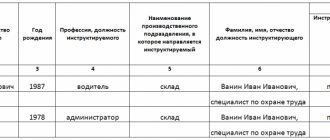
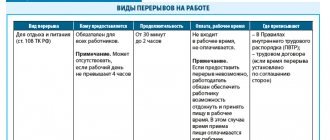
What is an internship as part of occupational health and safety training?
When should you do an internship?
What is a harmful production factor? Hazardous production factor?
How not to make a mistake when deciding whether to conduct an internship?
Who can be appointed as a trainee?
How is permission to work independently obtained?
What are the requirements for conducting an internship in the Draft New Procedure for Occupational Safety and Health Training?
Why and when do you need an internship?
From the contents of Art.
225, 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it is clear that on-the-job training is needed to, under the guidance of an experienced mentor, give the employee the necessary practical knowledge and skills for further independent work. Especially for work in compliance with occupational health and safety standards. Internship should not be confused with:
- with apprenticeship;
- with a probationary period;
- with student internship.
Find out more about a student’s internship in the article “How to write a reference for a student from an internship?” .
The order for an internship always follows the order for employment, and the internship time is counted towards the length of service. The trainee's working time is reflected in the time sheets and work schedules of the unit and is paid without fail in the amount established by the employment contract.
Internship is a form of fulfilling legal requirements for labor protection and safety. Therefore, the more difficult the working conditions, the higher the responsibility for its results, the greater the need for an internship.
Internship is required in professions related to:
- with servicing people using vehicles;
- using sophisticated equipment and complex production processes, when there is an increased risk for both the employee and others;
- working with dangerous objects and substances;
- with serving people in additionally regulated areas: public catering, education, medicine, etc.
Read about additional regulation in the field of public catering in the material “Features of using UTII for cafes and restaurants .
WHAT REGULATIVE ACTS ESTABLISH THE NEED FOR CONDUCTING INTERNSHIPS FOR EMPLOYEES
First of all, the need for an internship is established in Art. 212 and 225 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. At the same time, in Art. 225 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that the employer provides training for persons entering work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions in safe methods and techniques for performing work with on-the-job training and passing exams and conducting their periodic training in labor protection and testing knowledge of requirements labor protection during work.
Similar requirements for conducting an internship are contained in the rules on labor protection (hereinafter referred to as OSH) and standard instructions on labor protection (hereinafter referred to as TIO), many of which are also normative legal acts.
NORMATIVE BASE
In addition to the specified legal acts, the requirements for the need to conduct an internship are contained in the following documents:
• Regulations on the organization of training and testing of knowledge of working organizations supervised by the Federal Service for Environmental, Technological and Nuclear Supervision[8];
• Industrial safety rules for hazardous production facilities that use equipment operating under excess pressure[9];
• The procedure for professional selection and vocational training for employees hired for work directly related to the movement of vehicles of road transport and urban ground electric transport[10];
• Rules for technical operation of consumer electrical installations[11];
• MDK 3-02.2001 “Rules for the technical operation of public water supply and sewerage systems and structures”[12];
• Rules for the technical operation of gas stations (RD 153-39.2-080-01)[13];
• PTE TEU;
• PRP OE;
• PRP ONPO;
• Certain legal acts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
For your information
Separately, it is worth mentioning GOST 12.0.004-2015, which, although it has the status of voluntary application, contains a number of interesting provisions regarding the organization and conduct of internships.
How to apply for an internship correctly
In order for an employee’s internship to be completed correctly, the organization must have a set of internal documents:
- Regulations on internship.
Describes and approves the general procedure for assigning, completing and checking the results of an internship, and also determines how many days the internship lasts at the workplace.
- Internship program.
Details the necessary activities, the procedure and timing for their implementation and the responsible persons in relation to the employee.
- Internship order.
Published for a specific employee sent for an internship.
- Order on admission to independent work.
Published based on the positive results of the internship, after testing the knowledge and skills acquired during the internship.
Internship duration
In 2022, changes were introduced regarding the rules for conducting and completing internships in the workplace.
The main thing is that the rules regarding the deadlines have changed. Previously, the minimum time threshold was 3 days, and the maximum was 2 weeks. Now the function of determining the term can be assigned to the head of the structure where the citizen is hired. If the applicant has a specialized education and skills to perform similar work, the internship period can range from 3 to 19 days. The calculation is taken without taking into account weekends.
Provided that the applicant does not have the appropriate qualifications and does not have similar work experience, the internship period will be increased. It can range from 1 month to six months.
When an applicant gets a managerial position, the completion period for him is set in the range from 14 days to 1 month.
Who can conduct an internship?
Not all citizens working at an enterprise in similar positions have the right to conduct an internship.
This function can be assigned to:
- The most experienced employee and/or head of labor protection.
- A representative of the management team, if we are talking about the internship of a person who will subsequently occupy one of the management positions.
Rules
GOSTs establish the following rules for conducting internships:
- The process cannot be spontaneous, for its implementation
- The instructor is obliged to familiarize the applicant with all internal regulations affecting the production process, with the job description, with individual acts relating to labor protection and safety in a specific production within the framework of the position held.
- The period allotted for completing an internship for a specific position must be indicated in the training program.
- Based on the results of passing, an exam is taken to determine the applicant’s qualification level. The form and order of its implementation are recorded in the program.
it requires a training program that must be followed.
Based on the results of the exam, one of the following decisions is made:
- An employee who has undergone an internship is ready for further independent work.
- The applicant's qualifications are low and the material has not been fully mastered. It is prohibited to allow an employee to work independently.
If the result is the second option, the applicant has to complete the internship for another 1 month and take a new exam.
Internship Regulations
It should include, among other things:
- general provisions (introductory part);
- requirements for professional knowledge and skill of workers;
- goals and procedure for the internship;
- procedure for admission to work after completing an internship;
- features of internship for certain categories of employees (if necessary);
- goals and procedure for carrying out control activities;
- responsible persons and criteria for their responsibility;
- verification and registration of internship results;
- equipment requirements for the internship (if necessary).
Example:
The “Eat Without Problems” cafe is opening an additional takeaway outlet. The cafe management decided to hire 4 cooks to work in shifts. The responsibilities of the senior chef's shift at the point will be temporarily assigned to 2 cooks from among those who have been working for a long time. It was decided to bring products for the operation of the point from the main cafe. Due to the peculiarities of working at the outlet (trade without a hall and without waiters, takeaway, in disposable packaging), it was decided to change the internship procedure for new chefs.
To properly formalize their decisions, the cafe management develops and approves the Regulations on internships for employees of a remote location. It includes:
- New chefs are required to complete an internship in two stages:
- mainly cafe, under the guidance of an instructor;
- at the point, under the leadership of the shift supervisor.
- Goals of employee internship in a cafe:
- the chef must ensure the professional level of new employees;
- they are introduced to the technical and technological maps of dishes accepted in the cafe;
- they are explained the specifics of working on the equipment used in the cafe;
- they must master proprietary cooking technologies, skills in operating equipment, and become familiar with labor protection and safety rules, including special standards for catering establishments.
- Goals of the internship at the point.
The shift supervisor must ensure that new employees:
- cope with the mode and pace of work;
- comply with cooking technology and rules for working with equipment;
- We strive for high quality work, polite and friendly attitude towards customers.
The shift supervisor must train workers:
- proper packaging of ready-to-go meals;
- communicating with customers on receiving and issuing orders;
- rules for reception, storage, inventory of food supplies, procedure and rules for placing an order to the main cafe for the delivery of necessary products and packaging.
- Admission to independent work is permitted after the recommendation of the shift supervisor at the point and verification of the results of the internship by the chef.
- The head chef is responsible for allowing new employees to work independently. On the last day of the internship, in agreement with the shift supervisor, the chef comes to the point and checks the completion of all tasks listed in these Regulations.
- The results of the internship are documented in an internal inspection report, which is drawn up by the responsible person (chef). Positive results are the basis for an order for admission to independent work.
- The duration of the internship is:
- 5 work shifts - in the main cafe;
- 5 work shifts - at a remote location.
- Payment for trainee shifts is made in the amount of:
- 50% of the rate per shift for an internship in a cafe;
- 70% of the rate per shift – at the point.
- Clauses about the established duration of the internship at the workplace, as well as the procedure for its payment, are included in the employment contract.
Now let's move on to consider the question of how long an on-the-job internship lasts.
Basic provisions
According to the current labor legislation, training and internship for some categories of citizens when applying for a job becomes mandatory. And while the first event is carried out by most employers, not everyone arranges internships for employees.
Its implementation, depending on the position for which the applicant is accepted, is the right or obligation of the employer. The general need for an internship is enshrined in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and in clause 11.4 of GOST 12.0.004-2015. Individual rules and deadlines for professions and industries are fixed in separate regulations and by-laws.
For example, the internship of a crane operator, electrician, and slinger is regulated by PB-10-382-00. And according to the document, it is carried out at least once a year.
The duration of the internship for electrical technical personnel is recorded in PTEEP clause 1.4.11. Ranges from 2 to 14 work shifts.
An internship is a work process carried out by an employee under the guidance of an experienced mentor.
Purpose of the internship
The purpose of the internship is to:
- Training in practical skills of mastering a profession.
- Repetition and reinforcement of occupational health and safety standards.
- Demonstrate work skills to management.
The beginning of the internship process is always confirmed by an Order from the head of the enterprise, which is issued after the preliminary signing of the Employment Order.
A mandatory internship is required for persons whose professional activities are related to the following type of activity:
- Passenger and cargo transportation.
- Working on complex equipment, electromechanical machines, etc.
- Production that uses hazardous chemicals and explosives.
- Medical care, pedagogical process, public catering.
An internship may also be required for employees who have not participated in professional activities for a long period of time or have been absent from the workplace (for example, due to a long illness or while on parental leave). This is especially true if production conditions related to labor protection have changed during the absence.
If the law requires an internship, but this condition is not met, this act falls under administrative offenses. The responsible person is the employer, the head of the personnel department, the organization itself, etc. Punishment will follow under Art. 5.27.1 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. It provides for the imposition of a fine:
- The official will pay from 15 to 25 thousand rubles.
- For individual entrepreneurs, an amount of 15 to 25 thousand rubles is provided.
- Legal entities will be required to contribute from 110 to 130 thousand rubles.
An incoming employee has only one legal option to avoid a regulated internship. This will be a written order from the head of labor protection, approved by the head of the enterprise. The main condition for its preparation is that the applicant for a vacant position must have previously worked in a similar position for at least 3 years.
There are categories of enterprises that require an internship even for a simple transfer from one position to another. The entire period of its implementation must be included in the length of service and paid. Without completing an internship, it is unacceptable to accept positions in the following groups of enterprises:
- Employed in the chemical and oil refining industries.
- Woodworking enterprises.
- Fertilizer factories.
- Cafes, restaurants, bars and other catering establishments.
- Medical units, hospitals, etc.
What is the established duration of the internship - how many days does it last?
The duration of an on-the-job internship depends on the specifics of the enterprise’s activities and the specific employee. General requirements for it are given in clause 9.4 of GOST 12.0.004-2015 “System of occupational safety standards. Organization of occupational safety training. General provisions."
Thus, for workers in blue-collar professions and small and medium-sized enterprises who have the appropriate professional qualifications, the duration of the internship is determined by internship programs lasting from three to 19 work shifts, for workers in blue-collar professions without experience - lasting from one to six months. For managers and specialists, the duration of the internship is determined by the employer’s decision from two weeks to one month in accordance with their existing education, training and work experience.
That is, here is the same dependence as when determining whether an internship is mandatory: the more complex, qualified and responsible the independent work, the longer the internship period (a good example is medical internship, at least 1 year).
For jobs with special working conditions, the duration of the internship (and the examination after its completion) may be regulated by external legislation and industry regulations. For example, the duration and procedure for the internship of drivers of passenger vehicles are regulated by Regulation RD-200-RSFSR-12-0071-86-12 of the Ministry of Automobile Transport of the RSFSR of 1986.
In other cases, the duration of the internship is determined by the employer.
The period of internship at the workplace of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is established only for fixed-term contracts - no more than 2 weeks (Article 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Admission to perform work related to vocational education in the form of an internship
Art. 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows the conclusion of a fixed-term employment contract with employees if their work is related to training in the form of an internship. Since in this case the conclusion of an employment contract is provided, it must comply with the requirements for an employment contract in Art. 57 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
At the same time, labor legislation does not oblige hiring a “trainee” for the position, so an employee can be hired for another position provided for by the company’s staffing table.
But to conclude a fixed-term contract, the employer must ensure that the job for which the employee is hired is directly related to his internship and professional training.
The employment contract specifies not only the position (type of work), but also emphasizes that the work assigned to the employee is aimed at obtaining the necessary practical professional skills and abilities.
In addition, the employment contract with the intern must specify its validity period, which must correspond to the duration of the internship. The possible duration of the internship is not fixed by law (except for certain categories of employees indicated above), therefore the employer and the employee have the right, by agreement, to determine the duration of the internship and, consequently, the term of the employment contract.
It should be borne in mind that an internship can hardly last many years, so an internship period of 3-4 years may raise doubts among the court and inspection authorities if an employee applies to them.
Of course, work within the framework of this employment contract must be paid in amounts not less than the minimum wage.
Order on internship at the workplace. Sample
Example (continued)
The cafe's management has found a new chef and is now hiring him for an internship.
A sample internship order drawn up in accordance with the approved Regulations can be found here.
On-the-job internship program. Sample
The program can be drawn up as a separate document, or can be an appendix to the order. Must contain details and dates of the activities listed in the Internship Regulations in relation to a specific employee.
For a sample example, see Appendix 1 to the Internship Order.
Note! Completing an internship, including for the purpose of ensuring occupational safety and health, does not cancel the mandatory introductory safety training on the first working day.
Read about repeated safety briefings in the article “What is the frequency of repeated occupational safety briefings?” .
If you have access to K+, see how to summarize work safety training in the form of an internship. If you don't have access, get a free trial access and proceed to recommendations from K+ experts.
WHAT IS AN INTERNSHIP
In the legislation of the Russian Federation, the concept of “internship” is understood ambiguously. Thus, internship as a form of training in practical skills and abilities is directly related to obtaining vocational education (including additional) or undergoing vocational training and is regulated by the relevant regulations (hereinafter referred to as NLA) of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation[1].
Note!
Do not confuse an internship with a pre-employment test[2], which is conducted to determine the aptitude and suitability of an employee for the job assigned to him. These are unequal concepts.
Some legal acts have a definition of the term “internship”:
• on-the-job training of personnel under the guidance of the person responsible for training, after theoretical training or simultaneously with it for the purpose of practical mastery of the specialty, adaptation to service and management facilities, acquisition of skills for quick orientation in the workplace and other work techniques (Rules for the technical operation of thermal power plants[3]);
• practical development directly in the workplace of skills to perform a job or group of jobs acquired during professional training (Rules for working with personnel in electric power industry organizations of the Russian Federation [4] and Rules for working with personnel in oil product supply organizations of the Russian Federation [5]).
Internship as one of the forms of occupational safety training[6] is carried out under the direct supervision of an intern for the purpose of practical mastery (i.e., transfer of practical experience from the intern to the intern) of safe methods and techniques for performing work (for workers in blue-collar professions) or for the purpose of practical mastery best practices and effective organization of work (for managers and specialists).
For your information
Internship is inseparable from training in safe methods and techniques for performing work, but is necessary only for workers performing work in harmful and dangerous working conditions. Workers with safe working conditions are trained in safe methods and techniques for performing work during the initial briefing on labor protection in the workplace.
Results
Internship – opportunity (or necessity):
- for the employee – to obtain the necessary knowledge and skills for independent work;
- for the employer - to make sure that the employee is able to work in his place in compliance with the requirements of all external and internal regulations.
The obligation and duration of the internship are determined by the specifics of the specific job.
Sources: Labor Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Is it possible without a contract at all?
The above regulations on the employment of trainees state that the employer can draw up an agreement with them. This means that this is not a requirement, but only a possibility, and the execution of an agreement is not mandatory.
An employment contract must be concluded if an actual employment relationship is established between the trainee and the employer, namely:
- the student performs labor duties specified in the job description of the vacancy that is in the staffing table (unified form T-3);
- the student is accountable to the labor regulations adopted by the organization;
- The student is paid wages in a timely manner and in full.
If such relationships do not arise, it means that the trainee is not working, but only undergoing training. In this case, you can draw up a student agreement or not conclude any.
IMPORTANT! A concluded employment contract can only be fixed-term: after all, the practice has clearly defined start and end dates. Art. 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that internships and individual training require the conclusion of a fixed-term employment contract.