Rate of the simplified tax system “Income”
The tax rate shows how much percent of income the state will have to pay. In most cases it is 6%. But there are regions that have reduced the rate.
In Crimea and Sevastopol the rate is 4%. In Sevastopol, you can pay even less - 3%, if you run a business from the list of preferential activities. In the Chechen Republic, the tax rate depends on the number of employees and ranges from 1% to 6%.
In Moscow, St. Petersburg and Yekaterinburg, the simplified taxation system rate is standard - 6%.
Find out on the tax website in the section “Features of regional legislation” what rate is valid in your region.
If your income for the year exceeds 164.4 million or there are more than 100 employees, then the rate for any region will increase to 8%.
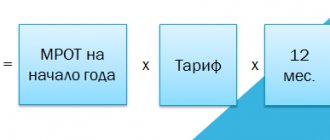
Calculation of the final tax amount of the simplified tax system
When calculating the annual tax, income can also be reduced by losses incurred in the previous year.
That is, to calculate the total amount:
- Subtract expenses and losses from previous years from income.
- Multiply by 15% or regional rate.
- Subtract advance payments calculated based on the results of previous reporting periods.
If advances transferred during the year exceed the final tax, it means that there is an overpayment to the budget. It can be offset against debts on taxes, penalties and fines. If there are no debts, the overpayment can be returned to the current account or offset against future tax payments.
Calculation example. Annual income - 886,000 rubles, expenses - 204,600 rubles. Last year's loss was 15,200 rubles. Advances paid: 1st quarter - 19,110 rubles, 2nd quarter - 10,695 rubles, 3rd quarter - 28,050 rubles. The tax rate is 15%.
Tax simplified tax system = (886,000 - 204,600 - 15,200) x 15% = 99,930 rubles.
Tax minus advance payments = 99,930 - 19,110 - 10,695 - 28,050 = 42,075 rubles.
What is considered income under the simplified tax system?
Income under the simplified tax system is everything you earn from your business. Basically, this is income from the sale of goods or services. For example, you developed a website and received 100 thousand rubles for the work. Record the same amount in the income of the simplified tax system and pay tax on it.
There are also non-operating incomes that are not directly related to the business, but they also need to be taken into account. These include:
- interest on the current account balance;
- fines and penalties from partners for violated terms of the contract;
- compensation for damage from the insurance company;
- exchange rate difference when buying or selling currency at a rate that is more favorable than that of the central bank;
- gifts and other free property received;
- other income from Art. 250 Tax Code.
Most often, you receive income in cash. But there are non-monetary incomes, for example, with barter and mutual offsets, when you exchange one product for another. Such income also needs to be taken into account - in rubles at the market value of a similar product.
Convert income in foreign currency into rubles at the central bank exchange rate in effect on the day you receive the money. We talked about this in more detail in the article “How to pay taxes when making payments in foreign currency.”