Labor Code on shift work schedules
If a company operates on a shift schedule, the employer must take into account the nuances provided for by labor legislation.
Shift work The Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 103) allows the following :
- if the duration of the production process is higher than the permissible duration of daily work;
- for the efficient use of equipment, increasing the volume of products (works, services).
Typically, internal company local acts and labor contracts establish the duration of workers' shifts and the order of their alternation with rest periods between shifts.
A ready-made solution with detailed explanations and examples of wording from ConsultantPlus will help you draw up an employment contract with a condition on a shift work schedule. If you do not have access to this legal system, a full access trial is available for free.
The materials on our website will help you understand the nuances of drawing up other documents that determine the work and rest schedule of employees:
- “Internal labor regulations - sample 2021”;
- "Unified form No. TD-1 - Employment contract."
To properly organize shift work, shift schedules are drawn up in compliance with the following conditions:
- the schedule may include working in several shifts (2, 3 or more);
- working 2 shifts in a row is prohibited;
- when drawing up a schedule, the employer will have to take into account the opinion of the trade union body (if there is one in the company);
- It is necessary to familiarize employees with the shift schedule at least 1 month before it comes into force.
Types of shift schedules
Depending on the company’s operating technology, shift schedules with different durations and a combination of working periods of time and rest periods may be established for different positions.
For example, for workers in such a specific field as railway transport, schedules with the following parameters can be developed:
- day and night shifts, rest after night work and a day off followed by a new work shift;
- 2 working days of 11 hours each (no night work) alternate with two consecutive days of rest;
- work shifts are combined with rest in the following combination: a working day after three days of rest.
The first form of shift work is typical for operators, station attendants, wagon inspectors and repairmen, rolling stock repairmen and other workers who provide round-the-clock reception, access and processing of rolling stock.
The specific nature of the activities of workers in the second group does not require round-the-clock presence at workplaces, but does not allow any breaks in daytime work shifts. Such workers include dispatchers for the accounting of cars requiring uncoupling repairs and other similar positions.
Working in the “every three days” mode is typical for the security service of premises and territory. We will consider further how to calculate a shift schedule for this category of workers.
What is shift work?
A shift work schedule is practiced by certain enterprises whose specific activities are focused on an almost continuous production process. The activity of employees working in shifts is not based on the traditional five-day work week, but on schedules developed by the organization itself.
There are three main options for a shift schedule:
- two twelve-hour working days alternate with the same number of days off (excluding night time). This routine is typical for dispatchers, as well as general workers;
- one full day of work is followed by three days of rest (this system is often used in medical institutions);
- day and night shifts, followed by a break and then a day off. After that, a new shift begins. This option is often practiced among workers who ensure the serviceability of rolling stock - mechanics, repairmen, and so on.
The minimum number of shifts is two, and the maximum is four. In order to organize the professional activities of employees, management creates teams that alternately replace each other in order to avoid possible interruptions in work.
Calculation of shift work schedule
To calculate the working time schedule for shift work “in three days”, you need to:
- establish a summarized accounting of working time (Article 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- reflect separately in the schedule work during the day and at night;
- take into account the legally established duration of breaks for rest and meals (no more than 2 hours and no less than half an hour, Article 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- personalize the accounting of time actually worked by each employee (Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
You can familiarize yourself with the documents used to record actual time worked using the materials on our website:
- “Unified form No. T-12 - form and sample»;
- “Unified form No. T-13 - form and sample».
Important! When drawing up a working time schedule, it is necessary to take into account the legally established condition of 42 hours of weekly continuous rest (Article 110 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
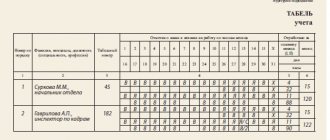
The results of calculating the parameters of the shift schedule and its results are usually presented in tabular form and posted for public viewing.
The employee must learn about the parameters of the shift schedule at least 1 month before it comes into force. The responsibility for such familiarization lies with the employer (Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Find out what are the nuances of providing annual leave to employees with a shift schedule from ConsultantPlus. Get trial access to the system and go to the Ready-made solution.
Features of remuneration
Moving away from the traditional five-day workweek requires the creation of alternative employee payroll strategies. Heads of organizations that practice shift work use summarized accounting of working hours. The unit of this calculation method is a fixed accounting period (be it a month, a year, etc.), on the basis of which the labor standard is determined. For each accounting period, a fixed tariff rate is developed, on the basis of which the amount of earnings is calculated.
Also, when determining wages, the following nuances are taken into account:
- day and night shifts are paid differently (the first is always cheaper than the second), and are indicated separately in the schedules;
- breaks allocated for rest and food are taken into account at the legislative level (the total duration of such time intervals per day ranges from half an hour to two hours, according to Article 108 of the Labor Code);
- activity recording is personalized - the hours worked by all employees are subject to mandatory recording, since they will be multiplied by the tariff rate when calculating wages.
At a set hourly rate
The tariff rate is a certain amount of money that an employee is entitled to for fulfilling labor standards for a fixed period of time. The basic rule of tariff rates is the established remuneration for a certain measure of work. According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, this rate must be reflected in the employment contract, from which the employee learns about it.
It is important to understand that the tariff rate is the minimum that an employee is guaranteed to receive if the standards are met. If desired, management can make raises or give bonuses that will lead to an increase in the employee’s salary. The total amount depends on two main criteria - the position held and the assigned category of specialist.
The time unit can be:
- hour. Rates are calculated by dividing the salary by the sum of the hours worked per month;
- day. Rates are applied when the number of working hours per day is fixed, but differs from the norms prescribed in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- month. Rates are used for standard working hours, stable schedules and fixed days off.
In accordance with the salary established for the employee
The salary has one main thing in common with the rate - it is also determined by employers for a fixed time period. Like the rate, the salary reflects the minimum income that is guaranteed to the employee upon full work. The salary also has special characteristics that distinguish it from all other remuneration systems:
- the salary amount is directly related to the employee’s qualifications, while the tariff rate depends primarily on the rank;
- factors such as the employee’s education, work experience and the availability of certain skills contribute to an increase or decrease in salary. The rate depends on the working conditions themselves - its complexity, intensity and accompanying circumstances.
The amount of the official salary is always specified in the employment contract. As with the rate, the actual salary of an employee may exceed the indicated figures, since management develops special incentive systems, bonuses and deductions to motivate employees.
With a shift work schedule of 2 every 2
The work schedule of two days after two is one of the most common in shift production. Less commonly, three after three or four after four days options may also occur. It is quite easy to understand how such a schedule works - an employee works a twelve-hour shift for two days in a row, and then rests for the next couple of days. This method of organizing working time is often used for vacancies that do not require qualifications - such as a cashier salesperson or a packer. However, medical workers, police officers, and firefighters can also adhere to a similar routine.
In order to calculate the salary due to an employee, the accountant determines the total amount of shifts worked for a specified period (usually a month). Employees have fixed standards that they must have time to work in order to receive wages in the agreed amount. If you miss a shift, your salary will be reduced. All hours that an employee does not work for one reason or another, he can “close” in subsequent accounting periods.
Work schedules are drawn up in such a way that each employee has the opportunity to work the required number of hours in one accounting period. According to the Labor Code, the optimal time an employee works per month is 167 hours. If desired, an employee can work overtime - payment for additional hours is carried out at a different rate. At the same time, shift employees cannot count on a bonus when working on weekends or holidays, since the specifics of such a schedule require employment regardless of holidays.
Features of payment at night
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, night hours mean the time period from ten in the evening to six in the morning. However, this does not mean that shifts starting before 22 hours cannot be considered night shifts - if a certain part of the time falls within the specified framework, then it will be paid at the night rate. This rule does not apply to daytime hours. For example, if an employee works from 20 pm to 6 am, then he will be paid for eight hours at the night rate.
Dark shifts are valued higher than day shifts, but the amount of extra pay for night shifts varies depending on the company. At the legislative level, there is one rule governing night time pay - the hourly premium must be at least twenty percent of the daily salary.
Remuneration for shift work: nuances
Payroll calculation for shift work has its own characteristics compared to similar calculations in a 5-day working week with days off at the end.
With a shift schedule, the usual weekends for everyone (Saturday and Sunday) can be scheduled as working days, and the shift worker’s rest will fall during working hours.
The calculation of wages for a shift worker is specific in that the number of working hours according to the schedule may differ from the norm in the direction of increase (planned overtime) or create a planned shortfall.
Important! When using summarized working time accounting, the annual number of overtime hours cannot exceed 120 (Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
To avoid errors in salary calculations during shift work, it is necessary to carry out a reconciliation procedure for the following indicators at the end of the accounting period established by the company:
- hours actually worked by the employee according to the schedule;
- number of working hours during the accounting period according to the norm.
If, upon comparison, the first indicator exceeds the second, it is necessary to calculate and pay for processing.
Important! In accordance with clause 5.5 of the resolution dated 05.30.1985 of the State Committee for Labor of the USSR No. 162, All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions No. 12-55, overtime is subject to payment in time and a half (the first 2 hours, falling on average for each working day of the accounting period) and double (subsequent hours of work).
A similar approach when paying overtime was confirmed by the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation (Section 5 of the review approved by the Presidium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation on February 26, 2014).
We will consider an example of calculating the salary of a shift worker with overtime in the next section.
Remuneration for shift work: features
As a rule, a company with a shift schedule establishes a summarized recording of working hours. Its peculiarity is that labor standards are determined within the accounting period: month, quarter or year. And the salary is calculated based on the tariff rate determined for this period.
Pay per shift is also calculated based on the hourly wage rate multiplied by the number of hours in the shift.
Example.
Semenov S.S. The salary is set at 40,000 rubles. The company has established a summarized recording of working hours. In March, all scheduled hours were worked (159 hours). The accounting period is 1 year (according to the production calendar, this is 1970 hours).
Salaries in different months may differ due to the different number of working hours in them.
The use of summarized accounting for shift workers is not mandatory. The organization has the right to establish another form of payroll, for example, time-based, based on salary. Payment for a shift work schedule with salary will be calculated in the usual manner. That is, if the working hours are fully worked according to the schedule, the employee will be paid the salary in full:
How to calculate salary for shift work
Let's look at an example.
The operational dispatcher has a summarized recording of working time with a recording period of 1 month. Work is carried out on a 2/2 schedule (2 working days of 11 hours each, followed by 2 days off).
According to the schedule, the dispatcher worked 165 hours for the month against the norm of 160 hours. The accountant made the following calculation (the hourly tariff rate of the dispatcher is 260 rubles):
- salary for hours worked: 165 hours × 260 rubles/hour = 42,900 rubles;
- processing hours: 165 – 160 = 5 hours;
- number of working days in the accounting period: 165 hours / 11 hours per shift = 15 days;
- calculation coefficient (average duration of overtime work per 1 working day of the accounting period): 5 hours / 15 days. = 0.33 hours/day. (does not exceed 2 hours a day, which corresponds to payment for overtime hours at one and a half times the rate);
- amount of additional payment for overtime work: 260 rubles/hour × 5 hours × (1.5 – 1) = 650 rubles;
- total salary: 42,900 + 650 = 43,550 rubles.
With the same approach, you can calculate differently:
- salary for standard hours: 160 hours × 260 rubles/hour = 41,600 rubles;
- additional payment for overtime: 5 hours × 260 rubles/hour × 1.5 = 1,950 rubles;
- total salary: 41,600 + 1,950 = 43,550 rubles.
The choice of calculation method does not affect the final result.
Holiday salary supplements for shift workers
With regard to payment for holidays that fall during work shifts, the general procedure established by labor legislation applies.
Important! In accordance with Art. 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, work on holidays is paid at least double the amount. Holidays and non-working days are listed in Art. 112 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Following the legally defined minimum level of holiday surcharges, the employer has the right to set its own amount of such surcharges. Their maximum limit is not regulated by law. The procedure for paying for holidays, like all other important nuances of salary calculations, must be reflected in the internal local act of the company (collective agreement, regulations on wages, etc.).
When calculating the salary of a shift worker, provided that in the billing month his work shifts coincided with non-working holidays, the following must be taken into account:
- if an employee starts his shift at 8:00 a.m. on a holiday and his shift lasts 11 working hours, all hours actually worked are subject to holiday surcharge in full;
- if part of the work shift falls on the night period (for example, from 20:00 on a holiday until the morning of the next day), the calculation of the holiday surcharge must be made only up to 24 hours of the holiday (in this case, 4 hours) - from 20:00 to 24 :00 holiday.
What are the features of remuneration for shift work on weekends and holidays?
If a working day falls on a holiday, labor is paid double. By agreement with the employee, he may be given an additional day off . In this case, payment is made as for a regular working day, and days off are not paid.
Work on Saturday and Sunday according to the schedule is not subject to additional payment. If these days are scheduled to be weekends, and the employee is invited to work, then in this case the work will be paid at an increased rate.
Night work must be specifically stipulated in the employment contract. By law, night hours are defined as the time of day from 10 p.m. to 6 a.m. Each enterprise sets its own allowances for work on night shifts. For example, it could be 20, 30 or 40% of the tariff schedule. The premium is set taking into account the position of the trade union. If a shift accounts for 50% of the night time, then it is called a night shift.
In such situations, remuneration for shift work occurs as follows: TC is multiplied by KS (where TS is the tariff schedule, KS is the number of hours worked). If the employee worked at night , then when calculating the amount of earnings, the amount is multiplied by 20%.
The shift work schedule must be drawn up once a month and communicated personally to each employee in advance (no later than 30 days).
Results
Shift work refers to working under flexible working hours. Labor legislation regulates the specifics of its organization, accounting and payment.
The employer needs to correctly calculate the duration of work shifts and rest breaks, draw up a shift schedule, promptly familiarize employees with it, record the time actually worked by employees, and then correctly calculate wages taking into account the peculiarities of shift work.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.