Making an entry in the work book upon termination of the contract
Do you continue to keep paper work records?
Sign up for a free trial access to ConsultantPlus and get a complete algorithm for working with paper work books, taking into account the latest changes in legislation. The fact of dismissal of an employee is confirmed by a corresponding order, on the basis of which an entry is made in the work book. The record contains the terms of dismissal and the grounds for termination of the employment relationship.
The procedure for making entries is regulated by the Procedure for filling out work books, approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated May 19, 2021 No. 320n.
The dismissal of an employee assumes that the entries that were made in the document while working for this employer are certified by the final signatures of management and the employee, as well as a seal (if any). This is evidenced by clause 36 of the Procedure under Order No. 320n. The employee’s signature may be missing if it is not possible to hand over the document to him personally.
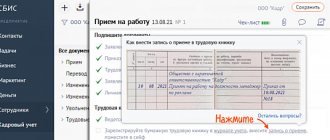
The dismissal record itself is made in the following order:
- in column 1 the serial number of the entry is entered;
- column 2 reflects the date of dismissal;
- column 3 contains information about the dismissal itself (its reasons);
- Column 4 provides information about the order on the basis of which the employment contract was terminated.
The entry on termination of the employment contract must include a reference to the basis - the corresponding article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
ATTENTION! The rules for maintaining work books in force from 09/01/2021 (approved by order of the Ministry of Labor dated 05/19/2021 No. 320n) do not provide for familiarization of the employee with the signature of the work records entered into the paper work book (previously, employees signed the dismissal record). Read more about the new rules for registering a work book, effective from September 2022, here.
Other information about the registration of a work book can be obtained from the article “Rostrud allowed to “stamp” work books.”
Forms of responsibility
If an employee fails to receive documents on time, he or she can count on compensation for material and moral damage for the time he was unable to get another job. A fine is imposed on the responsible executive of the HR department or organization in accordance with the provisions of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation .
Salary compensation
The responsibility of the employee and the employer under the employment contract is provided for in Article 232 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Issues of wage arrears to staff or damage to the organization if an employee violates working conditions are resolved mainly by agreement of the parties.
Moreover, the legislation clarifies that the employer can recover damages from the employee not in full, but only in part, but must pay it off in full.
Liability, terms and procedure for compensation for damage may be specified in the contract or additional agreement. In other cases, interaction between the parties is carried out in accordance with the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the debt can be reimbursed on a voluntary basis. The delay or refusal of the employer to issue a work book deprives the dismissed person of the opportunity to work and earn money, which affects the quality of life of the person and his family.
Article 234 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates the relations of the parties in case of incorrect registration of a work book. For legislation, there is no fundamental difference in refusal of issuance, delay or incorrect registration. The procedure for compensation for damage is specified in Article 394 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- The reason indicated by mistake is deleted by striking out with a link, signature and transcript of the entry made.
- The organization issues a new dismissal order and transfers it to the labor office.
- The victim receives wages calculated on average for the days of impossibility of employment.
At the same time, labor legislation does not consider it an error to record a dismissal by agreement of the parties if it occurred at one’s own request. This is not a barrier to employment and does not cause any harm.
Compensation for moral damage
Compensation is subject to moral damage caused to a quitter as a result of the actions of responsible persons of the organization. Along with the untimely issuance of documents, the payment of wages is also delayed.
A person fired from work is left without a livelihood, cannot find a job and cannot reach management personnel.
Compensation for moral damage occurs in court. According to the law, the dismissed person has three months to file an application. The court takes into account the severity of the harm caused, witness testimony and important facts.
Administrative penalties
For the untimely issuance of a work book to a resigned employee, the employer is liable under the provisions of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. A fine of 1 to 5 thousand rubles is imposed on an employee of the personnel department or other responsible employee appointed by order of the organization. The same amount will have to be paid to small business owners. For large enterprises, the fine ranges from 30 to 50 thousand rubles.
Administrative liability for an official or organization occurs in cases where a dismissed or resigned person files complaints with the State Labor Inspectorate or the Prosecutor's Office. The final authority is the court. In the event of a court decision in favor of the former employee, the employer pays all costs.
Obtaining a work book upon dismissal
The issuance of a work book upon dismissal is regulated by law. According to Art. 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it must be handed over to the employee on the last working day, which is considered the day of dismissal.
However, in some cases, on the day of dismissal, an employee may be absent from the workplace or refuse to receive a book. In such circumstances, you should send him a notice by mail containing a request to appear at the organization to receive a work book or an offer to send the document by mail. Postal forwarding is permitted only after receiving the written consent of the dismissed employee. Compliance with this procedure relieves the employer of further liability for late submission of the document.
For information about what actions need to be taken in some cases of dismissal of employees, see the article “How to properly arrange leave followed by dismissal.”
Responsibility for repeated violation
When the employer commits the same violation again, he will have to pay more (clause 2 of Article 5.27 of the Administrative Code). The extent of responsibility is as follows:
| Fine, rub. | ||
| Entity | IP | Head of the organization |
| 50000-70000 | 10000-20000 | 10000-50000 |
Important! The manager will no longer get off with a warning. Cash payments can be replaced by disqualification for a considerable period - a minimum of a year, a maximum of 3.
Example. Individual entrepreneur Molotov refused to issue a work certificate to his seller after his dismissal. Motivation - he did not provide an act of write-off of products. Molotov turned to the labor inspectorate. Experts discovered that the individual entrepreneur had already committed a similar violation and got off with a fine of 1,000 rubles. For repeated failure to comply with legal norms, he was fined 10 thousand rubles. fine and ordered to return the document to Molotov within 3 days. Otherwise, the inspection will help the employee file a claim in court.
Issuance of work books to third parties
Sometimes it is possible to transfer a document without the participation of the dismissed person. In the event of the death of an employee, the work book should also be drawn up in accordance with all the rules, the appropriate entries should be made and handed over to the relatives of the deceased. The document can be sent by mail upon their written request. Confirmation of the presence of a family relationship can be any document: birth certificate, marriage certificate, etc.
An authorized representative of a dismissed employee also has the right to receive a work book. In this case, you must present a completed power of attorney containing the following information:
- information about interested parties (principal and recipient), details of documents proving their identity;
- the nature of the entrusted actions performed;
- sample signatures;
- validity period of the document.
The issue of the book must be confirmed with a receipt from an authorized person confirming its receipt. If the issuance of a document is impossible due to refusal of receipt or lack of demand, it should be stored until required. The maximum storage period by the employer is 75 years if the document was completed after 01/01/2003, and 50 years if before 01/01/2003 (Rosarkhiv order No. 236 dated 12/20/2019).
For more detailed information about the storage periods for documents, see the article “What is the storage period for personnel documents in an organization.”
What to do if a labor payment slip is not issued on the day of payment from work?
On the day of dismissal, the employer is obliged to make a full payment and issue a work book (LC) to the dismissed employee (Article 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Labor is given at a different time only in the following situations:
- if the dismissed person refuses to receive documents drawn up upon his dismissal;
- if an employee is absent from work on the day of dismissal, in this situation he is sent a letter or written notification of the issuance of a work permit;
- in the event of expiration of a fixed-term employment contract with an employee on maternity leave, the duration of the employment contract (agreement) with whom was officially extended until the end of pregnancy or until the end of maternity leave on the basis of Art. 261 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- if the established last day of work does not coincide with the date of dismissal of the employee in case of absenteeism or dismissal on the basis of a corresponding court verdict.
Obviously, the first two options are possible only in connection with the initiative of the employee himself not to immediately collect the work book.
A delay in issuing a work permit at the initiative of the employer is considered illegal : for example, if a resigning employee:
- did not issue a bypass sheet;
- did not hand over any material assets (documents);
- did not complete the inventory;
- did not complete certain work, etc.
Where to go?
If there is a delay in issuing a work permit upon dismissal, the employee must send a written request to his employer demanding that such a document be returned to him within the appropriate time frame.
However, if such actions do not lead to the desired results, then you can proceed to the following legal options for solving this problem:
- send a written complaint to the labor inspectorate (Rostrud);
- file a formal complaint with the prosecutor's office of the Russian Federation;
- file a claim in court.
As a result, for failure to issue a work permit upon dismissal, the employer may be held administratively liable (Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). In addition, if such a guilty person goes to court, it is possible to recover compensation for lost earnings and compensation for moral damage, respectively (Articles 234 and 237 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In order for the employer to be held accountable, employees should submit an application to the territorial branch of Rostrud, that is, the local labor inspectorate. Rostrud brings the guilty person to justice on the basis of Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. In addition, the labor inspectorate sends an order to the employer to eliminate various violations of the law, including delays in issuing work permits.
When going to court regarding the delay in issuing a work book, an employee must keep in mind that the statute of limitations for such a labor dispute is three months (Article 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If you file a claim later, the employer will be able to claim that the statute of limitations has passed and the court will not consider the case .
If a claim is filed to receive compensation for lost earnings, the plaintiff (employee) is exempt from paying state duty (subclause 1, clause 1, article 333.36 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Responsibility of the employer for untimely transfer of the work book
So, the employer is obliged to issue a work book when dismissing an employee on the last working day or send documents in other ways if the dismissed person was not at the workplace.
In case of delay in issuing a document or making incorrect entries, the employer bears full responsibility. He is also obliged to compensate the employee for days of delay for a document not received in the amount of average earnings (Article 165 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The new day of dismissal is confirmed by an order, on the basis of which another entry must be made in the book. The previous entry is considered invalid.
IMPORTANT! Incorrect information in the document can be challenged by the employee in court.
But even if the employer does not refuse to make corrections, it may still be liable, including a claim for financial damages, if the employee was denied employment. Compensation is also provided in cases of illegal dismissal or transfer to another position without obtaining the consent of the citizen (Article 234 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The employer will also be held liable if he refuses to provide information to employees. This applies not only to the issuance of the document itself, but also copies. In these situations, management may face criminal liability based on the provisions of Art. 140 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. Punishment may include large fines or a ban on holding certain positions.
For information on how to build a personnel policy, including regarding the collection and storage of necessary documentation, see the article “Procedure for maintaining personnel records at an enterprise.”
NOTE! Issuing a document late without valid reasons is fraught with a fine for the organization in the amount of 30,000 to 50,000 rubles, as well as suspension of activities for up to 90 days. For entrepreneurs, the fine amount will be from 1,000 to 5,000 rubles. For repeated illegal actions of a similar nature, fines may be increased to 70,000 rubles. for legal entities and up to 20,000 rubles. for individual entrepreneurs (clauses 1, 4, article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
But under some circumstances, responsibility for the delay in issuing a work book is removed from the employer. This happens if the last working day does not coincide with the day of dismissal. For example, when dismissing a woman who is on maternity leave, it is not always possible to hand over a document to her on the same day due to her absence from the workplace. The same applies to persons who have committed truancy. In such cases, the document must be sent to the employee no later than three days after his application.
Is labor delay not an obstacle to employment in a new place?
In turn, the St. Petersburg City Court did not seek compensation from the organization at all for the work book not being issued to the employee on time. (Appeal ruling dated November 6, 2018 No. 33-22399/2018). The judges noted that the fact of delay in itself is not sufficient to qualify the employee for such compensation. The employee must also prove the existence of attempts at employment and refusals due to his lack of a work book. In addition, in the situation considered, although the employer lost the original work book, he made efforts to correct it, the judges indicated.
So, the HR service manager of the LLC agreed with the employer to dismiss her by agreement of the parties (clause 1 of part 1 of Article 77 of the Labor Code) and to send the work book by mail to her home address. After some time, it turned out that the work was lost.
The employer independently decided to issue the former employee a duplicate document, for which he sent requests to her previous places of work. As a result, the dismissed employee received the necessary papers only four months later and went to court, demanding to recover 170 thousand in compensation from the employer for the delay in issuing the work book.
The courts of two instances rejected the claim, pointing out that the employer is obliged to reimburse earnings for the period of delay in issuing a work book only if the former employee proves that he was unable to find a job without having documents in hand. The plaintiff informed the court about the fact of refusal to hire, but did not provide evidence of this.
As a result, the St. Petersburg City Court concluded that there were no grounds for compensating the employee for damages due to illegal deprivation of the opportunity to work.
The same argumentation is presented in the appeal ruling of the Moscow City Court dated November 14, 2016 in case No. 33-39997/2016. It’s funny that the Moscow City Court referred to its right to evaluate evidence according to its inner conviction (Part 1 of Article 67 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
As for the Nizhny Novgorod Regional Court, in its ruling dated 02/06/2018 in case No. 33-771/2018, the following was noted: a delay in issuing a work book is an obstacle to the employee taking a new job, and, as a result, entails the deprivation of the employee’s opportunity to work and receive wages. Accordingly, a legally significant circumstance is the establishment of the fact that the employee, after dismissal, applied to other employers for the purpose of employment and the fact that this was refused due to the lack of a work book. In this case, the responsibility to prove these circumstances rests with the employee. If we follow this logic, then an employee who has not provided evidence of applying to other employers for employment after dismissal and being denied this because he does not have a work book, has no right to compensation.
note
From the day the employee is notified of the need to appear for a work book or agree to have it sent by mail, the employer is released from liability for the delay in issuing a work book (clause 36 of the Rules for maintaining and storing work books, producing work book forms and providing employers with them).
Meanwhile, refusal to hire due to lack of a work book is illegal. In any case, it is not determined by the employee’s business qualities (Article 62 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 10 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2). True, on the basis of Article 65 of the Labor Code, a person applying for work presents the employer with a work book (except in cases where an employment contract is concluded for the first time or the employee enters work on a part-time basis). But if a person applying for work does not have a work book due to its loss, damage or for any other reason, the employer is obliged, upon a written application from this person (indicating the reason for the absence of a work book), to issue a new work book. This norm confirms that the absence of a work record does not prevent employment.
Results
The procedure for registering the dismissal of employees includes the mandatory issuance of relevant documentation, including a work book. The timely issuance of a work book upon dismissal with correctly entered entries is certified by the signature of the employee. Responsibility for further storage of the document is removed from the employer.
If it is not possible to transfer the work book, you must request permission in writing from the dismissed employee for postal forwarding.
In some cases, it is possible to transfer the document to authorized persons. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
How to make a payment
The employee’s application has a free form and the following required information:
- date of dismissal in accordance with the order;
- an indication of the actual date of receipt of the document;
- reference to the regulatory basis for receiving compensation - Art. 35 Resolution No. 225, art. 234 TK).
If the employer admits guilt and decides to pay, an order is issued. Compensation for moral damages (if paid) should be included in the order. The form of the document is not regulated by law and is drawn up in the usual manner. An order to change the date of dismissal and payment of compensation can be combined:
- the order confirms the new day of dismissal of the employee;
- the previously made entry about the day of dismissal is invalid;
- an order is made to make a new entry in the Labor Code;
- compensation is awarded.
A separate order on voluntary payment of compensation for the delay in issuing a work book looks shorter.
How much compensation is a dismissed person entitled to?
For the delay in issuing a work book, a dismissed person is entitled to appropriate compensation , drawn up on the basis of Art. 234 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The amount of such a payment is calculated based on the average daily earnings for each day of delay (clause 9 of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 922 of December 24, 2007, Article 139 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Such compensation for lost earnings is calculated using the following formula:
Average daily earnings x Number of working days during which the work book was not issued. Average daily earnings = (Salary amount for the last 12 full months) / (Number of working days worked for 1 year).
The salary amount in this formula includes salary, bonus, additional payments and allowances.
When calculating the average daily earnings of an employee, sick leave payments, vacation pay, as well as travel payments, absenteeism, downtime, etc. are not taken into account.
also obliged to compensate the dismissed employee for moral damage caused to the latter in the event of a delay in issuing the work permit. In accordance with Art. 237 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, such damage of a non-property nature is subject to compensation in monetary form.
When establishing the amount of compensation for moral damage, the court takes into account the degree of guilt of the defendant (employer), the period of non-issuance of the work permit, as well as the presence or absence of evidence that it was precisely because of such a delay that the employee was unable to find employment anywhere. When considering such a case, the requirements of reasonableness and fairness are taken into account (Article 1101 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The court may reduce the declared amount of compensation for moral damage at its discretion.