Business lawyer > Accounting > Taxes > Deduction code 104 and other codes for personal income tax
Taxes. Deduction codes
Taxes are what the financial viability of the state rests on. The richer the country, the higher the salaries of its citizens, and, consequently, taxes - the basis of prosperous and non-prosperous countries. If the state advocates that people pay taxes, the population would be happy to refuse them. But such is the system, its tax component is one of the pillars that supports our well-being.
In tax law there is such a thing as a deduction code. It is always associated with personal income tax. The state sets the amount of this tax. It is equal to 13%. Knowing this, every citizen of the Russian Federation can make independent calculations and get a figure that will be deducted from their salary as income tax. However, deduction codes change everything.
Tax deduction codes: table description
Let's consider frequently used tax deduction codes when filling out the 2-NDFL certificate (from 2022, instead of the 2-NDFL certificate, an application is filled out as part of the 6-NDFL calculation):
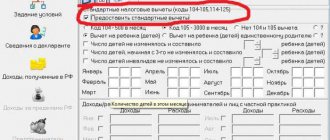
- 126 - code that is indicated when providing a standard deduction for a child under 18 years of age or a full-time student under 24 years of age in the amount of 1,400 rubles.
- 127 - standard deduction in the same amount provided for the 2nd child.
- 311 - property deduction for the purchase of housing, if the employee has expressed a desire to receive this deduction through the employer.
- 320 - social deduction for employee expenses on their own training.
- 321 - social tax for children's education.
ATTENTION! If an employee has brought several notifications, for example, about the right to property and social deductions, a separate page of the 2-NDFL certificate is filled out for each of them. On the second and subsequent pages, only the fields “TIN”, “KPP”, “Page”, “Certificate number”, “Reporting year”, “Characteristic”, “Adjustment number”, “Submitted to the tax authority (code)” are filled in. “Notification type code”, “Notification number”, “Date of issue of the notification” and “Code of the tax authority that issued the notification”.
Validity period for personal income tax certificate 2 for tax deduction
If a form is required for calculating a tax deduction when purchasing an apartment, the period of its legal validity is established by the regulatory authority. This certificate is included in the mandatory list of documents confirming the right to receive compensation for part of the previously paid personal income tax after purchasing real estate. In addition, you must provide:
- Declaration of income in the prescribed form;
- Confirmation of ownership of real estate;
- Identification;
- The mortgage agreement and all payment orders confirming the amount of expenses for the purchase of real estate or the payment of interest on the loan.
If property is acquired as joint property by spouses, then it is also necessary to send an application for the distribution of personal income tax compensation to the tax authority at the place of registration.
You should also take into account when the property for which the deduction is issued was acquired. If the purchase took place before 2014, then the right to compensation for part of the costs can only be used once. If the acquisition was in later years, then there are no such restrictions.
The maximum deduction amount is 260 thousand rubles for expenses on the purchase of real estate and 390 thousand when paying interest on a loan. If the applicant does not have enough income in one year to receive the required personal income tax compensation, he has the right to receive additional income in subsequent periods.
In conclusion, it should be noted that you can receive tax compensation in two ways - through the employer and to the Federal Tax Service, but all documents, including the described certificate, which contains information about the organization and the individual, must first still be submitted to the regulatory authority. When receiving a tax refund through an employer, you should receive a notice of the right to deduction and then present it to the accounting department. In the second case, you just need to wait for the funds to be transferred to the details specified in the application.
What are tax deduction codes for?
The tax deduction code is a digital code. A deduction is an amount that, if there are documented grounds, can be reasonably deducted from the tax base, thereby reducing not only it, but also the amount of tax accrued from this base.
The deduction code is required when filling out Appendix No. 1 to the calculation of 6-NDFL, an employee:
- a tax agent reporting form on the payment of income and the amount of tax withheld from it;
- tax agent reporting form on unwithheld tax on income paid;
- a document confirming the amount and types of income received by the taxpayer at the place of work, and the amount of personal income tax paid by him when applying to various authorities (for example, for a new job, to the Federal Tax Service, bank).
Find out whether the deduction code should be indicated in the application for its receipt from the sample compiled by ConsultantPlus experts, having received trial access to the system.
How to calculate tax: deductions and their application
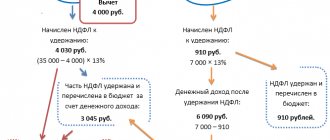
To calculate the tax amount, you need to subtract the deduction amount from the taxable base. In the case of deduction code 104, it will look like this: (salary amount - 500 rubles) * 13%.
In other words, if an employee is paid a salary of 10,000 rubles, and is entitled to a deduction of 500 rubles, then the employee can easily check the correctness of the tax calculation.
To do this, you need to subtract the deduction amount from your salary. That is:
10,000 – 500 = 9,500 rubles.
Now 9500 * 13% = 1235 rubles. This is the amount of tax that should be withheld.
That is, a tax deduction of 500 rubles monthly helps an employee receive 65 rubles. It is by this amount that the transferred tax is reduced.
Which deduction table is used in 2021-2022?
The last time adjustments to the table of deductions were made by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 28, 2021 No. ED-7-11 / [email protected] The following changes occurred in it:
- added code 280 - bet amount, which reduces the amount of winnings;
- added code 323 - the cost of medicines purchased by the taxpayer;
- code 324 has been changed - cost of medical services;
- added code 329 - fitness expenses;
- “WWII home front workers” was added to code 507;
- added code 511 - deductions from income in the form of winnings;
- code 512 has been added - a deduction from the amounts of financial assistance provided by an organization carrying out educational activities in basic professional educational programs.
Structure of the new table of deduction codes
The table of deduction codes consists of 14 sections named by types of deductions, and 1 additional code 620, which includes other types of deductions not listed in the table.
The sequence of sections and numbering of codes in them is as follows:
- standard deductions under Art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 104, 105,126–149;
- reducing the base according to Art. 214.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 201–203, 205–210;
- reducing the base according to Art. 214.3 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 211, 213;
- reducing the base according to Art. 214.4 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 215–220; 222–241;
- reducing the base according to Art. 214.7 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - code 280;
- reducing the base according to Art. 214.9 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 250–252;
- property deductions under Art. 220 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 311, 312;
- social according to clause 2 p. 1 art. 219 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 320, 321;
- social according to clause 3 p. 1 art. 219 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 323–326;
- social according to clause 4 paragraphs 1 art. 219 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - code 327;
- social according to clause 5 p. 1 art. 219 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 328;
- professional deductions under Art. 221 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 403–405;
- deductions for non-taxable income under Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 501–512;
- reducing the base according to Art. 214 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - code 601;
- investment deductions under Art. 219.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - code 618-619;
- other deductions - code 620.
The table ends with 5 notes referring to the document details on the basis of which social deductions should be applied.
What has changed in the list of deduction codes?
The new table of deduction codes has retained the main set of codes used in the old table, but at the same time a number of codes have been excluded from it, new ones have been added, old codes have been replaced with new ones, and deduction description texts have been adjusted.
Broken down by type of deduction, the changes look like this:
- Standard codes - excludes codes 114-125. Codes 126–149 have been introduced instead. Now they differ depending on who the deduction is provided to: natural parents (adoptive parents) or persons who replace them.
- Reducing the base according to Art. 214.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (transactions with securities and financial instruments of forward transactions) - in codes 205–207, instead of expenses on operations with financial instruments of forward transactions, expenses on operations with derivative financial instruments are now indicated, and codes 209–210 reflect no loss on operations with financial instruments of futures transactions, and losses on transactions with derivative financial instruments. Additionally, code 208 was introduced, which reflects losses on transactions with derivative financial instruments.
- Reducing the tax base for securities lending transactions in accordance with Art. 214.4 - instead of code 221, which was used to reflect the amount of expenses on transactions with securities accounted for in an individual investment account, codes 225–252 were introduced. Codes 250–252 have been added, reducing the tax base for transactions accounted for on an individual investment account in accordance with Art. 214.9 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- From investment tax deductions provided for in Art. 219.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, code 617 is excluded.
Standard deduction codes 104, 105, 126–149 in the 2-NDFL certificate
These deduction codes, which give the employee the right to a personal deduction either due to special merits or because he has children, are most often included in the 2-NDFL certificate. In the new table, those that have been used since 2012 are kept unchanged. They are divided into the following groups:
- codes 104 and 105 - personal deductions in the amount of 500 rubles. and 3,000 rubles, provided to a person who has special services to the country (combatants, liquidators of accidents at nuclear facilities, holders of state awards);
- deduction codes 126, 127, 128 - presented to parents, spouse of a parent, adoptive parent for the 1st, 2nd, 3rd (and subsequent) children under the age of 18 years or up to 24 years old if the child is studying;
- code 129 - for a deduction provided to the parent, spouse of the parent, adoptive parent, who is supporting a child under the age of 18 years or up to 24 years old, if the child is a disabled person of group I or II;
- codes 130, 131, 132 - deductions for a child under 18 years of age or up to 24 years of age if the child is studying; deductions are submitted to the guardian, trustee, adoptive parent, spouse of the adoptive parent;
- code 133 - for a deduction for a guardian, trustee, foster parent, spouse of a foster parent who is supporting a child under the age of 18 or under 24 years if the child is a disabled person of group I or II;
- codes 134, 136, 138 - double deduction presented to the only parent, adoptive parent for the 1st, 2nd, 3rd (and each subsequent) child under the age of 18 years or up to 24 years old if the child is studying;
- codes 135, 137, 139 - double deduction presented to the sole guardian, trustee, foster parent, adoptive parent for the 1st, 2nd, 3rd child under the age of 18 years or up to 24 years old if the child is studying;
- code 140 - for a double deduction provided to the only parent, the adoptive parent, who is supporting a child under the age of 18 or up to 24 years, if the child is a disabled person of group I or II;
- code 141 - double deduction provided to the sole guardian, trustee, foster parent who is supporting a child under the age of 18 or up to 24 years if the child is a disabled person of group I or II;
- codes 142, 144, 146 - double deductions for the 1st, 2nd, 3rd (and subsequent) children under the age of 18 years or 24 years old if the child is studying; such deductions are presented to one of the parents of their choice on the basis of an application for the refusal of the second parent to receive a tax deduction;
- codes 143, 145, 147 - double deductions for the 1st, 2nd, 3rd (and subsequent) children under the age of 18 years or 24 years old if the child is studying; deductions are presented to one of the adoptive parents of their choice on the basis of a statement of refusal of the second adoptive parent to receive a tax deduction;
- code 148 - double deduction for a disabled child under the age of 18 or a student under the age of 24 who is a group I or II disabled person, which is presented to one of the parents of their choice on the basis of an application for the second parent’s refusal to receive a tax deduction;
- code 149 - double deduction for a disabled child under the age of 18 or a student under the age of 24 who is a group I or II disabled person, who is presented to one of the adoptive parents of their choice on the basis of an application for the refusal of the second adoptive parent to receive a tax deduction .
For all the deductions to which a taxpayer with children is entitled, read the article “Tax deductions for children in 2022 (personal income tax, etc.) .
If you find it difficult to provide a deduction to an employee in a particular situation, use free access to ConsultantPlus and go to the Ready Solution.
Property deduction codes
There are 2 main types of property deductions related to the purchase of housing, which, with permission obtained from the Federal Tax Service, can be fully used at work:
- code 311 - deduction for direct expenses on the purchase or construction of housing;
- code 312 - deduction for interest paid for a mortgage related to the acquisition of housing, which also takes into account interest paid when refinancing mortgage loans.
To learn how to get a deduction for an apartment purchased with a mortgage, read the material “Tax deduction when purchasing an apartment with a mortgage (nuances)” .
What are deduction codes?
The legislation of the Russian Federation considers the circumstances due to which the tax base of a particular person can be changed due to deduction codes. Since circumstances can be very different, there are many codes. All of them are divided into six main categories:
- Standard – circumstances such as whether the taxpayer has children or special services to the state are considered.
- Social – the circumstances of the need for training, treatment, etc. are considered. We can talk about the taxpayer or relatives who are financially dependent on him.
- Property – the presence of a mortgage or housing construction are considered.
- For non-taxable income - this includes prizes, gifts, certain types of financial assistance, etc.
- Professional - these are royalties, expenses for creating a literary work, etc.
- Investment is the rarest category, relating mostly to those who work in the securities market.
The state returns deductions to the population only in cases where the conditions are met and documentary justification for the return of part of the personal income tax is provided.
In order to obtain the right to a deduction, the taxpayer must not only have a reason, but also a documented justification for it.
Social deduction codes
Since 2016, in a manner similar to the provision of property deductions (with a permit issued by the Federal Tax Service after checking documents confirming the right to deduction), it is possible to receive social deductions at the place of work. Their codes have not changed:
- code 320 - deduction for expenses for own education or full-time education of a sister (brother) under the age of 24;
- code 321 - deduction for expenses for full-time education of children (including foster children or wards) under the age of 24 years;
- code 324 - deduction for medical expenses for yourself, your spouse, parents or children (including adopted or warded children) under the age of 18;
- code 325 - deduction for contributions paid for voluntary health insurance for oneself, spouse, parents or children (including adopted or warded) under the age of 18;
- code 326 - deduction for expenses for expensive treatment;
- code 327 - deduction for expenses on paying contributions to non-state pension funds or under long-term voluntary life insurance contracts for yourself, your family members, close relatives;
- code 328 - deduction for additionally paid by the taxpayer savings contributions to the Pension Fund.
See also “Documents for obtaining a tax deduction for treatment” and “Application for a personal income tax refund for education - sample and form.”
For whom the deduction code 104 is entered
This mechanism was introduced by the state for additional support for citizens who have a special status and are listed in Article 218 (clause 1 subsection 2) of the Tax Code of Russia. These include:
- Heroes of the Russian Federation and the USSR, holders of the Order of Glory;
- participants in combat operations to defend the USSR, including WWII veterans and partisans;
- residents of besieged Leningrad, prisoners of concentration camps;
- persons affected by radiation as a result of accidents at military and civilian facilities, during testing, experiments, and scientific work;
- doctors, junior and nursing staff who worked at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in the period from April 26 to June 30, 1986;
- spouses and parents of military personnel who died defending the USSR and Russia.
The deduction can be used by citizens who donated bone marrow in the name of saving other people, as well as persons who were injured during the performance of their professional duties after the Chernobyl accident, and some other categories of the population.
Deduction codes for non-taxable income
Deductions for non-taxable income have not changed. However, they also appear in the 2-NDFL certificate quite often, so it makes sense to recall their list:
- codes 501 and 502 - deductions for the value of gifts given at work and prizes received at competitions;
- codes 503 and 504 - deductions for payment of financial assistance to employees and reimbursement of the cost of medicines;
- code 505 - deduction for prizes received as a result of participation in promotional events;
- code 506 - deduction for financial assistance paid to a disabled person by a public organization of disabled people;
- code 507 - deduction for financial assistance or gift given to a WWII participant;
- code 508 - deduction for financial assistance at the birth (adoption) of a child.
- code 509 - deduction for income issued by products to an employee of an agricultural producer;
- code 510 - deduction for additional savings contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation paid by the employer for the taxpayer.
Investment deduction codes
The bulk of these deductions are associated with operations that have a fairly limited distribution. Their codes are used by professional participants in the securities market to compile 2-NDFL certificates. Most regular employers do not require these codes.
Among this group, only deduction code 601 for dividend income may be of interest to an ordinary employer. From January 2022, as noted above, a new investment deduction with code 619 was introduced.
Results
Deductions allow you to reduce the tax base for personal income tax. All deductions are encrypted with special codes, which are recorded in the 2-NDFL certificate. The last code update was at the end of 2022.
Sources:
- Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 10, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 28, 2021 No. ED-7-11/ [email protected]
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.