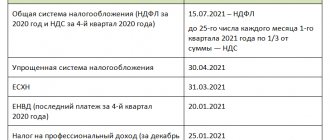
The main responsibility of every entrepreneur is to pay taxes in full and on time. The tax inspectorate closely monitors the fulfillment of this obligation, and in case of evasion, additional taxes are assessed.
Big Brother watches us tirelessly and is always ready to punish us for inaccuracy or evasion of paying taxes in full. Many entrepreneurs have already experienced this close attention. The budget needs money, and one of the ways to replenish it is by collecting taxes. That is why any business is checked for all kinds of tax evasion schemes and any movement in this direction is punished.
Grounds for additional accrual
The Federal Tax Service posted letter No. BS-4-11/ [email protected] “On Taxation” dated November 16, 2015. This regulatory act explains the grounds for additional assessment. In particular, payments can be increased when the tax office has established and proven the fact that the payer has received income not indicated in the declaration. Representatives of the Federal Tax Service must also find the source of income, its type and time of receipt.
Let's consider other grounds for additional charges:
- Discovering tax benefits achieved through business division.
- Formation of controlled legal entities.
- The accountant made a mistake when calculating taxes.
Additional assessment is carried out when in fact a person must pay a larger amount of taxes than necessary.
Publications
Context
Property tax for individuals tied to cadastral value - law
When authorities talk about various “tax maneuvers” to replenish the federal budget, we often treat this neutrally or even indifferently. But when such a “maneuver” concerns your personal wallet, many questions immediately arise.
Retroactive tax
An example from life: a person owns a small plot of land in one of the remote villages of the Moscow region. He regularly paid the annual tax of 95 rubles 03 kopecks for 15 acres - according to the receipt that came to him. The other day I received another receipt and was taken aback: not only did the payment increase 12 times - immediately to 1144 rubles, but it turns out that he also had to “pay in addition” for almost the same amount over the past two years. But in the paper there are no explanations, no references to the regulatory framework, nothing!
A reasonable question: is it legal to raise taxes “retroactively”? And how can a consumer understand which receipts are really worth paying unconditionally, and which ones should take their time and figure it out?
When a receipt arrives indicating that you “owe” the tax authorities for three years at once (although a year ago there were no claims against you, and the amounts were much more modest), you need to officially - in writing or in person - contact the local inspectorate finding taxable property and demanding clarification of the situation, recommends lawyer Anton Sonichev.
He believes that in the situation described above, the tax amount could increase for two reasons. Firstly, due to changes in the tax rate. Secondly, the tax could be calculated based on the cadastral (rather than inventory) value of the land plot. It is possible that both happened at the same time.
There is one “but”: it is possible to collect an increased tax for the last three years only if the rates increased three years ago, which, obviously, could not happen.
Retroactive accrual for past periods after an increase in the tax rate or cadastral value of land is illegal - see paragraph 2 of Article 5 of the Tax Code (TC) of the Russian Federation.
Therefore, when contacting the tax service, it is necessary to request the regulations on the basis of which such an increase occurred. These could be city resolutions or decisions to revise the cadastral value or increase the land tax rate. If explanations supported by documents are not provided, you need to contact a higher tax office (for example, the regional one), the city administration, the prosecutor's office, as well as the regional administration. There you need to outline the situation and also ask for an explanation of why the tax increase occurred, and also demand that a check be carried out on the legality of this increase and additional assessments of taxes for previous years.
Without thoroughly understanding the situation, you should not run to the bank and pay such a receipt.
That the coming year
The good news: if we talk only about land tax, it will not change next year. The news is worse: as of January 1, 2015, the property tax for individuals has been replaced by a property tax for individuals, the rates of which are much higher. Another good news: citizens will feel this only in 2016, when the time comes to pay new rates.
According to the new rules, the tax will be calculated from the cadastral value of the property (and not from the inventory value, as before). Thus, the national average rates of this tax will increase by 1.5-3 times.
Property tax rates have also changed. Now they are:
- 0.1% of the cadastral value - for residential buildings, residential premises, unfinished construction projects if the designed purpose of such objects is a residential building; single real estate complexes, which include at least one residential premises (residential building); garages and parking spaces; economic buildings or structures, the area of each of which does not exceed 50 square meters and which are located on land plots provided for personal subsidiary farming, dacha farming, vegetable gardening, horticulture or individual housing construction; - 2% of the cadastral value - for administrative and business centers, shopping centers (complexes) and premises in them, non-residential premises, the purpose of which, in accordance with cadastral passports of real estate objects or documents of technical registration (inventory) of real estate objects, provides for the placement of offices, retail facilities, public catering and consumer services facilities or which are actually used to house offices, retail facilities, public catering and consumer services facilities; for real estate objects formed during the current tax period as a result of the division of a real estate object or other action with real estate objects in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, as well as for tax objects, the cadastral value of each of which exceeds 300 million rubles; - 0.5% of the cadastral value - for other taxable objects that are not included in the above categories.
Who benefits?
Another positive news: the list of categories of citizens who are entitled to exemption from paying property taxes for individuals has not changed. Let us remind you that the legislator classifies many categories of citizens as beneficiaries. Among them:
— Heroes of the Soviet Union and Heroes of the Russian Federation; - persons awarded the Order of Glory of three degrees; — disabled people of groups 1 and 2, disabled since childhood; — pensioners; — participants of the Second World War; - “Chernobyl victims”; - family members of military personnel who have lost their breadwinner; — persons of creative professions (sculptors, artists, designers).
The latter are exempt from paying tax on premises (workshops) in which they engage in professional creative activities. The full list of beneficiaries is specified in Article 407 of Federal Law No. 284 of October 4, 2014.
However, it will no longer be possible to receive the benefit for all real estate objects registered in the name of the benefit recipient. Tax relief is provided for the following types of taxable items:
1) apartment or room; 2) residential building; 3) premises or structures; 4) economic building; 5) garage or parking space.
Important: the benefit can only be obtained for one property in each of the specified categories. “Simply put, a maximum of 5 real estate items can be exempt from tax: only one apartment or room, plus only one house or one dacha, plus only one room or structure, plus only one outbuilding, plus only one garage or parking space,” - lawyer Sonichev clarifies.
A person who, as of December 31, 2014, was granted a personal property tax benefit has the right not to resubmit an application and documents confirming the right to it to the tax authority.
Anyone who has the right to a tax benefit, but has not previously received it, submits an application and documents confirming the taxpayer’s right to a tax benefit to the tax authority of his choice (see paragraph 4 of Article 407 of Federal Law No. 284).
You must select an object to which the benefit will apply before November 1, 2015, of course, informing your tax office about this. Next year it will be possible to change the object falling under the benefit, and you will need to report this before November 1, but already in 2016.
At the same time, a taxpayer who has informed the inspectorate in advance about which particular property should be subject to preferential tax, after November 1 of the year, which is the tax period, can no longer arbitrarily change the object of taxation.
If the beneficiary is absent-minded or forgetful, and has not provided the inspectorate with a notification about the selected object, the relief will be provided in respect of one taxable object of each type with the maximum calculated amount of tax.
Not only for pensioners and disabled people
Under the new rules, each taxpayer receives deductions that are not subject to real estate taxes. These deductions are provided automatically and for absolutely all real estate properties, regardless of how many are registered for each individual citizen.
“So, in each apartment, 20 square meters of the total area of this apartment are not subject to real estate tax for individuals. For each room, this is 10 non-taxable square meters of the area of that room. For a residential building - 50 square meters of the total area of this residential building. And for a single real estate complex, which includes at least one residential premises (a residential building), the cadastral value is reduced by 1 million rubles, and only then the tax is calculated,” experts clarify.
By the way, according to the old rules, such deductions were not provided for at all.
Marina Alekhina
How to pay additional taxes
Let's look at an example of paying additional taxes if they were assessed during an on-site audit. It is necessary to draw up a payment order for the transfer of taxes. It is filled out on the basis of Appendix No. 2 to Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 106n dated November 24, 2004. In particular, the payer needs to fill out the fields correctly:
- In field 104 you need to enter the budget classification code. The codes were approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 150n dated December 30, 2009. If this is an order to pay taxes, you need to indicate code 182 1 01 01011 01 1000 110.
- In field 106 you need to indicate the basis for the payment.
- Field 107 indicates the frequency of tax payment.
- Fields 108 and 109 contain the details of the document on the basis of which the payment is made.
- Field 110 indicates the type of payment. If this is a tax transfer, you need to enter “TS”.
It must be remembered that the payer’s responsibility is not only to pay additionally assessed tax, but also to reflect transactions in accounting.
Accounting for additional accruals
Additional income tax may be charged if the following circumstances exist:
- Understatement of income by an entrepreneur.
- Inflated expenses.
- There are errors in the declaration.
If the understatement of expenses occurred in the previous period, the entrepreneur does not need to submit an updated declaration. The tax office itself will do this for him. In particular, representatives of the authority calculate the additional amount and then reflect it in the settlement card.
Sometimes there is a need to cancel expenses not only in accounting, but also in tax accounting. Let's look at an example. In the current year's accounting, it is required to reflect the profit of previous periods. A constant minus difference is created.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! In most cases, changes in accounting do not entail adjustments in tax accounting.
Example
In 2015, the company went through a control event. The subject was found to be working with non-existent suppliers in 2014. Payment for goods in the amount of 65,000 rubles was withdrawn. Based on this amount, an additional income tax was charged in the amount of 13,000 rubles (65,000 * 20%). During the on-site inspection, an unreasonable increase in depreciation in the amount of 14,000 rubles was also discovered. And in this area there was an additional charge of 2,800 rubles.
The accountant makes these entries in 2015:
- DT99 subaccount “Losses of previous periods” KT68. Additional tax assessment. Primary: on-site inspection report.
- DT02 KT91. Fixation of profit in the amount of 14,000 rubles from previous periods, discovered in the current period.
- DT99 KT68 . Conditional expense in the amount of 2,800 rubles.
- DT68 KT99 subaccount “PNA”. Fixation of the LAD.
- DT99 KT68. Additional tax assessment for the previous year.
Adjusting income is carried out according to the same scheme as adjusting expenses.
How to appeal additional tax assessment in court?
The right to appeal an additional tax assessment based on the results of an audit in court arises if other pre-trial methods of settlement have been exhausted.
The resolution on additional tax assessment is a non-normative act and is contested in accordance with Chapter 24 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation.
In order to appeal a tax authority decision that is non-regulatory in nature, you need to contact the arbitration court at the location of the tax authority with a statement of claim. The claim must contain demands for invalidation of the non-normative legal act.
The APC presents requirements for a claim to appeal an additional tax assessment:
- Name of plaintiff, defendant
- Details of the contested act
- Indication of the violated rights with reference to the relevant norms
In addition, you must attach:
- evidence of sending the claim to the defendant
- copy of registration certificate
- act being appealed
- documents that are the basis of the plaintiff’s arguments
- document confirming payment of state duty - 3000 rubles
The limitation period is 3 months.
The case is considered according to the rules of claim proceedings - in court hearings with the parties summoned. The consideration of the case by the court takes place within no more than 3 months, and if the case is complex – up to 6 months.
If the court refuses to satisfy the claims, an appeal and cassation appeal of the judicial act is possible.
USEFUL : order an appeal against the court decision with the help of our Ekaterinburg lawyer
Additional VAT calculation
The situation with additional VAT charges is quite ambiguous. The law does not provide precise instructions on where additional VAT amounts are recorded. However, there are some recommendations. In particular, additional VAT charges must be reflected in expenses only if this circumstance exists - the amount of additional charges forms the initial cost of products or services (Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), but it was accepted for deduction by mistake. When an inspection report is received, the amounts are reflected in the cost price if they are already involved in determining income tax (based on letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-07-11/222 dated June 7, 2008).
In all other circumstances, additional VAT is not included in expenses. The basis is subparagraph 19 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It states that the tax that was charged to the buyer cannot be accepted as an expense. However, there is an alternative opinion. In particular, VAT can be included in other expenses on production and sales that reduce the base (subclause 1 of clause 1 of Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In particular, some courts adhere to this position. An example is FAS Resolution No. A32-5096/2007-12/27 dated August 10, 2009.
If a person does not want to enter into conflicts with the tax authorities, then you should not include additional VAT charges in expenses. Only the permanent liability is reflected.
The Supreme Court prohibited additional taxes from being overtaxed
If a company or entrepreneur “saves” on taxes using illegal schemes, then tax authorities can uncover them. But you need to charge as much as if there was no abuse. You cannot add more taxes than a bona fide taxpayer would pay. The Supreme Court gave such directions in a recent case. “This is, in fact, a revolutionary idea for the practice of tax authorities and courts,” comments TAXOLOGY TAXOLOGY partner Federal Rating. Group Tax Consulting and Disputes (Tax Disputes) Group Tax Consulting and Disputes (Tax Consulting) Group Foreign Economic Activities/Customs Law and Currency Regulation Company Profile Alexey Artyukh. – Although the Supreme Court has already formulated such a position. But in this case it is expressed even more clearly in a situation where the fact of a violation is indisputable, and the only question is how much taxes it is fair to pay.”
- The Supreme Court recognized the right without consequences
July 29, 15:19 - The Supreme Court determined when the tax must be paid
October 11, 8:44 - The Supreme Court canceled the tax on demolished real estate
December 28, 12:26 - The Economic Board of the Supreme Soviet abolished the air tax
September 20, 8:01
Artyukh hopes that the clarification will help stop the practice of “confiscation taxation,” when inspectors force “malicious evaders” to pay additional VAT not at the expense of the buyer. At the same time, the tax authority refuses to take into account the economic meaning of the tax, explains the senior partner of the law firm Varshavsky and Partners Varshavsky and Partners Regional Rating. group Foreign trade activities/Customs law and currency regulation group Tax consulting and disputes group Arbitration proceedings (major disputes - high market) group Corporate law/Mergers and acquisitions group Dispute resolution in courts of general jurisdiction Company profile Vladlena Varshavskaya. According to her, this is a mandatory “markup” of the state on the sale price of goods, works and services, but it is paid by the buyer. The tax authority remembers that this is a markup, but sometimes forgets that it must pay it off. In other words, “it is impossible to add additional tax so that, without being presented to the other party to the real transaction, it is paid from the payer’s own funds,” explains Artyukh.
But this is precisely the situation in which individual entrepreneur Nadezhda Ugryumova found herself, who was engaged in the sale of fuels and lubricants. As the tax authorities found out, she artificially lowered her income in order to use the simplified taxation system (STS). To do this, Ugriumova fictitiously leased her gas station, first to her son, and then to her sister. Officials decided that this was an abuse. They added up the income of three entrepreneurs. It turned out that in 2013–2015 Ugryumova could not use the “simplified language”. She received an additional 4.5 million rubles. VAT, 1.4 million rubles. Personal income tax and tax according to the simplified tax system, as well as penalties and fines. Ugriumova did not allocate VAT in the documents (because she used the simplified tax system), so the tax authorities added it “on top” of the total amounts. They refused to deduct tax from the stated price.
Ugriumova appealed the tax authorities' decision, but she only managed to challenge the penalties. The 14th AAS and the AS of the North-Western District agreed with the tax approach. They came to the conclusion that VAT should be added to the price of the goods. After all, in the sales documents this tax was not highlighted as a separate line, and payments were made non-cash.
“Tax reconstruction” rules
The Supreme Court had a different opinion, pointing out the omissions of lower authorities. He recalled that taxes must be calculated based on the actual economic content of transactions (clauses 7 and 1 of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation of October 12, 2006 No. 53). When distortions are identified, it is necessary to add the amount of tax that a bona fide taxpayer would pay in this situation, the economic board explained. She indicated that the amount of tax cannot depend on the form of payment (cash or non-cash). And the fact that the seller did not highlight value added tax as a separate line only indicates that he used the wrong tax regime, as stated in the determination in case No. A05-13684/2017. If VAT is not indicated in the documents, this does not mean that the buyer agrees to an increase in the contract price when the tax authorities make justified claims.
- Pay taxes, but stay in the black: a guide for a lawyer
September 30, 16:24
In order to “restore the course of events” and calculate the correct VAT, you must keep in mind that it is paid by the buyer. Thus, the amount of tax must be determined as if VAT was initially presented for payment to third-party contractors, that is, the tax should be allocated from the proceeds, the Supreme Court panel chaired by Marina Antonova indicated. Otherwise, according to the three judges, it turns out that the individual entrepreneur pays tax on unearned income. With such instructions, the case was sent for review to the 14th AAS.
According to Artyukh, this is “not just a positive, but also in many ways a significant definition for many taxpayers.” Artyukh is convinced that “it is necessary to punish with fines, and not with increased taxes.”
- Evgenia Efimenko
- Economy Board of the Armed Forces
What to do if a large amount of taxes has been assessed
Representatives of the government agency carry out additional assessments based on the results of establishing the correctness of pricing for transactions. Additional charges are made only when the transaction price deviates from market prices by more than 20%.
When increasing the amount of taxes, tax representatives must be guided by Article 40 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This is an article that establishes the principles for determining the cost of goods and services. This regulatory provision specifies the grounds for additional charges. In particular, this is the percentage of deviation from market prices.
If an entrepreneur does not agree with the additional accrual, he can challenge the decision on the grounds that the representatives violated the provisions of Article 40 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For example, paragraph 3 of Article 40 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is often violated. In this case, tax authorities do not set market prices. When recalculating the tax, the cost indicator is used. Such a decision is declared illegal (paragraph 4 of the Letter of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court No. 71).
Pre-trial procedure for challenging additional tax assessments
Tax legislation establishes ways to challenge decisions of tax authorities. Based on the results of the tax audit, the tax authority makes a decision to recalculate the tax base and tax amount. In accordance with Art. 138 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, such a decision can be appealed by subordination - to a higher tax office, and to the court.
An appeal of the decision of the tax authority made based on the results of an audit, in the order of subordination, must necessarily precede a judicial appeal.
To appeal the subordination of the tax authority’s decision, an appeal is filed with a higher tax authority. The complaint is submitted through the inspection which made a decision within 10 days from the date of delivery of the decision to the representative of the organization.
If the decision came into force and was not appealed in the order of subordination before the date of entry into force, it can be appealed within a year to the tax authority of the subject.
Complaints are considered within a month, and in some cases the period can be extended by 15 days to request documents from the tax office that made the decision being appealed by the organization.
The decision based on the results of consideration of the complaint is communicated within three days. At the same time, this decision can also be appealed in the order of subordination.
The powers of a higher tax authority when considering an appeal or other complaint against a decision based on the results of a tax audit include the possibility of canceling the decision, as well as changing it or adopting a new one.