Is it possible to work without a work book?
Taking into account the legislation, there are only two possibilities for hiring an employee without a work permit (Labor Code of the Russian Federation of December 30, 2001). In this case, an agreement must be concluded with him. This can be done in the following cases:
- The employee performs his official duties part-time (Section 12, Chapter 44 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- The boss is an individual , but not an individual entrepreneur (section 12, chapter 48 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
It is not possible to hire and register an employee in any other way without registering with the labor manager.
In the case of one-time work , limited in duration and volume, the employer accepts the employee without being registered in the employment record, but concludes a different form of contract.
How to apply?
An employee can get a job without a work permit; to do this, together with the head of the organization, you need to choose the form of the contract:
- Contract agreement (civil law).
This document is usually drawn up when performing one-time work.
- Copyright agreement.
This document is drawn up if you need a person for short-term creative work.
- Agency contract.
One of the parties undertakes, for a fee, to perform any actions on behalf of the other party, the customer.
When an employee gets a job without a salary, his manager must make payments to the Pension Fund . The management may not give any guarantees, because this agreement exempts you from this.
For this reason, a minority agrees to work under such conditions, since even the correct amount of salary will not be easy to achieve in the event of dismissal.
Legislation
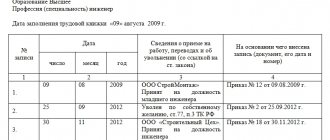
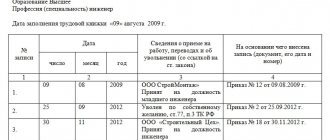
The corresponding entry about admission to a vacant position must be entered into the employee’s work book in accordance with Article 66 of the Labor Code.
It is this document that records the citizen’s length of service, on which the amount of accrued pension payments will subsequently depend.
And if, by an absurd accident, the contract concluded upon hiring is lost, the work book will help restore justice - the person will not lose years of accumulated experience. And in the absence of a book, it is impossible to prove anything even when applying to the judicial authorities.
Advantages and disadvantages
Many workers believe that there are many advantages , including:
- There is no fixed schedule. Thanks to this, it is possible to go to work when the employee deems it necessary.
- The subordinate chooses his own convenient working time.
- There is no need to follow orders from higher management.
few disadvantages to working under a contract:
- In most cases, when applying for a job, people expect that the employment relationship will last a long time. But, work under a rental agreement often has a certain period.
- It is possible to stop working under such an agreement only if the employer decides so. At the same time, he has the right not to warn the subordinate in advance.
- The employment contract does not provide for the required vacation, because the subordinate receives a salary for a specific amount of work.
- Under a rental agreement, there is no possibility to receive additional accruals, such as bonuses.
- Maternity leave and sick leave are not subject to payment.
- When accruing for sick leave, the period of work under such an agreement will not be taken into account.
- The term of work under the contract will be included in the insurance period only at the time of retirement age. If a citizen goes to work in another place, then this length of service is not taken into account.
- The manager is relieved of responsibility to the worker.
Is it possible to save on taxes when contracting a contract with an individual? Any manager will be interested to know:
Employer is an individual
Today, employment of citizens can also be carried out by individuals who do not register as an individual entrepreneur. A similar approach is allowed in cases of running a personal farm or other household, in order to receive help with household chores (gardeners, maids, cleaners). As a rule, in such relationships there is no commercial component on the part of the employer.
At the same time, the law obliges the employer, regardless of its status, to maintain certain forms of accounting for hired employees, pay taxes, insurance and other contributions for them. Therefore, the following points should be highlighted here:
- An individual who employs citizens is obliged to enter into an employment agreement with them. All further obligations regarding the preparation of reports, payment of contributions and taxes fall on the shoulders of the employer.
- Considering the lack of commercial purposes in hiring workers, the employer does not need to maintain his own accounting, personnel, have stamps, or open bank accounts. Therefore, registration of a work book is not provided here.
- It is possible to sign fixed-term and open-ended employment contracts. Conditions can be general or individual. The basic provisions of such agreements must comply with the basic requirements of labor legislation.
- Signing an employment contract in such cases is mandatory. They should not be replaced by other types of written agreements. Especially if the work will be performed on an ongoing basis.
Remember, any disputes with an individual employer will be resolved on the basis of a signed employment contract. Therefore, please read this document carefully before signing.
Is employment official without a work permit?
You should not be deceived and believe the promises of an employer who claims that employment is possible without entering information into the employment form or without signing a contract.
Unofficial work means that the company does not pay social insurance contributions, does not make contributions to the Pension Fund or health insurance. Upon reaching retirement age, a person will not be able to confirm his own experience, i.e. Time spent working for an unscrupulous company will not be counted.
- An employer violates an employment contract: what should an employee do, how to sue
The employer, removing all responsibility for the hired personnel, becomes a violator of the law with all the ensuing consequences.
For an employee, consent to informal employment means:
- lack of legal protection and wage guarantees;
- lack of vacation, vacation pay, temporary disability benefits, etc.
Having received an industrial injury or mutilation, it is quite difficult to obtain compensation even through the courts.
When a company replaces a regular contract with an employee with a GPC agreement, the official should be prepared to receive a fine under administrative liability in the amount of 10 thousand rubles, and the company will pay a fine of up to 100 thousand rubles for each identified case of violations. Acceptance of an employee under a GPC agreement by a private entrepreneur also entails a fine.
Disadvantages of working informally
Negative consequences for citizens:
- non-payment of wages;
- lack of social guarantees, for example, not providing employees with vacation or sick leave pay;
- the worker may be subject to forced labor and exploitation;
- high probability of problems with the law due to involvement in a criminal environment.
Information! Illegal employment is beneficial only to the employer; for citizens, illegal employment is associated with a lack of social guarantees and increased risk. The manager may be brought to tax and administrative liability, and even criminal punishment is possible for gross violation of the law.
Differences between documents
There are several parameters by which we can conclude how a contract differs from a book.
Table of differences between a book and a contract
| Differences | Employment history | Agreement |
| Procedure for document execution | A document that is individually issued for each employee. The form reflects all stages of activity, starting from the very first place of work. The form is filled out manually. | Each time a new contract is signed with an employee when changing duty stations. Job responsibilities, company, job title change. The document is printed on a computer. |
| Validity | The form remains legally valid at all times. | The contract is valid while the person performs duties at the place of duty. After dismissal, the validity period ends. |
| Persons authorized to make entries and certify a document | The work book is filled out by specialists from the HR department of all organizations where the person worked. | The new contract is filled out by the personnel department for each duty station. |
| Purpose of issuing the document | Based on the work record, one can draw a conclusion about the place and time of a person’s activity in different companies. | The agreement shows the rights and responsibilities of the specialist, rest and work regime. |
| Number of copies | An important difference is that the employee receives a single copy of the form. There is no other like it. If the document is lost, you need to make a duplicate. | When work is under contract, two copies of the contract are signed. One copy remains with the employee, and the second is kept by the employer. |
| Information the document contains | From the labor record you can find out information about where a person studied, served and worked. You can also conclude whether a person performed his duties well or poorly. The awards section shows whether the person has received awards for his work. Based on the grounds for dismissal, one can judge whether there were violations of discipline. | The contract shows exactly what the specialist did at the place of work, what duties he performed. Also, from the terms of the document, one can draw a conclusion about the amount of official salary, bonuses, and allowances. |
The form contains general information about the activity, the contract provides more complete information. The form is required to assign pension payments.
Also, there is another answer, what is the difference between the documents. The agreement can be changed when responsibilities change. It is enough to sign an additional agreement. The work record remains unchanged throughout the entire activity.
So, there is a difference between a work book and an employment contract. But there are also similarities between the documents.
The difference between work under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the GPC agreement
The main difference is that a person is deprived of the benefits provided for by the Labor Code. When registering under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the duration of working hours is regulated, and the right to weekends, vacations, and sick leave is given.
Fulfilling obligations under a civil law agreement (civil agreement) is another matter. The parties negotiate the term of cooperation and the amount of remuneration. Socially, a person is less protected. However, the employer must also pay contributions to the funds and withhold income taxes from employees.
But in some cases, a civil law contract is suitable. For example, to perform one-time work: installing plastic windows, renovating a room, and so on. The GPC agreement can be turned into a regular contract. Retraining occurs on the basis of Article 11 of the Labor Code and is permitted only through judicial proceedings.
As a rule, this situation arises when a person goes to court and provides evidence of systematic fulfillment of duties. The court may side with the plaintiff.
If an employee causes losses, then more can be recovered under the Civil Code. Damages and lost profits are compensated.
Why do you need a work book?
According to Art. 65 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, when applying for a job, an employee is required to provide a work book.
When concluding an employment contract, the employee does not provide a work book in the following cases:
- the employment contract is concluded for the first time;
- the employee gets a part-time job.
In accordance with Art. 66 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a work book of the established form is the main document on the employee’s work activity and length of service.
The employer keeps work books for each employee who has worked for him for more than five days, in the case where the work for this employer is the main one for the employee.
The following are entered in the work book:
- information about the employee;
- information about the work he performs;
- information about transfers to another permanent job;
- information about the employee’s dismissal;
- grounds for termination of the employment contract;
- information about awards for success in work.
Information about penalties is not entered into the work book, except in cases where the disciplinary sanction is dismissal.
Remote employment
The development of the global Internet, as well as information technology, has made it possible to separate some types of activities into a separate segment - remote employment. This type of labor cooperation is reflected in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Among the key points of such employment are:
- the employee independently determines his own workplace, as well as the basic resources for completing assigned tasks. Work tools may be provided by the employer. But this must be stated in the employment contract;
- hiring is carried out on the basis of a written employment contract. To do this, the parties sign it and send it to each other by email. An electronic signature may be used to confirm the authenticity of a signature;
- registration of a work book is not necessary here. This is done only at the written request of the employee. In the future, in case of dismissal, the work book is sent by registered mail;
- The employee is subject to all benefits and guarantees provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the collective agreement, and the employer’s local documents.
Recruitment procedure
There is a standard procedure for hiring a new employee, which includes providing certificates and certificates, conducting interviews with applicants, writing applications, concluding a contract, and preparing job descriptions.
Of course, the list of documents required for employment includes a work book (Article 65 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). But sometimes the applicant cannot provide it. If this is the first place of service, then he does not have a document confirming his experience. So is it possible to hire without a work book if the candidate already has professional experience? This will be discussed further.
Registration to the state without a document confirming the experience
The form of work books, the rules for their storage and maintenance are regulated by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 225 of April 16. 2020. Let us consider possible cases of hiring without a document on professional activity, guided by the norms of the resolution.
A work record book for an employee who has just begun his professional activity is drawn up by a specialist from the HR department within one week from the date of conclusion of the agreement.
It happens that this is not the applicant’s first place of employment, but there is no document confirming the length of service, because before that he worked under a contract for an individual. Then the personnel service also draws up a work book for the first time, and information about previous work experience is entered into it on the basis of a concluded employment agreement.
If your work record is lost, how can you get a job in such a situation? In this case, the employee should contact the organization of the last place of duty with a written statement about the loss. Within 15 days, an authorized representative of the enterprise must prepare a duplicate document, which the candidate will provide to the new employer. But if more than a year has passed since the loss, then the previous employer has the right to provide only a certificate confirming the fact of cooperation. Then the applicant passes this certificate to the new employer, who can issue a duplicate on its basis.
There are situations when, upon dismissal, the employer does not give the work book to the employee, citing unsigned workaround or other reasons. It is illegal. Therefore, the owner of the document can go to court, where he can also ask for compensation for expenses and moral damages (Article 234 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The procedure often takes a long time, so it is better to make sure in advance that the new manager has the opportunity to wait.
Registration to the state on the basis of an insurance certificate
It happens that the applicant was not officially registered, but only performed temporary work. But he has an insurance certificate, which was issued to him by one of his temporary employers. What should a HR specialist do in such a situation?
If an employee did not provide a work book when applying for a job, and in return presents only an insurance certificate, then the employer has the right to demand from him a certificate from his previous place of service. Then the employee writes an application requesting to issue a work book and indicating the reasons why it has not yet been issued. Based on this application, the HR specialist justifies the reason for registration without the main document on professional experience, and subsequently issues it for the new employee.
In the cases we considered, a document with information about professional activities is still issued after the admission procedure. But there are situations when it is possible to get a job without a work book in accordance with the letter of the law.
Combined work
In cases where an employee gets a part-time job, it is not necessary to make an entry in the work book. The fact is that this document must be located at the place of main work throughout the entire period of employment. In fact, this is the only reason why part-time work does not require a mark in the work book. Otherwise, a person holding a part-time position performs labor activities in accordance with the Labor Code.
The employee must take into account the following aspects, which must be observed by both employers:
- Leave must be taken at the same time at both places of work;
- In case of illness, sick leave must be provided to all organizations with which an employment contract has been concluded;
- Insurance and work experience are accrued at both places of work.
However, at the request of the employee, for ease of calculating work experience, an entry about an additional place of work can be made in the work book. To do this, from the place of additional employment, at the request of the employee, a certificate is provided with the information necessary for entry. The employee brings it to the accounting department or human resources department of the organization where he conducts his main work activity.
Work on the GPA
Another option to earn money legally without entries in the work book is to work under a civil contract. If the parties enter into such an agreement, their relations will be governed by the norms of the Civil Code, and not the Labor Code.
Cooperation under the GPA does not imply the drawing up and signing of an employment contract; the contractor does not receive the status of an employed person, which means he does not have the right to claim guarantees and compensation established by labor legislation (working hours, working hours, vacation, dismissal payments, etc.).
According to the GPA, the contractor undertakes to perform a specific amount of work or provide certain services to the customer. The customer, in turn, undertakes to pay for completed tasks. GPA work cannot be carried out on a regular basis.
Note! If, as a result of the audit, it is revealed that the parties who entered into the GPA are actually in an employment relationship, then it is the norms of the Labor Code that are subject to application, and not the Civil Code.
Table No. 3. Pros and cons of working on the GPA.
| pros | Minuses |
| The work schedule is determined by agreement of the parties. Typically, customers require results to be submitted by a certain date. The contractor must meet deadlines and provide a ready-made object or package of services. | There are no labor guarantees. |
| The contractor must not coordinate his vacation with the customer or work two weeks before terminating the relationship on his own initiative. | Payment of vacation pay, sick leave or maternity pay is not provided. |
| You can enter into a GPA with an unlimited number of customers at once. There are no limits on working hours, as is the case with part-time jobs. | High risk of the counterparty refusing to fulfill its obligations under the transaction. |
Sample civil contract
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation offers another version of the document regulating labor relations: a civil law contract (CLA). (Article 420 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) In such an agreement, the parties are the customer and the contractor. The task, terms of payment and deadlines for completing the work are clearly stated.
Consists in the following cases:
- contract;
- carrying out research, development and technological work;
- Paid provision of services;
- transportation, transport expeditions;
- agency;
Sample civil contract with an employee: in .doc format (Word file).
Agreement conditions:
According to the GPA, the employee is engaged exclusively in the activities and the amount of work that are prescribed in the GPA, he cannot be subject to disciplinary liability, does not obey the work schedule, does not endure a probationary period, but immediately starts work. If an employee has doubts about the fairness of remuneration, his interests can be appealed in court, based on the terms of the document signed by both parties. It is convenient for the employer to enter into such an agreement in that he is exempt from the need to pay benefits, sick leave, vacation pay, and reserves the right not to retain the job of a temporarily disabled employee.
Benefit for employers
The absence of a contract regulating labor relations allows employers to avoid the liability imposed by this document.
The main benefit for the organization (enterprise) and management is:
If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, please contact us through the online consultant form or call:
- Moscow.
- Saint Petersburg.
- in the absence of liability for delays in payment of wages;
- the ability to assign a salary that will be less than the minimum established by the government (minimum wage);
- the possibility of not including the employee in the staff (such an employee is automatically deprived of the protection of the trade union organization, since it actually does not know about his existence);
- the ability to refuse to an employee payment for vacation days, compensation for travel expenses for a business trip, or payment for overtime work;
- there is no need to ensure decent working conditions in the workplace;
- the possibility of not paying insurance contributions to the Pension and Insurance Fund for the employee.
In addition, the employer may dismiss such an employee on his own initiative without good reason or without giving notice.
The employee does not actually exist in this enterprise or organization! But his rights and obligations are not documented (theoretically, the employer does not violate anything).
If there is no employment contract
Labor relations arise on the basis of an employment contract. But if it has not been formalized, then on the basis of the employee’s actual admission to work with the knowledge or on behalf of the employer or his authorized representative (Article 16 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
This means that if you hire an employee, but do not formalize him in any way, and there are signs of an employment relationship, then it is considered that you have an employment relationship with him, as if an employment contract had been concluded. With all the ensuing consequences. But at the same time, evading the conclusion of an employment contract is in itself a violation of the law. The law requires that an employment contract be drawn up no later than three working days from the date the employee is actually admitted to work (Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
When an employment relationship is not formalized, other responsibilities that follow from these employment relationships are usually not fulfilled, such as labor protection, medical examinations (when they are mandatory), and the preparation of mandatory personnel documentation. All these violations are also subject to sanctions. Well, if settlements with the actual employee are carried out in draft form, then this is a separate big “story” - a violation of tax legislation (on payment of personal income tax) and legislation on the payment of mandatory contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, compulsory medical insurance funds and insurance against industrial accidents .
If the actual employee is not a Russian citizen, then his employment requires compliance with special rules of migration legislation. Responsibility is also provided for their violation.
What is the penalty for violating labor laws?
If the actual employment relationship is not formalized or formalized by a civil contract, the employee may apply to the court with a claim to recognize the relationship as an employment relationship. In this case, all irremovable doubts are interpreted in favor of the existence of an employment relationship (Article 19.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
This means that the court will most likely make a decision on concluding an employment contract and providing the employee with all the guarantees established by labor legislation. For example, on the provision of annual paid leave, maternity leave, payment of sick leave, and so on.
In addition to the court, inspectors of the State Labor Inspectorate (SIT) can recognize the relationship as labor as a result of an inspection. For violating the requirements of labor legislation, they are subject to administrative liability.
For evading the execution of an employment contract or for concluding a civil contract that actually regulates labor relations, an individual entrepreneur faces a fine of 5,000 to 10,000 rubles, a legal entity - from 50,000 to 100,000 rubles (Part 4 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation) .
For an individual entrepreneur, the amount seems small. But remember: for a repeated violation of the same type, the fine will be more significant - from 30,000 to 40,000 rubles for an entrepreneur and from 100,000 to 200,000 rubles for a legal entity. In addition, other violations arising from unregistered labor relations may be encountered along the way. The table below contains typical violations and the fines for them. This does not take into account responsibility for failure to withhold and transfer personal income tax to the budget, as well as failure to pay mandatory insurance contributions in the event that the tax inspectorate and extra-budgetary funds reveal the fact of black wages.
What is the probability of verification
There is currently a moratorium on conducting scheduled inspections of small businesses; Federal Law No. 480-FZ dated December 25, 2018 extended it until December 31, 2022. But the moratorium does not protect against unscheduled inspections.
The reason for unscheduled inspections of the State Labor Inspectorate is most often a complaint from an employee.
Judge for yourself how likely these risks are. According to Rostrud statistics, in the first half of 2022 (data for the second half of the year is not yet available) only 1% of the total number of legal entities and entrepreneurs were checked. But at the same time, 93% of all inspections were carried out unscheduled. And in 69% of cases, the basis for the inspection was someone’s statement or receipt of other information about a violation of the labor rights of citizens. Violations were detected in 67% of inspections. The figures for the whole of 2022 are close to these figures.
In other words, an inspection can be provoked by any conflict with an employee if he complains in retaliation that the employment relationship with him was not formalized as expected. No one is immune from this risk.
In addition, nothing prevents an employee from going to court and demanding that your relationship with him be recognized as an employment relationship. This usually happens when the actual employee demands any guarantees provided to him by labor legislation, and the actual employer denies him this.
It's not just about fines
Properly formalized labor relations are needed not only by the employee, but also by the employer. Firstly, official labor relations give the employer not only responsibilities, but also rights: for example, the right to demand compliance with the work schedule, the opportunity to enter into an agreement on full financial responsibility when the employee is entrusted with material assets. In addition, a formal employment relationship gives employees confidence in their continuity, and when people are committed to long-term work, they are more motivated to work hard, which will ultimately positively impact the performance of your business.
What if you have already concluded a civil law contract instead of an employment contract, or if your assistant has started work without any formalities? The best option: draw up an employment contract without waiting for a conflict situation.
In the next article we will tell you step by step how to properly formalize labor relations and what personnel documentation is needed, in addition to the contract itself.
How will they prove it?
Do not delude yourself that it is difficult to prove an employment relationship. If a person works for you, then he will probably have a lot of evidence. This could be your email correspondence with him, audio and video recordings, and, for example, shift and vacation schedules with his name, some documents of your business activities, which he fills out and signs on them due to the nature of his activity - invoices, acts, waybills, and so on. Even the presence of a permanent pass to the work area can play the role of proof of labor relations in conjunction with others. Someone may also give testimony - for example, your clients with whom your employee often communicates.
How are labor relations formalized?
The basic rules for formalizing labor relations are determined by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This usually happens according to this algorithm:
- A potential employee is being interviewed. Here his level of qualifications and experience are determined, available documents are preliminarily reviewed, and the basic conditions of future work are announced.
- After successfully completing the interview, the application process begins. In this case, the applicant is required to write an application addressed to the employer with a request for employment.
- The application is signed by the manager who has the right to employ employees. After this, an employment contract and an employment order (instruction) are prepared. After these documents are signed by the parties, the applicant becomes an employee.
- Before starting to independently perform labor functions, the employer is obliged to familiarize the employee with working conditions, internal labor regulations, the presence of harmful or dangerous factors, and the terms of the collective agreement. It is also necessary to conduct initial and introductory briefings on labor protection. All this is indicated in the employee’s personal file.
- If the contract has a probationary period, it is necessary to indicate the conditions for passing the test, as well as the procedure for summing up the results. This is important, because an employee who fails the test may be fired before the end of the employment agreement.
Remember, employment is always formalized exclusively in writing. Even if it was not initially possible to sign the relevant documents, they are drawn up as soon as possible and apply to the periods when the employee actually began working.
Dismissal without a work book under an employment contract
If you are dismissed without a work book under an employment contract, some rules apply for terminating the work agreement. They are as follows:
- If a person does not agree with the dismissal, then the other party has the right to apply to the court;
- Dismissal occurs from the day the court decision was made public;
- The parties to the agreement do not have the right to demand the return of what has already been performed under the agreement;
- If the dismissal occurred due to a gross violation of the provisions of the agreement by one of the participants, then the other has the opportunity to receive compensation for damages;
- In addition, it is possible to carry out dismissal by agreement of the parties.
Unofficial employment
But the employer must understand that if an employee violates something or causes damage to the company, then it is impossible to hold him accountable and officially recover the damage, since the employee is not registered. Maximum - the employer will not pay wages, but will not be able to go to court or law enforcement agencies, he will not have evidence of an employment relationship. In this case, the employee can go to court at any time, and if the employment relationship is proven, the employer will have to pay him wages, as well as other due payments (compensation for unused vacation, moral damages, penalties for delayed wages). Moreover, the salary may be collected again, because the employer will not be able to prove that the work was paid. In addition to payments to the employee, it is necessary to take into account that failure to draw up an employment contract is a separate violation provided for in paragraph 4 of Art.