Leave for workers in the Far North: terms of provision
A large number of preferences have been established for the population of the Far North and equivalent territories.
Among these is the provision of additional leave (Article 116 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Read more about all the benefits that northerners are entitled to in the article “What benefits are available to workers in the Far North?”
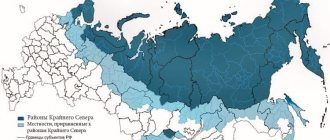
The list of regions belonging to the Far North of the Russian Federation, as well as those equivalent to it, was approved by Resolution of the USSR Council of Ministers of November 10, 1967 No. 1029, which continues to be applied today. This regulatory legal act may be supplemented by secondary legal acts, such as Decree of the Government of Russia dated April 24, 2007 No. 245.
For lists of areas belonging to the Far North and equated to it, see here.
In this case, the location of the employer for whom the person works does not matter. His office may even be located in the south of the Russian Federation, but additional leave will need to be paid for an employee working in the North. In turn, if an employee works in the south, and the employer is located, for example, in Chukotka, he does not have to fulfill the obligation to provide leave.
Inspector of the Federal Service for Labor and Employment E. A. Shirshova told how to pay for vacation for an employee sent to the Far North region.
Get trial access to the ConsultantPlus system and read the official’s opinion for free.
Shift workers working in the Far North and equivalent regions are also entitled to additional leave. At the same time, when calculating the length of service on the basis of which vacation is calculated, the days that employees spend getting to the place of work are also included (Article 302 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The effect of labor legislation, according to which a citizen working in the Far North receives the right to additional leave, fully applies to workers performing their labor functions remotely, provided that the contract is concluded in accordance with the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, it matters in which region the person officially lives - as a rule, this is determined by registration.
It is worth noting that when traveling to the Far North and to the constituent entities of the Russian Federation equated to it, northern vacations are not provided, with the exception of situations when employees are engaged in work related to the exploration of oil and gas fields, organize expeditions (clause 4 of the appendix to the order of the Ministry of Labor of the RSFSR dated 22.11.1990 No. 2).
Expenses for a northern vacation, as well as for paying for a regular one, can be used to reduce the tax base of the enterprise. But if the employer adds additional days to the legally guaranteed vacations provided for by local agreements, then they can no longer be taken into account for tax purposes (clause 24 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Territories belonging to other regions of the North
Resolution of the USSR Council of Ministers dated January 3, 1983 No. 12 defined the regions of the Far North and all territories that are equivalent to it. The list of other regions of the North is not fixed by any regulatory act. Moreover, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides such a category of northern territories in Art. 321 doesn't even mention it. However, the obligation to provide an eight-day northern additional permit to workers in such territories is established by Art. 14 of the Law of the Russian Federation No. 4520-I.
To classify a territory as a district under consideration, two conditions must be met:
- The territory is not recognized by the Far North, nor is it equated to it.
- It is subject to a percentage premium and a regional coefficient is applied.
The corresponding allowances and coefficients should be established by the Government of the Russian Federation, which follows from Art. 315–316 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. However, as of 2022, the relevant regulatory documents have not been published, therefore, by virtue of Part 1 of Art. 423 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in order to resolve the issue of recognizing a locality as a region of the North, one should be guided by the legal acts of the Russian Federation and the former USSR, which previously established coefficients and premiums. This is precisely the rule provided for in Part 1 of Art. 423 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (in particular, this is confirmed by order of the Ministry of Labor of the RSFSR dated November 22, 1990 No. 2).
Important! The opportunity to receive an 8-day “northern” vacation is the only privilege for workers in the northern regions that are not classified as the Far North and equivalent areas. Other benefits entitled to northerners (including compensation for vacation expenses) are not provided to them.
Northern holiday duration
In accordance with Art. 321 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as Art. 14 of the Law “On State Guarantees and Compensations” dated February 19, 1993 No. 4520-1, citizens have the right to count on additional paid leave:
- when working in the Far North - 24 days for work during the calendar year;
- when working in areas equated to the Far North - lasting 16 days for work during the calendar year.
Thus, the total annual vacation in the regions of the Far North can be 52 days, and in areas that are equivalent to it - 44 days (if we consider the standard 28-day vacation along with the northern one).
As is the case with regular vacation, public holidays that fall during the northern vacation period are not included in it and are not paid (Article 120 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Minor citizens have certain preferences when calculating leave - their total paid leave is 3 days longer than that of adult workers (Article 267 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation): if they work in the Far North, they can rest for a total of 55 days.
If a person has the right to other additional leaves provided for by the contract (for example, for irregular work), the days of northern leave are summed up with them, while replacing one additional leave with another is unacceptable (Article 322 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If additional leave is calculated for shift workers located in the Far North or in a region equivalent to it, then its maximum duration is, respectively, 24 or 16 days per 12 calendar months of work. The actual duration of the vacation is calculated proportionally - for example, if a person worked a total of 3 months on a shift (and was also on the way to it), then he is entitled to a northern vacation lasting 6 days.
About remuneration during shift work, read the material “Remuneration during shift work.”
Duration of vacation in the Far North
The Russian state guarantees every working citizen a vacation of at least 28 calendar days per year. It may be longer if this is expressly provided by law. Such exceptions include the vacation of northerners, which is extended in several ways.
Firstly, for some categories of government employees in the northern regions, an extension of the main rest period is provided: for example, for the judiciary it is no less than 45 working days, for prosecutors, police officers and employees of investigative bodies it is no less than 45 calendar days.
Secondly, all employees of the northern territories, in addition to days of rest under general conditions, have the right to receive additional ones, which are paid in the amount of:
- 24 calendar days when working in the Far North (geographically);
- 16 calendar days if they work in areas with similar climatic conditions;
- 8 calendar days, if the area is not classified in the above categories, but the Government has established northern salary supplements in it.
In addition to the specified vacations, northerners may be granted additional ones for other reasons, for example, due to hazardous production conditions.
Thus, the total rest time for northerners consists of the main days and all preferential days.
Northern vacation for part-time workers: nuances
Any types of paid leave for citizens working part-time are provided on a general basis (Article 321 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). But there are a number of nuances that characterize the implementation of this labor law norm in practice.
So, in Art. 287 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that guarantees and compensation for workers in the Far North can only be provided at the main place of work. This provision makes many employers doubt the legality of part-time workers’ demands to provide leave. But Rostrud, in letter dated 06/08/2011 No. 1599-6-1, indicates that it only applies to targeted measures to support employees. In particular, those that may be assigned as a result of the dismissal of an employee due to the closure of the employer, staff reduction, those that involve the receipt of medical services, payment of travel expenses and baggage transportation.
Thus, part-time workers can, in principle, use vacation in the regions of the Far North and territories equivalent to it, as follows from the norms of Art. 321 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In the provisions of Art. 286 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that leave for a part-time worker must be granted simultaneously with that which he enjoys at his main place of work, and if a person has not had time to work at an additional job for 6 months (the minimum length of service for main and northern leave), then in advance.
If the duration of the required vacation in a company in which a person works part-time is less than at his main place of work, he has the right to request leave from the company management at his own expense at the same time as that taken out at his main place of work. Theoretically, this is possible if at the main job a person is granted other additional leaves that are not provided at the place of part-time work - for example, for the same irregular working day.
What documents to request from an employee to account for income tax expenses if the employer paid for the travel of the employee and his family members to the place of vacation was explained by 3rd Class Advisor to the State Civil Service of the Russian Federation N. N. Taktarov. Get trial access to ConsultantPlus and study the official’s opinion for free.
What does a manager have to pay for?
According to Article 325 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer pays for travel to the place of rest, as well as back. There are several principles confirmed by law:
- the place of rest must be located within the Russian Federation;
- the payment is made to both the employee and his family;
- the break from work must be paid once every two years;
- compensation will not be carried forward to subsequent years and cannot be cumulative.
Funds are paid at the time of vacation. The same applies to resigning employees who are entitled to full payment under labor law.
Download for viewing and printing:
Article 325 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Compensation of expenses for payment of travel costs and baggage transportation to the place of use of vacation and back”
How does an additional northern vacation fit in with the main one?
In general, a citizen receives the right to use vacation in the Far North as soon as he has worked for 6 months in a company - as is the case with the main vacation (Article 322 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The length of total work experience in this case does not matter - unlike, for example, the situation when northern bonuses are added to a person’s salary.
A situation may arise in which a person works for a company for more than 6 months, but, in fact, in the Far North - only 1. In this case, he is only entitled to basic leave, unless the employer himself agrees to provide the employee with the opportunity to rest additionally.
Pregnant women and women who have just returned from maternity leave, minor workers, as well as citizens who have adopted children under the age of 3 months have the right to leave, main or additional, before the end of 6 months of work in the company (Article 122 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If the employer and employee have entered into a fixed-term contract, then leave is granted:
- also after 6 months (if the contract is longer than this period);
- upon expiration of the relevant agreement (if the contract is shorter than 6 months and otherwise is not established by agreement with the employer).
Vacation is calculated in proportion to the ratio of the duration of the contract and the calendar year.
Leave in the Far North and the main leave are summed up and form the total paid leave. It can be divided into parts, but the duration of at least one individual break in work must be at least 14 days (Article 125 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
A special situation is in the field of education. For teachers of schools and universities, the bulk of vacation is provided in the summer. In practice, this means that teachers, as a rule, use both types of leave, main and northern, at the same time.
To learn how northern experience affects the calculation of a pension, read the article “Calculation of northern experience for men upon retirement .
Can I share or recall?
“Northern” working holidays are formed from main and additional leave. It can be divided into parts, but one break in work must be at least 2 weeks (Article 125 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Dividing vacation will be considered illegal if the number of days does not allow it to be divided according to legal norms. An employee of an enterprise rests according to an internal schedule or upon personal request.
Nordic holidays and weekends for parents
If a citizen working in the north has children under the age of 16, then his employer, upon written application from the employee, must provide him with an additional day off every month, albeit without compensation (Article 319 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, once a year a citizen has the right to receive paid leave of at least 14 days in order to accompany a minor child who enters an educational institution located in another area. This leave should be granted for each child only once (Article 322 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). To use the relevant preferences, you must:
- the parent had sufficient experience to receive leave;
- the parent provided the employer with a document from the educational institution confirming the child’s participation in the entrance exams.
IMPORTANT! We are not talking about “extra” vacation days: the norms of Art. 322 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation only gives the parent the right to receive paid (main or northern) leave on specific days, in fact having an advantage when drawing up a vacation schedule in the company.
When does the legal right to preferential travel for northerners arise?
Let's look at some popular questions regarding preferential fares for northerners.
When can I exercise my right to preferential leave?
To deal with this issue, let us again turn to Article 325 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the first paragraph of which states that
If you got a job in an organization in January 2022, then you will have the right to annual paid leave after six months, that is, in July 2022. At the same time as this right, you will have the right to preferential leave in 2022. That is, you can use preferential leave in the first year after employment.
How often can I take advantage of preferential holidays in the north?
You have the right to use preferential leave once every two years. If you used the right to preferential leave for northerners in 2022, then the next time you will be able to use this right is in 2022. If you do not take advantage of the right to preferential leave in 2022, this right will be transferred to the next calendar year, i.e. 2021.
An employee, once every two calendar years, has the right to pay the cost of travel and baggage transportation to the place of use of vacation and back within the territory of the Russian Federation and back by any type of transport (air, railway, sea, river, bus), including personal with the exception of taxis.
Vacation compensation in the Far North
We noted above that the number of rest days can be formed from those represented by the northern vacation and those corresponding to the main vacation. However, this does not mean that the corresponding leaves have the same legal status in other legal relations.
So, if we are talking about vacation compensation (payment of vacation pay, provided that the employee remains at work for the corresponding period and continues to receive a salary), then the main vacation (28 days) cannot be compensated (Article 126 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In turn, vacation in the Far North, as well as the main one unused in previous years (provided that it was formed after compulsory 28 days off per 1 year of work), can be compensated, except in cases where employment contracts are concluded with pregnant women and minors.
All types of unused vacation are compensated upon dismissal of an employee (Article 127 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Read more about compensation paid without dismissal here.
How to calculate the number of days of additional vacation
In general, the number of days of additional leave due in the North is determined by the formula:
| Kdo = Dx/12 × Cr – Oi |
Where:
- Kdo - the number of vacation days in the Far North during the working year;
- Dks - the number of days of additional leave provided in the region;
- Сг – vacation time worked by the employee in the North;
- Oi – the number of days of additional use already used in the current year. vacation.
Each month, each employee receives:
- Far North: 12/24 = 2 days ;
- areas equivalent to the North: 16/12 = 1.33 days ;
- other territories with surcharges: 8/12= 0.67 days .
KEEP IN MIND
Current legislation does not contain a ban on providing northern leave in advance by agreement of the parties to the employment contract.
Results
Citizens working in the Far North and in areas equivalent to it have the right to receive significantly longer leave than if they worked under normal conditions. In addition, northerners have the right to receive priority leave to accompany children entering educational institutions. If a person working in the North has children, then he has the right to take additional days off at his own expense. Northern workers also have the right to leave at their own expense while traveling to their vacation destination. All northern preferences are guaranteed by law for citizens both at their main place of work and in the case of part-time work.
Sources:
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation
- Order of the Ministry of Labor of the RSFSR dated November 22, 1990 N 2
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Law of the Russian Federation of February 19, 1993 N 4520-1 “On state guarantees and compensation for persons working and living in the Far North and equivalent areas”
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Features of providing rest
Reading the Labor Code is a very entertaining and useful activity. The northerner reader will learn from Article 321 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation about all the features of the provision and legal regulation of recreation.
Employees working in the Far North and equivalent territories are provided with additional leave in addition to the annual one. The same benefits apply to part-time workers and shift workers.