Every organization may face a situation where it is necessary to downsize its workforce or staff. When laid off, the employee is entitled to certain payments. These include: compensation for unpaid vacation, severance pay, average earnings for the second and third months after dismissal. The expert “What to do Consult” talks about how to calculate and within what time frame to pay the amount due to the employee.
Payments that an employee is entitled to during layoffs can be divided into two categories:
- standard, to which the employee has the right, regardless of the grounds for dismissal;
- additional ones that are due to employees who are laid off due to layoffs. This includes earnings saved during employment. Let's take a closer look at each of the categories.
Standard payments
Regardless of the grounds for dismissal, the employee is entitled to wages (including compensation and incentive payments) and monetary compensation for unused vacation, if there are still days off (Part 4 of Article 84.1, Part 1 of Article 127, Part 1 of Article 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ). Such compensation is due to employees for the entire period of work. The position is confirmed in Letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated January 25, 2021 No. 14-2/OOG-521.
Compensation is calculated, as for any other reason for dismissal, based on average earnings.
You can learn how to calculate average earnings from SPS ConsultantPlus: Ready-made solution: How to calculate average earnings {ConsultantPlus}.
The number of days is calculated based on the months worked using the formula: 2.33 days for each month (Rostrud Letter No. 5921-TZ dated October 31, 2008).
When dismissal due to reduction, there are features of calculating the number of days of unused vacation. Employees who have worked from 5.5 months to 1 year are entitled to vacation compensation for a full working year (clause 28 of the Rules on regular and additional vacations).
This rule applies when the employee has been working for the first year. Compensation for the second and subsequent years of work is paid in proportion to the time worked (Rostrud Letter No. 164-6-1 dated 03/04/2013, Rostrud Letter No. 2368-6-1 dated 08/09/2011).
However, there is also such judicial practice when compensation was recovered from the employer for a full year, while the employee’s experience in a particular organization was several years (Bulletin of judicial practice of the Moscow Regional Court for the IV quarter of 2015, Appeal ruling of the Irkutsk Regional Court dated November 12, 2014 in the case No. 33-9318/2014). Based on this, if an annual compensation is paid, this is not a violation of the law, since the employee’s situation has not worsened.
Payments upon dismissal at one's own request
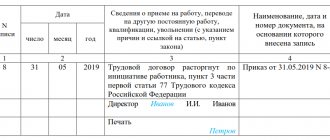
An employee has the right to resign at his own request (Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The accountant must issue the final payment on his last day of work. In 1C: ZUP, a calculation note is generated according to the unified form T-61, but a document independently developed by the organization can also be filled out. It must contain the required details for the primary accounting document and be enshrined as an appendix in the company’s accounting policies.
The calculation includes two mandatory amounts of funds:
- salary for unpaid time until the termination of the employment relationship;
- compensation for unused vacation.
The law does not provide for any other payments upon dismissal of one's own free will for an employee. However, a company may, in its local documentation, provide for certain types of payments or compensation upon dismissal, including on this basis.
A situation is possible in which a person quits before the end of the year used to calculate vacation, i.e. part of the payment was used in advance. In such a situation, accrued vacation pay must be recalculated and overpaid funds must be withheld from the final calculation. However, their value cannot be more than 20% (Article 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The employee can return the rest of the debt for unworked vacation days on a voluntary basis.
From the final payment, the employer has the right to withhold other amounts of debt, for example, unpaid advance payments or incorrect accruals. But he can do this only with the consent of the dismissed employee with the basis and amount of deduction (Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Severance pay
Severance pay is paid on the day of dismissal. An exception is employees hired under a fixed-term employment contract, the validity of which does not exceed two months. However, if payments are provided for by local regulations of the employer, collective or labor agreement (part 4 of article 84.1, part 1 of article 140, part 1 of article 178, part 1 of article 318, part 3 of article 292 , Part 3 of Article 296 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), they need to be produced.
According to the existing rule, the severance pay due upon layoffs is equal to the employee’s average earnings for the first month after dismissal. The calculation of the amount depends on the conditions under which the person worked (part 1 of article 139, part 1 of article 178, part 1 of article 318 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clauses 9, 13 of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 24, 2007 No. 922, Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated November 13, 2019 No. 34-P, Letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated March 11, 2021 No. 14-1/OOG-2066).
Normal work schedule : average daily earnings multiplied by the number of working days and non-working holidays in the first month after dismissal.
Summarized working time recording : average hourly earnings multiplied by the number of working hours according to the employee’s schedule in the first month after dismissal.
If an employee is employed in seasonal work, then upon layoff, he is paid severance pay in the amount of two weeks' average earnings (Article 296 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Please note: the employer’s internal documents, labor or collective agreement may provide for an increased amount of severance pay (Part 8 of Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If this is not the case, a labor dispute may arise in the event of non-payment.
There is judicial practice on the issue of mandatory increased payments, but it is ambiguous.
There are decisions made in favor of the employee. For example, Determination of the Ninth Court of Cassation of General Jurisdiction dated May 28, 2020 No. 88-3699/2020. In this case, an additional agreement to the employment contract was concluded between the employee and the employer, which stated that in the event of dismissal due to reduction, in addition to mandatory payments, compensation in the amount of 20 average monthly earnings is due. The employer did not fulfill these conditions, so the woman went to court. During the meeting, the defendant referred to the fact that this condition is not mandatory, its amount is too high, and the plaintiff, by putting forward demands, is abusing her rights. Despite these arguments, the court sided with the worker. The fact is that labor legislation allows you to establish an increased amount of benefits. And in this case, this amount was agreed upon by the parties in an additional agreement to the employment contract, so we can say that at the time of signing the document, both the employer and the employee agreed on its amount.
However, the courts do not always side with the dismissed employee. For example, Resolution of the Presidium of the Vologda Regional Court dated July 23, 2018 No. 44G-27/2018.
The woman was dismissed due to redundancy (clause 2, part 1, article 81). The employer has made all payments due in this case. But the additional agreement to the employment contract provided for an increased amount of severance pay - four official salaries. The employer did not make the additional payment, the employee filed a lawsuit. However, the decision was made in favor of the organization. The thing is that this payment is not mandatory - it is not enshrined in any way in local regulations. In addition, such compensation would provide a short-term employee with significant advantages over other team members.
Calculation of average earnings for compensation payment
All redundancy payments for employees in 2022 are calculated based on the average earnings of each of them. To determine the amount due to each person, it is necessary to calculate exactly the average salary. There is a special formula for this; we also talked about the features of calculating such an average value in a separate material. So the formula looks like this:
Average earnings per day = the amount of wages and other payments to the employee for the 12 months preceding the layoff period divided by the days actually worked during the same 12 months
The calculation does not include the amounts of temporary disability benefits and vacation pay that the employee received in the corresponding period. Therefore, they must be subtracted from the total amount before dividing by 12. Once the amount of salary for one day is determined, the amount of severance pay can be calculated. For this, the following formula is used:
Severance pay = average daily earnings multiplied by the number of working days in the first month after dismissal
A similar formula is used to calculate compensation for subsequent periods, as well as the amount that is due to persons in case of early dismissal. Although you can also use a separate formula for it:
Compensation for early dismissal = average daily earnings multiplied by the number of working days falling in the period from the next day after dismissal to the day of expiration of the two months that relied on the notice.
Working days for these and other formulas are calculated individually for each person in accordance with his personal work schedule in the organization. For example, they may differ between office professionals and those who work shifts.
Average earnings for the period of employment
The average monthly salary for the duration of employment is paid to everyone, except for workers hired for a period of less than two months. This follows from parts 2, 3 of Art. 178, part 3 art. 292, part 2, 3 art. 318 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
For those employed in seasonal work, a payment is provided - the average amount of payment for two weeks. It is severance pay and is paid on the last day of work (Article 296 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The rest of the employees are entitled to an average salary for three months. If an employee worked in the Far North or in an equivalent area and quits his main place of work, then he is paid the average salary and saved for six months.
In this case, the average earnings for the first month after the layoff is the severance pay; additional compensation is not required. Average earnings for the second, third and subsequent months (relevant only for workers in the Far North) are calculated only if the person did not get a new job during this period.
Calculation examples
Let's look at an example of how benefits can be calculated.
Employee Alexandrova A.A. was given a notice of dismissal dated 03/01/2018 with information about the reduction of her position from 06/01/2018. Her salary was 16,000 rubles per month.
This means that on the last day of work she must receive her salary, vacation compensation, and benefits for the period from 06/01/2018 to 07/01/2018 (even if a new job has already been found).
If there is no new job, the former employee sends an application for a new payment with the presentation of the required documents upon the end of two months from the date of dismissal, i.e. 08/01/2018.
Another, third, payment is made no earlier than 09/01/2018
Second month after layoff
The average salary for the second month after the layoff is paid if the employee himself applied for this amount. He must submit an application in writing no later than 15 days after two months have passed since his dismissal (Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In order to receive this payment, a person must provide (clause 12 of the Regulations on the procedure for the release, employment of workers and employees and the provision of benefits and compensation to them):
- passport;
- work book (if maintained) or information about work activity.
The calculation of the payment is the same as in the case of severance pay: working and non-working holidays for the second month after the layoff are taken into account. For employees with summarized working time recording - the number of working hours according to the schedule in the second month after dismissal.
Payment for a full month is due only if the person was not employed for the entire period. If during the second month after dismissal he finds a new job, then the average salary is paid only for those days when he was not employed. This follows from Part 2 of Art. 178 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The payment period is 15 calendar days from the date of application (Part 4 of Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Deadlines for receiving mandatory payments
Mandatory payments have certain features and deadlines for receipt:
- On the day of departure, the employee receives a salary. In the same way, compensation for vacation that was not used is subject to receipt. Redundancy benefits are paid on the same date.
- The second amount of funds to be received is carried out at the end of the second month from the date of dismissal. To receive it, the employee is sent to the former employer with a package of documents, which includes an application and a work book without records of a new place of work.
- The third financial tranche is provided when the third month is completed, subject to the above conditions.
The 2022 redundancy benefit, as in 2022, is payable from the funds of the employer with whom the employee separated.
If payments due to the employee are not made on the date of termination of the contract or on the day following the employee’s request for payment (if he is not present on the date of dismissal), the employer should pay them taking into account interest (monetary compensation). The amount of compensation is not less than 1/150 of the current key rate of the Bank of Russia of the amount of amounts not paid on time, for each day of delay from the day that follows the specified payment deadline until the day of settlement in fact, inclusive.
Third month after layoff
In order to receive average earnings for the third month after layoff, in addition to your passport and work book (information about your work activity), you must present a decision from the employment service.
If the employer does not agree with the decision of the employment service, then it can be challenged in accordance with Part 1 of Art. 218 CAS RF.
And here there is judicial practice, where decisions were made in favor of the employer.
For example, Determination of the First Cassation Court of General Jurisdiction dated June 15, 2021 No. 88-13122/2021. The woman was laid off. Within two weeks from the date of dismissal, she contacted the employment service, but within three months from the date of dismissal she did not get a job - there were no suitable vacancies. The woman provided the employer with a solution from the employment center to receive payment for the third month after dismissal. The organization's management did not agree with this and went to court. The first instance sided with the worker. The court noted that there were significant obstacles to employment: retirement age, living in rural areas, loan obligations and mandatory payments. The plaintiff appealed this decision. The employer provided evidence: during the disputed period, the employee performed labor duties in the organization, where she was subsequently officially registered. Therefore, the court of the next instance sided with the employer, since the woman was actually employed during the disputed period.
When they will only pay if agreed upon with the employer
Upon resignation of one's own free will
If the contract is terminated at the request of the employee, then no incentive or compensation payments are provided for by law, that is, severance pay is not provided for voluntary dismissal. But if management wants to reward an employee for long and fruitful work, they will award a bonus on their own initiative; such cases are known.
By agreement of the parties
Typically, dismissal by agreement occurs on an individual basis. The amount of the fee is not established, so payment is made by mutual agreement of the parties. The problem of the amount of payment, how to calculate severance pay upon dismissal by agreement of the parties, is solved within the framework of individual agreements.
But the salary, which was not paid to the employee for the period worked, is issued without fail on the last day of work.
Upon retirement
Labor legislation does not provide for severance pay upon retirement, but in accordance with Part 4 of Art. 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, similar bonuses are allowed to be prescribed in the employment contract or they may be provided for by internal regulations of the organization itself. Such payments are provided at the request of the employer and are not regulated by law. The organization has the right to establish any number of financial assistance measures without restrictions. This type of help is, rather, gratitude for the work.
Part-timers
If a part-time worker is laid off, the average salary for the second and third months is not paid. The fact is that such an employee is already employed, whereas in order to receive payments it is necessary to confirm the lack of work, and this person has it (Parts 2, 3 of Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
However, there is an exception. If an employee working part-time does not have a main place of work at the time of layoff. In this case, the payments provided for in Parts 1 - 3, 5 of Art. 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, are carried out according to general rules. In order to receive payments, a person needs to confirm that they are not currently working.
The position is confirmed by judicial practice. For example, the Appeal ruling of the Krasnoyarsk Regional Court dated January 11, 2017 in case No. 33-270/2017.
The woman worked as a leading accountant and part-time as an accountant for paid services. The position she held part-time was reduced, and she resigned from her main position of her own free will. After her dismissal, she turned to management for payment of her average monthly salary for the period of employment. The employer refused, citing the fact that she was dismissed from her main position at her own request, and part-time workers were not entitled to such a payment. The woman went to court, which ruled in her favor. The woman did not have a main place of work, registered with the employment center and submitted all the necessary documents to the employer. The refusal to pay was declared unlawful.
Who will be paid for 14 days
A dismissal payment in the amount of two weeks' average earnings is due in the following cases:
- Upon termination of an employment contract for medical reasons. If an employee is recognized as completely disabled or for any reason does not want to transfer to a new workplace, then he is entitled to severance pay upon dismissal for health reasons, two weeks’ pay and wages for the time actually worked. It is important to note that if an employee quits due to health reasons, but at his own request, then compensation is not paid.
- The legislator established severance pay upon dismissal from the army, which is compensation in the amount of two weeks' earnings and is paid upon conscription into the army or assignment to an alternative service replacing it.
- In case of dismissal upon reinstatement of the employee in service by a court decision.
- If an employee refuses to take a position when the company moves to another city or region.
- If you disagree with changes to the terms of the employment contract in the manner prescribed by Art. 74 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Pensioners
The dismissal of pensioners occurs according to general rules, however, in matters of payment of average monthly earnings for the third month of unemployment, judicial practice is ambiguous.
On the one hand, in Art. 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that such payment is made in exceptional cases. But such employees also receive a pension, and therefore significant circumstances are needed that can be considered exceptional within the meaning of the provisions of Part 2 of Art. 178 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This position was adhered to by the courts in the Appeal ruling of the Moscow Regional Court dated 08/15/2016 in case No. 33-22262/2016 and in the Appeal ruling of the Moscow Regional Court dated 10/03/2016 in case No. 33-27023/2016.
But there is also other judicial practice. For example, the Appeal ruling of the Moscow City Court dated December 16, 2020 in case No. 33-417144/2020, 2-3691/2020. An employee of retirement age was fired due to layoffs, after which she contacted the employment service. There were no suitable vacancies for her, and she was unable to get a job. Therefore, the employment center issued the woman a decision to maintain her average earnings for three months from the date of dismissal. The employer did not agree with this and went to court, but his demands were not satisfied. The court noted that the provisions of Part 2 of Art. 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation equally apply to people who have reached retirement age and receive payments, since they, like others, can contact the employment service for assistance in finding employment. A similar opinion is expressed in the Letter of Rostrud dated December 28, 2005 No. 2191-6-2.
In order to avoid labor disputes, we recommend maintaining the average monthly salary for such employees.
Payments to union members
Employees who were elected to the trade union and released from their main job are paid the average salary not by the organization, but by the all-Russian (interregional) trade union in the following order.
Their average earnings for the period of employment, but not more than six months, are retained upon dismissal due to:
- the inability to provide the previous or other equivalent job (position) at the end of the employee’s term of office in the trade union;
- liquidation of the organization.
If an employee undergoes retraining or training, then his average salary can be retained for up to a year after dismissal.
Such rules are established by Article 375 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Calculation
The fact is that the average amount of earnings per day is calculated for the day on which the employee worked, and not for the one indicated in the calendar . To correctly calculate the benefit amount, you need to take the wages received 12 months before the employee was fired.
In this case, you do not need to take into account vacations and sick leave. Next, you need to divide the resulting value by the working day in the above-mentioned periods, which are marked in the production calendar.
Weekends and vacation pay are not taken into account because during these periods the employee did not fulfill his work duties.
Is severance pay taxable due to a reduction in headcount or workforce? If we are talking about a tax such as personal income tax, then all of the above payments are not subject to taxation of this type.
The only exceptions to this are the salary that is paid for the month of dismissal and compensation for vacation that the dismissed employee did not use. This is regulated by Articles 208, 210 and 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
How long?
- If the dismissal of employees occurred due to staff reduction or liquidation of the enterprise (Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), then the employer is obligated to make compensation payments to them over the next 2 months.
- If after dismissal a citizen registers with the employment center no later than 14 days, then he has the right to receive money for the third month. This is possible if he has not been able to find a job up to this point.
How to get it after being fired for the 3rd month?
Reference! Not all people who have been laid off at an enterprise have the opportunity to receive monetary compensation for the third month after losing their job.
The main difference between payments for this period is that the decision to issue funds is made by the employment center.
In order to subsequently receive the right to financial support for three months, an employee must:
- obtain a work book in which to check the presence of a record of dismissal on the basis of clause 2, part 1 of Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- within two weeks from the date of dismissal, contact the employment center with a package of necessary documents for registration;
- attend events assigned by an employment center employee.
If a citizen was registered with the employment service for 3 months, but was never employed, then the citizen is issued a certificate stating that he is listed as unemployed, which gives him the right to receive cash payments from the employer for the third month.
Categories of employees and maximum allowable amount of payments
Today, among people who work every day for their own benefit or the benefit of the state, there are certain categories for whom other rules for the payment of severance pay upon dismissal have been invented. For example, a civil servant is legally paid his average salary for the last three months of his work .
This happens if the organization in which he served is going through bankruptcy or is simply downsizing. And at the same time, the amount of such payment is calculated without taking into account the severance pay itself .
In addition to all this, if a civil servant has not found a position that would suit him in terms of the level of qualifications and profession that he has, then by law he will be in a special reserve, which is present in the register of civil servants.
The length of service of such citizens will last for one year after dismissal..
A collective-type employment contract in such a situation can make the legal position of such a person even sweeter.
The fact is that the law establishes only the minimum amount of severance pay, and its maximum amount is determined by the above-mentioned collective agreement. This figure could be anything. Is income tax withheld from severance pay upon redundancy?
An interesting point is that the above-mentioned severance pay, which is paid in the amount of three months' earnings, according to the law, should not be subject to income tax .
It can only be accrued if the total payment amount exceeds the assigned one. In the event of a layoff, only the money that was paid from above is subject to tax on severance pay.
For workers who work in unfavorable climatic conditions, according to the law, the total amount of benefits that is not taxed is doubled. It is equal to six monthly earnings of such an employee.
How to calculate the amount of payments, with formula and examples
An employee who loses his job due to layoffs at the company is entitled to severance pay. Its size is equal to the average monthly earnings, and payments are calculated on the basis of Part 3 of Art. 139 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 24, 2007 No. 922.
Average monthly earnings are calculated using the formula:
the amount of accrued salary for days worked in the billing period ÷ the number of days actually worked.
Cash payments to a laid-off employee for the period of searching for a new job are calculated from the date following the last return to work. For the 1st month he receives severance pay, therefore, financial assistance for the 2nd month of the employment period is carried out with offset of previously received benefits (Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
For example, engineer Topolev S.A. was dismissed from the company due to staff reduction on December 2, 2022. The engineer worked on a 40-hour work week with a salary of 30,000 rubles. The estimated period will be from 12/01/2016 to 11/30/2017. To calculate the average monthly salary, only actual earnings are taken into account without taking into account temporary disability benefits and vacation pay. In the billing period from December 1, 2016 to November 30, 2017, the employee worked 219 working days, including vacation and sick leave.
Average earnings per day = 30,000 × 12 (amount of earnings) / 219 work. days=1,643.8 rub.
Severance pay for layoffs is paid for the period from December 3, 2017 to January 2, 2018, which includes 20 working days.
Amount of severance pay = 1643.8 × 20 = 32,876 rubles.
Within 2 months after the layoff, Topolev S.A. did not find a new job, and therefore has the right to receive cash assistance in the amount of average earnings for the period from December 3, 2017. until 02.02. 2022, in which there are 39 working days.
The amount of average earnings should be 1643.8×39=64,108.2 rubles. But, since the employee has already been paid severance pay upon layoff, it is taken into account, and the payment will be equal to 31,232.2 rubles. (64,108.2 – 32,876).
If engineer Topolev S.A. contacted the employment center in a timely manner, then if he fails to find a new job, he will be able to apply for average earnings for the third month after layoff from 02/03/2018 to 03/02/2018. For 19 working days, the payment will be 31232.2 (1643.8×19) rubles.
The main mistakes when calculating severance pay to an employee laid off from work
The process of laying off employees entails large costs for the employer, so most organizations that dismiss their subordinates from service due to a reduction in the number of staff try by hook or by crook to avoid unnecessary expenses. Most often, they insist that the employee write a letter of resignation of his own free will or offer a transfer to another position. However, this cannot be done. The current legislation clearly defines the sequence of the staff reduction procedure, as well as information regarding all payments and their taxation. Therefore, every employer is obliged to adhere to the correct dismissal “scheme” in order to avoid problems with the law.