On the eve of a non-working holiday
In Art. 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides a complete list of public holidays established in the Russian Federation. In accordance with Art. 95 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, on the previous day the shift or work day must be shortened by exactly an hour. However, this does not affect the formation of wages in any way.
In enterprises where activities cannot be arbitrarily terminated or suspended, employees experience overtime that must be compensated. In accordance with Art. 95 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in this case he is provided with monetary compensation for overtime work or additional hours of rest.
Summarized working time recording
For workers engaged in round-the-clock continuous work, as well as in other types of work where, due to production (work) conditions, the established daily or weekly working hours cannot be observed, summarized working time recording is introduced.
Typically, such work is carried out in accordance with shift schedules (work schedules). The shift duration can be set, for example, 10 hours, 12 hours.
The organization sets its own accounting period. This can be a maximum of a month, quarter, half year or year. In this case, the sum of hours worked during this period cannot exceed the normal number of working hours in the accounting period.
Let us remind you that the normal working hours are 40 hours per week (Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, the total number of working hours for the accounting period should not exceed the norm for the same period of time according to the production calendar.
When is vacation paid on a non-working holiday?
According to Part 4 of Art. 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, for salaried workers, the presence of holidays in the reporting month does not affect earnings.
For workers on a different schedule, for example, for piece workers, the presence of long days off can significantly affect wages. In such cases, part 3 of Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation for the day when no employment was carried out, non-salaried employees are provided with additional payments according to the standards established in the local regulations of the enterprise.
Remuneration for shift work schedules
Source: Journal “Payment in state (municipal) institutions: accounting and taxation”
The editors of the magazine received many questions related to wages during a shift work schedule. In this regard, in this article we will explain situations related to the preparation of a shift schedule, payment of labor, provided that the shift falls at night, a non-working holiday, as well as payment for overtime and overtime during shift work.
First, let's say a few words about what shift work is. According to Art. 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation , shift work is work in two, three or four shifts, introduced in cases where the duration of the production process exceeds the permissible duration of daily work, as well as for the purpose of more efficient use of equipment, increasing the volume of products or services provided. When applying shift work in an organization, this circumstance must be enshrined in a local regulatory act and an employment contract with the employee, if his work mode differs from the work mode adopted by this employer.
During shift work, each group of workers must perform work during the established working hours in accordance with the shift schedule. In this case, working two shifts in a row is prohibited.
Is it possible to set a shift schedule in such a way that the number of hours per month exceeds the standard hours according to the production calendar? According to Parts 2 and 3 of Art. 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, during shift work, employees work for the established working hours in accordance with the shift schedule. When compiling it, it is necessary to take into account the opinion of the trade union (other representative body of employees) (if there is one), as well as the following features of the shift work schedule:
- the duration of working hours should not exceed the established norm ( Part 2 of Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ). Moreover, if the organization has introduced summarized recording of working hours, then when determining the normal number of working hours, it is necessary to take into account the features provided for in Art. 104 Labor Code of the Russian Federation ;
- for certain categories of employees, the duration of the work shift should not exceed the established limit ( Article 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation );
- the work shift immediately preceding a non-working holiday is reduced by one hour ( Part 1 of Article 95 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation );
- the night shift is reduced by one hour without further work ( part 2 of article 96 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation );
- work for two shifts in a row is prohibited ( part 5 of article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation );
- weekly uninterrupted rest should not be less than 42 hours ( Article 110 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ).
The shift schedule is a mandatory document for the parties to the employment contract, therefore the organization does not have the right to involve an employee in work outside the schedule, with the exception of some cases of involvement in overtime work ( Articles 99 , 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ).
From the above provisions of the Labor Code it follows that the shift schedule must be drawn up so that the employee’s working time does not exceed the normal number of hours for this category of persons during the accounting period. Therefore, overtime work cannot be included in the shift schedule. Hours worked overtime by an employee are determined based on the time sheet. It should be taken into account that overtime work should not exceed four hours for each employee for two days in a row and 120 hours per year ( Part 1 , 6 of Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ).
How is working time recorded during shift work? In part 4 art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation stipulates that the employer is obliged to keep records of the time actually worked by each employee. To record working time, timesheet forms approved by Order No. 173n (working time sheet (form 0301008) and time sheet recording the use of working time and payroll (form 0504421)). Note that the procedure for recording working hours during shift work must be recorded in the internal labor regulations, and can also be reflected in the shift schedule.
The institution has established a shift schedule. Can an employer provide a rest and meal break of three hours? According to Art. 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, during the working day (shift), the employee must be given a break for rest and food lasting no more than two hours and no less than 30 minutes, which is not included in working hours. In this case, the time for granting a break and its specific duration are established by internal labor regulations or by agreement between the employee and the employer. From the provisions of this article it follows that labor legislation establishes a minimum (30 minutes) and maximum (two hours) break duration. Thus, the employer does not have the right to provide employees with a rest break lasting more than two hours.
An employee of an organization has part of their shift at night. How is he paid for his night work in this case? Article 149 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that when performing work in conditions deviating from normal (in particular, such work includes work at night), the employee is made appropriate payments provided for by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, collective and labor contracts, agreements, local regulations. The amounts of payments established by collective and labor contracts, agreements, and local regulations cannot be lower than those provided for by labor legislation and other regulations containing labor law norms.
According to Art. 96 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the time from 22.00 to 6.00 is considered night time. Each hour of such work is paid at an increased rate compared to work under normal conditions ( Article 154 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ). Let us note that according to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated July 22, 2008 No. 554 “On the minimum amount of increase in wages for work at night,” each hour of work at night is paid with an increase in the tariff rate by no less than 20%.
Thus, based on the provisions of labor legislation, employees working in shift work are entitled to additional payment for night work.
Let's give an example of calculating additional pay if part of the shift falls on night hours.
Example 1.
The employee of the institution has a shift work schedule (two shifts), the duration of the evening shift is from 16.00 to 24.00. It works from Monday to Friday. According to the schedule for March, the number of evening shifts is 11. The employee is given a salary of 22,000 rubles. We will calculate the additional payment for night work, provided that each hour of night work is paid 20% higher than the tariff rate.
In March, the employee worked a standard of 168 hours, which corresponds to the standard according to the production calendar with a 40-hour work week. So, at night there are two hours per shift (from 22.00 to 24.00), a total of 22 hours (2 hours x 11 shifts). The hourly tariff rate will be 130.95 rubles. (RUB 22,000 / 168 hours). The additional payment for night work will be 576.18 rubles. (22 hours x RUB 130.95 x 20%).
In March, the employee’s shift coincided with a non-working holiday, and several more hours fell at night. How is such a shift paid in this case? Work on a non-working holiday is work that is performed under conditions deviating from normal, as is work at night ( Article 149 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ). In this regard, the employee is made appropriate payments provided for by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, collective and labor contracts, agreements, and local regulations.
According to Art. 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation , if a work shift falls on a non-working holiday, it is paid in the following amounts:
- for piece workers - at no less than double piece rates;
- employees whose work is paid at daily and hourly tariff rates - in the amount of at least double the daily or hourly tariff rate;
- employees receiving a salary (official salary):
- in the amount of no less than a single daily or hourly rate (part of the salary (official salary) for a day or hour of work) in excess of the salary (official salary), if the work on a weekend or non-working holiday was performed within the monthly working hours;
- in the amount of no less than double the daily or hourly rate (part of the salary (official salary) for a day or hour of work) in excess of the salary (official salary), if the work was carried out in excess of the monthly working hours.
At the same time, this article states that the employer can set the specific amount of wages on a day off or a non-working holiday independently, but not lower than the amounts provided for by law.
Thus, if an employee’s shift falls on a non-working holiday and several more hours fall at night, he is entitled to two additional payments:
- for work on a holiday ( Article 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation );
- for work at night ( Article 96 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ).
This means that in this case the shift must be paid as follows:
- hours actually worked on a non-working holiday are paid at least double (except for the case when, at the request of the employee, he is given another day of rest);
- wages for each hour of night work should be increased by at least 20%.
Let's give an example of calculating wages for work on a shift that falls on a non-working holiday.
Example 2.
Let's use the conditions of example 1. Let's add that by agreement with the employee, he was assigned a shift on a non-working holiday (from 16.00 to 24.00). We will calculate additional pay for working on a holiday.
The additional payment for work on a non-working holiday will be RUB 2,095.20. (RUB 130.95 x 8 hours x 2).
Additional payment for night work – 52.38 rubles. (RUB 130.95 x 2 hours x 20%).
As a result, the additional payment for this shift will be equal to 2,147.58 rubles. (2,095.20 + 52.38).
The employee of the institution has a shift work schedule: two days of work from 9.00 to 20.00, two days off. How to correctly calculate the salary of this employee (he works overtime hours)? If an institution cannot comply with the daily or weekly working hours established for a given category of workers, it is allowed to introduce summarized recording of working hours ( Article 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ). Such accounting is introduced to ensure that the duration of working hours during the accounting period (month, quarter, etc.) does not exceed the normal number of working hours. The accounting period cannot exceed one year, and for recording the working time of workers engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions - three months. The procedure for introducing summarized recording of working time is established by the internal labor regulations.
If the accounting period in an institution is equal to a month, employees working on a 2/2 schedule must work according to the norm established by the production calendar for each month. Time worked in excess of this number of hours will be considered overtime and must be paid as overtime in the manner provided for in Art. 152 Labor Code of the Russian Federation :
- the first two hours of work - no less than one and a half times the rate;
- subsequent hours - no less than double the amount.
In addition, the institution may establish other additional payments for overtime work, but not lower than those provided for in Art. 152 Labor Code of the Russian Federation .
Their sizes are determined by collective, labor agreements or local regulations. Also, at the request of the employee, overtime work, instead of increased pay, can be compensated by providing him with additional rest time, but not less than the time worked overtime. Some nuances associated with determining the standard working time for the period. According to Art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation , working time is the time during which an employee, in accordance with the internal labor regulations and the terms of the employment contract, must perform labor duties. The business trip period is not working time, but due to its functional purpose it is equivalent to it, since according to Art. 167 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is a trip of an employee by order of the employer for a certain period of time to fulfill an official assignment outside the place of permanent work. In this regard, for posted workers, the standard working time is reduced for the duration of their business trip.
Also, for employees on vacation or temporarily disabled, the standard working time is reduced during the employee’s absence, since vacation and the period of temporary disability do not count as working time. Such clarifications are presented in Letter of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated December 25, 2013 No. 14-2-337 .
Let's give an example of calculating additional pay for overtime work during shift work.
Example 3.
Let's use the conditions of example 1. Let's add that the employee worked 172 hours in March. The institution has established a summarized recording of working time, the accounting period is a month. We will calculate additional pay for overtime hours.
According to the production calendar, with a 40-hour work week, the standard working time for March is 168 hours. Thus, the number of overtime hours is 4 hours (172 - 168).
Consequently, the additional payment for overtime work for March will be 916.65 rubles. (RUB 130.95 x 2 hours x 1.5 + RUB 130.95 x 2 hours x 2).
How is a work shift that falls on a non-working holiday paid if the employee has overtime (overtime) during that shift? According to the Explanation of the State Committee for Labor of the USSR, the Presidium of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions dated 08.08.1966 No. 13/P-21 (hereinafter referred to as the Explanation ), if an institution has established a summarized accounting of working time, work on holidays is included in the monthly standard working time.
In addition, for employees with summarized recording of working hours, special features are provided for recording and paying overtime hours if, during the accounting period, work was performed on holidays in excess of the norm. Since work on holidays is included in the monthly working time standard, when calculating overtime hours, such work performed in excess of the working time standard should not be taken into account, since it is already paid in double amount. Due to the fact that payment for overtime work and work on weekends and non-working holidays is made at an increased rate, the simultaneous accrual of payment at an increased rate on the basis of Art. 152 , 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation will be unlawful ( clause 4 of the Explanation , Decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of November 30, 2005 No. GKPI05-1341 ).
Example 4.
The shift of an employee of the institution coincided with a non-working holiday, and during this shift he had overtime of two hours. How is such a shift paid in this case?
In this case, payment is made in accordance with Art. 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation , that is, hours actually worked on a non-working holiday are paid at least double the amount. In this case, two hours of overtime work are not paid additionally, since they are already paid at an increased rate, namely double, since the work was performed on a non-working holiday.
From the shift schedule it follows that an employee of the institution cannot fully work out the normal working hours in March. How is he paid for the time he is not working? According to Art. 155 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation , in case of failure to comply with labor standards or failure to fulfill labor (official) duties through the fault of the employer, payment for labor is made in an amount not lower than the average salary of the employee, calculated in proportion to the time actually worked. So, if the employer has drawn up a shift schedule in such a way that the employee cannot work out the full working time, he must pay wages in an amount not lower than the employee’s average wage, calculated in proportion to the time he actually worked.
Example 5.
The salary of an institution employee is 20,000 rubles. This employee had 13 12-hour shifts in March, amounting to 156 hours. The accounting period is a month; the institution has a 40-hour work week. We will calculate the number of hours of deficiency and the amount of their payment.
According to the production calendar for 2015, in March the standard working time is 168 hours. Therefore, the shortfall time is 12 hours (168 - 156). This defect occurred due to the fault of the employer, since he did not provide his employee with work. Thus, it is necessary to apply Art. 155 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation , which states that in case of failure to comply with labor standards, failure to fulfill labor (official) duties through the fault of the employer, remuneration is made in an amount not lower than the average salary of the employee, calculated in proportion to the time actually worked.
Article 139 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation notes that for all cases of determining the amount of average wages (average earnings) provided for by the Labor Code, a uniform procedure for its calculation is established. At the same time, the Regulations on the specifics of the procedure for calculating average wages were approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 24, 2007 No. 922 . According to clause 13 of this provision, when determining the average earnings of an employee for whom a summarized recording of working time has been established, except in cases of determining the average earnings for paying for vacations and paying compensation for unused vacations, the average hourly earnings are used.
In this example, the calculation period is the period from 03/01/2014 to 02/28/2015. The employee worked it in full (1,899 hours). Thus, his average earnings will be 126.38 rubles. ((RUB 20,000 x
12 months) / 1,899 hours). This means that the employee’s salary for November will be 19,715.28 rubles. (RUB 126.38 x 156 hours).
* * *
In conclusion, we once again draw your attention to the fact that work under shift conditions must be enshrined in the local regulatory act of the institution and the employment contract with the employee if his work mode differs from the work mode adopted by the employer. In this case, the shift schedule must be drawn up in such a way that the employee’s working time does not exceed the normal number of hours for this category of persons for the accounting period. If an employee’s shift takes place under conditions that deviate from normal conditions (night work, weekends and non-working holidays, overtime work), the employee is paid the appropriate payments provided for by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, a collective agreement, agreements, local regulations, employment contracts.
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 15, 2010 No. 173n “On approval of forms of primary accounting documents and accounting registers used by public authorities (state bodies), local governments, management bodies of state extra-budgetary funds, state academies of sciences, state (municipal) institutions, and Guidelines for their use."
Hello Guest! Offer from "Clerk"
Online professional retraining “Accountant on the simplified tax system” with a diploma for 250 academic hours . Learn everything new to avoid mistakes. Online training for 2 months, the stream starts on March 1.
Sign up
How to pay for “holiday” work
The rules are established in Part 1 of Art. 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (general provision - no less than double):
- for piece workers - no less than double piece rates;
- for employees receiving earnings at daily and hourly rates, the rate is also doubled;
- Accordingly, salaried employees are entitled to the necessary additional payment. Its size depends on whether the work was performed within or in excess of normal working hours (single daily or hourly rate and double).
What working hours are established in the company?
Correct remuneration for an employee depends on the working hours established in the organization.
The working hours are established by each employer in the internal labor regulations.
Need to install:
- type of work week (five-day with two days off, six-day with one day off, work week with days off on a rotating schedule);
- type of working time recording (daily, weekly, summarized);
- duration of daily work (shift);
- number of shifts per day;
- alternation of working and non-working days;
- time of breaks from work;
- start and end times of work.
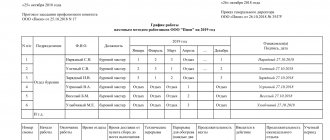
The start and end times of daily work (shift) are indicated in the schedule. The work schedule of employees must be specified in employment contracts and approved by order of the manager.
An organization can establish the following methods of recording working hours:
- daily – with a six-day working week;
- weekly – with a five-day working week;
- summarized - in continuously operating organizations or with a rotational method of organizing work.