Input data
In this material we will look at a simple example to understand how an individual entrepreneur should act when calculating taxes and contributions . Our entrepreneur will meet the following criteria:
- Pays tax at a rate of 6% , that is, it uses the simplified tax system with the object’s income.
- Does not attract hired workers.
- Does not work with individuals, therefore does not use a cash register. The contractors of the individual entrepreneur are entrepreneurs and legal entities with whom he pays through a bank account.
Rate of the simplified tax system “Income”
The tax rate shows how much percent of income the state will have to pay. In most cases it is 6%. But there are regions that have reduced the rate.
In Crimea and Sevastopol the rate is 4%. In Sevastopol, you can pay even less - 3%, if you run a business from the list of preferential activities. In the Chechen Republic, the tax rate depends on the number of employees and ranges from 1% to 6%.
In Moscow, St. Petersburg and Yekaterinburg, the simplified taxation system rate is standard - 6%.
Find out on the tax website in the section “Features of regional legislation” what rate is valid in your region.
What must be paid
An entrepreneur using the simplified tax system is exempt from paying many taxes:
- Personal income tax in relation to own income;
- VAT (with some exceptions, for example, on export transactions);
- Property tax applied when carrying out business activities (with the exception of real estate, which are taxed based on cadastral value).
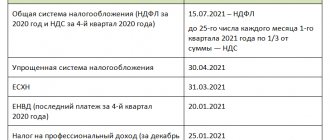
The only tax that a simplified entrepreneur who works independently pays is the tax in connection with the application of the simplified tax system. In our case, this is 6% of the income received. The tax is paid throughout the year in advance payments :
- for the first quarter - no later than April 25;
- for half a year - no later than July 25;
- for 9 months - no later than October 25.
The final payment is made at the end of the tax period (year) until April 30 of the following year.
The rule applies: if the last day of the payment deadline falls on a weekend, then this deadline is postponed to the first working day.
There are also sectoral taxes that are paid when carrying out specific activities (for example, water tax, mineral extraction tax and others). Their tax under the simplified tax system does not replace them.
In addition to taxes, individual entrepreneurs are required to pay insurance contributions to the Pension and Medical Funds . Starting this year, the amounts of contributions have been fixed, whereas previously they were tied to the minimum wage. For 2022, the entrepreneur must pay for himself:
- Pension insurance contributions : From income up to 300 thousand rubles - 32,448 rubles. Payable by December 31, 2022.
- For income exceeding 300 thousand rubles - 1%. Payable by July 1, 2022. A maximum has been set equal to 8 times the amount of fixed contributions from paragraph 1. That is, the maximum individual entrepreneur will pay is 32,448 * 8 = 259,584 rubles.
IP on simplified tax system 6%
Simplified taxation at a rate of 6% is applied by individual entrepreneurs on the same basis as other taxpayers (Article 346.12 of the Tax Code).
The exception is that for individual entrepreneurs there is no limit on the amount of income received for 9 months of the year for switching to the simplified tax system from the next tax period (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated March 1, 2013 No. 03-11-09/6114). However, it is necessary to meet the general limit of permissible income for the year.
For individual entrepreneurs, there is also a limitation on the number of employees and the residual value of fixed assets (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 01/20/2016 No. 03-11-11/1656, dated 03/27/2015 No. 03-11-12/16911, dated 02/13/2015 No. 03 -11-12/6555, dated 09/19/2014 No. 03-11-06/2/47029, dated 08/14/2013 No. 03-11-11/32974, Federal Tax Service dated 10/19/2018 No. SD-3-3/7457).
Those entrepreneurs who are engaged in the extraction and marketing of minerals (except for those that are widespread), manufacture excisable products, or have chosen a single agricultural tax are deprived of the right to take advantage of the simplified taxation system.
Also, those individual entrepreneurs who have not notified the tax authorities about the transition to a simplified tax system in accordance with the established paragraphs do not have the right to use the simplified tax system. 1 and 2 tbsp. 346.13 Tax Code of the Russian Federation deadlines.
For information on the procedure for notifying tax authorities when switching to the simplified tax system, read the article “Application for transition to the simplified tax system in 2022 - 2022 (sample)” .
Accounting
In terms of accounting, everything is quite simple. An individual entrepreneur does not keep accounts and does not submit annual financial statements. However, he is required to keep tax records. For this purpose, the entrepreneur must fill out a book of income and expenses for entities using the simplified taxation system. In it, the entrepreneur records all his income transactions.
Expenses of an individual entrepreneur on the simplified tax system with the object “income” are not taken into account, therefore column 5 of Section I of the accounting book is not filled out. However, it is necessary to reflect the insurance premiums paid in the book. They are reflected in Section IV.
Using the book of income and expenses, the individual entrepreneur calculates the tax payable in the reporting period. Information is entered into the book based on an extract from the current account.
Is it possible to reduce the minimum tax of the simplified tax system on insurance premiums?
If a company or entrepreneur is in a special regime with a 15% tax, then the simplifier is obliged to record the data of his commercial activities in the book of income and expenses.
If the expenses turn out to be significant and the tax is less than 1% of the total income for the entire reporting period, then the amount of tax must be paid based on the minimum tax rule - 1% of all revenue, even if the activity resulted in losses.
Tax under the simplified tax system is calculated based on the results of activities for the year. For companies and individual entrepreneurs with the simplified tax system, two payments are calculated at a rate of 15%:
- normal - according to the scheme, all revenue minus costs incurred, multiplied by the rate;
- minimum - 1% of revenue.
If the regular tax turns out to be less than the minimum, then the minimum tax is accepted for payment, from which the amount of payments made to the funds is in no way deducted.
However, you should know that:
- the difference between ordinary and minimum taxes can be included in expenses based on the results of the next reporting years;
- When the minimum payment is actually paid, advance contributions to the budget made during the reporting year are taken into account, and the overpayment is counted towards the payment of advance payments next year.
For more information about tax calculation under simplified conditions, read the article “Single tax under the simplified taxation system of the simplified tax system.”
Tax calculation
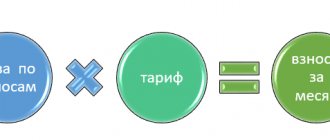
Calculating the advance tax payment is not difficult. It is calculated according to the formula: Advance payment = Tax base * 6 / 100, where the tax base is equal to the entrepreneur’s income for the reporting period on an accrual basis.
For example, an individual entrepreneur earned (cumulative income):
- for the first quarter - 0 rubles;
- for the first half of the year - 20 thousand rubles;
- for 9 months - 130 thousand rubles;
- for the year - 295 thousand rubles.
Advance payments (before deduction of insurance premiums) will be:
- for the first half of the year - 20,000 * 6 / 100 = 1,200 rubles;
- for 9 months - 130,000 * 6 / 100 = 7,800 rubles;
- for the year - 295,000 * 6 / 100 = 17,700 rubles;
Further, the advance payment can be reduced by the amount of insurance premiums paid during the period. The reduction mechanism is discussed in detail below. In addition, the tax payment is subject to reduction by the amount of advance payments previously paid in the year for previous periods. The formula takes the form:
Payment amount for the period = Advance payment for the period - Amount of contributions paid in the period - Advance payment paid for previous periods of the year
What counts as income
In terms of income accounting, there are the following rules:
- Income is accounted for on a cash basis. This means that they are recognized on the date they are actually received. The individual entrepreneur from our example receives his income to the bank, therefore, they are recognized on the date of receipt of funds into his current account.
Note! This rule also applies to prepayments against future deliveries. The entrepreneur must include this amount in his income on the date of receipt of the advance payment. If the transaction does not take place, that is, the advance payment is returned, this operation is reflected in the book of income and expenses in the period when the return was actually made. It must be indicated with a minus sign. Accordingly, this amount will reduce taxable income.
- Some types of income are not included in the taxable base , namely: Amounts of loans and borrowings, as well as amounts of funds received to repay loans and borrowings.
- Amounts of income that are subject to other tax rates. This includes bond coupons, dividends and other types of income.
- Amounts of income that are taxed in accordance with other taxation regimes. Often an entrepreneur combines two systems, for example, simplified tax system and UTII or simplified tax system and patent.
- Amounts of funds that are not income. This includes, for example, funds for the return of defective goods, erroneously credited by the bank or amounts transferred by the counterparty.
The following table shows a fragment of the Book of Income and Expenses of our individual entrepreneur for the first half of the year.
Table 5. Example of filling out Section I of the Income and Expense Accounting Book
| No. | Date and number of the primary document | Contents of operation | Income taken into account when calculating the tax base | Expenses taken into account when calculating the tax base |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 1 | 20.04.2021 № 1 | Payment under agreement dated 04/20/2021 No. 1 | 20000 | |
| 2 | 23.04.2021 № 2 | Prepayment under agreement dated 04/23/2021 No. 2 | 30000 | |
| 3 | 30.04.2021 № 3 | Refund of prepayment under agreement dated 04/23/2021 No. 2 | -30000 | |
| Total for the second quarter | 20000 | |||
| Total for the half year | 20000 |
Calculation of the simplified tax system when limits are exceeded from 2022
From 2022, the tax rate that the simplifier must apply will depend on the amount of income and the number of employees. If income does not exceed 164.4 million rubles, and the average number of employees does not exceed 100 people, pay tax at the current rate in the region - from 1 to 6%. If these values are exceeded, the tax rate under the simplified tax system for “income” increases to 8%, regardless of the presence of a reduced regional rate.
An increased rate of 8% may be applied until the organization loses the right to use the simplified tax system. In 2022, this occurs if the following conditions are violated:
- Revenues do not exceed 219.2 million rubles since the beginning of the year;
- The average number of employees for the reporting and tax periods does not exceed 130 people.
Increased rates must be applied from the beginning of the quarter in which revenues exceeded 164.4 million rubles or the number of employees exceeded 100 people. Advance payments for previous reporting periods do not need to be recalculated. The formula is as follows:
Advance payment for the period with excess = Income for the previous reporting period × 6% + (Income for the period with excess - Income for the previous reporting period × 8%) – tax deduction.
An example of calculating an advance payment at a rate of 8%
The income of Istochnik LLC in 2022 exceeded 164.4 million rubles. At the end of the first half of the year, revenue amounted to 110 million rubles, and at the end of 9 months, 170 million rubles. The advance payment for 9 months must be calculated at the increased tax rate of 8%.
Advance payment for 9 months: (110 million rubles × 6%) + ((170 million rubles - 110 million rubles) × 8%) = 11,400,000 rubles.
The accrued advance payment can be reduced by a tax deduction for insurance premiums paid for 9 months in the amount of 260,000 rubles. And also for advance payments paid for the 1st quarter and half of the year, in the amount of 6,600,000 rubles.
Advance payment for 9 months of 2022: 11,400,000 rubles - 6,600,000 rubles - 260,000 rubles = 4,540,000 rubles.
Thus, Istochnik LLC must pay an additional 4,540,000 rubles by October 25, 2022.
For calculating tax at the end of the year, the procedure is almost the same. Divide the tax base between the periods in which you applied standard and increased rates. To receive additional tax at the end of the year, reduce it by advance payments and tax deductions.
An example of calculating tax for the year at a rate of 8%
At the end of the year, Glubina LLC earned 190 million rubles. Income for the first half of the year amounted to 120 million rubles, for 9 months - 165 million rubles.
Tax at the end of 2022: (120 million rubles × 6%) + ((190 million rubles - 120 million rubles) × 8%) = 12,800,000 rubles.
The assessed tax can be reduced by advance payments paid during the year.
Amount of tax to be paid additionally for 2022: 120,000 = 2,000,000 rubles. Additionally, this amount can be reduced by deductions.
Calculation of insurance premiums
For the year in which the entrepreneur registered, he must pay contributions not in full, but in proportion to the number of days that he was considered an individual entrepreneur . Let's say it is entered into the register on April 16, 2022 . This means that in 2022 he is an entrepreneur for 8 full months and another 15 days of April. The calculation will be as follows:
- Pension contributions from income up to 300 thousand rubles:
- 32448 / 12 * 8 = 21632.00 rubles - for 8 months of 2022;
- 32448 / 12 / 30 * 15 = 1352.00 rubles - for 15 days of April;
- 21632.00+1352.00=22984.00 rubles - total in the Pension Fund.
- Medical fees:
- 8426 / 12 * 8 = 5617.33 rubles - for 8 months of 2022;
- 8426 / 12 / 30 * 15 = 351.08 rubles - for 15 days of April;
- 5617.33+351.08=5969.00 rubles - total in the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
In total, an individual entrepreneur registered on April 16, 2022, for this year must pay up to 300 thousand contributions on income in the amount of 22984.00 + 5969.00 = 28953.00 rubles .
Features of paying insurance premiums to deduct their amount from advance payments
An individual entrepreneur without employees has the right to reduce advance tax payments by the amount of insurance premiums that he paid in the tax (reporting) period . Moreover, the tax amount can be reduced down to zero. In other words, if during the reporting period the entrepreneur’s income was small, and the contributions paid completely covered it, he may not pay tax.
The rules for reducing the advance payment are as follows:
- It is reduced within the calculated amount . That is, if the contributions paid are greater than the amount of the advance payment, the tax cannot go negative. Let’s say the advance payment is 15 thousand rubles, and the amount of contributions paid is 17 thousand rubles. The payment will decrease by 15 thousand and will be equal to zero, and the “extra” 2 thousand rubles will not be transferred and will not be compensated.
- It is reduced by the amount actually paid during that period , not calculated for the period. It does not matter for what period the tax was paid - for the current period (advance payment), for the tax year (surcharge on income over 300 thousand rubles) or for previous years (payment of debt). For example, in May 2021, an entrepreneur made an additional tax payment for 2022 on income exceeding 300 thousand rubles. By this amount, the entrepreneur will be able to reduce the advance tax payment for the first half of 2021.
Let's look at how paying contributions affects the amount of the advance payment. 20,000 rubles in April . Let's assume that he doesn't expect more income for the first half of the year. The amount of the advance tax payment for the tax for the first half of the year will be 20,000 / 100 * 6 = 1,200 rubles.
Above, we calculated that by the end of the year the individual entrepreneur must pay 28,953.00 rubles in insurance premiums. Our entrepreneur decided in April to pay 1,200 rubles towards contributions, thereby reducing the amount of the advance tax payment to zero.
Now let’s say that by the end of the summer the business of the individual entrepreneur went uphill and he managed to earn money every month from August to December. At the same time, he paid the remaining amount of insurance premiums in equal installments every month (except for April). The data is presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Income and contributions of individual entrepreneurs by month
| Month | Income | Paid dues |
| April | 20 000 | 1 200 |
| May | — | 3 469 |
| June | — | 3 469 |
| Total for six months | 20 000 | 8 138 |
| July | — | 3 469 |
| August | 50 000 | 3 469 |
| September | 60 000 | 3 469 |
| Total for 9 months | 130 000 | 18 545 |
| October | 40 000 | 3 469 |
| november | 45 000 | 3 469 |
| December | 80 000 | 3 469 |
| Total for the year | 295 000 | 28 953 |
In Table 2, individual entrepreneurs’ income, advance tax payments and contributions paid are presented as a cumulative total.
Table 2. Income, contributions and tax amounts by period (cumulative total)
| Period | Income | Advance tax payment (6%) | Actual contributions paid | Tax payment for the period taking into account contributions |
| I quarter | — | — | — | — |
| Half year | 20 000 | 1 200 | 8 138* | 0 |
| 9 months | 130 000 | 7 800 | 18 545* | 0 |
| Year | 295 000 | 17700 | 28 953* | 0 |
*The amount of contributions paid exceeds the amount of the advance tax payment.
Now let's see what would happen if the individual entrepreneur did not pay contributions from May to August, deciding to leave them at the end of the year. The calculation results are in Table 3.
Table 3. Other procedure for paying contributions
| Month | Income | Paid dues |
| April | 20 000 | 1 200 |
| May | — | — |
| June | — | — |
| Total for six months | 20 000 | 1 200 |
| July | — | — |
| August | 50 000 | — |
| September | 60 000 | 5 000 |
| Total for 9 months | 130 000 | 6 200 |
| October | 40 000 | 5 000 |
| november | 45 000 | 5 000 |
| December | 80 000 | 12 753 |
| Total for the year | 295 000 | 28 953 |
Cumulative data and advance tax amounts are in Table 4.
Table 4. Income, contributions and tax amounts by period (cumulative total)
| Period | Income | Advance tax payment | Paid dues | Payment amount for the period |
| I quarter | — | — | — | — |
| Half year | 20 000 | 1 200 | 1 200* | 0 |
| 9 months | 130 000 | 7 800 | 6 200** | 400 (7800—6200-1200) |
| Year | 295 000 | 17700 | 28 953* | 0 |
*The amount of contributions paid exceeds the amount of the advance tax payment.
**The amount of contributions paid is less than the amount of the advance tax payment.
This table shows that the total amount of contributions for the year exceeded the amount of tax. However, over the 9-month period, the individual entrepreneur received tax due, since the contributions at that time were paid less than the amount of the advance payment.
How to reduce the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses”
First of all, the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses” reduces expenses. Remember that not all expenses can be taken into account when calculating tax. The list of allowable expenses is contained in Section 346.16 of the Internal Revenue Code. Expenses that cannot be attributed to any type from the list should not be taken into account in the tax. Read more in the article “Costs on the simplified tax system”.
Accounting for minimum tax in expenses
If last year you paid the minimum tax (1% of income), then when calculating the tax for this year, you can take into account in expenses the amount by which the minimum tax exceeded the single tax of the simplified tax system.
For example: Income for last year: 600,000 ₽; Expenses: 595,000 ₽. Single tax simplified tax system = (600,000 - 595,000) × 15% = 750 rubles. Minimum tax = 600,000 × 1% = 6,000 ₽. We paid the minimum tax, because... it is 5,250 ₽ more.
When calculating the tax for this year, 5,250 ₽ can be taken into account in expenses.
Let's calculate the tax for the current year: Income: 500,000 ₽, Expenses: 450,000 ₽. Tax simplified tax system without taking into account the minimum tax: (500,000 - 450,000) × 15% = 7,500 rubles. Let's write off the excess of the minimum tax as expenses: (500,000 - 450,000 - 5,250) ×15% = 6,713 rubles. The savings amounted to 787 ₽.
Controlling authorities allow the minimum tax to be taken into account only at the end of the year. In most cases, the courts support them, although there is legal precedent in favor of reducing the advance payment for the quarter. Elba will help you correctly calculate tax taking into account expenses, and remind you of the deadlines for payment and reporting.
Write off losses as expenses
You can reduce your tax even further by using losses incurred in previous years. To do this, you can use losses for the last 10 years and not yet used to reduce taxes.
For example: Loss last year: 50,000 ₽; Minimum tax last year: 10,000 rubles. Income for this year: 800,000 ₽; Expenses for this year: 300,000 rubles.
Because last year there was a loss, the simplified tax system was 0, and I had to pay the minimum tax; this year you can write off the amount of the loss and the amount of the minimum tax as expenses:
Tax simplified tax system = (800,000 - 300,000 - 10,000 - 50,000) x 15% = 66,000 rubles.
The savings amounted to 9,000 rubles.
The earliest losses should be written off first, but no more than the previous 10 years. Losses can be used to reduce tax only when calculating the final payment for the year. Advance payments cannot be reduced due to losses.
Payment of taxes and contributions
An individual entrepreneur pays all payments for himself according to the details of the tax office . To generate a payment invoice, you can use the official service of the Federal Tax Service. The first thing you need to know from the details is the budget classification code. Using it, the service can independently determine the type and name of payment. The individual entrepreneur must have all other details in the documents from the tax office and the Pension Fund.
Entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system of 6% should use the following codes (2021):
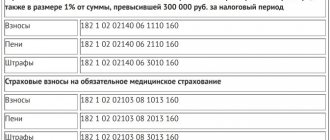
- for tax payment - KBK 182 10500 110;
- to pay contributions to the Pension Fund - 182 10210 160;
- to pay contributions to the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund - 182 10213 160.
The generated payment order can be taken to the bank or used as a template for filling out a payment order in Internet banking.
Details for paying tax on the “income” object in 2021–2022
- In field 101 “Taxpayer status” indicate 13 - the value for individual entrepreneurs (according to the new rules) or 01 - for companies.
- In field 18 “Type of operation” enter 01.
- In field 21 “Payment order” indicate 5.
- In field 22 “Code”, select 0 (when paying tax or advance payment) or the code specified in the Federal Tax Service’s requirement.
- In field 24 “Purpose of payment” write: “Advance payment” or “Payment of the simplified tax system for the object “income””.
- In field 104 “KBK” enter 182 1 0500 110.
- In field 105 “OKTMO” the code is indicated in accordance with the territorial affiliation of the individual entrepreneur or company.
- In field 106 “Base of payment”, select depending on the specific situation: TP (current payments), PD (payment of debt).
- In field 107 “Tax period” indicate the corresponding period for which payment is made: GD.00.2021, KV.01.2022, KV.02.2022, KV.03.2022. The next years will be similar.
- In field 108 “Document number” enter 0 for payment of tax and advances. In case of payment based on penalties from the Federal Tax Service, the tax authorities’ request number. At the same time, according to the new rules, a letter code must be placed in front of the number - the basis for the payment (for example, TR for payment of a claim, AR for payment under a writ of execution).
- In field 109 “Document date” enter 0 (when paying an advance); when paying tax - the date of signing the declaration submitted to the Federal Tax Service. When paying on demand, the tax office will indicate the date of the demand.
The easiest way to find details for paying taxes in 2022 is on the Federal Tax Service website. There is a special service there. We talked about it in more detail here.
You can see samples of payment orders for paying tax under the simplified tax system with the object “income” in the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. Get trial access to K+, it's free.
About the rules for maintaining a register necessary for calculating tax under the simplified tax system, read the material “How to keep a book of income and expenses under the simplified tax system (sample)?” .
Reporting
Individual entrepreneur reporting on the simplified tax system without employees is as simple as possible. He must submit a declaration once a year before April 30 of the year following the reporting year. We have devoted a separate article to the detailed filling out of the declaration under the simplified tax system of 6%.
You should not violate the deadlines for filing a declaration, since this can result in a fine of 5% of the amount of unpaid tax for each full or partial month of delay. In this case, the fine will be no less than 1 thousand rubles , but not more than 30% of the tax amount. In addition, the tax authority may decide to suspend operations on the entrepreneur’s current account if the declaration is not received by the Federal Tax Service 10 days after the deadline for filing.
In addition, theoretically, the tax office may request the entrepreneur to check the book of income and expenses.
Since the individual entrepreneur does not have employees, he does not submit reports related to them. I must say, this is quite an impressive volume of all kinds of forms, and some need to be submitted monthly. The entrepreneur also does not report for his own contributions to compulsory health insurance and compulsory medical insurance.
How to reduce the simplified tax system “Income”
An entrepreneur's income always increases the tax amount. But not all receipts are income: replenishment of an individual entrepreneur’s account with personal money, chargebacks, loans and borrowings. Such income does not need to be taken into account when calculating the simplified tax system. We talked about this in more detail in the article “STS “Income”: how to report and how much to pay.”
Reducing the simplified tax system on insurance premiums
Tax on the simplified tax system “Income” can be reduced by insurance premiums. To do this, follow three rules:
- Individual entrepreneurs without employees can reduce the tax completely, and individual entrepreneurs with employees and LLCs can reduce the tax by no more than 50% of the tax amount.
- The tax is reduced by: – insurance premiums of individual entrepreneurs for themselves: 43,211 rubles for 2022 + 1% of income more than 300,000 rubles; – contributions for employees to the tax office for pensions, medical and social insurance, as well as to the Social Insurance Fund for injuries; – sick leave for the employee for the first three days.
- Contributions must be paid in the same period for which you calculate the tax. For example, the tax for the first quarter can be reduced by insurance premiums paid from January 1 to March 31. It does not matter for what period the contributions were paid.
We recommend paying individual entrepreneur insurance premiums for yourself quarterly. This way you will evenly reduce advance payments for the simplified tax system, and by the end of the year you will not be able to overpay.
Elba will tell you how much to pay in contributions and how to reduce taxes. The service will automatically calculate the tax payable and prepare a declaration according to the simplified tax system along with a book of income and expenses.
Reducing the simplified tax system for trade tax in Moscow
Individual entrepreneurs and LLCs that are registered in Moscow can reduce the trade tax. If you trade in the capital, but are registered in another region, you will have to pay tax in full.
The simplified tax system tax is completely reduced by the trade fee. The 50% limit as a reduction in insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs with employees and organizations does not apply, because the tax is reduced in addition to the amount of insurance premiums. The final amount of tax payable may be zero even for the organization and the individual employer.