Direct production costs of used equipment
In your accounting policy, indicate which costs are classified as direct:
Direct-direct costs
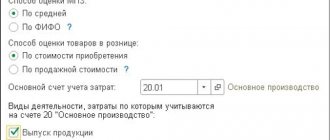
In 1C, direct production costs of BU related to specific products are reflected according to Dt 20. There is no need to make special settings in the UE:
- Dt 20 - Subconto Products must be filled out
.
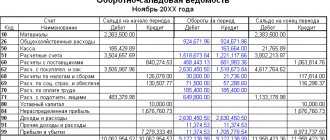
Reports – Balance Sheet
Direct-indirect costs
Direct costs that cannot be attributed to a specific unit of production, but can be attributed in general to a certain type of finished product (Nomenclature group) are reflected according to:
- Dt 20 – in documents of subconto Products is NOT filled in
.
Reports – Balance Sheet
At the end of the month, when calculating the actual cost, the total direct costs of the accounting department must be distributed into the cost of specific products, works, and services.
Define the distribution base in the UE:
Distribution of direct and indirect costs in 1C
Main thing – Accounting policy
Closing the month – Certificates and calculations – Cost of manufactured products
Closing account 26
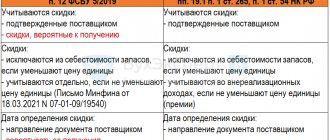
Not included in the cost of production (clause 26 of FSBU 5/2019):
- excess costs associated with improper organization of production or an emergency;
- administrative expenses (not directly related to specific products);
- costs of advertising, storage (which is not part of the technological process);
- other costs not related to those necessary for production.
Production costs that form the actual cost of WIP and GP are recommended to be taken into account in accounts 20 “Main production” without filling out the sub-accounts Products , “Auxiliary production” and “General production expenses”. For example, take into account the salary of the shop manager on the account, and not on the account. Here, reflect the expenses of departments that service production but do not produce products. For example, Laboratory costs.
Closing account 26 to account 90.08
If in the Main - Accounting Policy section it is established that account 20 is used, then only administrative expenses should be taken into account on the account, since it is completely closed in the current period.
After completing the procedure for closing the month “General business expenses”, the account is fully credited to account 90.08.1 “Management expenses” in accounting and financial accounting (clause 26 of FSBU 5/2019). Check account closure using the Account Analysis (Reports – Standard Reports). There cannot be an account balance at the end of the month.
The organization until 2022 distributed costs from account to account 20. For example, to the Nomenclature Group “Cold Water Supply”. How to organize such a calculation from 01/01/2021?
If we are talking about the protection of regulated tariffs, then this functionality is implemented in the CORP version.
In the CORP version, management costs can be distributed among product groups in proportion to the distribution base specified in the accounting policy. To do this, Nomenclature groups the Chart of Accounts to account 90.08.1 .
There are no plans to introduce such functionality in the PROF version.
Closing account 26 to account 90.02
If there is no production and all costs are accounted for in the “General business expenses” account, then the use of account 20 is not indicated in the Accounting Policy (Main – Accounting Policy).
In this case, all expenses are covered in:
- BU - to account 90.02.1 “Cost of sales”;
- NU: indirect expenses - to account 90.08.1 “Administrative expenses”;
- expenses set as direct in the income tax settings - to account 90.02.1 “Cost of sales”.
Check account closure using the Account Analysis (Reports – Standard Reports). There cannot be an account balance at the end of the month.
Trading organizations record costs on account 44 “Sales expenses”. If part of the costs is reflected on the account (for example, rent, communications, administration salaries), then in 1C the same rules apply as discussed above).
Classification of NU costs (OSNO)
At NU
costs associated with production and sales are divided into:
- direct
- refer to expenses at the time of sale of products, works, services, in the cost of which they are taken into account (Article 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation); - for general expenses
– in full they relate to the expenses of the current period.
The list of direct expenses is determined in the accounting policy (clause 1 of Article 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The composition of direct costs must be economically justified and determined in accordance with the technological process and type of activity.
In 1C, the list of direct costs of the NU is specified in the UE settings:
The list must be created every year:
The distribution of direct costs for specific products, works, services is carried out according to the same method as specified in the accounting system:
Printing accounting policies
You can print the Accounting Policy from 1C from its settings form in the Main - Settings - Accounting Policy section.
Before printing, all settings must be made, since the completeness of the reflection of all elements in it is affected not only by the UE settings, but also by the functionality settings.
- Functionality settings
We have successfully discussed how to set up an accounting policy in 1C 8.3 and how to fill out an accounting policy in 1C 8.3 using an example.
No direct costs when providing services
Is it acceptable to have no direct expenses if our activity is services?
When producing GPs, performing work, or providing services, the composition of direct expenses in accounting and accounting records is determined by the organization independently and is indicated in the Accounting Policy. For some types of activities, especially when providing services, it is impossible to identify expenses that are directly related to a specific service.
. Therefore, there may be no direct costs, for example:
- provision of consulting services;
- accounting outsourcing;
- intermediary services, etc.
Direct expenses refer to the expenses of the period at the time of sale of products, works, and services. To avoid claims from tax authorities, classify
costs as indirect costs only if there is no real possibility of classifying them as direct
(Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 26, 2020 N 03-03-07/55268).
For services ONLY:
- It is permissible in NU not to distribute direct expenses to the balances of work in progress, but to completely reduce the income of the reporting period (clause 2 of Article 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
UE settings in 1C when providing services
There may be no direct costs when providing services:
- disable the checkboxes for accounting for expenses on account 20
, expenses will be reflected on Dt 90.02 Kt 26 at the end of the month.
If there may still be direct costs for services, then:
- check the box to record expenses on account 20;
- if work in progress for services is not generated, then select the cost write-off method Excluding revenue
.
Grouping costs by economic elements
Used to analyze the financial results of an enterprise. It differs from classification by item in that all expenses are distributed according to types that characterize their economic content. Each economic element includes an extensive list of articles that are homogeneous in their economic content. For example, the element material costs. It includes items such as raw materials, fuel, tools, etc.
Such a classification makes it possible to determine the cost structure and the share of an individual element in the entire cost. Grouping by economic elements might look like this:
- Material expenses
- Depreciation
- Labor costs
- Depreciation
- Social contributions Needs
- other expenses
Since in 1C: Accounting 8.3. Since the “Cost Items” directory is hierarchical, you can create groups by economic elements.
However, grouping by cost elements does not allow determining the unit cost of production. Grouping costs by costing items serves this purpose.
Distribution of costs by item groups
How to distribute the costs of renting property among item groups on account 20?
Costs on account 20 in accounting are divided into:
- Direct-direct – relate to specific products and are not distributed
- distributed between products within NG
To distribute among all NG across all divisions, costs should be charged to account 25 for the general division.
Distribution of costs into direct and indirect
The lease agreement specifies the area of the premises (some of them are used for production, some are offices, and some are a GP warehouse). The UPD is issued for the total amount of area. Can we independently distribute the rental amount and, in accordance with the use of the premises, attribute costs to direct or indirect?
Yes, you can - in proportion to the area of the premises. To do this, in 1C you need to reflect services on several lines in different cost accounts.
Are the costs of renting the premises occupied by both production workers and the AUP direct or indirect?
The costs of renting premises used for management and production purposes must be distributed between indirect and direct in proportion to the occupied area of the premises. Costs can be classified as indirect expenses only if there is no real possibility of classifying them as direct expenses (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 26, 2020 N 03-03-07/55268).
What direct or indirect expenses include the cost of a hammer, which we use both in production and in the office?
Direct costs in trade
Are there direct costs in wholesale trading?
In BU
There is no need to determine a list of direct and indirect costs for trade. The expenses taken into account at the time of sale of goods will be:
- cost of goods formed in accordance with FBSU 5/2019 and Accounting Policy.
Direct expenses at NU
in trade are defined in Art. 320 Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- amounts paid to the supplier;
- costs for delivery of purchased goods.
The remaining costs are considered indirect; no additional settings are required in 1C.
To access the section, log in to the site.
See also:
- Clarifications on the mandatory application of FSB 5/2019 “Inventories” from 2021
- Closing cost accounts from 2022 taking into account FSBU 5/2019 (PROF)
- Closing cost accounts from 2022 taking into account FSBU 5/2019 (KORP)
- Example of accounting policies for production, trade, works, services (simplified methods) (OSN)
- Product release options and their differences when calculating costs
- [06/08/2021 entry] Practice of application of FSB 5/2019 Inventories in 1C - Part 3
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Related publications
- Indirect production costs (account 25) from 2022 ...
- Provision of services: direct costs are taken into account at the time of their implementation Services can be freely alienated by one person to another person - exactly...
- Test No. 45. Provision of services: direct costs are taken into account at the time of their implementation...
- Are the costs of equipment repairs direct or indirect? The Supreme Court did not approve the allocation of costs for the repair of equipment involved...