Let's expand on the concept of net present value (NPV) of an investment project, give a definition and economic meaning, use a real example to look at calculating NPV in Excel, and also consider a modification of this indicator (MNPV).
Net present value (NPV, Net Present Value, net present value, net present value, net present value) - shows the effectiveness of an investment in an investment project: the amount of cash flow during its implementation period and reduced to the current value (discounting).
Take our proprietary course on choosing stocks on the stock market → training course
Net present value. Calculation formula
Take our proprietary course on choosing stocks on the stock market → training course
where: NPV – net present value of the investment project;
CFt(Cash Flow) – cash flow during time period t;
IC (Invest Capital) – investment capital, represents the investor’s costs in the initial time period;
r – discount rate (barrier rate).
★ Investment appraisal in Excel. Calculation of NPV, IRR, DPP, PI in 5 minutes
So, in order to calculate NPV, it is necessary to predict future cash flows for the investment project, determine the discount rate and calculate the final value of income reduced to the current moment.
Take our proprietary course on choosing stocks on the stock market → training course
Making investment decisions based on the NPV criterion
The NPV indicator is one of the most common criteria for evaluating investment projects. Let us consider in the table what decisions can be made at different NPV values.
| Estimation of NPV | Making decisions |
| NPV≤0 | This investment project does not provide coverage of future expenses or provides only break-even and should be rejected from further consideration |
| NPV>0 | The project is attractive for investment and requires further analysis |
| NPV1>NPV2 | The investment project (1) is more attractive in terms of present value income than the second project (2) |
Positive and negative aspects of this indicator
Any analysis of indicators at an enterprise carries some economic meaning and this is very important when there is a separate employee who can do this.
Important! Since regular calculations of one or another coefficient or indicator make it possible to timely identify problems that have arisen in the organization, analyze the further course of action, what to do and what needs to be done .
So, for example, if a situation arises in search of an investor, in order to improve the situation in the organization, it will be very clear to present him with a calculation of net present value, which, firstly, will demonstrate the situation at the moment and in the future, due to the infusion of investor fund flows and then it will be clear whether it is worth investing in this enterprise or whether it is better to close it and not plunge further into losses.
| pros | Minuses |
| Allows you to calculate almost all possible risks associated with investing in a given project | Inaccuracy of calculations, because it is impossible to foresee everything accurately in advance, there is always a degree of error |
| The investor clearly sees the whole picture, from liquidity and profitability to losses | The inflation rate also affects the calculation |
The amount of net present value is closely related to such an analysis tool as the PPI (project profitability index). This parameter clearly demonstrates the investor’s benefits from participating in the chosen business. In order to determine the value of the IPP, it is necessary to divide the total discounted income by the amount of planned expenses.
For this purpose, the formula is used: “ƩCFt/(1 + i)t/IC”.
- In the case when the IPP value exceeds “0”, the investor will recoup all invested funds.
- When this parameter has a negative value, there is a high risk of losing existing capital.
In order to better understand the meaning of the parameter under consideration, we should consider a practical example. As an example, let's take a manufacturing company that is introducing a new range of products to the market (in stages over three years). The cost of implementing this project is two million rubles at the first stage (the period during which “t” is equal to zero). In the next stages, lasting twelve months, investors need to spend one million rubles (t=1–3).
NPV= “-2/(1+0.1)0+(2-1)/(1+0.1)1+(2-1)/(1+0.1)2+(2-1)/(1+01.3) 3=-2+0.9+0.83+0.75=0.48
According to the above calculations, we see that the profit amount will be 480,000 rubles. This project is positive and you can invest money in it, which is beneficial for investors.
Calculate and forecast future cash flow (CF) in Excel
Cash flow represents the amount of cash that a company/enterprise has at a given point in time. Cash flow reflects the financial strength of a company. To calculate cash flow, it is necessary to subtract the outflow (CO, Cash Outflows) from the inflow of funds (CI, Cash Inflows), the calculation formula will look like this:
Determining the future cash flow of an investment project is very important, so let’s consider one of the forecasting methods using MS Excel. Statistical forecasting of cash flows is only possible if the investment project already exists and is operating. That is, funds are needed to increase its capacity or scale it. I would like to note that if the project is a venture project and does not have statistical data on production volumes, sales, costs, then an expert approach is used to assess future cash income. Experts compare this project with analogues in this area (industry) and assess the potential for possible development and possible cash flows.
When forecasting the volume of future receipts, it is necessary to determine the nature of the relationship between the influence of various factors (forming cash receipts) and the cash flow itself. Let's look at a simple example of predicting future cash flows from a project depending on advertising costs. If there is a direct relationship between these indicators, then you can predict what cash receipts will be depending on costs using linear regression in Excel and the “TREND” function. To do this, we write the following formula for advertising costs of 50 rubles.
Cash Flow (CF). B12=TREND(B4:B11,C4:C11,C12)
The size of the future cash flow will be 4831 rubles. with advertising costs of 50 rubles. In reality, determining the size of future revenues is influenced by a much larger number of factors, which should be selected according to the degree of influence and their relationship with each other using correlation analysis.
Take our proprietary course on choosing stocks on the stock market → training course
Determining the discount rate (r) for an investment project
Calculating the discount rate is an important task in calculating the current value of an investment project. The discount rate represents the alternative return that an investor could have received. One of the most common purposes for determining a discount rate is to estimate the value of a company.
To estimate the discount rate, methods such as the CAPM model, WACC, Gordon model, Olson model, E/P market multiples model, return on equity, Fama and French model, Ross model (ART), expert assessment, etc. are used. There are many methods and their modifications for estimating the discount rate. Let us consider in the table the advantages and initial data that are used for the calculation.
| Methods | Advantages | Initial data for calculation |
| CAPM model | Taking into account the impact of market risk on the discount rate | Quotations of ordinary shares (MICEX exchange) |
| WACC model | The ability to take into account the efficiency of using both equity and borrowed capital | Quotations of ordinary shares (MICEX exchange), interest rates on borrowed capital |
| Gordon model | Accounting for dividend yield | Quotations of ordinary shares, dividend payments (MICEX exchange) |
| Ross model | Taking into account industry, macro and micro factors that determine the discount rate | Statistics on macro indicators (Rosstat) |
| Fama and French model | Taking into account the impact on the discount rate of market risks, the size of the company and its industry specifics | Quotations of ordinary shares (MICEX exchange) |
| Based on market multiples | Accounting for all market risks | Quotations of ordinary shares (MICEX exchange) |
| Based on return on equity | Accounting for the efficiency of using equity capital | Balance sheet |
| Based on expert assessment | The ability to evaluate venture projects and various factors that are difficult to formalize | Expert assessments, rating and point scales |
A change in the discount rate has a non-linear effect on the change in net present value; this relationship is shown in the figure below. Therefore, when choosing an investment project, it is necessary not only to compare NPV values, but also the nature of the change in NPV at different rates. Analysis of various scenarios allows you to choose a less risky project.
You can read in more detail about the discount rate and modern methods and formulas for calculating it in my article: Discount rate. 10 modern calculation methods.
Concept and content of NPV value
Before moving on to the topic of NPV, talking about what it is and how to calculate it, you need to understand the meaning of the phrase that makes up the abbreviation. For the phrase “Net present value” in the domestic economic and mathematical literature you can find several traditional translation options:
- In the first version, typical for mathematical textbooks, NPV is defined as net present value (NPV).
- The second option - net present value (NPV) - along with the first, is considered the most used.
- The third option – net present value – combines elements of the first and second transfers.
- The fourth version of the translation of the term NPV, where PV is “current value,” is the least common and is not widely used.
Regardless of the translation, the NPV value remains unchanged, and this term means that
NPV is the net present value of value. That is, cash flow discounting is precisely considered as the process of establishing its (flow) value by bringing the cost of total payments to a certain (current) point in time. Therefore, determining the value of net present value (NPV) becomes, along with IRR, another way to assess the effectiveness of investment projects in advance.
At the level of the general algorithm, in order to determine the prospects of a business project according to this indicator, the following steps need to be taken:
- assess cash flows – initial investments and expected receipts,
- set the cost of capital - calculate the rate,
- discount incoming and outgoing cash flows at an established rate,
- sum up all discounted flows, which will give the NPV value.
If the NPV calculation shows values greater than zero, then the investment is profitable . Moreover, the larger the NPV number, the greater, other things being equal, the expected profit value. Given that the lenders' return is usually fixed, anything the project brings in above it belongs to the shareholders - with a positive NPV, the shareholders will earn. The opposite situation with NPV less than zero promises losses for investors.
It is possible that the net present value will be zero. This means that the cash flow is sufficient to replace the invested capital without profit. If a project with an NPV of zero is approved, the size of the company will increase, but the share price will remain unchanged. But investing in such projects may be related to the social or environmental objectives of the initiators of the process, which makes investing in such projects possible.
Calculate Net Present Value (NPV) Using Excel
Let's calculate net present value using Excel. The figure below shows a table of changes in future cash flows and their discounting. So, we need to determine the discount rate for a venture investment project. Since it has no issues of ordinary shares, no dividend payments, and no estimates of return on equity and debt capital, we will use the method of expert assessments. The evaluation formula will be as follows:
Discount rate = Risk free rate + Risk adjustment;
Let's take a risk-free rate equal to interest on risk-free securities (GKOs, OFZs, these interest rates can be viewed on the website of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, cbr.ru) equal to 5%. And adjustments for industry risk, the risk of the impact of seasonality on sales and personnel risk. The table below shows estimates of adjustments taking into account these identified types of risk. These risks have been identified by experts, so when choosing an expert you need to pay close attention.
| Types of risk | Risk adjustment |
| Risk of seasonality affecting sales | 5% |
| Industry risk | 7% |
| Personnel risk | 3% |
| 15% | |
| Risk-free interest rate | 5% |
| Total: | 20% |
As a result, adding up all the adjustments for the risk affecting the investment project, the discount rate will be = 5 + 15 = 20%. After calculating the discount rate, it is necessary to calculate the cash flows and discount them.
Take our proprietary course on choosing stocks on the stock market → training course
Two options for calculating net present value NPV
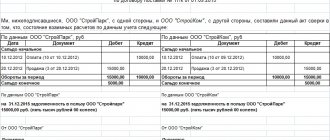
The first option for calculating net present value consists of the following steps:
- Column “B” reflects the initial investment costs = 100,000 rubles;
- Column “C” reflects all future planned cash receipts for the project;
- Column "D" records all future cash expenses;
- Cash flow CF (column “E”). E7= C7-D7;
- Calculation of discounted cash flow. F7=E7/(1+$C$3)^A7
- Calculate the present value (NPV) minus the initial investment cost (IC). F16 =SUM(F7:F15)-B6
The second option for calculating net present value is to use Excel's built-in NPV (net present value) financial function. Calculation of the net present value of a project minus initial investment costs. F17=NPV($C$3;E7;E8;E9;E10;E11;E12;E13;E14;E15)-B6
★ Investment appraisal in Excel. Calculation of NPV, IRR, DPP, PI in 5 minutes
The figure below shows the resulting net present value calculations. As we can see, the final result of the calculation is the same.
Taking inflation into account when calculating
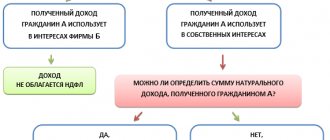
Is inflation taken into account when calculating NPV?
Inflation always affects project financing. The higher its level, the lower the estimated net present value NPV. In order to reflect the impact of inflation on the NPV, the discount is adjusted to the projected inflation rate. The interest rate will be calculated as follows:
R = (1 + r) × K
Ingredients of the formula:
- R – final discount rate taking into account inflation.
- r – discount rate;
- K – inflation rate.
Modification of net present value MNPV (Modified Net Present Value)
In addition to the classic net present value formula, financiers/investors sometimes use its modification in practice:
Where:
MNPV – modification of net present value;
CFt – cash flow in time period t;
It – cash outflow in time period t;
r – discount rate (barrier rate);
d – level of reinvestment, interest rate showing possible income from reinvestment of capital;
n – number of analysis periods.
As we see, the main difference from the simple formula is the possibility of taking into account the profitability from reinvestment of capital. Evaluation of an investment project using this criterion has the following form:
| MNPV value | Making a decision based on criteria |
| MNPV>0 | The investment project is accepted for further analysis |
| MNPV ≤0 | Investment project is rejected |
| MNPV1 > MNPV2 | Comparison of projects with each other. Investment project (1) is more attractive than (2) |
Advantages and disadvantages
What are the advantages and disadvantages of determining NPV?
Consideration of the development of the project throughout the entire period of its implementation.
Possibility of constructing a cash flow graph and its subsequent analysis.
Accounting for variable interest rates.
Based on the data obtained from several projects, it is possible to form a balanced investment portfolio.
The indicator is absolute, so risks are not taken into account and there is no safety reserve.
The discount rate is constantly changing. Because of this, there is a high probability of receiving incorrect data.
There is no idea of the exact profitability of the project.
To minimize risks, all profits should be calculated at a minimum. An investor may unknowingly abandon a profitable project.