When is an advance payment issued according to the Labor Code?
The wording of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation applicable to the field of wages does not use the term advance.
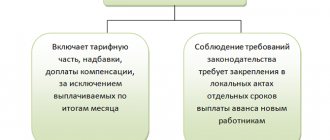
Instead, the concept “salary for the first half of the month” is used. The Law “On Amendments...” dated July 3, 2016 No. 272-FZ introduced some amendments to the Labor Code on advance payment. Part 6 art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation now requires that salaries be paid to staff at least once every half month. Moreover, the exact dates of issue are approved in the local regulations (LNA) of the enterprise:
- in the regulations on remuneration;
- internal labor regulations (ILR);
- collective agreement
You can also specify specific dates for the payment of wages for the 1st and 2nd parts of the month in one of the clauses of the employment contract.
The main clarification of this article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that wages must be paid no later than 15 days after the end of the month for which they were accrued. This version of the article came into effect on October 3, 2016.
The Ministry of Labor, in its letter No. 14-1/B-911 dated September 21, 2016, proposes issuing the advance part of the salary from the 16th to the 30th (31st) day of the current month, and the final payment for the second half - from the 1st to the 15th of the next month.
Paying wages to a new employee
If a new employee gets a job with the employer in the second half of the month, then he is not entitled to an advance at the end of the month. For the first time he will receive his salary only next month, no later than the 15th. Accordingly, the required period for payment of wages will be increased, but this will not be a violation, but only if for the rest of the employees the payment of wages is made on time. It is also possible to regulate such payment in an employment, collective agreement or wage regulations (
Deadlines for issuing salary advances: new rules
The new rules for the payment of advance payments require not only to more clearly define the terms for issuing advance payments and wages, but also to tighten the responsibility of employers for non-compliance with the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which will be described in more detail below.
But the Labor Code does not provide specific explanations either about the amount of wages for the first half of the month, or about the methods for calculating these amounts. Enterprise managers and accountants can only rely on the opinion of the supervisory and control agencies of the Russian Federation, which in their letters actually consider this issue in more detail. Another additional source of information can be the experience of judicial practice in this area of application of the law.
Thus, the rules for paying advances in practice can have a variety of interpretations.
According to officials, the employer's LNA must indicate specific dates for payment of advance payments and wages. At the same time, it is not allowed to determine the dates of payment of salaries in the form of a period - for example, from the 2nd to the 6th of the month or from the 24th to the 29th, since this creates the possibility of violating the frequency of salary payments every half month, approved by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This opinion is confirmed by letters from the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated November 28, 2013 No. 14-2-242 and Rostrud dated June 20, 2014 No. PG/6310-6-1.
IMPORTANT! If the employer’s LNA contains a clause on the payment of wages once a month, such documents are considered invalid due to discrepancies with the tenets of labor legislation.
Case Study
The day of payment of wages in accordance with the order for the enterprise was expected to be June 7. Due to haste and an error, the financier withdrew money from the bank and transferred it to the staff on June 2. Moreover, taxes and contributions to state funds were paid in full on June 2. The bank did not notice the error; the accountant’s actions remained without question.
When checked by a Rostrud inspector, such actions were not regarded as a mistake or an offense . The management of the enterprise promptly noticed that the staff received the money prematurely and issued a corresponding order, which set the payment day on June 2 and an additional third payment day on June 12. Thus, the fifteen-day interval between salary payments was not violated.
Is it possible to issue an advance before the due date?
When asked whether it is possible to pay an advance ahead of schedule, a positive answer is allowed. After all, the Labor Code specifies the minimum number of payments regarding wages: “at least every half month.” Which implies the possibility of making payments more often, if the employer wishes. That is, wages can be paid three times a month, or four, or even every day, if such terms are provided for by company policy.
Provided that the internal LNA of the enterprise establishes payment of wages twice a month, a slightly different situation arises. Payment before the due date is permissible only if the appointed date for payment of the advance falls on a holiday or weekend. Then, according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, settlements with employees are carried out on the day preceding the given weekend or holiday. That is, if the agreed date for issuing the advance falls on a Saturday, Sunday or Monday, which is a non-working holiday, the issuance of the wage advance must occur on the eve of the non-working day, for example on Friday.
Paying an advance ahead of schedule in any case other than a weekend or holiday may pose risks for the employer, even if this does not impair the employee’s labor rights. After all, then the requirement of labor legislation to pay wages every half month is not observed.
What risks exist when paying an advance ahead of schedule?
Is it possible to issue an advance ahead of schedule at the request of an employee? In this situation, everything depends on the amount he asked. If the requested amount exceeds the salary, there is a risk in terms of withholding personal income tax. If the salary balance is small or does not exist at all, then there will be nothing to withhold personal income tax from. Tax authorities can reclassify such a payment as an interest-free loan agreement and charge additional personal income tax at a rate of 35% of interest savings, and impose a fine on the employer for failure to fulfill the obligations of the tax agent.
This is not to mention the risk of firing an employee who has received payment for time not yet worked. In this case, it will be almost impossible to return the money paid in advance to the company. Therefore, an advance at the request of an employee is most often issued when a small amount of money is requested.
To do this, the employee must write a statement addressed to the head of the enterprise indicating the reasons for this request. You may need to attach supporting documents to your application. Next, an order is issued for early payment of the advance, on the basis of which the accounting department pays this employee the requested amount.
Let's consider the procedure for calculating the amount of advance payment.
Responsibility for late payments
The employee can go to court.
As with delayed or non-payment of wages, untimely payment of advance funds may result in administrative liability for an employer of any type of activity.
However, the amounts of fines for government agencies, legal entities and individual entrepreneurs vary significantly.
Such an offense is punishable by fines, namely:
The same applies to individual entrepreneurs;
Thus, as it becomes clear, late payment of an advance is strictly punishable by law, despite the fact that payments ahead of schedule are not prohibited by law and are regulated only by local regulations.
In general, the payment of funds to an employee is strictly regulated by the current norms of labor legislation and other by-laws.
At the same time, violation of such legal requirements is strictly punished by law - a fine or complete removal from office.
Thus, if you believe that the employer is violating your legal rights, then you can always demand compliance with them, justifying your comments with the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. If the employer does not correct the situation, then you can always file a complaint against his actions with government control and supervision bodies: the Prosecutor's Office of the Russian Federation, the Labor Inspectorate, and also in court.
Remember that the law always tries to protect the interests of both parties when disputes arise. However, in order to prove the illegality of your boss’s actions, you will have to collect a solid base of evidence: statements, invoices, payslips, employment contracts, and so on.
From this video you will learn about calculating salary advances.
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
Source
How to pay an advance, common payment methods?
There are 3 main ways to calculate the advance:
- advance in a fixed amount;
- advance in the amount of a percentage of the salary;
- The amount of the advance is calculated in proportion to the time worked.
The first case is almost never used, as it carries great risks for the employer. For example, if the company has a provision for issuing a certain amount of advance, the employer will be obliged to pay it even to those employees who did not actually work in the first half of the month due to illness, vacation or any other reason. If at the end of the month the salary of this employee turns out to be less than the advance payment, the accounting department will have nothing to withhold personal income tax from. In addition, based on the same Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as on the basis of the letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated February 25, 2009 No. 22-2-709, wages for each half of the month should be given to the employee in approximately the same amount.
Let’s take a closer look at how an advance is issued when using the last two payment methods.
Documents that must be provided to the employee
Example
As noted above, the procedure for paying such monetary benefits as financial assistance is fixed in the internal regulatory documents of the organization.
To receive financial support, an employee must submit an application addressed to the head of the enterprise, which must reflect the reasons for receiving this type of payment, as well as attach the relevant documents.
Let's take a closer look at what documents you will need to present to your manager in each of the above situations.
The need for expensive treatment:
- a doctor's note;
- agreement for the provision of paid services with the clinic;
- documents confirming payment for medications;
- prescriptions certified by the signature and seal of the attending physician;
- documents about the need for expensive treatment.
Significant monetary damage:
- Documents that confirm the fact of the situation and were issued by an authorized organization.
- A copy of the certificate of material damage, certified by the relevant authority.
Wedding, birth of a child:
- marriage certificate (copy);
- birth certificate (copy).
Death of close relatives:
- Death certificate (copy).
- A document that can be used to confirm relationship with the deceased.
Other difficult life situations:
- single mother's certificate;
- document confirming the presence of disability;
- documents confirming another difficult situation of the employee.
Preferred calculation methods
There are 3 common options for calculating the percentage of salary when determining an advance:
- 50% of salary. Here, at first glance, everything is easy and clear: the salary is divided in half, and you don’t have to worry about unnecessary calculations. But another problem arises. At the end of the month, the employee is given a final payment minus 13% personal income tax from the entire salary amount for the reporting period. As a result, the salary for the second part of the month is significantly lower than the amount of the advance. And this contradicts the instruction about approximately equal parts of wages for each half of the month worked.
- 43.5% of salary. This figure is obtained as a result of simple calculations in order to avoid problems with personal income tax. Thirteen percent of the mandatory tax is subtracted from one hundred percent of the salary and divided by two.
- 40% of salary. According to statistics, most enterprises that use the method of calculating an advance as a percentage of salary round up 43.5% to 40%. In this case, the actual salary amounts are approximately equal for each half of the month.
When using a percentage of the salary when calculating the advance for the first half of the month, it is also possible to avoid some difficulties with withholding personal income tax if the employee was absent from work, for example, sick or on vacation. Therefore, the most objective way to determine an advance is to calculate the amount for the time actually worked. This method ideally meets the recommendations of labor law. At the same time, in order to optimally calculate the amount of advance payment to company employees, the responsible accountant must know the amount of time actually worked according to the time sheet for the first half of the month.
Advance amount
The amount of the advance is determined by the employer.
Many employees and employers ask the question: how much should the advance payment be based on the amount of funds? Are there clearly defined boundaries, and what are they in the current period?
Of course, there are advance amounts, and they, like many other norms and requirements in the field of labor legislation, are established by the relevant code of the Russian Federation.
Typically, the advance is calculated based on the amount of salary or the amount of time actually worked during piece work - on the volume of work performed. However, according to the law, the advance cannot be more than 50% of the salary.
But at the same time, the amount of the advance, depending on the terms of the concluded employment contract, can vary in the range from 20% to 50%, respectively.
In no case can the advance exceed half of the monthly salary, that is, 50% of the salary.
This is explained by the fact that if an employee is dismissed, there will be no problems with his final payment.
How is salary calculated for the first half of the month?
The new rules for paying advances in 2022 have forced accountants to think about what exactly should be included in the calculated wage amounts for the first and second half of the month in the current period and how to pay the advance in 2022. Letter No. 14-1/B-725 of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated August 10, 2017 provided some clarification regarding this issue. According to the department, when calculating the advance part of the salary, the following should be taken into account:
- The salary portion or the employee’s tariff rate for the time worked in the first half of the month.
- Allowances and bonuses, the calculation of which does not depend in any way on the fulfillment of work duties, the fulfillment of monthly working hours and on the final assessment of the employee’s performance for the entire month. Such allowances include additional pay for night and evening hours, allowances for professional skills, for length of service and for combining positions, as well as other allowances that meet these conditions.
Also, when calculating the advance payment, the following are not taken into account:
- Incentive payments (bonus payments), the calculation of which depends on the achievement of key performance indicators based on the results of a given period, that is, based on the results of work for the month.
- Financial assistance and social benefits.
- Payments of a compensatory nature, the calculation of which can be made only after the end of the month or directly depends on the fulfillment of working hours for the entire month. Such payments include additional payment for weekends and non-working holidays, as well as for overtime work.
Also, according to the letter in question, if an employer reduces wages for the first half of the month, he thus worsens the employee’s labor rights and infringes on him in the world of work.
Advance – what is it and for whom?
To begin with, it would be nice to understand what an advance is, why it is needed and to whom it is paid.
An advance is a certain percentage of the salary that is paid to the employee in the middle of the pay period. Every accountant knows this definition.
Or, in simple terms, an advance is part of the salary that the employer pays you in the first half of the month.
Depending on the type of activity, as well as on what conditions are specified in the employment contract, the amount of the advance may vary in one direction or another.
What are the consequences for an employer of refusal or error in assigning an advance?
Part 6 art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not imply deviations from the established framework, even at the request of employees. That is, even a personally written statement from an enterprise employee about the desire to receive wages once a month does not relieve the employer from liability. Clause 6 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation provides for a fine for such a violation:
- for officials - from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles; this applies to managers and accountants;
- for those who carry out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity - from 1,000 to 5,000 rubles;
- for legal entities - from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles.
A repeated similar offense is regulated by clause 7 of the same article of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation and is punishable by large fines:
- for officials - from 20,000 to 30,000 rubles or disqualification for a period of one to three years;
- for those who carry out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity - from 10,000 to 30,000 rubles;
- for legal entities - from 50,000 to 100,000 rubles.
When such offenses are detected, the labor inspectorate is adamant regarding both fines and disqualification of responsible officials.
For a situation where the payment of wages once a month is regulated by the internal local regulatory act of the enterprise, there is Art. 236 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, financial liability is imposed on the employer, regardless of his guilt. Each employee who has not been paid wages in accordance with the norms of labor legislation is entitled to compensation in the amount of no less than 1/150 of the key rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in force for the given period. This percentage is calculated from amounts not paid on time, for each new day of deferred payment, counting from the day following the due date of payment until the day of actual settlement with the employee.
Let's study the algorithm for calculating income tax and how the advance is paid, taking into account personal income tax.
Early payment of wages
However, some companies are concerned that if the first part of the salary is paid early, it will take more than half a month before the second payment is made. Will there be a violation in this case?
If the company’s internal documents set exact deadlines for paying salaries, for example, the 15th and 30th, then you need to adhere to exactly these deadlines. However, there are also situations when it is necessary to pay wages ahead of schedule. For example, before the New Year holidays, some companies try to pay the advance for December ahead of schedule, for example, on the 28th or even the 25th. The next payment of the main part will be on January 15, respectively, more than 15 required days will pass between these dates. Let's look into this situation. According to the Labor Code, payment of wages earlier than the approved date is possible only if the payment day falls on a weekend. In this case, the salary is issued on the eve of the due date of payment. And this is not a violation (136 Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
But if the payment was made on the 28th instead of the 30th, this may already constitute a violation, since the required period between payments of 15 days will be exceeded. The Labor Inspectorate may prosecute for such a violation under Article 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses. However, there will be no penalty for a one-time early postponement of salary payments. The main thing is that this is due to the forced conditions that have developed within the company. For example, the chief accountant goes on vacation, and no one else can issue salaries. In this case, an order to pay wages ahead of time will be required.
Important! Paying wages ahead of schedule is possible only if the approved payment date falls on a weekend, or in a particularly extreme case. It is important that subsequent payments occur on time.
How are taxes and contributions calculated on salary advances?
When setting up an advance, accounting workers may come up with reasonable questions: are they required to withhold personal income tax from the advance amount and should they also take care of calculating insurance premiums. After all, following the rules of labor legislation, the advance must also be considered wages. Comments on this matter were repeatedly given in letters from the Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service.
As it is written in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, namely in paragraph 2 of Art. 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: the day on which the employee actually receives income in the form of wages is the last date of the month for which wages are accrued. Accordingly, at the time of payment of the advance for the first half of the month, personal income tax does not yet exist. There is no need to withhold personal income tax from the advance amount. As a result, during the payment of the advance there is no need to:
- calculation and withholding of personal income tax;
- payment of contributions to extra-budgetary funds;
- calculation of premiums for accident insurance.
There is one controversial issue regarding the calculation of personal income tax. It applies to cases where the advance is paid on the last day of the month. In accordance with the ruling of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated May 11, 2016 No. 309-KG16-1804, if the payment of wages falls on the last day of the month, a basis for calculating personal income tax arises. At the same time, the Ministry of Finance, in its letter dated November 23, 2016 No. 03-04-06/69181, considers this approach to be incorrect on the basis that at the end of the working day of the last date of the month, accounting employees do not yet have complete information about the exact amount of time worked for reporting month, nor the amount of bonus payments.
Option
To avoid claims, you can issue money in three installments. That is, in advance, as the employee requests, and on regular dates. At the same time, payments on the 20th and on the day of payment for the month may be less, taking into account the amount that was paid ahead of schedule.
However, there is also a risk of questions from the tax inspectorate. They may think that they gave out not an advance or a salary ahead of schedule, but an interest-free loan. Then the employee receives a material benefit in the form of savings on interest. It and the amount of personal income tax must be determined on the last day of each month when the employee used the money (subclause 7, clause 1, article 223 of the Tax Code). The tax must be withheld from the next next payment, and transferred to the budget on the next business day. Judges support this approach (resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the East Siberian District dated March 27, 2013 No. A58-4544/12).
If you want to help an employee, apply for financial assistance or a loan. Assistance is not subject to personal income tax up to 4 thousand rubles. (clause 28 of article 217, clause 11 of clause 1 of article 422 of the Tax Code). The employee is required to repay the borrowed money and also pay personal income tax on interest savings.
***
How the advance is paid in 2022 - this question is specified in the theses of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, where this term is designated as wages for the first half of the month. Each employer is required to pay wages to employees of his company at least 2 times a month and no later than 15 days from the date of expiration of the period for which it is issued. It is preferable to calculate the advance amount taking into account the actual time worked. There is no need to withhold personal income tax from the advance payment. Failure to comply with the deadlines for payment of advance payments and wages is fraught with heavy fines for the manager and responsible person, as well as disqualification for repeated violation.