What are the income and deduction codes for personal income tax in 2022:? A table with codes and explanations is given in this article. In different tables with decoding codes of income and deductions for personal income tax for 2020.
Also see:
- Certificate form 2-NLFL in 2022
- New deadlines for submitting 2-NDFL in 2022
Appendix to the 2-NDFL certificate in 2022
The appendix to the 2-NDFL certificate must be filled out separately for each tax rate (clause 1.19 of the Procedure for filling out the 2-NDFL certificate). It states:
- income that you paid to an individual in cash and in kind, as well as in the form of material benefits;
- tax deductions from these incomes provided to individuals (except for standard, social and property ones).
The fields of the Appendix to the certificate are filled in as follows:
- in the “Month” field – the serial number of the month;
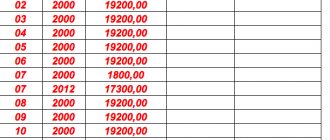
- in the “Income code” field – a code depending on the type of income of an individual (for example, the code for salary is 2000, the code for vacation pay is 2012);
- in the “Amount of Income” field – the entire amount of income accrued and actually received by an individual this month;
- in the “Deduction Code” field – the code corresponding to the deduction provided (for example, the code for deduction from the cost of a gift is 501);
- in the “Deduction Amount” field – the amount of the deduction provided. It cannot exceed the amount of the relevant income.
Here's an example:
Who should pay personal income tax on income in kind?
If income in kind was received from an individual who is not registered as an entrepreneur, then the individual who received such income must report personal income tax to the tax authority and make payments for it. This conclusion is based on the provisions of paragraph 1 of Art. 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which states that individuals who are the source of income are not tax agents, which means they are not obliged to withhold and pay personal income tax on income received by other individuals.
For more information about who is recognized as a tax agent for personal income tax and what his responsibilities are, read the material “Tax agent for personal income tax: who is, responsibilities and BCC.”
If income in kind was issued to an individual by an organization or entrepreneur, then there are 2 possible scenarios:
- The organization or entrepreneur, in addition to income in kind, paid the individual income in cash. In this case, she must fulfill the duties of a tax agent, i.e. calculate personal income tax on income in kind, withhold it from income paid in cash (clause 4 of article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), transfer the withheld tax to the budget and report to the tax authorities on the amounts of calculated, withheld and paid personal income tax.
NOTE! The amount of personal income tax withheld from the cash income of an individual to pay off personal income tax debt calculated from the natural income of the same individual should not be more than half of the individual’s income paid in cash (Clause 4, Article 226).
How to correctly calculate the amount of personal income tax? What reporting should I submit for this tax? When should I pay it to the tax authorities? You will find answers to these questions in our article “General procedure for calculating and paying personal income tax.”
- The income was paid only in kind, or, more precisely, after the payment of income in kind, payment of income in cash to an individual was not made until the end of the current year. In this situation, the obligation to pay personal income tax and submit a declaration with its calculation passes to the individual due to the fact that the organization (IP) is physically unable to withhold tax on natural income in cash equivalent.
But at the same time, the organization (IP) is obliged to inform the tax office and the taxpayer about the amount of calculated tax and the impossibility of withholding it. The message must be submitted in the form of form 2-NDFL with sign 2. The deadline for submitting this message is until March 1 of the year following the tax period in which the income in kind was issued (clause 5 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the tax will be paid by the “physicist” himself, having received a corresponding notification from the tax authorities.
A third situation is also possible, when to pay the tax calculated on the natural income of an individual, there is not enough money withheld from the cash income of the same individual. We decided to give an explanation of how to proceed in this case in the form of an example presented below.
Condition
In March 2022, Sigma LLC presented S.P. Zaitsev with a laptop worth 35,000 rubles as a gift. That is, the employee received income in kind. The organization must collect and pay personal income tax from the income received. But not from the entire amount of income, but minus 4,000 rubles. (note: gifts worth up to 4,000 rubles are not subject to personal income tax, clause 28 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In addition to the gift, in March 2020, the employee received a salary in cash in the amount of 7,000 rubles, and then quit. Standard deductions are not provided to S.P. Zaitsev, who works part-time at Sigma LLC. The employee did not receive any more money until the end of the year.
Calculation
The amount of personal income tax that an employer must withhold from in-kind income received in the form of a laptop is 4,030 rubles: (35,000 – 4,000) × 13%.
The amount of personal income tax that the employer must withhold from cash income is 910 rubles: 7,000 × 13%.
The amount of cash income minus personal income tax on it was 6,090 rubles: 7,000 – 910.
In March, the employer withheld from the income of S.P. Zaitsev to pay personal income tax on income in kind (laptop) the amount of 3,045 rubles: 6,090 × 50%.
The balance of the personal income tax debt from the laptop as of the end of March was 985 rubles: 4,030 – 3,045.
At the end of the tax period (2020), the organization sent a message to the tax inspectorate and S.P. Zaitsev about the impossibility of withholding the amount of personal income tax from natural income in the amount of 985 rubles. Tax authorities should also be notified of this fact.
Find out how to inform the Federal Tax Service about the impossibility of withholding personal income tax from an employee’s income in ConsultantPlus. Get free demo access to K+ and go to the Ready Solution to find out all the details of this procedure.
Income codes for 2-NDFL in 2022: decoding
Here are the main income codes that need to be reflected in the 2-NDFL certificate:
- 2000 - salary;
- 2012 - vacation pay;
- 2300 - temporary disability benefit;
- 2002 - award for production results;
- 2010—payments under GPC agreements (except for copyright ones);
- 1010 — dividends;
- 2013 - compensation for unused vacation.
The full list with a transcript is given in Appendix No. 1 to the Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 10, 2015 N ММВ-7-11/
Is it necessary to indicate the BL in the document and in what cases?
Let's consider whether sick leave is included in the 2-NDFL certificate, whether it is necessary to indicate BL in the report and in what cases this should be done. Average earnings are due only to those employees who were absent from work for a valid reason. Confirmation of the disease is a sick leave certificate.
Important! The accountant calculates the benefit within 10 calendar days from the date of submission of the document, and pays the accrued amount along with the next salary.
Such payments are subject to personal income tax and are mandatory reflected in the 2-NDFL report.
The list of the following insured events obliges the employer to pay temporary disability benefits and include withheld tax amounts in the report:
- Examination and testing.
- Treatment in a sanatorium after hospitalization.
Why sometimes the BL is not included in the reporting?
You can get sick leave at a medical institution not only due to illness, but also in case of pregnancy. The right of a woman working under an employment contract to receive maternity benefits through her employer is established by law. According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the BIR allowance is included in the list of payments not subject to any taxes. It is not necessary to include such payments in full in the 2-NDFL report.
Deduction codes in section 3 of the help
In Sect. 3 certificates 2-NDFL reflect standard, property, social deductions and data on notifications issued by the tax authority. Deduction codes must be selected from Appendix No. 2 to the Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 10, 2015 N ММВ-7-11/ Let's give examples:
- 126 - standard deduction to the parent (adoptive parent) for the first child;
- 127 - standard deduction to the parent (adoptive parent) for the second child;
- 311 - property deduction for the purchase of housing;
- 312 - property deduction for interest on a loan for the purchase of housing;
- 320 - social deduction for the employee’s expenses for his training;
- 321 - social deduction for employee expenses for educating children.
Here is an example of reflecting deductions in section 3 of the help:
Expense codes for 2-NDFL in 2022: decoding
Some income specified in Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, are taxed only to the extent that exceeds a certain limit. This non-taxable limit in the 2-NDFL certificate is called a deduction. The codes of such deductions must be indicated in the Appendix to the certificate in accordance with Appendix No. 2 to the Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 10, 2015 N ММВ-7-11/, for example:
- 501 - deduction within 4,000 rubles. per year from gifts to individuals;
- 503 - deduction within 4,000 rubles. for a year with financial assistance to an employee or former employee who retired due to disability or age;
- 508 - deduction within 50,000 rubles. with one-time financial assistance to an employee upon the birth (adoption) of a child.
What income in kind is subject to personal income tax?
To begin with, let’s determine which payments are classified as natural income subject to personal income tax. For clarification, please refer to clause 2 of Art. 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which states that income received by an individual in kind and subject to personal income tax includes:
- salary received from the employer in the form of goods, products, services;
- goods and services received by an individual from individuals or legal entities free of charge or subject to partial payment;
- goods and services (for example, food, training, recreation, etc.) received by an individual, but paid for by organizations or entrepreneurs.
At the same time, there is no need to withhold and pay personal income tax on the cost of goods and services that were issued to an individual for the performance of his labor duties (clause 3 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
ConsultantPlus experts explained in detail how to reflect an employee’s income received in non-monetary form in 6-NDFL. To do everything correctly, get trial access to the system and go to the Ready solution. It's free.
Example
Amounts allocated by the employer for travel and accommodation of employees are considered to be payments in kind. Accordingly, they are considered the income of individual employees and are subject to personal income tax (letters from the Ministry of Finance dated September 15, 2014 No. 03-04-06/46030, dated September 15, 2014 No. 03-04-06/46035). But this rule does not apply to the employee’s travel and accommodation expenses incurred during his business trip: there is no need to collect personal income tax from them, since these expenses were incurred to fulfill the employee’s labor duties in relation to the employer.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the procedure for assessing personal income tax on travel expenses in a separate article “We pay personal income tax on travel expenses in 2022.”
Personal income tax is also not assessed on natural income that cannot be personified. For example, drinking water, snack food (cookies, candy, etc.) and other items and services intended for consumption by several employees and for which it is labor-intensive to track how much and which employee used them.
Situation
provides free meals to all its employees, regardless of their position and job responsibilities. Catering services are provided by a third party.
Question
Should free meals received by employees be subject to personal income tax?
Answer
Yes need. The food received by employees is their natural income, which must be subject to personal income tax (clause 2 of article 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Moreover, when calculating the natural income of workers, it is necessary to take into account the amount of VAT presented (clause 1 of Article 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The personal income tax must be calculated on the date of receipt of primary documents confirming the amount of expenses for the provision of free food.
The amount of income received in the form of free meals for each employee is calculated based on his work schedule and the menu he chooses.
NOTE! If an employer must provide its employees with free food in accordance with the law, then in this case personal income tax on in-kind income received in the form of free food or food does not need to be withheld (clause 3 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Additional question
Is it necessary to withhold personal income tax from the cost of free food if it is organized on a buffet basis?
Answer
There are 2 possible answers here: yes and no.
On the one hand, the cost of free meals provided in the form of a buffet is almost impossible to distribute to each employee. This means that personal income tax is not withheld from income in the form of free meals.
But officials do not agree with this position. They believe that income in the form of free meals organized on a buffet basis should be subject to personal income tax. Moreover, the calculation of the received in-kind income must be made on the basis of a timesheet, cost of food and other documents (letters of the Ministry of Finance dated 05/17/2018 No. 03-04-06/33350, dated 04/18/2012 No. 03-04-06/6-117) . Fortunately, the majority of arbitration courts do not support this position, based on the fact that such a calculation is incorrect due to the lack of individualization (resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated August 20, 2009 No. F09-5950/09-S2, FAS Far Eastern District dated June 15, 2009 No. F03-2484/2009, Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North Caucasus District dated March 12, 2008 No. F08-478/08-265A).
On the other hand, there were situations when the court supported the tax authorities in assessing additional personal income tax on free meals in the form of a buffet, without taking into account the fact that the calculation of the timesheet and the cost of food does not make it possible to determine the exact amount of in-kind income received by each employee (resolution FAS Volga District dated June 22, 2009 in case No. A55-14976/2008).
Advice from experts nalog-nalog.ru
If there are significant monthly expenses for organizing free buffet meals for your employees, it is still better to ensure that they are individualized (for example, using special individual cards), so that in the future you can determine the amount of income received by each employee , and calculate the personal income tax amount based on it. Otherwise, the tax authorities will definitely file claims for non-payment of personal income tax and request all kinds of documents in order to independently determine the amount of in-kind income received in the form of free food.
If the costs of free food in the form of a buffet are insignificant or are of a one-time nature (for example, when holding banquets), then in this case you can safely not calculate the amount of income received by each employee in the form of free food, and, accordingly, not subject to personal income tax. .
To make it easier to determine whether income in kind issued to an individual by an organization or entrepreneur should be taxed, we suggest taking a two-question test presented in the diagram below.
For more information about income not subject to personal income tax, read our material “Income not subject to personal income tax.”