What is a current account
The predominant part of settlements between legal entities is carried out in a non-cash format - by transferring funds from the account of one counterparty to the account of its transaction partner.
The intermediary function in such transfers is performed by the bank. And in order for non-cash money transfers to become possible, the company needs to open a current account with a bank. The bank client can use this account both for storing available funds and for conducting settlement transactions, as well as withdrawing cash from it (in cases established by law).
IMPORTANT! Currently, there are no legal provisions requiring individual entrepreneurs to have a current account. Only enterprises have such an obligation. However, entrepreneurs who do not have a current account may, in practice, encounter problems when concluding agreements with partners.
The bank assigns a specific number to each current account, and each client a personal account to record cash flow. Non-cash payments within a current account are carried out by the bank strictly with the consent of the client - the owner of this account. And only in some cases can money be written off forcibly.
When opening a current account for an individual entrepreneur or legal entity, the bank transmits information to the Federal Tax Service. An organization can receive a certificate from the Federal Tax Service about open current accounts. Find out how to do this in ConsultantPlus. Get trial access to the system and go to the Ready-made solution. It's free.
To learn how and when a bank can dispose of a client’s money without his consent, read the article “Direct debit is...”.
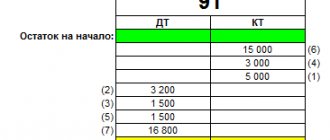
The general scheme of cash flow in the current account is as follows:
Synthetic accounting of business operations carried out using a current account in accounting is kept on account 51 “Current account” (Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n). This account is classified as active: its debit reflects the balance of the business entity’s free funds, as well as any cash receipts, and the credit records all write-offs.
Legal regulation of transactions on current accounts
The procedure for transactions on the current accounts of organizations is regulated by current legislation, rules, instructions and regulations of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation (Fig.1).
Finished works on a similar topic
Course work Accounting for transactions on current accounts 490 ₽ Abstract Accounting for transactions on current accounts 280 ₽ Test paper Accounting for transactions on current accounts 200 ₽
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
Figure 1. Regulatory documents governing the accounting of transactions on current accounts
In addition to the above documents, there is a wide list of other legislative acts directly or indirectly regulating transactions on the current accounts of enterprises.
Basic transactions for the current account
We have grouped the most popular transactions for account 51 in the table.
| Situation | Debit | Credit |
| Receipts to the current account | ||
| Payment received from buyer | 51 | 62 (sub-account “Payment”) |
| Advance received from buyer | 51 | 62 (sub-account “Advances”) |
| Refund of prepayment by supplier | 51 | 60 (sub-account “Advances”) |
| Claim paid by supplier | 51 | 76 (sub-account “Claims”) |
| Received funds from other persons | 51 | 76 (corresponding subaccount) |
| Dividends received | 51 | 76 (sub-account “Dividends”) |
| Refund of tax, contribution | 51 | 68, 69 |
| Contribution to the authorized capital received | 51 | 75 |
| Cash deposited into account | 51 | 50 |
| Received money on account (through transfers on the way) | 51 | 57 |
| Received money from another bank account | 51 (sub-account of the recipient's bank) | 51 (sub-account of the sender's bank) |
| Interest accrued on account | 51 | 91 |
| Receipt of credit, loan | 51 | 66, 67 |
| Budget funding received | 51 | 86 |
| Debits from current account | ||
| Payment made to supplier | 60 (sub-account “Payment”) | 51 |
| Advance paid to supplier | 60 (sub-account “Advances”) | 51 |
| The advance was returned to the buyer | 62 (sub-account “Advances”) | 51 |
| Paid upon claim to buyer | 76 (sub-account “Claims”) | 51 |
| Cash received from the account to the cash desk | 50 | 51 |
| Write-offs (withdrawals) of money through transfers while in transit | 57 | 51 |
| Money transferred to another account | 51 (sub-account of the recipient's bank) | 51 (sub-account of the sender's bank) |
| Paid by cash account to other persons | 76 (corresponding subaccount) | 51 |
| Taxes and fees paid | 68, 69 | 51 |
| Written off as payment for banking services | 91 | 51 |
| Salary transferred | 70 | 51 |
| Accountable funds paid | 71 | 51 |
| Dividends paid | 75 | 51 |
| Loan issued to employees | 73 | 51 |
| Settlements have been made with the customs service | 76 (corresponding subaccount) | 51 |
| Repayment of a loan | 66, 67 | 51 |
ConsultantPlus experts told us how to withdraw cash from a bank. Get free demo access to K+ and go to the Ready Solution to find out all the details of this procedure.
Accounting for transactions on bank accounts
Transactions on current accounts are regulated by the following documents: Civil Code, Central Bank Regulation 03.10.02 “On non-cash payments in the Russian Federation”, Chart of Accounts, other documents.
In accordance with the Civil Code, a bank account is a bank account opened for a legal entity or individual in a bank on the basis of a bank account agreement providing for settlement transactions related to the implementation of business activities for a legal entity, and not related to the implementation of business activities for an individual.
A legal entity (enterprise) enters into an agreement with a bank, under which the bank undertakes to accept and credit funds received to the account opened for the client (account owner), carry out the client’s orders to transfer and withdraw the corresponding amounts from the account and carry out other operations on the account.
To open a current account, you must submit the following documents to the bank:
1) application for opening an account (the application form can be obtained directly from the bank);
2) notarized copies of constituent documents and certificate of state registration of the organization;
3) a certificate of registration of the organization with the tax office;
4) a notarized card with sample signatures of the manager (first signature), chief accountant (second signature) and the organization’s seal;
5) a copy of the certificate of assignment of statistical codes to the organization.
You can open as many current accounts as necessary for the operation of the organization. The number of current accounts is not limited by law. The fact that the organization has opened a bank account must be reported to the tax office within 10 days (Article 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If this requirement is not met, the organization may be fined
Two types of transactions can be carried out through a current account: debiting money; crediting money.
The bank debits money from your current account according to your order. Such an order is issued by payment order. Without your consent, the bank can write off money only in exceptional cases, for example, by a court decision, at the request of the tax inspectorate to pay tax arrears and penalties accrued as a result of an audit.
The procedure for writing off funds from a current account:
1. If there are funds on the account, the amount of which is sufficient to satisfy all the requirements presented to the account, these funds are written off from the account in the order in which the client’s orders and other documents for write-off are received (calendar priority), unless otherwise provided by law.
2. If there are insufficient funds in the account to satisfy all demands placed on it, funds are written off in the following order:
- first of all, write-offs are carried out according to executive documents providing for the transfer or issuance of funds from the account to satisfy claims for compensation for harm caused to life and health, as well as claims for the collection of alimony;
- secondly, write-offs are made according to executive documents providing for the transfer or issuance of funds for settlements for the payment of severance pay and wages with persons working under an employment contract, including under a contract, for the payment of remuneration under an author's agreement;
- in the third place, write-offs are made on payment documents providing for the transfer or issuance of funds for settlements of wages with persons working under an employment agreement (contract), as well as on contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation and mandatory funds health insurance;
- in the fourth place, write-offs are made on payment documents providing for payments to the budget and extra-budgetary funds, deductions to which are not provided for in the third place;
- fifthly, write-offs are made according to executive documents providing for the satisfaction of other monetary claims;
— in the sixth place, write-offs are made for other payment documents in calendar order.
Debiting funds from the account for claims related to one queue is carried out in the calendar order of receipt of documents.
The primary documents for transactions on the current account are:
1. Payment order (form N 0401060). Based on this document, the bank (where the organization’s current account is located) will write off the organization’s funds and send them in the necessary directions:
— payment for goods (work, services);
— transfer of taxes to the budget;
— transferring them to the account of another organization;
- other payment.
2. Payment request (form N 0401061). Based on the payment request, the buyer's (customer's) bank will write off funds from his current account and credit them to your current account.
The debiting of funds from the payer's (buyer's) account upon payment request can be made: with acceptance (that is, with his consent); without acceptance (that is, without his consent).
3. Cash check. To withdraw cash from your current account, you must obtain a book of cash receipts (checkbook) from the bank that services your organization.
A cash check consists of two parts: a tear-off sheet and a check counterfoil.
The tear-off sheet indicates the purpose of receiving funds, the amount that is withdrawn from the current account, as well as the passport details of the person receiving the money.
Funds received from a check must be spent only for the purposes specified on it. The tear-off sheet of the cash receipt is handed over to the bank employee, who issues cash. The counterfoil remains in the checkbook and must be kept by the organization for 5 years.
The check is valid for 10 days from the date of its issue. If this period has expired, the bank will not accept the check.
Cash received by check must be posted to the organization's cash desk. To do this, you must issue a cash receipt order.
4. Announcement for cash contribution (form N 0402001) . The form consists of three detachable parts: the actual announcement for a cash contribution, a receipt and an order.
The announcement for a cash contribution must be filled out in one copy. Simultaneously with the announcement, an expense cash order must be issued, since cash is withdrawn from the organization’s cash register.
Transactions on current accounts are regulated by the following documents: Civil Code, Central Bank Regulation 03.10.02 “On non-cash payments in the Russian Federation”, Chart of Accounts, other documents.
In accordance with the Civil Code, a bank account is a bank account opened for a legal entity or individual in a bank on the basis of a bank account agreement providing for settlement transactions related to the implementation of business activities for a legal entity, and not related to the implementation of business activities for an individual.
A legal entity (enterprise) enters into an agreement with a bank, under which the bank undertakes to accept and credit funds received to the account opened for the client (account owner), carry out the client’s orders to transfer and withdraw the corresponding amounts from the account and carry out other operations on the account.
To open a current account, you must submit the following documents to the bank:
1) application for opening an account (the application form can be obtained directly from the bank);
2) notarized copies of constituent documents and certificate of state registration of the organization;
3) a certificate of registration of the organization with the tax office;
4) a notarized card with sample signatures of the manager (first signature), chief accountant (second signature) and the organization’s seal;
5) a copy of the certificate of assignment of statistical codes to the organization.
You can open as many current accounts as necessary for the operation of the organization. The number of current accounts is not limited by law. The fact that the organization has opened a bank account must be reported to the tax office within 10 days (Article 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If this requirement is not met, the organization may be fined
Two types of transactions can be carried out through a current account: debiting money; crediting money.
The bank debits money from your current account according to your order. Such an order is issued by payment order. Without your consent, the bank can write off money only in exceptional cases, for example, by a court decision, at the request of the tax inspectorate to pay tax arrears and penalties accrued as a result of an audit.
The procedure for writing off funds from a current account:
1. If there are funds on the account, the amount of which is sufficient to satisfy all the requirements presented to the account, these funds are written off from the account in the order in which the client’s orders and other documents for write-off are received (calendar priority), unless otherwise provided by law.
2. If there are insufficient funds in the account to satisfy all demands placed on it, funds are written off in the following order:
- first of all, write-offs are carried out according to executive documents providing for the transfer or issuance of funds from the account to satisfy claims for compensation for harm caused to life and health, as well as claims for the collection of alimony;
- secondly, write-offs are made according to executive documents providing for the transfer or issuance of funds for settlements for the payment of severance pay and wages with persons working under an employment contract, including under a contract, for the payment of remuneration under an author's agreement;
- in the third place, write-offs are made on payment documents providing for the transfer or issuance of funds for settlements of wages with persons working under an employment agreement (contract), as well as on contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation and mandatory funds health insurance;
- in the fourth place, write-offs are made on payment documents providing for payments to the budget and extra-budgetary funds, deductions to which are not provided for in the third place;
- fifthly, write-offs are made according to executive documents providing for the satisfaction of other monetary claims;
— in the sixth place, write-offs are made for other payment documents in calendar order.
Debiting funds from the account for claims related to one queue is carried out in the calendar order of receipt of documents.
The primary documents for transactions on the current account are:
1. Payment order (form N 0401060). Based on this document, the bank (where the organization’s current account is located) will write off the organization’s funds and send them in the necessary directions:
— payment for goods (work, services);
— transfer of taxes to the budget;
— transferring them to the account of another organization;
- other payment.
2. Payment request (form N 0401061). Based on the payment request, the buyer's (customer's) bank will write off funds from his current account and credit them to your current account.
The debiting of funds from the payer's (buyer's) account upon payment request can be made: with acceptance (that is, with his consent); without acceptance (that is, without his consent).
3. Cash check. To withdraw cash from your current account, you must obtain a book of cash receipts (checkbook) from the bank that services your organization.
A cash check consists of two parts: a tear-off sheet and a check counterfoil.
The tear-off sheet indicates the purpose of receiving funds, the amount that is withdrawn from the current account, as well as the passport details of the person receiving the money.
Funds received from a check must be spent only for the purposes specified on it. The tear-off sheet of the cash receipt is handed over to the bank employee, who issues cash. The counterfoil remains in the checkbook and must be kept by the organization for 5 years.
The check is valid for 10 days from the date of its issue. If this period has expired, the bank will not accept the check.
Cash received by check must be posted to the organization's cash desk. To do this, you must issue a cash receipt order.
4. Announcement for cash contribution (form N 0402001) . The form consists of three detachable parts: the actual announcement for a cash contribution, a receipt and an order.
The announcement for a cash contribution must be filled out in one copy. Simultaneously with the announcement, an expense cash order must be issued, since cash is withdrawn from the organization’s cash register.
Current account transactions and primary documents
The bank carries out non-cash transfers on the basis of special forms. These include payment orders and demands.
A payment order is an administrative document of the account owner, obliging the bank to transfer a certain amount of money to the recipient's account opened in this or another bank.
The article “How to fill out a payment order in 2022 - 2022 - sample?” will help you fill out this document correctly.
With the help of payment orders, orders for funds transfers are issued:
- for goods supplied, work performed, services rendered;
- to pay taxes and contributions to the budget and extra-budgetary funds;
- to repay loans and pay interest on them;
- for processing other expense non-cash transactions.
Payments are made in a certain form and must be accepted by the bank regardless of the availability of funds in the current account of the client transferring them.
For information about what the fields of a payment order mean, see the article “How to decrypt a payment order?”
The purpose of the payment request is somewhat different. It is an administrative document not of the payer of funds (as is the case with a payment order), but of the recipient and contains a requirement to transfer a certain amount from the debtor’s account to the creditor’s account. At the same time, settlements with payment requests may require the prior acceptance of the payer, or may be carried out without it.
Read more about this document and its execution in the article “Procedure for filling out a payment request - sample”.
Documentation of transactions on the organization's current accounts
Are you an expert in this subject area?
We offer to become the author of the Directory Working conditions Documentation of transactions on current accounts provides for:
- a bank statement, on the basis of which the accountant makes entries in the journal of business transactions;
- payment orders, on the basis of which the bank carries out an operation to transfer funds;
- payment requests - a settlement document that contains a requirement for the payer to transfer funds to the recipient company;
- collection orders, which, unlike payment requests, are satisfied in an indisputable manner;
- checks, on the basis of which the bank is ordered to issue the specified amount of money to the drawer;
- letter of credit - instructions from the buyer's bank to the supplier's bank to pay the supplier's invoice on the terms specified in the letter of credit statement
- promissory notes and bills of exchange are written promissory notes.
How to open a current account for an individual entrepreneur
To open a current account, an entrepreneur must provide to the bank (clause 4.7 of the Bank of Russia instructions “On opening and closing bank accounts, deposit accounts, deposit accounts” dated May 30, 2014 No. 153-I):
- passport;
- a card signed by the individual entrepreneur, as well as another authorized person (if necessary), for example, an accountant;
- documents confirming the authority of the persons indicated in the card to dispose of funds;
- licenses and patents (if any), if they are directly related to the legal capacity of the entrepreneur to enter into an agreement on the basis of which an account is opened.
Many banks make it possible to do this online. Necessary:
- fill out an application on the credit institution’s website and provide your contact information;
- wait for the operator to call and tell you what documents are needed and how they can be provided. Some banks do not require a mandatory visit to the office; it is enough to arrange a meeting in a public place within the city;
- after the bank verifies the documents, you need to sign an agreement (come to the office of the credit institution or arrange a meeting in another convenient place).
An entrepreneur has no obligation to notify the tax office about opening a current account. The bank will do this within three days (clause 1.1 of Article 86 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Accounting for current account transactions
To carry out settlement and monetary transactions, organizations that have an independent balance sheet and are endowed with their own working capital open a current account at bank institutions.
The procedure for opening, closing and re-issuing settlement or current accounts is regulated by special banking instructions.
To register, open (re-register previously opened) settlement and current accounts, the following documents are provided to the bank:
1. application for opening an account;
2. document on registration of an enterprise or organization;
3. charter of the organization with a mark of registration with the local government body or a copy thereof, notarized by a higher organization or body conducting registration;
4. a duplicate of the notice of assignment of the payer’s account number;
5. certificate from the authorities of the social protection fund and BRUSP "Belgosstrakh" on registration as a payer of mandatory insurance contributions and other payments;
6. card with sample signatures of officials who have the right to manage the account, and the seal of the account owner in two copies.
If at least one of the signatures is replaced or supplemented, a new card with sample signatures of all persons having the right of first or second signature is presented.
The bulk of payments due to their owner is received into the current account: proceeds from the sale of work, services, products, materials and other assets; short-term (long-term) bank loans can be credited.
From the current account the following is made:
− payment of invoices from suppliers for materials received, services provided, and work completed;
− calculation of taxes and fees;
− with the social protection fund;
− with the authorities of Belgosstrakh;
− cash is issued for wages, travel expenses, and household needs.
To process transactions on a current account, standard forms of payment documents are used. The main ones:
1. payment request;
2. payment order;
3. payment request-order;
4. cash settlement checks, etc.
In certain cases provided for by law, the bank may forcibly debit funds from the current account.
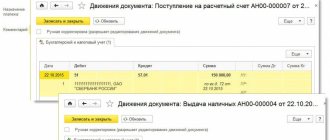
Enterprises and organizations periodically (daily or at other times established by the bank) receive an extract from their current account from the bank. Documents are attached to the bank statement, on the basis of which the movement of funds in the current account is made. The bank statement should be read backwards. The bank statement replaces the analytical accounting register for the current account and serves as the basis for accounting records.
Accounting for transactions on the current account is kept in account 51 “Current account”.
The receipt of funds into the current account is reflected in the following accounting entries:
| db | CT | |
| 51 | 50 | For the amount of cash received from the cash register and deposited into the current account |
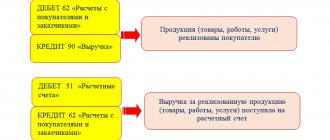
| 51 | 90 | Receipt of funds for sold products (when reflecting the sale of products at the moment the money is received in the current account) |
| 51 | 62 | The amount transferred by buyers (customers) for goods, works, services sold (taking into account sales as they are shipped and invoices are presented for payment) |
Expense transactions:
| db | CT | |
| 50 | 51 | for the amount of cash received at the cash desk |
| 60 | 51 | for the amount of paid supplier invoices |
| 66,67 | 51 | for the amount of repaid loans, borrowings and interest on them |
| 68 | 51 | for the amount of taxes and non-tax payments transferred to the budget |
| 69 | 51 | for the amount of transferred payments to the social protection fund |
| 76 | 51 | for the amount of payments transferred to Belgosstrakh and other creditors |
With the journal-order form of accounting, transactions on the current account are recorded in the journal-order No. 2 and statement No. 2.
Accounting for funds in foreign currency, special bank accounts and transfers in transit
To summarize information about the availability and movement of funds in foreign currency in foreign currency accounts in banks in the territory of the Republic of Belarus and abroad, active account 52 “Currency account” is intended.
In this case, transactions can be performed in the following currencies:
− US dollar;
− euro;
− Russian ruble.
At the same time, in parallel, all transactions are translated into Belarusian rubles at the National Bank exchange rate.
All bank transactions in foreign currency for reflection in the organization’s accounting records are translated into ruble equivalent at the current exchange rate, periodically published in the official press.
This is necessary to control the actual movement of funds in various currencies.
The following sub-accounts can be opened for account 52 “Currency account”:
1. current currency account;
2. transit currency account;
3. special currency account;
Transactions on foreign currency accounts are reflected in accounting on the basis of bank statements and monetary settlement documents attached to them.
A separate journal-order is maintained.
For separate accounting and control over the availability and movement of funds held on letters of credit, on limited check books, as well as those intended for targeted events, special bank accounts are opened for enterprises and organizations.
An enterprise can use account 57 “Transfers in transit” - it is intended to summarize information on the flow of funds (transfers_ in transit.. Mainly, this account reflects the proceeds from the sale of goods by organizations engaged in trading activities, deposited in the cash desks of credit institutions or cash desks post offices for crediting to a current or other account of the organization, but not yet credited for its intended purpose.
To carry out settlement and monetary transactions, organizations that have an independent balance sheet and are endowed with their own working capital open a current account at bank institutions.
The procedure for opening, closing and re-issuing settlement or current accounts is regulated by special banking instructions.
To register, open (re-register previously opened) settlement and current accounts, the following documents are provided to the bank:
1. application for opening an account;
2. document on registration of an enterprise or organization;
3. charter of the organization with a mark of registration with the local government body or a copy thereof, notarized by a higher organization or body conducting registration;
4. a duplicate of the notice of assignment of the payer’s account number;
5. certificate from the authorities of the social protection fund and BRUSP "Belgosstrakh" on registration as a payer of mandatory insurance contributions and other payments;
6. card with sample signatures of officials who have the right to manage the account, and the seal of the account owner in two copies.
If at least one of the signatures is replaced or supplemented, a new card with sample signatures of all persons having the right of first or second signature is presented.
The bulk of payments due to their owner is received into the current account: proceeds from the sale of work, services, products, materials and other assets; short-term (long-term) bank loans can be credited.
From the current account the following is made:
− payment of invoices from suppliers for materials received, services provided, and work completed;
− calculation of taxes and fees;
− with the social protection fund;
− with the authorities of Belgosstrakh;
− cash is issued for wages, travel expenses, and household needs.
To process transactions on a current account, standard forms of payment documents are used. The main ones:
1. payment request;
2. payment order;
3. payment request-order;
4. cash settlement checks, etc.
In certain cases provided for by law, the bank may forcibly debit funds from the current account.
Enterprises and organizations periodically (daily or at other times established by the bank) receive an extract from their current account from the bank. Documents are attached to the bank statement, on the basis of which the movement of funds in the current account is made. The bank statement should be read backwards. The bank statement replaces the analytical accounting register for the current account and serves as the basis for accounting records.
Accounting for transactions on the current account is kept in account 51 “Current account”.
The receipt of funds into the current account is reflected in the following accounting entries:
| db | CT | |
| 51 | 50 | For the amount of cash received from the cash register and deposited into the current account |
| 51 | 90 | Receipt of funds for sold products (when reflecting the sale of products at the moment the money is received in the current account) |
| 51 | 62 | The amount transferred by buyers (customers) for goods, works, services sold (taking into account sales as they are shipped and invoices are presented for payment) |
Expense transactions:
| db | CT | |
| 50 | 51 | for the amount of cash received at the cash desk |
| 60 | 51 | for the amount of paid supplier invoices |
| 66,67 | 51 | for the amount of repaid loans, borrowings and interest on them |
| 68 | 51 | for the amount of taxes and non-tax payments transferred to the budget |
| 69 | 51 | for the amount of transferred payments to the social protection fund |
| 76 | 51 | for the amount of payments transferred to Belgosstrakh and other creditors |
With the journal-order form of accounting, transactions on the current account are recorded in the journal-order No. 2 and statement No. 2.
Accounting for funds in foreign currency, special bank accounts and transfers in transit
To summarize information about the availability and movement of funds in foreign currency in foreign currency accounts in banks in the territory of the Republic of Belarus and abroad, active account 52 “Currency account” is intended.
In this case, transactions can be performed in the following currencies:
− US dollar;
− euro;
− Russian ruble.
At the same time, in parallel, all transactions are translated into Belarusian rubles at the National Bank exchange rate.
All bank transactions in foreign currency for reflection in the organization’s accounting records are translated into ruble equivalent at the current exchange rate, periodically published in the official press.
This is necessary to control the actual movement of funds in various currencies.
The following sub-accounts can be opened for account 52 “Currency account”:
1. current currency account;
2. transit currency account;
3. special currency account;
Transactions on foreign currency accounts are reflected in accounting on the basis of bank statements and monetary settlement documents attached to them.
A separate journal-order is maintained.
For separate accounting and control over the availability and movement of funds held on letters of credit, on limited check books, as well as those intended for targeted events, special bank accounts are opened for enterprises and organizations.
An enterprise can use account 57 “Transfers in transit” - it is intended to summarize information on the flow of funds (transfers_ in transit.. Mainly, this account reflects the proceeds from the sale of goods by organizations engaged in trading activities, deposited in the cash desks of credit institutions or cash desks post offices for crediting to a current or other account of the organization, but not yet credited for its intended purpose.