In the article we will analyze what it is - a shift method or work schedule, what it is, and we will tell you everything about it. For most employees, this is a good way to earn more, and for employers, it is an opportunity to provide remote sites with staff on a permanent basis. This is how research and expeditions are carried out, and areas of industry and production are developed. This is a traditional form of the labor process in areas of activity where it is impossible to ensure the movement of workers from workshop to home on a daily basis. This includes logging and gas or oil production. People stay for some time right at the plant in dormitories. It remains to figure out how it functions.
How to understand the shift work method, what it is
This is the name for permanent or shifting (seasonal) activity, where people do not return home during the day, but rest on the territory of the organization in specially designated places.
This is a specific form of labor relations, therefore separate acts have been thought out for it, which we will discuss below.
A company can introduce a similar type for certain specialties, people, or for all its employees at once. For example, if a company is located in a sparsely populated region, then it is better to recruit managers and specialized professionals for shifts. So they will be constantly in production.
If workers have to travel to and from work every day for more than 3 hours every day, then it is better to prepare an order and invite them to work on a shift basis.
Most often this is practiced in areas of the Far North and equivalent areas, as well as in areas where it is necessary to quickly erect a new workshop, open an enterprise or build a building.
The main challenge of the approach is the need for a large amount of labor. Despite the fact that such work is paid more expensively and requires more effort and money to set up, companies are willing to do it. Because the result and an established production process are much more important. For example, in the oil industry and when constructing bridges, it is important to comply with all technological and time standards.
When is it necessary to use a rotational work organization method?
In the modern economy, there are some economic sectors that, due to the specifics of their functioning, require workers to be located at a considerable distance from their permanent place of residence. Such activities may be associated with the construction of various construction projects, the organization of transport routes, the creation of closed military facilities, etc. To carry out these works, it is necessary to organize relationships between enterprises and workers who are sent on shift to perform their professional duties.
Resolution No. 794/33-82 contains a list of organizations that can primarily use shift work as a form of organizing labor relations between the employer and staff. In particular, these are enterprises related to the oil or gas industry, transport and communications, construction or geological exploration, forestry, etc.
Regulation by law
Every person, before he finds a job under such conditions, should understand how this is reflected in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Article 297 clearly states that this can be called a type of activity in which a specialist cannot return to his place of registration every day. This type cannot be classified as business trips, since a shift is considered to be working all the time, including rest between shifts and part of the day at work.
It should not last more than 1 month, but in special cases and by prior agreement, the employer can increase this period. Shift is no more than 12 hours, if more, then this is overtime, which is paid separately. The order in which shifts will take place is also determined in advance by management and specified in the documentation that the employee will sign.
Weekends during a shift are days off that are either paid according to special rules or counted towards the period when the employee will be at home. There are no holidays or vacations at the facility; rest begins only when a person gets to their place of residence.
What is working on a shift basis: what does it mean according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
This is a special form of the labor process, which is based on the inability to get home every day. The company undertakes to organize the transportation of people in both directions, to provide conditions for livelihoods and accommodation at the plant or near the production site.
Company order
Before making such a decision, an enterprise usually carries out calculations that help to understand how effective and expedient it is to move to this type of interaction with personnel.
If this should pay for itself, then the administration creates a document according to which it completely switches to this type or introduces it as an additional one.
The papers state:
- the fact that the company now has a similar variety;
- how time will be counted;
- for what period is it summed up;
- terms of payment;
- the level of the bonus, if there is one - in government institutions this is regulated by law;
- coefficients by region;
- “northern” allowances, if the organization is located in the relevant region;
- how long the shift is, how many days to work and rest;
- Mandatory - signatures of all employees who have read the document.
Let's sum it up
- The shift work method not only has a number of common features that distinguish it from other possible work modes. The fact that it can be used in completely different industries gives it a specificity that is specific to each of these industries. However, the specific conditions for using this method are detailed by each employer independently.
- The conditions for using the rotation method that apply to a particular employer are fixed by him in an internal regulatory act - the regulation on the rotation method. This document operates along with other internal documents devoted to issues of labor organization and remuneration. The regulations on the shift method are approved before the start of this method, and its contents are brought to the attention of workers who will work in this mode, against signature.
Ready-made solutions for all areas
Stores
Mobility, accuracy and speed of counting goods on the sales floor and in the warehouse will allow you not to lose days of sales during inventory and when receiving goods.
To learn more
Warehouses
Speed up your warehouse employees' work with mobile automation. Eliminate errors in receiving, shipping, inventory and movement of goods forever.
To learn more
Marking
Mandatory labeling of goods is an opportunity for each organization to 100% exclude the acceptance of counterfeit goods into its warehouse and track the supply chain from the manufacturer.
To learn more
E-commerce
Speed, accuracy of acceptance and shipment of goods in the warehouse is the cornerstone in the E-commerce business. Start using modern, more efficient mobile tools.
To learn more
Institutions
Increase the accuracy of accounting for the organization’s property, the level of control over the safety and movement of each item. Mobile accounting will reduce the likelihood of theft and natural losses.
To learn more
Production
Increase the efficiency of your manufacturing enterprise by introducing mobile automation for inventory accounting.
To learn more
RFID
The first ready-made solution in Russia for tracking goods using RFID tags at each stage of the supply chain.
To learn more
EGAIS
Eliminate errors in comparing and reading excise duty stamps for alcoholic beverages using mobile accounting tools.
To learn more
Certification for partners
Obtaining certified Cleverence partner status will allow your company to reach a new level of problem solving at your clients’ enterprises.
To learn more
Inventory
Use modern mobile tools to carry out product inventory. Increase the speed and accuracy of your business process.
To learn more
Mobile automation
Use modern mobile tools to account for goods and fixed assets in your enterprise. Completely abandon accounting “on paper”.
Learn more Show all automation solutions
Which companies can use this method?
More often than others, it is used by those who open enterprises in the regions of the North and areas related to them. But in recent years it has been actively used in “ordinary” areas, because in the Labor Code there are no restrictions on areas, and the delivery time can be significantly reduced.
The main condition is the presence of an object, which is inconvenient to get to due to its remoteness or lack of roads. If a specialist has to travel more than 3 hours each time, then it is advisable to offer him a shift.
Sometimes the tax service tries to challenge the legality of its use, but usually the court sides with the employers.
Why is this not a business trip?
Sometimes personnel services confuse shift work with travel, but there are differences:
- Payment. A seconded specialist’s salary will include a working day and small tariff allowances. The shift worker draws up a special document in which all tariffs, terms and conditions are prescribed. Workers are considered to work full days.
- Body check. Before going to another city for a couple of days, you will not need to undergo an examination and confirm your health.
- Deadlines. There are no restrictions on weeks of stay for a business traveler. Upon his return, he goes to work. If people go to development, then they cannot be there for more than 1-3 months, after which a rest period follows.
- Goals. People go on a business trip to fulfill a specific assignment - to increase sales, to launch a line. The rotation method simply involves a regular 12-hour shift.
Work on a rotational basis - registration according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Shift workers are registered for work through a corresponding employment contract, which structurally displays the following information:
- Employee and employer data.
- General provisions.
- Terms of payment.
- Temporary mode of work and rest.
- Working conditions plus guarantees and compensation.
- Compulsory insurance (social, pension, medical).
- Rights and obligations of the employee and employer.
- Their responsibility.
- Training in safe working methods.
- Final provisions.
- Details and signatures of the employee and employer.
Sample employment contract
Shift: what kind of schedule is this, what does it mean - working conditions
This type of employment is beneficial not only to workers, but also to the enterprise. But it's important to understand that for people it involves daily, often strenuous physical activity for a certain number of days in a row. Sometimes this is a deterioration in the usual lifestyle and distance from home and family. Not everyone can do this, which is why most companies limit their hiring to men. But these are not the only restrictions. Let's look at this issue in more detail.
Who has the right to work
There are two important factors according to which applicants are selected for each position - profession and physical health. Often the shift is located in places remote from the city and populated areas. Therefore, a person with chronic diseases should not go to the Far North.
Determines whether you can go to work, doctor. He also issues the appropriate certificate for the employer. Which doctors will have to be visited regularly between shifts is determined by the enterprise and the direction of its activities. This is enshrined in local acts.
Restrictions
There are several categories of people for whom this type of activity is unacceptable:
- pregnant and lactating women;
- guardians or parents of at least three children - one of the adults must remain with the wards;
- persons under 18 years of age;
- those who have not undergone a medical examination for any reason.
How to organize a rest and work schedule
Here time is calculated differently. The entire period is taken into account from the moment a person boards the train heading to the object until the day he returns home. A working day does not exceed 12 hours, unless otherwise specified in the contract. One employee cannot be assigned two shifts in a row.
The interval between shifts is called inter-shift. The employee spends it outside the company and is paid like a standard vacation.
Article 299. Duration of watch
(as amended by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
A shift is considered to be a total period, including the time of work performed at the site and the time of rest between shifts.
The duration of the shift should not exceed one month. In exceptional cases, at individual sites, the duration of the shift may be increased by the employer to three months, taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization in the manner established by Article 372 of this Code for the adoption of local regulations.
Ready-made solutions for all areas
Stores
Mobility, accuracy and speed of counting goods on the sales floor and in the warehouse will allow you not to lose days of sales during inventory and when receiving goods.
To learn more
Warehouses
Speed up your warehouse employees' work with mobile automation. Eliminate errors in receiving, shipping, inventory and movement of goods forever.
To learn more
Marking
Mandatory labeling of goods is an opportunity for each organization to 100% exclude the acceptance of counterfeit goods into its warehouse and track the supply chain from the manufacturer.
To learn more
E-commerce
Speed, accuracy of acceptance and shipment of goods in the warehouse is the cornerstone in the E-commerce business. Start using modern, more efficient mobile tools.
To learn more
Institutions
Increase the accuracy of accounting for the organization’s property, the level of control over the safety and movement of each item. Mobile accounting will reduce the likelihood of theft and natural losses.
To learn more
Production
Increase the efficiency of your manufacturing enterprise by introducing mobile automation for inventory accounting.
To learn more
RFID
The first ready-made solution in Russia for tracking goods using RFID tags at each stage of the supply chain.
To learn more
EGAIS
Eliminate errors in comparing and reading excise duty stamps for alcoholic beverages using mobile accounting tools.
To learn more
Certification for partners
Obtaining certified Cleverence partner status will allow your company to reach a new level of problem solving at your clients’ enterprises.
To learn more
Inventory
Use modern mobile tools to carry out product inventory. Increase the speed and accuracy of your business process.
To learn more
Mobile automation
Use modern mobile tools to account for goods and fixed assets in your enterprise. Completely abandon accounting “on paper”.
Learn more Show all automation solutions
What does a full cycle look like?
To take into account everything that needs to be reflected in the calculation sheet, you need to calculate:
- hours and days that a person will get to the object and back;
- moments spent directly on performing direct duties;
- weeks of inter-shift rest.
To automate and optimize production processes, we recommend using special software from Cleverence, with which you can effectively organize the work activities of an enterprise.
Work and rest schedule during shifts according to the Labor Code
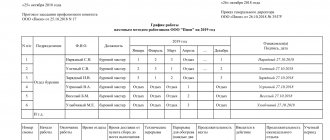
The work and rest regime when organizing work on a rotational basis is reflected in a special schedule, which is developed and approved by the employer, and the opinion of the elected body of the trade union organization must be taken into account. The developed local regulatory act is required to be studied by all employees of the organization with whom labor relations of this kind are formalized. Employees must be familiarized with this document no later than 2 months before its approval and entry into force.
In addition to the shift work schedule, the schedule also includes the time required to transport employees from the initial assembly point to the final point of performance of their work duties and back. This time is not included in the working period, and therefore may well fall on days related to the period of inter-shift rest.
What does a shift method or work schedule mean, like this
In order to normalize time and provide the company with specialists at every moment, you will have to create a special output sheet, where all activity cycles will be entered. All shifts and specific people who will go out are registered, indicating the hours. The document also states the inter-shift rest and the period required for the journey. The manager is responsible for its preparation and maintenance.
Such a paper is placed in the room where the whole team gathers, for example, in the dining room or locker room, so that everyone can remind themselves what time they should start.
Peculiarities of working on a rotational basis: shift duration
As we said above, in the standard case it does not exceed 12 hours. But for individual positions and individuals it is different. In addition, technological breaks and lunch must be included in this period.
It is prohibited to work for more than 24 hours; a person must be given the opportunity to rest after this.
The company sets the total occupancy time at each site independently. By law it is 15, 30 or 60 days.
The rest of the day after the end of work duties is considered rest, but the employee continues to remain on the employer’s premises. He will only travel between shifts.
What is a watch and where is it used?
The shift method of work according to the Labor Code is regulated by Chapter 47. In general, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation understands the shift method (the shift itself) as the sum of the time of work and the rest interval between shifts.
Work on a rotational basis () is limited in duration to a period of a month. Exceptions include special cases at individual sites, due to which the specified period may be extended to 3 months (for this, the opinion of the workers’ trade union body, if there is one, must be taken into account). In its absence, they act within the framework of Art. 74 TK
The shift method of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides a guarantee of providing workers with housing when they are at the work site (Article 297).
The designated type of activity is used in oil and gas and coal mining, development of precious metals, fishing, logging, as well as in the field of transport, construction, geology and others.
How is it paid?
This method of work should be distinguished from the standard one, as there are some differences. Additional allowances are paid, tickets are provided to get to and from the site on holiday, and accommodation is provided if this is not provided. It is taxed in the same way as any other income.
There are several types of remuneration systems:
- piecework;
- hourly;
- tariff;
- salary
Bonuses are also paid for achievements, delivery of a separate section or for a completed stage.
Summarized time tracking
This indicator is used if the day or week is not standardized and it turns out to be too difficult to calculate. In this case, the schedule includes a certain number of hours worked for the required period from a day to a year. Paid upon actual payment for the period of time taken into account.
Article 300. Recording of working time when working on a rotational basis
When working on a rotational basis, a summarized accounting of working time is established for a month, quarter or other longer period, but not more than for one year.
The accounting period covers all working time, travel time from the location of the employer or from the collection point to the place of work and back, as well as rest time falling within a given calendar period of time.
(as amended by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
The employer is obliged to keep records of the working time and rest time of each employee working on a rotational basis, by month and for the entire accounting period.
Staff benefits and tariffs
We have given simple explanations of what it is to work on a free shift. Now let's dwell on the nuances of bonuses and allowances for harmfulness/"northern".
In accordance with the law, employees can be paid extra from the budget (federal or regional) or from the management of a private company. The reason for the accrual may be laws and acts of the state or a specific enterprise. For example, in Siberia and the Far East they can pay up to 30% of the already accrued wages.
If the working hours are irregular
By law, the employer is not required to pay extra. Some companies calculate it as overtime, but more often the hours are simply added to paid leave. What will be outside the norm and how this will be compensated must be agreed upon with the staff.
If working conditions are difficult
Everyone who works in the Far North or neighboring regions is paid a bonus; it is considered in isolation from the regime in which the worker serves. The order of the Labor Code is established and regulated.
Additional leave
Everyone who works in this way has the right not only to annual rest. If they are in a region that can be equated to Siberia, 16 calendar days are added.
Commentary on Article 301 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
According to the terminology of Article 100 of the Labor Code, the regime of work and rest, which is referred to in the title of Article 301 of the Labor Code, is the regime of working time and rest time. Its features are regulated by Article 301 of the Labor Code, as well as by-laws in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Currently, one of the main special acts remains the Basic Provisions on the Shift Method of Organizing Work, approved on December 31, 1987 N 794/33-82, which resolve issues that are not reflected in Chapter 47 of the Labor Code.
Taking into account the above provisions and standards, when establishing working hours and rest time when working on a rotational basis, you must be guided by the following:
— the duration of daily work (shift) should not exceed 12 hours, as stated in paragraph 4.2 of the Basic Provisions;
- on the basis of Part 5 of Article 103 of the Labor Code, work for two shifts in a row is prohibited;
- the duration of daily (between shifts) rest, in accordance with paragraph 4.3 of the Basic Provisions, taking into account breaks for rest and food, can be reduced to 12 hours;
- the number of days off in the current month should not be less than the number of full weeks of this month, as established by Part 1 of Article 111 of the Labor Code and clause 4.3 of the Basic Provisions, on the basis of which days off can be provided on average for each working week, and not necessarily during each calendar week;
— weekends can fall on any day of the week (clause 4.3 of the Basic Provisions);
— the shift work schedule is brought to the attention of employees no later than two months in advance, as is expressly stated in Part 1 of Article 301 of the Labor Code. The shift work schedule is usually approved for a year.
During shift work, the length of the working day (shift) may change according to the shift schedule. Shift work schedules are used that provide for a reduction in the length of the working day (shift) at the beginning and end of the week and an increase in the middle of the week.
In order to compensate for the existing overtime, it is possible to reduce the duration of the working day (shift).
The shift work schedule can be common for employees of the entire organization, its individual divisions, or maybe individual.
Individual schedules can be used to take into account the specifics of work related to ensuring:
— continuity of leading engineering, technical and managerial personnel by reflecting in the schedule the appropriate time for acceptance and transfer of volumes of work and affairs by heads of structural divisions and foremen (foremen);
— transfer of appropriate vehicles, devices, mechanisms and units by combining schedules (usually daily) for machine operators and drivers of various shifts;
— safety of material assets by allocating a reserve of time in the schedule for the transfer of values;
— compliance with the rules governing the duration of shifts and the use of summarized recording of working time, in case of actual deviations from the general (usual) work schedule on a shift.
In case of incomplete work time in the accounting period or on a shift, calendar working hours falling on days of absence from work are deducted from the norms established by the schedule, in accordance with clause 4.5 of the Basic Provisions.
In the absence of a trade union body, the employer must take into account the opinion of another representative body of employees, or in the absence of one, approve the shift work schedule independently.
“The time required to deliver workers to and from their shifts,” which is referred to in Part 2 of Article 301 of the Labor Code, is determined in the schedule, taking into account the schedule of the relevant modes of transport. The specified time is called “days on the way to the place of work and back”, and in Part 1 of Article 302 of the Labor Code - “days on the way from the employer’s location (collection point) to the place of work and back”, Part 5 of Article 302 of the Labor Code defines - “days of travel from the location of the organization (collection point) to the place of work and back.”
The legal essence is the same. The most accurate is the wording of Part 1 of Article 302 of the Labor Code. It is best used when developing and approving regulations on the rotation method for a particular employer.
Despite the fact that days on the way to and from work are not included in working hours, on the basis of Part 2 of Article 301 of the Labor Code, for these days the employee is paid a special bonus, as well as a daily tariff rate (salary) in accordance with Parts 1, 5 Article 302 of the Labor Code.
Inter-shift rest, taking into account parts 3 - 4 of Article 301 of the Labor Code, is additional days of rest provided in connection with work outside the normal working hours in the accounting period according to a special calculation. That is, inter-shift rest is a kind of vacation, provided not annually, but several times a year for the time worked in each period of the summarized accounting.
This type of rest is one of the features of the legal regulation of labor on a rotational basis, which exists, although not mentioned in Article 107 of the Labor Code.
In contrast to paragraph 4.3 of the Basic Provisions on the shift method of organizing work, Part 3 of Article 301 of the Labor Code provides for the summation of hours of working time overtime, which are subsequently used to calculate the duration of inter-shift rest.
In accordance with Part 3 of Article 301 of the Labor Code, only overtime hours within the limits of the shift work schedule are subject to summation. Overtime beyond the scheduled working hours is overtime.
It is considered normal, on the basis of Part 4 of Article 301 of the Labor Code, the duration of working hours provided for by the work schedule on a shift within the accounting period, and not by the general norms of the Labor Code (40-hour work week, etc.), which must be observed by this schedule only in average for the accounting period.
The number of additional days of rest (rest between shifts) is determined by dividing the total number of overtime hours by 8 hours (the normal length of a working day for a 5-day work week of 40 hours).
With a shortened working week, the division is not made by 8 hours, but by the number of hours obtained by dividing the established duration of the shortened working week by five days.
If the remainder of this division is not a multiple of a whole day, then overtime hours are accumulated over the course of a calendar year up to whole working days. Later, additional days of inter-shift rest are provided.
When an employee is dismissed or the calendar year expires, the specified hours are paid based on the tariff rate (salary), as determined by paragraph 5.4 of the Basic Provisions on the Shift Method of Work Organization.
Inter-shift rest must be provided taking into account Part 2 of Article 300 and Clause 4.3 of the Basic Provisions, within the accounting period and at the place of residence.
Clause 7.1 of the Basic Provisions obliges the employer to provide annual leave to shift workers after they have taken inter-shift rest. Days of inter-shift rest are included in the length of service, which gives the right to annual basic and additional leave, including length of service for work in harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions.
In cases where the end of an employee’s annual leave falls on the inter-shift rest days of the team in which he works, then the employee before the start of his shift may be:
- due to production necessity in order to prevent downtime that arose for organizational reasons, he was transferred to another job according to the rules of Article 74 of the Labor Code;
- transferred to another shift shift (another structural unit) in accordance with Part 3 of Article 72 of the Labor Code.
As one of the options, by agreement of the parties, leave without pay may be granted.
For shift workers who leave before the end of the accounting period, the date of dismissal (with their consent) can be indicated taking into account the due days of rest between shifts. This allows us to do this in paragraph 4.3 of the Basic Provisions on the shift method of organizing work.
If an employee simultaneously has the right to unused annual leave, then he can receive it in kind with subsequent dismissal, on the basis of Article 127 of the Labor Code, after the end of the inter-shift rest period. The date of dismissal will be the last day of vacation.
The same rules apply to medical and pharmaceutical workers serving rotation workers. The tariff rate (salary) for paying for inter-shift rest days is taken without the use of regional coefficients and allowances for work in the Far North and equivalent areas, which is consistent with clause 5.4 of the Basic Provisions on the rotational method of organizing work.
Clause 6 of the conditions and procedure for remuneration of medical and pharmaceutical workers serving workers and employees transferred to the rotation method of organizing work stipulates that the days of inter-shift rest for the specified medical and pharmaceutical workers in connection with work beyond the normal working hours during the accounting period are paid from calculation of the official salary received by the day of this rest, and the duration of the working day established by law.
Payment for inter-shift rest is made in the amount of the tariff rate (salary), unless otherwise established by the labor or collective agreement (Part 4 of Article 301 of the Labor Code).
Taking into account Articles 8 and 9 of the Labor Code, the parties to these agreements may agree to increase the specified amount. Lowering it will worsen the situation (reduce the level of rights and guarantees) of workers compared to the Labor Code, therefore such a norm cannot be adopted.
The form of overtime work, which, in accordance with Article 99 of the Labor Code, recognizes work performed by an employee at the initiative of the employer outside the established working hours, daily work (shift), as well as work in excess of the normal number of working hours during the accounting period, can be acquired by overtime in excess of the normal working hours time on watch.
Thus, with a shift method, overtime will be considered work that is performed:
- in excess of the duration of daily work (shift) provided for by the schedule;
- within the duration of daily work (shift) provided for by the schedule, but in excess of the maximum duration of such work (shift) established by law (for example, over 12 hours);
- in excess of the normal number of working hours during the accounting period.
The reasons for working overtime may vary. The most common is the non-arrival of shift personnel.
Engagement in overtime work is carried out according to different rules than engagement in work within the work schedule on a shift.
Payment for inter-shift rest days in the amount of the tariff rate (salary), provided for in Part 4 of Article 301 of the Labor Code, is made when these days are provided in the form of compensation for overtime within the accounting period.
If during the shift period there was involvement in overtime work, then it must be compensated in accordance with the rules of Article 152 of the Labor Code (one and a half, double pay or in other forms).
Payment for days of inter-shift rest provided in connection with work in excess of normal working hours within the accounting period, as well as compensated upon dismissal, in accordance with Articles 139, 300 of the Labor Code, is taken into account in all cases of calculating average earnings.
If temporary disability occurs during the inter-shift rest period, temporary disability benefits are not issued. If it continues after the end of the specified period, then the benefit is paid from the day the employee must begin work. The amount of the benefit is determined based on the number of working hours according to the schedule drawn up in accordance with the rules of Articles 300, 301 of the Labor Code, missed due to temporary disability.
For example, an employee missed five ten-hour working days due to temporary disability. The benefit should be paid for 50 hours of work (10 hours x 5 days) and not for 40 hours as in the case of a regular work schedule with an eight-hour workday and a five-day 40-hour week.
Taking into account paragraph 2 of the conditions and procedure for remuneration of medical and pharmaceutical workers serving workers and employees transferred to a rotational method of organizing work, the working hours and rest time for these groups of workers in each case are determined taking into account the specifics of production, as well as in accordance with the standards, provided for shift workers by Chapter 47 of the Labor Code and the Basic Provisions on the shift method of organizing work.
How do they pay for shift shifts?
Since all the time that a person is at the enterprise, in some cases it can be considered irregular, it is important to compensate for it. Therefore, the personnel department must act according to the algorithm when making calculations:
- how long it was necessary to work normally;
- actual quantity according to schedule;
- the standard, processing or deficiency is determined by law;
- the volume of working days that the company is obliged to pay staff is established;
- excess hours are converted into a tariff rate or calculated based on salary.
Advantages and disadvantages
This variety has its positive and negative sides. Advantages:
- excellent pay and earnings;
- you can find a position in another region, even if there is nowhere to work in your own;
- there is a long rest between two trips;
- there is a higher probability of gaining knowledge and unusual experience, since you are always in a state of immersion in tasks at the site;
- free accommodation and often meals;
- There is an opportunity to take a break from gadgets.
But there are also disadvantages:
- usually hard work in remote regions;
- the whole team is nearby, it’s difficult to be alone, you have to stay in the same area with them for a long time;
- long daily working hours;
- not all specialties are in demand;
- having to live far from home, family and friends;
- living conditions are often camp;
- it is impossible to exclude the possibility of fraud by the employer.