Main purpose
To indicate the specific period of time for which the fiscal reporting form was compiled, a special codification is provided. The code is a two-digit number, for example, 31 is the period in the tax return, 21 is in the DAM calculation, or 50 is in another form.
This codification is a very convenient grouping of reporting according to the time of its formation. For example, this code allows you to quickly determine for what period of time the taxpayer made the calculation and calculated the tax to the budget.
For each type or tax reporting code (TRR), an individual codification procedure is provided, indicating the code of the tax billing period in the document. Let's look at how codes are determined for the main types of reports to the Federal Tax Service.
The category and status of the taxpayer does not matter to determine the coding. That is, the Federal Tax Service approves codes individually for each form or report form, regardless of the type of payer of fees, contributions and taxes. That is, this coding is used by legal entities, individual entrepreneurs, private practices, and ordinary citizens.
Peculiarities
You may be interested in: How an advance is calculated: the calculation procedure, rules and features of registration, accrual and payment
As a rule, a settlement period is not a one-time period, but a recurring period of time, which is introduced in the financial system for the convenience of mutual settlements. It is after this period that the results are summed up, calculations and other financial transactions are completed.
You may be interested in: Technology for installing foundation piles: features, instructions
There are no specific deadlines for the billing period. It is often determined individually and is always specified in the contract between the parties. It is upon its completion that calculations must be made.
VAT declaration
The current VAT reporting form, as well as the procedure for filling it out, was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 26, 2021 No. ED-7-3 / [email protected] ; it is used from reporting for the 3rd quarter of 2022. In the declaration, tax periods for VAT are indicated by two-digit numbers, in which the first digit is 2, and the second determines the quarter number in chronological order. For example, to indicate the 3rd quarter of 2022 for the value added tax return - 23.
And tax period number 21 is the first quarter. There are four codes for value added tax reporting; there are also:
- 22 - second quarter;
- 24 - fourth quarter.
Similar rules are established for the rest of the fiscal reporting, which must be submitted quarterly. When filling out water tax reporting forms, indicate similar codes.
IMPORTANT!
Please note that similar encoding is used in forms where there is no cumulative total from the beginning of the year and quarter numbers are encrypted, and not 6 or 9 months or a year.
Calculation of average earnings for benefits
Events related to the birth of a child are also subject to payment. The woman receives maternity benefits and, for the first year and a half of the baby’s life, child benefits. Their size is also tied to average earnings. Maternity pay makes up 100 percent of the average salary. And the child benefit is 40 percent of this amount every month, but not less than the lower limit determined by the state (Article 11 of Law No. 255-FZ).
To calculate payments, you should be guided by regulation No. 375.
For calculations, the average salary for the two calendar years before the year of maternity leave is used. The time spent working in another place is also taken into account (clause 6 of the regulations). The average earnings include all employee accruals for which contributions to the Social Insurance Fund are accrued.
If an employee goes on a second maternity leave without going to work and, accordingly, he was not paid a salary for the last two years, then to calculate the average amount of wage payments, unpaid years can be replaced. For this purpose, the two years preceding the initial decree are taken. Years can be changed only if, as a result, maternity and child benefits will be larger (clause 11 of the regulation).
To calculate the amount of benefits, the average daily earnings are used (clause 15 of the regulation). It is determined by the formula (clause 15 (2) of the regulation): SDNZ = earnings for the billing period / by the number of calendar days in this period.
The following are excluded from the calculation:
- sick days;
- maternity leave;
- Holiday to care for the child;
- release from work with retention of salary, if no contributions were accrued for it.
In this case, the average daily salary cannot be more than the amount obtained by dividing the maximum values of the bases for calculating contributions in force in the two years preceding the leave by 730.
Accordingly, the calculation of this value is carried out according to the formula: maximum size of the SDNZ = maximum values of the bases for the 2 previous years / 730.
In addition, if the employee has had no salary at all over the last two years or its monthly amount did not exceed the minimum wage, then the average earnings are taken to be equal to the minimum wage (clause 11(1) of the regulation). Average daily earnings from the minimum wage are calculated according to the formula (clause 15 (3) of the regulation): minimum SDNZ = minimum wage on the date of vacation x 24 / 730.
Calculation example
The employee will go on maternity leave starting January 18. In the last two years, contributions subject to contributions amounted to: 663,000 rubles: in 2022 - 339,000 rubles in 2022 - 324,000 rubles.
The total number of calendar days in 2022 and 2022 is (365,366) = 731. Since the woman was on sick leave for 21 days in the calculation period, only (731 - 21) = 710 days are included in the calculation.
SDNZ: 663,000 /710 days. = 993.80 rubles.
In 2022, the limits for insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund are 865,000 rubles, in 2020 - 912,000 rubles.
SDNZ in the maximum possible amount: (865,000,912,000) / 730 = 2,434.25 rubles.
The smallest possible amount of SDNZ: 12,792 (2022 minimum wage) x 24 / 730 = 420.56 rubles.
Income tax return
The codification of “profitable” reporting is somewhat different from the quarterly forms. Thus, the profit declaration is filled out with an accrual total from the beginning of the year. The way the half-year is designated in the report differs from the “quarterly” method. The number 3 is always ahead, followed by the serial number of the reporting period. And only in the reporting for the 1st quarter they indicate a code that begins with the number 2.
Define numbering as follows:
- for the first quarter, indicate 21;
- 31 is the report for the 1st half of the year;
- 33 is information for the first 9 months of the reporting year;
- 34 - annual reporting from January to December.
If a company submits profit reports monthly, then a completely different codification is applied. For example, 35 is the first month of the year, 36 is the second, 37 is the third, and so on.
IMPORTANT!
Please note that period 31 is not provided for in the income tax return. This value is never used when completing this reporting form.
The key rules for filling out income tax reporting are regulated in the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 23, 2019 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] (as amended on September 11, 2020).
Tax period 50 is used in the income tax return if the company was in the process of reorganization or liquidation. That is, use code 50 to reflect the last fiscal period during the reorganization (liquidation) of the organization.
What do you need to know?
It is important for clients who use credit cards to know that neglecting interest payment dates is strictly not recommended. Otherwise, there are delays and subsequent penalties from banks, as well as negative consequences in the form of a damaged credit history.
This is why it is important to know what the days of the billing period are and why you need to be able to calculate them correctly.
- First of all, this allows you to control the accrual of interest on your credit card. As soon as the grace period ends, the bank automatically charges interest for the use of borrowed funds. If you don't make the payment on time, you won't be able to avoid this.
- It is important to understand that the end of the credit card billing period is the day when the funds should already be credited to your account. In this case, it is better to carry out their actual application in advance. This is due to the fact that funds may be delayed.
- The settlement period for different banks may have different durations. This is important to consider for those customers who use credit cards from several financial institutions. In this case, you can easily get confused. To prevent this from happening, it is important to know the billing period.
Consolidated group information
Often, information on income tax is generated not for one individual entity, but for several companies or separate divisions at once. Such associations are called a consolidated group. For these taxpayers, it is not important which quarter the reporting period is 31; they designate the first quarter differently.
If a report to the Federal Tax Service is provided by such a consolidated group, then a specific coding is indicated in the income tax return:
- value 13 is provided to indicate fiscal information generated for 1 quarter. of the year;
- coding 14 - information provided by a consolidated group of taxpayers for the first half of the year;
- designation 15 - the report was generated by a group of taxpayers for the first nine months (January-September);
- numbers 16 indicate that the information in the declaration is provided for the full financial year from January to December for a consolidated group of taxpayers.
Salary reports
Reports on wages, insurance premiums and withholding taxes provide individual coding.
For the 6-NDFL report, a separate reporting period is provided - code 90, which indicates the year before the reorganization and (or) liquidation of the reporting company. Use a similar code to create a single calculation for insurance premiums. But if the organization reports in a standard mode, then the coding provided for indicating information on an accrual basis is used. For example, what period code 34 in the RSV is information for the year.
General values for salary reports:
- 21 - the first three months of the year: January, February, March;
- 31 - 1st half of the year or the first 6 months on an accrual basis;
- 33 – 9 months from the beginning of the year;
- 34 is a full calendar year, or 12 months from January to December.
The status and category of the taxpayer does not play any role. That is, organizations (legal entities), individual entrepreneurs, and ordinary citizens are required to use the code when drawing up the 3-NDFL declaration and other forms of fiscal reports and declarations.
It is worth noting that tax period code 34 in almost all types of reporting forms in the Federal Tax Service indicates a full calendar year (January-December). Please note that in reporting on transport tax, according to the simplified tax system, a unified calculation of insurance premiums and in other forms, the year is everywhere.
How to determine the number of days in a billing period
Once you have determined the billing period for calculating average earnings, you need to calculate the number of working days in this period. The procedure for calculating the number of days in a pay period depends on whether the employee worked all the days included in the pay period or not.
If the employee has worked the pay period completely, you need to determine the number of working days in the pay period according to the calendar of a five-day work week.
When determining the number of working days, holidays and weekends are not taken into account.
EXAMPLE Employee of Passive LLC A.N. Ivanov has been sent on a business trip since July 7 of this year. During the business trip, Ivanov is paid an average salary. The billing period includes the 12 calendar months preceding the business trip. Let's assume that Ivanov worked out the billing period completely. Then the total number of working days of the billing period will be:
| Month of billing period | Actual number of working days |
| Last year | |
| July | 23 |
| August | 22 |
| September | 21 |
| October | 23 |
| november | 20 |
| December | 21 |
| This year | |
| January | 20 |
| February | 19 |
| March | 20 |
| April | 22 |
| May | 19 |
| June | 20 |
| Total | 250 |
The payroll period may not be fully worked by the employee, since the payroll period does not include days on which:
- the employee received temporary disability benefits or maternity benefits;
- an employee raising a disabled child was provided with additional paid days off (Article 262 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- the employee was on leave without pay (Article 128 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- the employee was released from work with full or partial retention of wages;
- the employee did not work due to downtime (for example, due to the suspension of the organization or workshop);
- the employee did not participate in the strike, but due to it was not able to perform his work.
Thus, from the calculation period it is necessary to exclude periods for which payments were accrued based on average earnings, with the exception of breaks for feeding the child.
If the billing period has not been fully worked out, then it is necessary to calculate the number of working days worked in the billing period according to the calendar of a five-day working week.
EXAMPLE Let's return to the previous example and change its conditions a little. Let's assume that Ivanov was on vacation in August last year and worked only 3 days, in January of this year he was sick and worked only 10 days, in May of this year he was on study leave and worked only 2 days. In this case, the number of working days in the reporting period will be:
| Month of billing period | Actual number of working days |
| Last year | |
| July | 23 |
| August | 3 |
| September | 21 |
| October | 23 |
| november | 20 |
| December | 21 |
| This year | |
| January | 10 |
| February | 19 |
| March | 20 |
| April | 22 |
| May | 2 |
| June | 20 |
| Total | 240 |
If an employee has worked for an organization for a period that is less than the estimated period (for example, two months), then in this situation only the number of working days actually worked by the employee until the payment is taken into account.
EXAMPLE Employee of Aktiv LLC A.N. Ivanov was hired on July 16 of the current year. On September 4 of the current year, Ivanov donated blood, and for this day he is entitled to payment of average earnings. If the organization determines that 12 calendar months are used as the billing period (from the 1st to the 30th (31st) day) preceding the period during which the employee retains the average salary, then the calculation period will include 21 working days (from August 1 to August 31 of the current year).
Coding in financial statements
Digital codes for financial statements are determined by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 66-dated July 2, 2010. In the balance sheet and other financial forms, not only reporting periods are coded. To encode them, the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia No. ММВ-7-1 / [email protected] dated November 13, 2019 is used, from which it follows that the reporting period code 34 in the financial statements, as well as in the tax statements, denotes a calendar year. This designation is applicable to the balance sheet, forms No. 2, No. 3, No. 4, No. 5 and others.
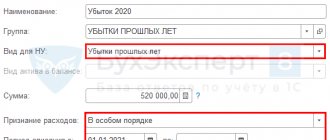
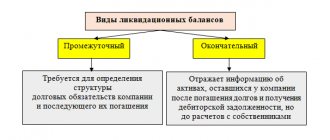
But if an organization reports for the first time for an incomplete calendar year, it uses designation 94. A separate special designation is provided for the liquidation balance sheet. When an organization is liquidated, reporting period 90 in the balance sheet is the last months of work during the summing up. It is indicated when submitting the liquidation balance sheet to the Federal Tax Service.
Amounts included in the calculation of average earnings
What charges are taken into account in the calculations is briefly discussed in Art. 139 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: these are all payments within the framework of the company’s remuneration system. This issue is discussed in more detail in clause 2 of Regulation No. 922. It specifies what exactly is to be taken into account:
- wages, including piecework, as a percentage of sales, goods, commissions;
- monetary remuneration for civil servants;
- fees in media editorial offices;
- teachers' salaries for overload;
- allowances and additional payments, including for professional skills, combination, length of service, knowledge of other languages;
- payments related to working conditions;
- bonus accruals and remunerations made within the framework of the company’s remuneration rules;
- other types of salary payments.
Payments with social characteristics and that are not payment for work should be excluded from the calculation. We are talking about financial assistance, payment for travel, lunches, vacations, housing and communal services and other similar payments.
Ciphers and codes in payment orders
When preparing payment orders to pay fiscal obligations in favor of the Federal Tax Service, a completely different encoding is used. The payment slip indicates a ten-digit code in the format XX.XX.YYYY, where XX is the letter and numeric designation of the time period for which the taxpayer transfers the tranche to the state budget, YYYY is the calendar year for which budget payments are calculated.
For example:
- quarterly calculations - KV.0X.2021. Payment of VAT for the 3rd quarter - KV.03.2021;
- monthly payment, for example, for September, is designated MS.09.2021;
- semi-annual payment: PL.01.2021 - for the first half of the year and PL.02.2021 - for the second;
- payment based on the results of the calendar year is indicated as GD.00.2021.
Encoding table
As we noted above, remembering the encodings for each form and type of fiscal declarations and other reporting is quite difficult. An error when filling out the form will be costly for the company. For example, an accountant will indicate an incorrect code in the report, therefore, tax authorities will not take into account the submitted information and will impose a fine for late provision of information.
To eliminate errors when filling out forms and forms in the Federal Tax Service, use a professional guide, which presents all the current encodings for the types of fiscal forms.
Here are all the tax period codes for the declarations:
The concept of tax period
In the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in Art. 55 clause 1 provides a definition of the term “tax period”. It should be understood as a limited time interval, at the end of which the results of activities are summed up and the tax base is formed. After the end of the specified interval, entrepreneurs and legal entities have tax obligations that must be repaid within a fixed period.
NOTE! The tax period does not always have to coincide in length with the reporting period.
There can be several reporting periods in one tax period. For each type of tax, the size of the tax period is legally approved: from 1 month to 1 year. You can find out the duration of the time interval from the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in separate chapters of which the procedure for calculating tax liabilities is described.