Payment for shift work: general points
The rotation method differs from all other systems for organizing the work and rest regime of workers primarily in that it provides a number of additional legislative guarantees to workers involved in work on a shift basis (Article 302 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
All shift workers are guaranteed by the Code:
- shift pay as a method of labor;
- payment or free provision of housing;
- payment for days of round trip travel and days of delay in travel due to weather conditions based on the daily rate.
For shift workers working in the Far North or equivalent areas, the following are guaranteed:
- additional increasing coefficients (regional - depend on the area of work);
- allowances for work in the North (the so-called northern, calculated as a percentage of earnings);
- additional paid holidays - the number of days depends on the area of work.
The collective and/or labor agreement may also provide for other guarantees, such as the provision of free food during shifts.
Payroll when applying a work schedule on a rotational basis can be carried out using remuneration systems (or a combination of them for different cases):
- tariff system;
- salary systems;
- time-based;
- time-bonus;
- piecework;
- piecework-bonus;
- other methods and forms of remuneration not prohibited by law.
With the rotational method, remuneration is based on general economic methods. Payroll calculation is based on the tariff rate per hour or per unit of production. The tariff schedule may cover all positions and professions of the enterprise, or may apply only to certain categories of workers, leaving others on the salary system.
Work on a rotational basis according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and its advantages
Like any form of labor organization, it has its pros and cons. From an employee's point of view, the main advantages include:
- Increased earnings.
- The ability to choose an activity without being tied to your place of residence.
- Savings on rent and food and the resulting opportunity to save.
- Long rest after each watch.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation strictly regulates the shift method, which means that there are no more risks when working away from home than in an office next door. So the only drawback can be considered the poor infrastructure of the villages and the inconvenience of the schedule for family people. Although the advantages significantly outweigh them.
Order
Salary for shift work
In general, wages on a rotational basis consist of the following components:
- payment for work performed during the shift - according to tariff rates, categories, production standards;
- payment for overtime hours - is summed up once per accounting period (month, quarter, year - depends on the internal remuneration policy of the enterprise) upon its completion;
- payment for additional days of inter-shift rest (paid days off) for overtime on shift (Article 301 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clause 4.3 of the Basic Provisions on the shift method of organizing work, approved by Resolution of the USSR State Committee for Labor of December 31, 1987 No. 794/33-82 [hereinafter referred to text - Basic provisions No. 794/33-82]);
- allowances: for shift work,
- for the area of work (the Far North and areas equivalent to it),
- for particularly difficult working conditions,
- for harmful working conditions;
Working hours during the shift method are recorded on a cumulative basis.
You can find out more about the features of this method of recording working time here: “Total recording of working time - examples of calculation.”
Possible allowances
Shift allowance is compensation (similar to daily allowance) that shift workers receive for specific working conditions.
Let's figure out what legislative document establishes the amount of the shift allowance. The formation and accrual of this compensation are regulated by regulations of the Government of the Russian Federation and government bodies at various levels.
RF PP No. 51 of 02/03/2005 establishes a premium for federal-level enterprises. Compensation is calculated as a percentage of salary. For example, in the northern regions they compensate 75% of the salary, in Siberia and the Far Eastern region - 50%, in other regions (at enterprises with shift shifts) a similar bonus is 30%.
The additional payment is made based on each day of actual stay at the workplace (in this case, shift), as well as travel time there and back.
Some organizations pay a fixed bonus. Regardless of the type of compensation (fixed or as a percentage), the accrued amount must be reflected in local documents - a collective agreement, regulations on remuneration, regulations on additional payments and allowances.
Compensation and allowances for shift work
As a rule, employers make compensation payments to shift workers - payment for travel from the place of assembly/place of residence to the place of work and back (tickets) and days of travel (tariff or average daily earnings for days on the road). An enterprise can reimburse the cost of travel, or it can issue tickets to its employees, purchasing them centrally from transport companies. Sometimes large companies organize the transportation of their employees on special flights, ordering airplanes, watercraft, and railway cars. Aspects of payment for travel to employees will be discussed in more detail below.
The shift allowance replaces daily travel allowances. The bonus for working on a shift basis is calculated for all days of the shift and for the days the employee is on the road on the way to the shift and back. The amount of allowances at commercial enterprises is established by collective agreement. For state-owned enterprises, there are regulations establishing the amount of allowances.
Details related to the payment of bonuses for shift work are discussed in the Guide “Shift Work” from ConsultantPlus. Get trial access to the system for free and proceed to the explanations.
Industry standards must be taken into account when calculating salaries. Especially if the company is a party to an industry agreement. If such an agreement is not signed by the enterprise, it may be equal to the norms of industry standards, but they will not be binding for the enterprise.
The amount of the bonus for shift work can be set:
- as a percentage of the salary (tariff rate);
- in a fixed amount.
Features of payroll calculation
The shift method of work (payroll calculation, we will look at examples for 2022 in detail in the article) is used in cases where other remuneration systems are impractical or impossible to use.
Work on a shift shift involves calculating wages on a rotational basis: examples of such activities are construction, resource extraction enterprises, drilling rigs. Depending on the industry specifics of the company, the place of work itself may be located at a significant distance from the employee’s place of residence. That is why many resource extraction and construction organizations plan work schedules in such a way that employees do not experience difficulties commuting to work every day, often in difficult weather conditions. For this purpose, shift watches are introduced.
Payroll calculation using the rotation method - example
Foreman Ivanov I.I. works at an enterprise that uses a rotational work schedule.
Shift work conditions are as follows:
- Shift work schedule: 15/15(16). 16 days of rest are provided in months in which there are 31 days, 14 days of rest in February. In our example, the month under consideration is December 20XX.
- In December, the shift begins on the 5th. 4 days of the month (from the 1st to the 4th) - the road to the shift. The end of the watch is on the 19th, from the 20th to the 23rd - the road from the watch.
- The working shift on watch is 11.5 hours all days except the day before the end of the watch. On this day, work lasts 11 hours.
Question: Why are there no days off for 15 days of work during a shift?
Answer: in accordance with table 3.1 “Recommended work and rest regimes” of the Guidelines for optimizing work and rest regimes for rotational and expeditionary rotation methods of organizing work in the North, approved. Ministry of Health of the USSR 04/25/1988 No. 4614, with a 15-day work schedule, shifts are organized in such a way that by changing shifts from the day shift to the night shift, the required number of hours for inter-shift rest is formed (according to clause 4.3 of the Basic Provisions No. 794/33-82, the duration of inter-shift rest including lunch breaks - at least 12 hours).
- The hourly tariff rate is 300 rubles/hour.
- Compensation for shift work is 700 rubles/day.
- Payment for travel time is 100% of the daily wage based on an 8-hour working day.
- The accounting period is quarter. For our example, we provide salary calculations for December and calculate payment for hours worked overtime in the accounting period. The employee worked for the 4th quarter of 20XX: in October - 184 hours, in November - 172 hours, in December - 172 hours. Or 528 hours per quarter when the norm is 519 hours.
ATTENTION! In the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, officials have developed rules for working on a rotational basis. Initially, they were valid until the end of 2022. But the government, by Decree No. 2310 dated December 28, 2020, extended the validity of these rules until the end of 2022.
Read more about the temporary work rules for shift workers in the review from ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
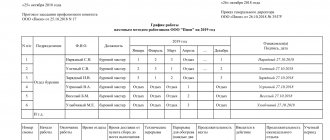
We remind you that the employer is required to draw up a work schedule for the entire accounting period (in our case, a quarter). In our example, this is table 1.
The following markings are used to indicate days in the schedule:
- DD - days on the road;
- RD - working days of the shift;
- Airborne Forces - a day off during a shift between shifts (in our case there are no such days);
- On weekends.
In order to more clearly display the periods of work and rest of I. I. Ivanov, we present the calendar of December 20XX with the calculation of days on the road, on shift and days of inter-shift and inter-shift rest:
- from December 1 to December 4 - 4 days on the way to the place of work;
- from December 5 to December 19 - 15 days on duty;
- from December 20 to 23 - 4 days on the way home;
- from December 24 to December 31 - 7 days off.
Only 8 days on the road, 15 working days, 8 days of rest.
1. Number of hours worked per month:
14 × 11.5 + 1 × 11 = 172 hours.
2. The employee worked 15 days. With a 40-hour work week and a normal work shift, the number of hours that an employee would have worked for the same period in December (see paragraph 4 of clause 4.5 of Basic Provisions No. 794/33-82):
15 working days × 8 hours = 120 hours.
3. Number of days of shift work:
(172 – 120) / 8 = 6.5 days.
For these days, paid days off are provided (paragraph 3 of article 301 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clause 4.5 of the Basic Provisions No. 794/33-82). The December report card takes the form presented in Table 2.
When drawing up the report card, we use form T-12, approved. Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 5, 2004 No. 1. The employer is obliged to keep records of working hours, as stated in Art. 91 and Art. 300 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. At the same time, the form for recording working hours can be independently developed by the enterprise. In our case, the enterprise established in its accounting policy that the T-12 form is used to record working time.
In this case, payment for weekends will be carried out in the following way: 6 days - for 8 hours, 1 day - for 4 hours.
We mark work days, days off and paid days off in the same way as indicated in the T-12 form, namely:
- days off between shifts and between shifts - B;
- working days during a shift - VM;
- paid days off - OV.
4. Let's calculate the salary for the time worked:
172 hours × 300 rub./hour = 51,600 rub.
5. Supplement for shift work:
(15 days of watch + 8 days of travel) × 700 rub./day = 16,100 rub.
6. Payment for overtime (paid days off):
6.5 days × 8 hours × 300 rub./hour = 15,600 rub.
7. Payment for days on the road:
8 days × 8 hours × 300 rub./hour = 19,200 rub.
8. Total wages for December:
51,600 + 16,100 +15,600 + 19,200 = 102,500 rub.
9. In addition, in December it is necessary to pay the employee for hours of overtime work according to the summarized schedule. From the conditions of the example, it is known that the employee worked 516 hours during the quarter, which is 5 hours more than the standard. These hours are paid double:
5 × 2 × 300 = 3,000 rub.
In total, for work on a rotational basis in December, the enterprise is obliged to pay foreman Ivanov I.:
102,500 +3,000 = 105,500 rub.
Calculation example
Let us give an example of calculating the shift method of work in construction. P.P. Petrov is employed by the NPO Stroitel. Construction work is being carried out at a distance of 300 km. Standards for 2022:
- working days - 247;
- working hours - 1970.
Schedule for Petrov P.P. for April 2022 - from April 8 to 15 and from April 22 to 29. Service time - 12 hours. In total, Petrov worked 14 shifts of 12 hours each. The day off is Sunday.
Travel days to the collection point (there and back) are April 7 and 16, April 21 and 30, that is, 4 days.
Inter-shift rest is from April 17 to April 20, that is, 4 working days.
The employee’s salary is 70,000.00, the bonus, in accordance with the collective agreement, is 30%, northern or regional coefficients are not established.
Let's calculate the salary of Petrov P.P. for April 2022
The daily rate will be (70,000 × 12) / 247 = 3,400.81 rubles, the hourly rate - (70,000 × 12) / 1,970 = 426.40 rubles.
Actual hours worked - 426.40 × 12 hours × 14 cm = 71,635.20 rubles.
Days on the road - 3400.81 × 4 = 13,603.24 rubles.
Inter-shift rest - 3400.81 × 4 = 13,603.24 rubles.
Shift allowance taking into account days on the road - (70,000 / 30) × (16 days of work + 4 days on the road) × 30% = 14,000 rubles.
Total payments to Petrov P.P. for April 2022 will amount to RUB 71,635.20. + 13,603.24 rub. + 13,603.24 rub. + 14,000 rub. = 112,841.68 rubles.
Calculating the salary of an employee working on a rotational basis in the North
Payroll calculation for an employee working on a rotational basis in the North has its own peculiarities.
Regional coefficients have been established that must be used when calculating wages. So, if in the above example Ivanov I.I. worked in the Far North, in the Khanty-Mansiysk region, then the northern coefficient applied to his salary is 1.7.
In addition, there is also a bonus for working in the North (“northern”). This premium depends not only on the region, but also on the length of service of the employee in the Far North and in equivalent regions.
Let’s assume that Ivanov I.I.’s northern bonus is 50%.
Then Ivanov I.I.’s salary for working on shift in December 20XX:
172 × 300 × 1.7 + 172 × 300 × 0.5 = 87,720 + 25,800 = 113,520 rubles.
We add all additional payments and compensations calculated in the example above. The final salary of I. I. Ivanov:
113,520 + 16,100 + 15,600 + 19,200 + 12,000 = 176,420 rub.
To clarify the principle of application of northern surcharges and their sizes, read the article “The size of the northern surcharge in the Far North regions.”
Setting up accruals for paying for time worked
Typical hourly wages are calculated for all hours of planned working time. Because For shift workers, in addition to the time worked, special types of time appear on the time sheet (days on the road, rest between shifts), the standard accrual will be calculated for these hours. This calculation does not suit us, so we will create a new accrual. We will do this by copying the standard charge Payment at an hourly rate .
If the program does not have a standard accrual Payment at an hourly rate , then you should check the setting of the Apply hourly payment in the Salary calculation settings (Settings - Payroll calculation - Setting up the composition of accruals and deductions - Hourly payment - Application of hourly payment).
On the Time Accounting for the new Accrual , select the designation in time accounting - Shift . As an additional type of time, we will indicate Night Watch . We will leave the remaining settings unchanged.
If for other non-rotation workers the standard hourly rate payment , you can change its settings and not create a new accrual. However, if current employees with regular work hours are also assigned Hourly Pay , their settings cannot be changed.
Even if NON-shift workers are not currently paid at an hourly rate , but it was accrued previously, it is not advisable to change its settings. This may lead to erroneous results in case of recalculations. Therefore, it is safer to set up a separate accrual.
In order to additionally calculate the Night Work Supplement for hours of night work , you need to change the settings for this accrual. Let's open the settings for Additional payments for work at night and on the Time Tracking we will indicate an additional type of time Night shift .
Security: payment after the watch
If a person works in security on a rotational basis, then inter-shift rest is provided to him on the same conditions as other employees working on a rotational basis. Security guards usually have overtime after their shift. Therefore, they are calculated paid days off in the same way as in the example above. At the end of the accounting period (month, quarter or year), security staff may be paid overtime based on a double tariff rate.
Moreover, if payment for the main shift time has already been made, then the employer makes an additional charge for overtime (overtime for the accounting period), as in the example above. An employee has the right to receive additional days of rest instead of extra pay for overtime (Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
More details about the rules for calculating payment for overtime work can be found in the article “How is overtime work paid according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation?”
Calculation of payment for inter-shift rest
Inter-shift rest is the difference between the time actually worked during the shift period and the standard working time for a 40-hour work week.
To make payment, you first need to calculate the standard time per shift (working days only) according to the production calendar. Then subtract the resulting norm from the actual hours worked and divide by the established number of working hours per day (8 hours in a 40-hour week) - you get the paid number of days of inter-shift rest. For a day of inter-shift rest, the daily tariff rate is charged (for an 8-hour working day), unless the employer has established a higher level of payment.
Payment for travel from shift upon dismissal
If an employee quits while on shift, a legitimate question arises: is the organization obligated to pay him for travel from the shift upon dismissal? First, let’s consider whether the organization is obliged to pay the shift worker’s travel and in what amount.
There are several starting points for making a decision on paying for workers’ travel to and from their shifts:
- from place of residence to place of gathering;
- from the gathering place to the place of work;
- from place of residence to place of work.
ATTENTION! In accordance with sub. 2 p. 1 art. 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, all types of compensation payments (within the limits established by law) related to the employee’s performance of his job duties are not subject to insurance premiums for payers who are organizations, individual entrepreneurs or individuals - employers. The procedure for paying compensation to employees for travel expenses to their place of work must be fixed in a collective agreement and employment contracts.
Regarding the question of whether the employer is obliged to pay for travel from the place of work to the place of residence for an employee who quit after the end of the shift, there cannot be a clear answer. If this clause is not separately stated in the employment contract with the employee, then the employer is not obliged to pay for travel. The person quit - he ceased to be an employee of the enterprise, and the employer’s obligations to him ceased from the moment of his dismissal.
If a person, working in the Far North, quits and at the same time took leave, then the employer is obliged to pay for his travel to the place of vacation. Since in this case, the employment relationship ends only from the end of the vacation or another date different from the end date of work on the shift.
Taxation
We looked at how the salary of a shift worker is calculated and what a shift bonus is; taxation in 2020 is the next question.
Being essentially a compensation payment, additional payment to an employee working on a shift shift is not subject to personal income tax (clause 3 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) or insurance contributions (clause 2 of clause 1 of Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Compensation is not included in the list of payments - exceptions that are not subject to contributions for accidents and occupational diseases, which means that such contributions are charged on this allowance in accordance with current legislation (125-FZ).
Separately, it is worth mentioning the taxation of alimony for a shift worker. The calculation of alimony for shift work and its taxation are carried out according to the general rule (RF PP No. 841 of July 18, 1996, Art. 101 Federal Law-229 of October 2, 2007), however, shift compensation, which is included in the total amount of accrued remuneration for labor, is subject to taxation also not subject.
Results
Remuneration for shift work has its own characteristics. Payment is made for work performed during the shift according to tariff rates, categories, and production standards. In addition, bonuses are paid for work on a shift basis, for days on the road, for the area of work (the Far North and areas equivalent to it). Overtime work is paid based on the results of the accounting period. The main difficulties for an accountant of a commercial enterprise arise if the local acts of the enterprise do not clearly define the procedure for calculating and paying wages to persons involved in work on a rotational basis.
Sources:
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation
- Resolution of the State Labor Committee of the USSR, the Secretariat of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions, the Ministry of Health of the USSR dated December 31, 1987 No. 794/33-82
- Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 5, 2004 No. 1
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Taxation of shift allowance
Based on Article 302 of the Labor Code, the bonus for working on a rotational basis is considered a compensation payment.
This allowance is not subject to insurance premiums (Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), or personal income tax (clause 3 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) (see letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2022 No. 03-15-05/18583).
Read also: “Allowances for shift workers are not subject to insurance premiums and personal income tax”
Also, it does not need to be subject to contributions for insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases (clause 2, clause 1, article 20.2 of the Federal Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ).
By the amount of these allowances, the company has the right to reduce taxable profit by including such costs in labor costs (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 3, 2009 No. 03-04-06-01/313).
The allowance for work on a rotational basis in accounting is for the organization an expense for ordinary activities and relates to labor costs (clauses 5, 8 of PBU 10/99, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 6, 1999 No. 33n).
Read also: “Providing meals for shift workers is not subject to VAT, but gives the right to a deduction”
We calculate wages for hours worked
This calculation depends on the remuneration system used in your company:
- <if>the employee’s work is paid on the basis of an hourly tariff rate:
- <if>the employee’s work is paid on the basis of a daily tariff rate:
- <if>the employee’s work is paid on a salary basis, then the calculation is made in two stages.
STEP 1. Calculate the hourly part of the salary. There are two possible options for this calculation. The option you choose must be specified in the company’s local regulations (for example, in the regulations on shift work).
OPTION 1. Taking into account the average monthly number of working hours for the calendar year:
This option is convenient because the hourly part only needs to be calculated once at the beginning of the year and can then be applied throughout the year. In addition, pay for shift workers will be more equal.
OPTION 2. Taking into account the standard working hours of a particular month according to the production calendar:
With the second option, the hourly part of the salary will be different in different months. Therefore, pay for shift workers will be less uniform.
STEP 2. We calculate the employee’s salary for the time worked:
Let's sum it up
- The amount of compensation for shift work is determined by regulations for budgetary institutions and local regulations for private companies.
- The amount of the bonus can be either fixed or dependent on the salary or tariff rate.
- Amounts of shift allowance are not subject to personal income tax and insurance contributions, but may reduce the base for income tax.
Hello Guest! Offer from "Clerk"
Online professional retraining “Accountant on the simplified tax system” with a diploma for 250 academic hours . Learn everything new to avoid mistakes. Online training for 2 months, the stream starts on March 1.
Sign up
Watch and personnel
An employer who uses a rotational method of organizing labor and paying for it has a number of obligations to employees in accordance with the law:
- tracking the working time of each employee on shift (duration - no more than a month, in exceptional cases - up to 3 months);
- summary recording of working hours;
- provision of housing and three meals a day;
- organization of medical examinations, payment of sick leave;
- payment not only for labor, but also for travel to the place of work, the use of a number of allowances for labor;
- advance preparation and approval of a work schedule and familiarization of employees with it, with a shift duration of no more than half a day.
Attention! The duration of the shift is calculated in total with the rest time from shift to shift (Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Art. 299).
Employees must be familiarized with the schedule no later than two months before starting work. The document must be approved by the trade union of the employing organization. When drawing up a schedule, you should keep in mind that working without a rest break, in two shifts in a row, is strictly prohibited.
Shift workers may be provided with the following types of payments:
- salary;
- allowance for the shift, taking into account travel time for each day of the shift;
- payment for overtime between shifts;
- coefficients for complexity, work intensity, hazardous working conditions, depending on the industry;
- “climate” allowance, if work is carried out in the corresponding regions, the so-called northern one, etc.
Attention! The shift bonus has a fixed amount only for employees of federal structures (30% - general rate, Siberia, Far Eastern region - 50%, Northern region - 75% of the average daily rate). Commercial structures set its dimensions independently.
All working and rest conditions must be clearly stated in the employment agreement, collective agreement, and other legal acts of the organization. In accordance with labor legislation, the following are not allowed to work on a rotational basis:
- pregnant women;
- minors;
- persons for whom a certain climate is harmful for medical reasons;
- women with children under 3 years of age.
Nuances of calculating “shift” amounts
When making calculations, an accountant should keep in mind some important points:
- If according to the employee’s schedule the norm is set for more than 8 hours, up to 12 hours, then overtime is compensated by charging amounts for inter-shift (inter-shift) rest. However, if production needs require an employee to work a shift beyond the schedule, then he should be paid for overtime: the first 2 hours at one and a half times the rate, the subsequent ones at double the hourly rate. If the organization has adopted a daily tariff rate, the hourly rate should be calculated based on it by dividing by the number of working hours according to the schedule.
- The employee benefits listed above are exempt from contributions and income tax. In this regard, the employer often abuses the use of compensation, whose share in the wage structure prevails over the basic amounts. This situation is unfavorable for the employee in the long term and can lead to legal proceedings against him.
- The issuance of funds in exchange for providing mandatory three meals a day to employees is not recognized by law as compensation. It is subject to taxes and contributions according to the standard scheme.
- Compensations, along with basic labor payments, are taken into account in income tax expenses and the simplified tax system.
Main
Remuneration for workers on shift is distinguished by a variety of forms and nuances of calculation. All of them are prescribed in local regulations, employment contracts (agreements) and are applied in strict accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Mandatory bonuses for shift workers are not subject to contributions to funds and personal income tax, since they are compensation payments. At the same time, these amounts are included in calculations for reducing income tax and the simplified tax system.