Both the employee and the company management have the right to terminate the employment contract. However, if for the former there are practically no restrictions when initiating such a procedure, and he can leave almost at any time, for the employer, dismissal of employees is associated with certain difficulties. The fact is that he can pay off an employee only if there is one of the grounds outlined in Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Under what article is dismissal initiated by the employer?
Unlike a hired employee, who, in accordance with the text of Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, can demand termination of the employment agreement at any time and, having worked the required two weeks, receive a payment, the management of the organization, when dismissing an employee, is obliged to indicate a specific reason. The grounds for terminating an employment contract initiated by the employer are listed in Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It is not by chance that the grounds are enshrined in law.
Information
In the “employee-employer” tandem, the first is a priori considered the more vulnerable party. Therefore, reflection in the Labor Code of the main reasons for dismissal is a universal protection of the interests of hired employees.
What should you do if your employer fires you without warning?
Any dismissal must be confirmed by a statement; they cannot be fired without reason. For example, the employer fired at his own request, but the employee did not write such a statement. If the employer did this, it is necessary to seek help from regulatory and supervisory authorities.
Where to go for help? Violations of the rights of employees in the world of work are committed by:
- labor inspectorate;
- the prosecutor's office;
- court.
In order for an employer to be held accountable for illegal dismissal, it is necessary to write a complaint and submit it to the appropriate authority. You can immediately contact the court and supervisory authority. However, there is no limitation period for applying in pre-trial proceedings, but for applying to court it is established by Article 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
to go to court to resolve a dispute over illegal dismissal. The period begins from the moment the dismissed person is given the order.
We correctly draw up an application to the supervisory authority
To contact the labor inspectorate or the prosecutor's office with a complaint about illegal dismissal, you must correctly draw up an application. According to Art. 7 of Law No. 59-FZ, the complaint must include the following information:
- information about the body to which the complaint is filed;
- information about the applicant - full name, passport data, residential address, contact details;
- information about the employer - full name, full name and position of the manager, legal address, document on the basis of which the activity is carried out;
- the reason for the complaint - what rights were violated, when it happened, you need to describe the situation in detail;
- requirements - to conduct an inspection or reinstate a person in his position;
- personal signature and date of writing.
In order for the supervisory authority to accept a complaint for consideration, it must meet the following requirements:
- be in writing - oral appeals are not a reason to conduct an inspection on the fact of a violation;
- signed by the applicant - anonymous complaints will not be accepted for consideration;
- reliable and relevant.
complaints to the State Tax Inspectorate about illegal dismissal
complaints to the prosecutor's office for illegal dismissal
What actions should the inspection body take?
Upon complaint, the supervisory authority must conduct an unscheduled inspection at the enterprise. The duration of this process depends on the size of the enterprise. For example, at micro-enterprises the inspection must be carried out within 15 hours.
If during the audit it turns out that the employer violated the rights and fired the person without reason and without warning, he will be held accountable.
If the dismissed employee expressed a desire to be reinstated, the employer will be required to do so within one day after the decision is made.
We draw up a claim correctly
You don’t have to contact the supervisory authority, but go straight to court. An illegally dismissed employee has this right. But this must be done within 1 calendar month from the date of receipt of the work book or a copy of the order for review.
You need to contact the judicial authority:
- at the location of the employer;
- at the place of residence of the plaintiff - an illegally dismissed employee;
- at the place of execution of the contract, if it is specified in the employment agreement, and it differs from the location of the employer and the place of residence of the plaintiff.
Liquidation of an organization
The procedure for closing an organization is defined in Articles 61-63 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The grounds for liquidating a company are outlined in Article 61 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. They act as:
- Judgment;
- The decision made by the founders of the enterprise.
When a company closes, all workers lose their jobs. However, in this case, employees have certain guarantees, since the law specifies that dismissed employees should be the first to receive a payment with compensation for days worked.
Reduction
At the initiative of the employer, the list of places at the enterprise may be reduced. Employees holding positions are subject to calculation. In this case, dismissal is carried out according to a certain gradation: first of all, employees with the least qualifications and productivity among those occupying a certain position, for example, managers, are removed from the workplace. But if workers are equal according to these criteria, then Article 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes a preferential right to retain a place for the following categories:
- Persons with more than two dependents;
- Breadwinners are the only ones receiving income in the family;
- Employees who were injured during their work in this company;
- Disabled combatants and WWII;
- Employees undergoing advanced training conducted at the initiative of the employer.
For circumstances beyond the control of the employee or employer
In such cases, according to Art. 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, include:
- military conscription (the key fact is that the person has received a document confirming the conscription);
- reinstatement of the former employee by decision of the court or the state labor inspectorate (before dismissal, the person must be offered all available vacancies in the area; if the transfer is refused, the person is fired);
- non-election to a position (applies to those with whom an agreement was concluded in connection with election to a position for a certain period (including based on the results of a competition);
- imprisonment by court verdict;
- disability for medical reasons;
- death or recognition as missing (if an individual entrepreneur terminates his activities due to death, the day of termination of employment relations is the day of death of the entrepreneur. The basis is the death of the employer, payments are made at the expense of his property and inheritance by court decision. The death of an employee must be confirmed by an official document, the amount payments and work book are issued to close relatives);
- emergency circumstances;
- administrative punishment (disqualification, ban on holding certain positions);
- expiration of the contract, suspension for a period of more than 2 months;
- denial of access to state secrets, if necessary;
- cancellation of the decision on reinstatement.
Severance pay for the listed reasons is paid only to those called up for military or alternative service, persons recognized as disabled, and persons dismissed due to the reinstatement of those previously dismissed. The amounts are calculated from the average salary for the previous two years of work, recalculated for two weeks.
The procedure for terminating an employment contract at the initiative of the employer is the same as in the usual manner, and involves the issuance of an order, familiarization with it, issuance of a work book and final payment.
In all cases, the order and work book reflect the corresponding paragraph of Art. 83 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Employee mismatch for position
If an employee does not have the skills necessary to work in the given position, he may also be subject to dismissal. However, before signing an order in accordance with which the employee will be calculated, the employer must convene a commission to conduct certification designed to confirm the incompetence of the employee.
For your information:
The inspection is usually carried out once a year, however, if insufficient knowledge or defects in work are detected, it can be initiated ahead of schedule.
Gross violation of labor duties
The category of gross violations according to Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation includes:
- Failure to maintain secrets protected by law;
- Absenteeism;
- Direct violation of established labor protection rules;
- Appearing at the workplace in a state of intoxication with alcohol or drugs;
- Causing damage to property of the institution that does not belong to the employee, its appropriation, embezzlement.
Attention
When such violations are recorded, the law allows the employer to immediately pay the employee.
Other reasons
In addition to the above reasons, an employer may dismiss on the following grounds:
- Change of owner of the organization’s property;
- Guilty actions of an employee involved in servicing valuables or money turnover, leading to loss of trust;
- Amoral behavior;
- Providing false information and documents;
- An unjustified decision of a manager or other official, as a result of which damage was caused to the property values of the company or its branch;
Some other reasons for dismissing an employee are also reflected in other provisions of labor legislation. An additional list is established by Articles 71, 278, 312.5, 336 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
For your information:
Also, other actions leading to dismissal may be indicated directly in the employment contract.
Multiple violations of discipline
The law also provided for the possibility of dismissing an employee who regularly violates labor discipline and does not plan to improve. In this case, you need to follow these steps:
- To establish the fact of violation of labor discipline - non-compliance must be recorded in an act or other document (Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Demand an explanation from the culprit (Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). An offer to provide explanations must be made in writing; if the person is absent, it must be sent by mail.
- To identify the presence of an outstanding reprimand or reprimand - no more than a year should pass from the moment of involvement in the first case (Articles 81, 194 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Make sure there are no valid reasons for violation of discipline. For example: if you are absent from work, you need to make sure that the employee did not donate blood, did not get into an accident, does not have a court summons, etc. Determine whether the woman is pregnant (Article 81, Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) .
- Issue an order (Article 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), familiarize the perpetrator with it against his signature, or draw up an act (Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Make an entry in the work book.
- Issue final payment and work book on the day of dismissal. Here, if an employee causes material damage to the enterprise, resolve the issue of compensation (Articles 232, 238 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
IMPORTANT!
I draw your attention to the fact that the duties for which a person is involved must be established by an employment contract, internal labor regulations, job descriptions, technical rules (and the contract must contain a reference to the last two).
The procedure for dismissing an employee at the initiative of the employer
In order for the employee calculation procedure to be considered justified, the employer must comply with the requirements of the law and consistently complete all stages of dismissal.
Preparation of necessary documents
Dismissal must be confirmed by an appropriate document. Depending on the dismissal of an employee from a position, the following documents may be used:
| Reason for dismissal | Document being drawn up |
| Closing a business | Decision of a judicial authority or board of founders |
| Position mismatch | Protocol reflecting the decision made by the certification commission |
| Staff reduction | Manager's order |
| Failure to fulfill official duties | An order for disciplinary action, or a Representation written by the immediate director of the enterprise |
| Change of company owner | Certificate confirming amendments to the registration papers of the organization |
| Being intoxicated at work | Inspection protocol and violation report |
| Absenteeism | Certificate of absence |
| Disclosure of secrets | Protocol of internal investigation |
| Loss of trust | Judgment |
| Damage to company property or its waste | An audit report drawn up by the tax service |
| Immoral behavior, theft of property | Act on the commission of an act that entailed administrative liability |
Issuance of an order
Based on a document explaining why the employee is leaving, an order is issued to pay the employee. The paper is drawn up in accordance with the mandatory form adopted by the Government of the Russian Federation - No. T-8. If we are talking about the calculation of several employees, an order drawn up according to template No. T-8(a) is used. The document includes:
- Full name of the head;
- Company details;
- Information about the employee;
- Reason for calculation;
- Date of preparation.
Attention
The order is certified by the signature of the immediate director of the organization or his authorized representative.
Registration of an order
The completed dismissal document is transferred to the HR department of the enterprise. Its details are entered into a special accounting book. A copy is made of the paper and placed in the personal file of the dismissed employee. Another copy of the document can be provided directly to the employee.
Familiarization of the employee with the order
Article 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation contains a provision on the mandatory provision of a dismissal order to the employee for review. In this case, the latter must sign and indicate the date of reading the paper.
If the employee ignores the need to sign the order, or his whereabouts are unknown, a corresponding mark is placed on the paper.
Important
If the employee does not agree to endorse the document, then a written refusal is drawn up, which is certified directly by the person being dismissed and three witnesses.
Formation of a note-calculation
Upon dismissal, the employee claims to receive compensation payments for the unused vacation period, as well as sick leave. They are calculated on the basis of a special calculation note, which reflects unpaid days or additional time that needs to be worked.
Direct employee payment
On the day of official dismissal, the employer must pay the employee the full amount of money due, and also hand over the work book in his personal file. A similar provision is recorded in Article 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Creating a settlement record
Information about dismissal is reflected in the accounting documentation of the enterprise, as well as in the employee’s personal card. Entries are made by personnel department employees with mandatory certification by the signature of the dismissed person.
What payments are due?
When dismissing the employee, the employer must pay the employee in full on the last day of work. Payments include:
- wages for the days worked;
- additional payments to wages;
- compensation for unused vacation;
- severance pay (in cases provided for by law). If it is not possible to pay the due funds on the day of dismissal due to the employee’s absence, these amounts must be issued no later than the next day upon submission of the request for payment. If the company is liquidated, the employee will receive severance pay. The calculation will be made from the average monthly earnings. The employee will receive compensation in the amount of 2 months' salary while looking for another job. In some cases, the salary will remain for the 3rd month. If the chief accountant, manager, or his deputy are dismissed when the owner of the institution changes, they will be paid an average monthly salary for 3 months. If the contract is terminated due to inadequacy of the position or for medical reasons, the person will receive compensation in the amount of two weeks' salary upon dismissal. If the institution has a collective agreement, the document may provide for other payments in the event of dismissal. If dismissal at the will of the employer concerns a pensioner, the latter will be provided with payments and compensation. In addition, the employer can provide the employee with incentive payments for a high level of professionalism.
Thus, it is not easy for the employer to terminate the contract and dismiss the employee on his own initiative. When using this format of dismissal, the manager must strictly adhere to the provisions established by the legislator.
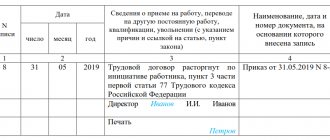
Making an entry in the work book
The wording of the reason for dismissal entered into the employee’s work book directly depends on the grounds provided for in Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In general it looks like this:
- First, the fact of calculation itself is displayed. The entry must begin with the word “Fired.”
- The following is the basis for dismissal. The wording must correspond to the reason indicated in Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (for example): “in connection with the liquidation of the enterprise”, “in connection with the inadequacy of the position held”.
- Then the regulatory framework is entered, that is, the clause of the article containing the specified reason for the calculation. For example, paragraph 1 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Rules for writing an application
It is immediately worth noting that the dismissal of a subordinate at the initiative of the employer does not involve writing a statement . All actions are carried out on the basis of an order issued by the head of the organization. In this case, an entry is made in the work book in accordance with one of the wordings set out in Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (for example, “one-time gross violation of labor duties”).
However, there are some nuances here. A lot depends on the reason why the decision was made to remove a particular employee from his position.
So, if the basis was a gross violation of discipline or any other serious offense, then in most cases the employee is asked to write a letter of resignation of his own free will. This is done to ensure that the offender does not have problems with further employment.
As a rule, this application is prepared in any form on A4 paper. However, its content should include the following information:
- Input data (“header” of the document) - here the full name of the head of the organization in whose name the application is written is written, as well as information about the employee himself (name of position, department, full name).
- Next, in the center of the paper, the name of the document is indicated - usually the following standard wording is used: “Application for resignation of one’s own free will.”
- Then a reference is made to Art. 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and it is indicated that the applicant wants to leave his position on his own initiative. At the same time, the desired date of dismissal is also indicated.
- At the end of the application, the date of its preparation and the employee’s signature are indicated.
However, it is worth remembering that not in every situation you should agree to write a letter of resignation on your own initiative. This mainly concerns staff reductions, as well as the liquidation of the organization.
In this situation, with such proposals, the employer is trying to free itself from the obligation to pay compensation to the employee. If the latter writes such a statement, then in the future he will lose a large sum of money that is due to him by law. Moreover, in this case it will be difficult to challenge such an action by the employer.
Terms of dismissal. Is work needed?
If the justification for dismissal is closure of the company or layoff, management must notify the employee in advance. It is legally established that notification of the liquidation of an organization and layoffs must be made 2 months before dismissal.
When there is a change of staff due to the arrival of a new director, the dismissal of employees hired by the predecessor is carried out within a three-month period, calculated from the date the current management takes office.
Information
Unlike cases of settlement by agreement of the parties or at the request of the employee himself, dismissal at the initiative of the employer does not entail the need to work off. In fact, the day of termination of the employment contract is considered the employee’s last working day.
During the probationary period
It is possible to dismiss an employee at the initiative of the employer during a probationary period due to Part 1 of Art. 71 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, if the test result is unsatisfactory.
To make it easier in the future to prove a person’s insolvency as an employee, upon hiring it is necessary to draw up a list of tasks and specific requirements that must be fulfilled. To successfully complete these tasks, you must solve them.
During the probationary period, the employee can be dismissed at any time at the initiative of the employer, while confirming the inadequacy of the position held.
To do this, it is necessary to document every fact of non-fulfillment of assigned tasks. And in the event of a conflict situation, the organization will be able to use these documents to prove the incompetence of the dismissed person.
It can be:
- acts on defective products;
- reports and memos from immediate supervisors and colleagues about the poor performance of their duties by the subject;
- protocols of the commission based on the results of passing the test period;
- reports from the subject on the results of his activities;
- orders for disciplinary action during the probationary period.
An important point is a written notification 3 days before the end of the term indicating the reasons for termination of the contract at the initiative of the employer.
It takes into account the following nuances:
- form - written only;
- deadline - no later than 3 days before the end of the term;
- the reason is an unsuccessful result, a negative assessment of the work by management.
Please note that the contract should have reflected the test clause. If it is not there, the employee is considered accepted without testing (Article 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If the warning period is not met and the person continues to work after the expiration of the period, he is considered to have passed the test.
Payments due upon dismissal
In case of dismissal initiated by the management of the organization, in accordance with Article 127 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it is first necessary to compensate for the employee’s vacation days that were not used during the validity period of the employment contract. A full payment is also made to the employee for the time worked.
Further payments depend on the reason for dismissal. Employees whose employment contract is terminated due to the closure of an organization or due to a reduction in staff are eligible for certain compensation.
Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the need to transfer to the employee an amount equal to the average monthly earnings. In the future, the dismissed person can apply for an average salary within 2 months if he was unable to find a job during this period of time.
By agreement of the parties
Dismissal by agreement of the parties is possible on the initiative of both the employer and the employee himself. This basis for termination of an employment contract is mentioned in Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and is described very briefly. Such dismissal is allowed at any time, which is logical, because the parties act by mutual agreement. The employer should act in this case as correctly as possible and not allow coercion of the employee or other influence on his expression of will. Otherwise, subsequently, based on a complaint from a dismissed citizen, the dismissal may be declared illegal. Particular attention should be paid to the wording of the agreement.
Employees who cannot be fired
The employer will not be able to pay off all employees at will. The following citizens are legally protected from dismissal:
- Pregnant women, as noted in Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- Single fathers and mothers who have a child under 14 years of age. And in the case of disabled children – 18.
- Minors. To formalize the dismissal, you will need to notify the Commission on Minors' Affairs and the Labor Inspectorate and obtain consent from both organizations, as stated in Article 269 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- Employees on vacation.
- Employees who have issued sick leave.
Important
In all cases there is an exception. Dismissal can be made if the company ceases to exist.