of the briefing is to inform the subject of certain strict and guiding rules to ensure the safe performance of the prescribed work tasks. Specific requirements establish the most optimal order, conditions and sequence of work activities. In accordance with GOST, there are 5 types of instruction:
- introductory;
- primary
- repeated;
- unscheduled;
- target.
The choice of a leader depends on the individual circumstances of the current situation and the degree of need to convey this or that information - this is what determines in what cases targeted instruction is carried out.
When designing a program, first of all, measures for organizing work activities, conditions for maintaining good hygiene and actions aimed at creating safety in a separate company for an individual employee and his workplace are determined - this concerns what constitutes targeted instruction.
The fact that activities have been completed and information has been communicated to target persons must be noted in special journals.
Procedure and timing of labor safety briefings?
| Type of instruction | In what cases is it carried out? | Who is it for? | Who conducts |
| Introductory | - when applying for a job | to all employees | occupational safety specialist/responsible person appointed by order |
| Primary | - when applying for a job | to all employees Exception: employees who are exempt from training by order of the head of the organization in accordance with clause 2.1.4. Resolution No. 1/29 of January 13, 2003 | immediate supervisor of work appointed by order |
| Repeated | - regularly, at least once every 6 months or at least once every 3 months, if the work is associated with increased danger and this requirement is established by industry regulations on labor protection | to all employees Exception: employees who are exempt from training by order of the head of the organization in accordance with clause 2.1.4. Resolution No. 1/29 of January 13, 2003 | immediate supervisor of work appointed by order |
| Unscheduled | — at the request of supervisory authorities; — after an emergency or accident occurs; — when launching new equipment; — when new labor protection requirements come into force; - after a long production downtime. | the list of employees is determined by order of the head of the organization | immediate supervisor of work appointed by order |
| Target | — when performing one-time work not related to direct job responsibilities; — when eliminating the consequences of accidents and natural disasters; — when performing work according to the work permit; — when organizing public events and excursions. | the list of employees is determined by order of the head of the organization | immediate supervisor of work appointed by order |
Where is the targeted training with employees recorded?
Even if a permit is issued, in which a mark indicating completion of the instruction is affixed, the company must have a separate journal. Its form is recommended in Appendix A.6 of GOST 12.0.004-2015. If you have difficulty filling it out, check out the sample.
For those cases when a work permit is not issued, column No. 5 of the journal indicates the type of work that will be performed.
The journal for this type of training, as well as the introductory briefing journal, is prepared separately, in accordance with clause 2.1.3 of the Ministry of Labor Resolution 1/29. There is an opinion expressed by the State Labor Inspectorate on the website onlineinspektsiya.rf that if you have a work permit, no entry is made in the journal. But in checklist No. 28, approved by Order of Rostrud dated November 10, 2017 No. 655, the presence or absence of such a journal is recorded.
Features of conducting labor safety briefings
In practice (employers) the question very often arises: is it necessary to provide instructions on labor protection to employees who work at home, remotely or in the office, and, at first glance, do not face any threats or dangers in their activities?
We remind you: all employees, without exception, undergo induction training, regardless of the location and nature of the work performed.
Instructions on labor protection in the workplace are also mandatory for all employees. But here the employer has the right to include some positions/professions not related to the use, operation, maintenance, testing, adjustment and repair of equipment, the use of electrified or other mechanized hand tools, storage and use of raw materials, which, as a rule, include employees office, to the list of those exempt from on-the-job training.
Order of conduct
To begin with, the people who are responsible for conducting the training are selected, and the list of employees who are required to familiarize themselves with the rules is certified.
The procedure is entirely up to the instructor. Participants can independently study the material, but an oral verification of the acquired information is a mandatory requirement. At the end of the training, an entry is made in the journal that everyone has listened to the information, which is certified by the signature of each employee.
In general, the program includes the following information:
- introductory part, which describes the specific situation, the nature of the work being performed and the characteristics of the place where it will be carried out;
- information about the necessary tools and materials that will be used to perform the task. It also describes the working rules, possible dangerous situations that may arise;
- instructions on preparing the work site for operation;
- rules of conduct for an employee if a dangerous situation could not be avoided;
- information about personal protective equipment, rules for working with them;
- a memo about emergencies that occurred at similar enterprises at different times, and rules of behavior in such circumstances.
Registration of labor safety briefings
It is important to remember that it is not enough for an employer to simply provide instructions on labor protection. All labor safety briefings must be completed with an oral assessment of the knowledge and skills acquired by the employee. Only after successful completion of the instructions does the employee receive the right to begin performing his/her job duties.
The fact of undergoing labor safety briefings is recorded in the appropriate journals with the obligatory indication of the signature of the person being instructed and the signature of the instructing person, as well as the date of the event.
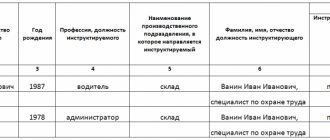
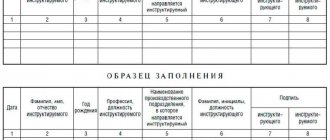
Completion of induction training is recorded in the “Logbook of registration of induction training on labor protection”.
Recommended journal format:
Completion of initial, repeated, unscheduled and targeted briefings is taken into account in the “Logbook of registration of briefings on labor protection in the workplace.”
Recommended journal format:
When entering information about an unscheduled briefing into the log, it is necessary to indicate the reason for it, as well as the number and name of the manager’s order.
Rules for conducting and completing workplace training
There are two types of training that always take place in the workplace.
- Primary
- Repeated
Sometimes unscheduled events are organized at the workplace. This happens if the reason is innovations directly related to the workshop, conveyor belt, etc. For example, changing technological processes or upgrading machines.
In all other cases (if the basis for the briefing is changes in the law, the requirements of the inspector, etc.), an unscheduled briefing can be carried out away from production - in the hall, assembly hall, etc.
IMPORTANT
There is a form for registering on-the-job training.
It is listed in GOST 12.0.004-2015 (approved by order of Rosstandart dated 06/09/16 No. 600-st). But the use of this GOST is voluntary. Therefore, organizations and individual entrepreneurs have the right to develop their own form of journal. Prepare labor safety documents in a special service Try for free