Termination of a relationship is not always painful and sad; sometimes it is natural and fully meets the interests of both parties, especially when it comes to the “employee-employer” relationship. Termination of the contract is provided for and strictly regulated in the legislation of the Russian Federation, and the list of reasons for this is exhaustive. This means that new clauses cannot be added to it, even if they are justified by other regulations.
Question: In what order and on what grounds can the general director and employees be fired if an organization has learned of its upcoming exclusion from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities by the tax inspectorate due to unreliable information? View answer
However, compared to the “old spill” versions of the Labor Code, there are significantly more grounds for dismissal, which is a definite plus for the employer and expands the scope of action for employees. Today there are 18 of them in the Labor Code. The main thing is that these grounds are used lawfully, which is especially important if you need to get rid of an employee who does not want such an outcome.
On what grounds can an employee be dismissed at the initiative of the employer ?
Let's consider all the grounds for dismissal of employees provided for by the modern Labor Code of the Russian Federation, with special emphasis on the initiative of the employer.
Whose will is determining
Whether the grounds for dismissal belong to one of the following groups depends on which party expresses a desire to end the relationship.
- Employee initiative.
- Employer's desire.
- The reason does not depend on either party.
- The parties came to an agreement.
ATTENTION! A separate point can highlight the reasons for dismissal related to significant changes in the terms of the employment contract and, accordingly, the employee’s refusal to accept them: on the one hand, the employee of his own free will does not want to put up with inevitable changes, on the other hand, without the employer’s will to change, the employee would not have to refuse.
When the employment relationship ends
Possible reasons for dismissal from work are established by law. In particular, they are the following reasons:
- An agreement (agreement) between the subjects of legal relations.
- Expiration of the agreement.
- Termination of the agreement on the initiative of the employer.
- Transfer of an employee with his consent to another employer.
- Refusal of an employee to work due to a change in ownership of property, in connection with reorganization procedures in the company.
- An employee’s refusal to work due to changes that are not specified in the contract.
- Refusal of an employee to be transferred to another type of work due to his state of health, confirmed by the conclusion of specialists.
- Refusal of an employee to be transferred to another region.
- Circumstances that occurred due to force majeure.
- Violation of the provisions of the Labor Code if they exclude the possibility of continuing work activity.
Rights of a dismissed employee
An employee dismissed on the basis of any article of the Labor Code has the right to:
- payment of wages in full on the day of dismissal;
- compensation for vacation days that were not used by him;
- payment for sick leave (if any);
- receiving a work book with the corresponding entry.
What are the special grounds for dismissing a foreign employee ?
Additional payments, severance pay and compensation provided for certain reasons for dismissal, in each case have their own legislative justification (we do not consider this issue here).
Payments and compensations
Regardless of who initiated the termination of the working relationship, the following payments must be made to the employee on the last working day:
- wages for days worked;
- compensation for unused vacation;
- bonuses and payments provided for by the collective agreement or other internal documents of the company.
It is worth noting that in some cases the employer is legally required to pay a dismissed employee severance pay. Thus, in the event of a layoff, the dismissed person retains his salary for the period of employment up to three months after the layoff (Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). He is also entitled to severance pay, the amount of which, as a general rule, is the average monthly salary (Part 4 of Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). But there are exceptions:
- the amount of compensation may be greater if this is provided for in the collective labor agreement;
- seasonal workers receive two-week earnings (Part 3 of Article 296 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- employees under a fixed-term contract concluded for a period of up to 2 months do not receive benefits (Part 3 of Article 292 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- Individual entrepreneurs and religious organizations independently determine the amount of benefits (part 2 of article 307 and part 2 of article 347 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition to payments, on the last day of work, the dismissed person must receive his work book and other documents related to work (orders, certificates, etc.). If he cannot come for them in person, all documentation can be sent to him by mail with the written consent of the former employee.
Sample resignation letter
Sample letter of dismissal for absenteeism
The employee's desire is the law
Art. 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is the simplest and most “grounded” of all reasons to terminate cooperation. It does not require any explanation or additional conditions: no one can force another person to work if he does not want to. To resign from a position at your own request, it is sufficient to express this desire in writing 14 days before the date of departure. In some cases, this period may be reduced or even not required at all:
- upon dismissal from the probationary period;
- during sick leave;
- from maternity leave;
- by agreement with the employer.
If, before the expiration of 14 days, the employee changes his decision and wants to remain in his position, he has the right to withdraw his application or write a new one, canceling the first one.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! The employer's consent is not required for voluntary dismissal; a written notice (application) is sufficient. If the manager refuses to accept it, the law provides for the employee the opportunity to send an application by mail with automatic termination of work after the legal two weeks.
Grounds for dismissal of an employee at the employee’s initiative
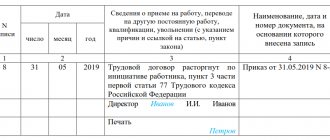
According to clause 3, part 1, art. 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee can resign at his own request, and the procedure for terminating the contract in this case is described in Art. 80 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The following circumstances may be the reason:
- intention to get a job in another company;
- moving;
- disagreement with changes in working conditions;
- illness that prevents further performance of official duties;
- retirement;
- other circumstances.
The resignation letter must indicate the following:
- name of the organization, full name the leader and his position (who is addressed);
- FULL NAME. and the position of the applicant;
- document's name;
- request to terminate the contract on the basis of Art. 80 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- date of dismissal;
- signature with transcript and date.
The employee is not required to report on the reasons for his departure, however, Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the only rule that he must follow - to notify the employer of his decision two weeks in advance. This period begins the day after the employer receives the resignation letter, which may be:
- delivered to the manager personally;
- sent by registered mail with notification;
- sent by email, if the letter is certified by the employee’s electronic signature;
- sent by telegram certified by the operator, who must verify the identity of the sender.
In some cases, the two-week period of “working off” can be reduced: for example, if the parties were able to agree on early termination of the contract, if the employee is engaged in seasonal work or is on a probationary period. In this case, you need to notify management three days in advance (Articles 71 and 79 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The legislator also provided for an increased notice period for the employer for a certain category of employees. For example, if the general director decides to leave his post, then he must notify the highest management body of the organization of his intention one month in advance.
Agreement between the parties upon dismissal of an employee
Agreement of the parties (Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) is the basis for dismissal, which also has the fewest pitfalls. If both parties have agreed to terminate cooperation, this means that there is no mutual dissatisfaction between them that could become a reason to challenge the dismissal.
This basis comes into effect when the employee’s decision to leave his position must necessarily be supported by the employer’s consent. This situation may arise if the resigning employee, for example, is working under a fixed-term employment contract, the term of which has not yet expired.
The same reason may include the transfer of an employee to another employer by mutual consent.
Since the “leitmotif” of separation is the general decision of the parties, they also agree on all related issues, in particular, on the date of termination of cooperation.
"Nothing personal"
Some of the reasons for which an employee may be dismissed from his position do not depend in any way on himself or on the employer. These include the following situations.
- The employee is called up to join the armed forces or to alternative service replacing the army.
- If by decision of a court or labor inspectorate an employee who previously occupied it and was unfairly dismissed is reinstated to a position, then the employee currently working is naturally dismissed unconditionally.
- A court verdict has entered into force, prohibiting or excluding the possibility of holding the previous position.
- If the position is to be filled by election, but the employee was not elected.
- Medical justification (total permanent disability, confirmed by an appropriate conclusion).
- Extraordinary circumstances recognized as such by a decision of the Government of the Russian Federation or a regional government body (martial law, disasters, natural disasters, social upheavals, serious accidents, epidemics, etc.).
- Death of the employee or employer (of course, we can only talk about an individual). The recognition of any of these persons as missing or dead by court is also equivalent to this.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION! Reasons for dismissal that do not depend on the will of the parties come into force if it is impossible to transfer the employee to another position or he does not agree to this.
Loss of trust
This is one of the most common reasons for dismissing employees who serve cash or commodity assets - cashiers, storekeepers or salespeople. The reason is that such an employee committed an act because of which his superiors doubted his cleanliness and honesty. Such offenses include failure to comply with the rules for working with cash registers or shortages.
Situation: the employee was accused of a shortage, no check was carried out, they demanded that she write a letter of resignation of her own free will, otherwise they promised to expel her under the article. She asked our experts: “Can I be fired under an article without my knowledge for a deficiency if guilt has not been proven?” The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not give such powers to her superiors: first, it is necessary to conduct an internal investigation, demand written explanations from the employee, and only on the basis of this information make a decision whether the employee is guilty or not. If the procedure is not followed, the employee has the right to challenge the decision to dismiss in court. Read more: how to file a dismissal due to loss of trust.
Involuntary dismissal
Here we analyze the reasons for dismissal, which are associated with the employee’s reluctance to accept the changed working conditions. In this case, we are not talking about the employee’s desire to leave his position; he is forced to do so by circumstances that he has no power to change. These could be:
- offer of vacant positions due to changes in health status (offers may be unacceptable for the employee, although legal from the point of view of the Labor Code - Parts 3 and 4 of Article 73);
- significant changes in the terms of the employment contract without the employee’s consent (Part 4 of Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- reluctance to change the location of work if the employer moves to another location;
- refusal to work under another employer, i.e. when there is a change of owner or jurisdiction of the organization (Article 75 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
IMPORTANT INFORMATION! The agreement or refusal of an ordinary employee in the last point is a key point, since for directors, their deputies and the chief accountant it can become an unconditional reason to leave their position at the initiative of the new employer. All other categories of employees during a change of ownership or reorganization do not have the right to be dismissed on this basis, unless they refuse to continue working.
Dismissal for violation of labor discipline
If the manager decides to dismiss an employee at the initiative of the employer due to his guilty actions, this must be done in the following order:
- Receive documented information (act, memo) about the employee’s misconduct.
- Appoint a commission of inquiry.
- Take a written explanation from the offending employee (Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- If the culprit refuses to explain, draw up a report about this.
- Draw up a report with the commission’s conclusions about what happened and the measures to be taken against the offender.
- Dismiss the employee, but only on the condition that he has already had disciplinary sanctions before. You cannot be fired for the first violation, with the exception of gross violations.
- Next, you need to issue an order and pay the dismissed person on the last working day. It is possible to withhold something from the salary if such an employee was a financially responsible person and an appropriate agreement was concluded with him, as well as in the event of direct effective damage and other cases.
All necessary documents should also be handed over on the last working day. This condition is absolutely mandatory for all situations involving termination of employment.
If the employee does not want to resign
The most “slippery” group of reasons for dismissal (Articles 71 and 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) is termination of contracts at the initiative of the employer. Most often, the employer’s wishes contradict the wishes of the employee himself, otherwise the dismissal would fall into another group - at his own request or by agreement of the parties. In cases where an employee not only leaves, but has to be fired, you need to be especially attentive to all the nuances of registration and legislative support for dismissal, because a dissatisfied employee will look for reasons to appeal, and if his claim is granted in court, the employer will face serious problems.
It is possible to get rid of an unwanted employee if his guilty actions are proven, and, in some cases, if there were no such actions. In each situation, the law regulates its grounds and procedure for dismissal.
We fire the culprit
The law provides a closed list of grounds for such dismissal. If there was an initiative by the employer, but the documents indicate a reason not included in this list, the dismissal will be considered illegal with all the ensuing consequences. What actions of an employee are considered guilty, giving legal grounds for his dismissal from his position?
- Failure to fulfill the duties specified in the employment contract in the presence of a disciplinary sanction . The presence of such a penalty indicates that violations were committed repeatedly. Clause 5 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that this basis can only be applied within a year after the imposition of a disciplinary sanction (only in this case will the repeated offense be proven). Dismissal will be made for repeated failure to fulfill job duties.
- Gross violation of duties, committed even once. Such serious violations include:
- absenteeism;
- disclosure of secrets protected by law;
- theft, embezzlement, damage to property at the place of work, proven in court;
- violation of labor protection requirements with serious consequences (accident, accident due to the fault of the employee or their threat);
- being at work “under the influence” or in a narcotic trance.
- Documentary lies when concluding an employment contract (providing falsified documents or fraudulent information).
For certain categories of workers, the list of culpable actions is further expanded:
- an employee with educational functions committed an immoral act;
- the head of an organization or branch or the chief accountant made an incorrect decision due to which the organization suffered damage;
- a financially responsible employee did something that caused management to lose confidence in him.
Not guilty, but can't work
An employer can part with an employee when the latter no longer suits him for objective reasons. It is possible that the dismissal occurs not due to the personal qualities of the employee, but due to the circumstances that forced the employer to choose him as the person to be dismissed. The absence of the employee’s fault in the presence of the employer’s initiative can provoke dismissals in the following cases.
- The number or staff of the enterprise is being reduced (clause 2 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The employer needs to be careful that an employee from a socially protected category is not laid off during periods prohibited for this, as well as having priority, other things being equal, selection. For such dismissal to be valid, the person being released must receive 60 days' notice.
- Liquidation of a company or termination of the activities of an individual entrepreneur (clause 1 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). There will be no disagreement here - absolutely everyone is fired on this matter, including those in preferential categories, as well as people on sick leave and vacations.
- The employee ceased to correspond to the position or his work (clause 3 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). When it comes to non-compliance due to health conditions, the medical report plays the “first role”. But when the problem is the employee’s lack of qualifications, it must be proven. To do this, the employer must conduct a certification, based on the results of which such a decision can be made. Certification must be legal, that is, enshrined in the internal acts of the company, carried out by a special commission and applied not only to the employee about whom doubts have arisen, but also to all employees of this category. It cannot be sudden; according to the situation, it must be regular. If, according to the conclusion of the certification commission, the employee’s qualification level does not correspond to his position, he may be fired, despite all his reluctance.
- The employee did not complete the probationary period . This is the same discrepancy with the position held, only confirmed in a simpler way. In order to ensure that dismissal during the probationary period is not contested, care must be taken to ensure that cases are confirmed that the subject failed to cope with his duties. In practice, no one prohibits an employee who does not want to have a notice of dismissal in his work book as having failed the test, from resigning of his own free will or by agreement of the parties.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! If an entrepreneur wants to part with an employee whose employment contract is expiring, he does not need to look for any reasons for this - it is enough to announce the termination of the contract due to the expiration of the term. If you ignore the end of a fixed-term contract and do nothing, the relationship will automatically be considered extended on an indefinite basis.
Failed test
A probationary period is a period during which the parties evaluate each other. During this time, both the employee and the company administration have the opportunity to terminate the relationship much faster than usual. This is one of those cases when the answer to the question whether the director can dismiss an employee without his consent is affirmative: it is enough to send written notice to the subject before the end of the test, no later than three days before the expected termination of the relationship.
The notice explains the reasons for this decision. A dismissed citizen has the right to appeal it in court.
Advice for employers regarding problematic dismissals
If an employee does not want to leave his job, and the employer no longer wants to cooperate with him, all the legal nuances and subtleties of such dismissal must be observed. In the process, problematic situations may arise related to the employee’s opposition to measures aimed at releasing him from his position. Let's consider how the employer should respond to them more correctly in order to achieve his goal without being at risk of being sued for illegal dismissal.
- Opposition to foreclosure . Disciplinary action is a prerequisite for dismissal for an employee’s guilty act committed repeatedly. However, it cannot be imposed without an explanation provided by the employee regarding his behavior. What to do if an employee refuses to provide an explanation or delays giving it in order to delay the imposition of a penalty, since it can only be applied within a month after the offense? In this case, the most reliable thing for the employer will be to create a special commission, the purpose of which will be to identify the cause and degree of guilt of the employee. Based on the results of the protocol, a report on the guilt (or innocence) of the employee is drawn up, and he is invited to participate in the meeting. If he refuses to sign an act establishing his guilt, then the commission members, consisting of 3 people, will attest in writing to this refusal, which is sufficient evidence for the court. The same procedure must be followed if the employee does not sign the notice of dismissal order.
- The employee refuses to receive the required funds upon dismissal . By law, all necessary compensation and wages must be given to the employee on the day of dismissal. If this is not done, it may be considered illegal. If an employee refuses to receive funds without signing the appropriate statement, the employer has the right to deposit them into his account and notify him of this by registered mail, or send them by postal order. Documents confirming the transfer of funds are recognized by the court.
- The employee does not pick up the work book . You need to send him an invitation by mail with a notification to come and receive your document. This will remove the risk of accusations that the book is not given to the employee.
- The employee took sick leave before being fired. A person on sick leave cannot be fired. Even if the dismissal order was issued before the notice was opened, the dismissed person can claim in court that at the time of dismissal he was on sick leave, which will actually be true. In such a difficult case, the employer can act according to one of the following schemes:
- if the employee filed such a claim, you can file a counterclaim claiming the illegality of the sick leave (if it was issued with violations, the court will declare it invalid, and the basis for the employee’s claim will automatically disappear);
- you can make changes to the dismissal order by writing the date following the end of the sick leave specified in the document provided by the employee (this requires an additional order to make changes and, of course, recalculation of severance payments);
- You can replace the basis for dismissal in the order if the employment contract stipulates the need to promptly inform the employer about your absence due to illness (then unexpectedly appearing sick leave becomes a violation of labor discipline).
With these measures, the employer minimizes the risks associated with a problematic dismissal if it is not possible to reach a reasonable compromise, which is still the best option.
For absenteeism and alcohol - clause 6 of Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Violations of discipline can be serious. For one rude thing you can be fired immediately. This is also a disciplinary sanction. But there is no need to save the previous ones.
All gross violations are recorded in paragraph 6 of Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. These include absenteeism and alcohol or drug intoxication at work.
A gross violation is documented in the same way as a simple violation. A memo or act, explanation, order of dismissal no later than a month from discovery.
Absenteeism
Absenteeism is when a person does not come to work or is absent for four hours in a row.
There is no good reason for absenteeism: illness, accident, death of a relative. Time off and vacations without the request of the manager are also considered absenteeism. This is explained in paragraph 39 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2.
Example of absenteeism:
A specialist at a bank on the eve of a working day at 11:30 pm asked the director for a day off via a WhatsApp message. Silence was considered consent. When she returned to work, she was given absenteeism and fired.
The specialist appealed the absenteeism, but the court did not return the job.
The time off was not approved, which means it’s absenteeism. There is an absence from work report and a memo from the director, an explanation, an order. We met the deadlines. Dismissal for absenteeism is fair and documented correctly - case 33-12011/2019.
Intoxication
Alcohol and drug intoxication must be proven.
The act with witnesses is suitable. The court believed the witnesses that the store clerk was drunk behind the counter - case No. 33-5383/10.
The stronger option is a breathalyzer or a doctor’s report. For example, a breathalyzer helped in a dispute about the dismissal of a trolleybus driver - case No. 2-3639/2018. There is a possibility - take a test or call a doctor.