In Russia, citizens have many different forms of government support. Here you can count not only on benefits and payments, but also on so-called deductions. They are of interest to many residents of the country. Today we have to find out what a property deduction is. This will help you save on purchasing real estate. But how? And what is required to receive a deduction for property? Having understood all these issues, everyone will be able to achieve the desired result in the shortest possible time.
Definition
What is a property deduction? This is usually called the return of part of the money spent on the purchase of real estate on account of income taxes paid in a particular tax period.
You might be interested in: What type of activity is covered by a patent? Patent for individual entrepreneurs for 2022: permitted types of activities
Current legislation states that a citizen has the right to a property deduction not only when buying, but also when selling housing or land. In this case, it will be possible to partially or completely avoid paying income tax on the amount received for the sold property. This is due to a decrease in the tax base for personal income tax by a certain amount.
Most often, property deduction refers to the first interpretation of the corresponding concept. The population is mainly faced not with paying taxes on the sale of real estate, but with the return of money for the purchase of it.
Typical errors in calculations
Mistake #1. Receipt by a parent of a social deduction for the child’s education, while only the child is indicated in the supporting documents (contract, payment documents).
According to the regulatory authorities, in order to receive a deduction, the child’s parent must be named in the contract for the child’s education (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 22, 2013 N 03-04-05/50508, dated October 28, 2013 N 03-04-05/45702, dated September 13. 2013 N 03-04-05/37885, dated 07/10/2013 N 03-04-05/26681, dated 06/21/2013 N 03-04-05/23536). If a child is indicated in the payment documents, for example, in a receipt for a cash receipt order, then, according to the Russian Ministry of Finance, he will have the right to receive a deduction (Letter dated November 15, 2007 N 03-04-05-01/367).
Mistake #2. Claiming a deduction for medical expenses in the event that such expenses are paid by the employer for the taxpayer.
In para. 6 pp. 3 p. 1 art. 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that a social deduction is provided if payment for the cost of medical services and purchased medications was not made at the expense of employers. This means that if the taxpayer did not spend his own funds to pay for medical services (medicines), then he cannot claim a deduction. After all, the social purpose of this deduction is to return to the taxpayer part of the funds spent on treatment.
Mistake #3. Applying for a property deduction when purchasing a land plot for individual construction before registering ownership of a house built on the specified plot.
In cases of acquisition of land plots for individual construction, the right to a property deduction arises only after construction and registration of ownership of the house.
What is provided for?
You may be interested in: Limitation period for bank loans for individuals
What is a property deduction? This is reimbursement of part of the expenses incurred when purchasing real estate. But not everyone can take advantage of this right and not always.
Property deductions are provided for the following items:
- apartment;
- room;
- residential block in a townhouse;
- house;
- land plot for building a house;
- land purchased for residential purposes;
- shares in the listed property.
It will no longer be possible to reduce the personal income tax base for any objects or return part of the money spent. This is not provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Types of property deductions
Buying a home can be done in different ways. The maximum refund will depend on this. Some people pay the entire amount under the contract at once, while others prefer to take out a mortgage. In both cases, the buyer theoretically has the right to obtain a tax deduction.
Property return can be divided into several types:
- basic;
- mortgage
In the first case, part of the funds spent directly on the purchase of housing will be returned. In the second, the citizen will be able to reimburse the interest paid on the loan.
You may be interested in: Keynes's multiplier in his theory
Important: when applying for a mortgage, it is allowed to draw up both the main and mortgage property deductions.
Reasons for refusal
Federal Tax Service employees may refuse to provide a refund for various reasons. The main reasons include:
- lack of necessary documents;
- the presence of significant errors in the submitted papers, which must be eliminated when filling out the documents again;
- incorrectly drawn up declaration;
- the applicant does not have the right to a deduction;
- It turns out that the submitted documents are fake.
If it really turns out that a citizen tried to obtain a benefit using forged documents, then this will not only become a basis for refusing the deduction, but also a reason for bringing the applicant to criminal liability. Therefore, the preparation of the necessary package of documents should be approached responsibly.
How much can you return?
What is a property deduction? Answering this question should no longer be a problem for citizens. How much money will be returned in the end? What do you need to know about this?
Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that when purchasing a home and applying for the main property deduction, a citizen can count on a deduction of two million rubles. The repayment interest rate is 13%. Accordingly, you can return a maximum of 260,000 rubles.
The situation with mortgages is somewhat different. The deduction is calculated from an amount equal to three million. This means that the state can return a maximum of 390,000 rubles to the applicant.
If we talk about the sale of housing, then the personal income tax base is allowed to be reduced by a million. This is the maximum offered by the state.
Important: you cannot demand more money than a citizen transferred in income taxes for a particular tax period.
When is a refund not provided when purchasing real estate?
There are situations when even when purchasing an object it is impossible to receive a benefit. The tax deduction law contains the following exceptions:
- Previously, the citizen had already managed to exercise his right, therefore he had exhausted the return limit;
- housing was purchased using government funds as part of subsidies;
- the employer's money was used during the purchase of the property;
- the citizen does not have an official income, so personal income tax is not transferred for him, which leads to the inability to apply for this type of benefit;
- the buyer is a pensioner, and since no tax is charged on the pension, he will not be able to return it;
- real estate is purchased from a close relative, so the transaction is considered interdependent.
The above points must be taken into account by every citizen, since if he tries to deceive the tax inspectorate, this will not only lead to a refusal to receive a refund, but may also become the basis for bringing the offender to justice. His actions may be regarded as fraud, so it is advisable to understand the rules for applying for this type of benefit in advance.
When the right or time for registration arises
According to Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the right to a property tax deduction arises for a citizen in the year in which he made the relevant transaction. But it can be realized within a limited period of time.
The statute of limitations for property deductions is 3 years. This means that after three years from the date of sale or purchase of real estate, a person will not be able to apply to the authorized bodies for personal income tax compensation.
In Russia, you can apply for a tax deduction for several tax periods at once (1 period = 1 year). Namely, for all three years at once. Very convenient, especially when it comes to paying off a mortgage.
Training expenses and the procedure for obtaining deductions
Who is entitled to receive a social deduction for personal income tax in connection with training expenses
You can apply for a personal income tax refund if you paid:
1) own training in educational institutions;
2) as well as training:
- their children under the age of 24 in educational institutions for full-time education.
- wards under the age of 18 (former wards under the age of 24) in educational institutions for full-time study;
- brothers (sisters) under the age of 24 in educational institutions for full-time study.
Note! The form of training and the age of the trainees is important. Under conditions other than the above, it is impossible to obtain a deduction.
Example 1. For example, Karaulova M.K. entered into an agreement with a higher educational institution for the education of her son on a full-time and part-time basis. In this case, she has no right to count on receiving a social tax deduction. In addition, when paying for tuition for other persons (spouse, grandchildren, etc.), a deduction cannot be provided either.
How much can I receive a social deduction for personal income tax for training?
The Tax Code limits the amount of actual training expenses incurred to the maximum amounts:
- 120,000 rub. for the tax period for your own education and education of your brother (sister)
- 50,000 rub. per year for the education of children and wards of the taxpayer for each student.
Example 2. Let’s assume that the actual expenses incurred for the education of two children of the Demidov spouses amounted to 85,000 rubles in the current year. – 45,000 and 35,000 rubles. respectively. Consequently, the total amount of expenses can be taken into account in full, since it does not exceed the limit set at RUB 50,000. for each child (RUB 45,000 < RUB 50,000; RUB 35,000 < RUB 50,000). Both spouses have the right to claim a social deduction (see →How to get a tax deduction for a child’s education in 2022)
For what periods is a social tax deduction for personal income tax provided in connection with training expenses?
You can apply for a deduction within three years from the date the tuition payment was made. If the tuition was paid for at a time for the entire period, then the deduction will be provided within the established limit. It will not be possible to claim the remaining expenses as a deduction in future periods. If the deduction could not be fully used in the current year, then its balance is not carried over to the next year. It will remain unused.
Basic conditions
What a property deduction is is now clear. But how to get it? And who has the right to it according to the law?
There are conditions that must be met when claiming a tax deduction. At the moment they look like this:
- The applicant must be a resident of the country.
- The purchased housing must be located on the territory of Russia.
- A citizen must have official income, subject to income tax of 13 percent.
At first glance, it seems that pensioners and the unemployed cannot exercise the right under study, even if they have purchased real estate. Actually this is not true.
Important: parents, guardians and adoptive parents can apply for a tax deduction for housing registered in the name of a child under 18 years of age.
Who can count on the benefit?
Before you apply for a tax deduction, you should decide who exactly can count on it. It is provided exclusively to persons who have official income, so funds are regularly contributed to the budget in the form of personal income tax for them. Therefore, citizens have the right to a tax deduction:
- officially working in different companies, so their tax agent for personal income tax is the head of the enterprise;
- engaged in entrepreneurial activities, but the use of simplified regimes is not allowed, since they do not require paying personal income tax;
- working pensioners;
- those who have other incomes that are officially registered with the Federal Tax Service, therefore citizens themselves calculate and pay personal income tax, and also annually submit a 3-personal income tax declaration to the inspectorate.
Therefore, it is first important to make sure that this benefit can be obtained. Providing a tax deduction significantly reduces the tax amount when selling a property or allows you to receive a large amount of money when buying a home.
Opportunity for the elderly
In Russia, property deductions for pensioners raise a lot of questions. If an older citizen works, he uses the right under study on a general basis. Otherwise, problems cannot be ruled out.
You might be interested in: What is the purpose of an audit, audit objectives
Pensioners are granted the right to a property deduction with the possibility of transferring personal income tax. This means that an elderly non-working citizen can apply for a deduction taking into account the income taxes paid over the last three years.
Rules for drawing up a declaration
Most often, applicants have difficulty generating a declaration in Form 3-NDFL. The procedure can be performed manually or using a computer. The rules for filling out the document include:
- All places where the applicant officially works must be indicated;
- based on the data available in the 2-NDFL certificates, information is entered on the amount of the citizen’s income for the year of work;
- the full cost of the purchased object is given;
- the deduction is calculated;
- The applicant's signature is placed on each page.
If a citizen prefers to apply to the Federal Tax Service, then he will have to fill out this document annually.
What does it include
Everyone should understand what a property deduction includes. More precisely, what expenses will be taken into account when registering it.
If an apartment is purchased, a person can include in expenses:
It happens that people buy not apartments and rooms, but houses or land plots for individual housing construction. In this case, the following amounts will be considered expenses:
- for developing a house project;
- for building materials;
- for finishing materials;
- paid for the purchase of the residential building itself;
- paid for construction and finishing works;
- for carrying out communications to housing.
All listed expenses are documented. Otherwise, they will not be taken into account. In both cases, when applying for a mortgage, the interest paid on the loan for housing will be taken into account.
Important: when applying for a deduction when selling real estate, these expenses must also be taken into account.
Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Property tax deductions. Terminological comment
Clause 1 of Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
1) When determining the size of the tax base in accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 210 of this Code, the taxpayer has the right to receive the following property tax deductions, provided taking into account the specifics and in the manner provided for by this article:
1) property tax deduction upon the sale of property, as well as share(s) in it, share(s) in the authorized capital of the company, upon withdrawal from the membership of the company, upon transfer of funds (property) to the company participant in the event of liquidation of the company, upon reduction the nominal value of a share in the authorized capital of the company, upon assignment of rights of claim under an agreement for participation in shared construction (under an investment agreement for shared construction or under another agreement related to shared construction);
2) property tax deduction in the amount of the redemption value of the land plot and (or) other real estate located on it, received by the taxpayer in cash or in kind, in the event of seizure of the specified property for state or municipal needs;
3) property tax deduction in the amount of expenses actually incurred by the taxpayer for new construction or the acquisition on the territory of the Russian Federation of residential houses, apartments, rooms or a share(s) in them, the acquisition of land plots or a share(s) in them provided for individual housing construction , and land plots or share(s) in them on which the acquired residential buildings or share(s) in them are located;
4) property tax deduction in the amount of expenses actually incurred by the taxpayer to repay interest on targeted loans (credits) actually spent on new construction or the acquisition on the territory of the Russian Federation of a residential building, apartment, room or share(s) in them, the acquisition of land plots or shares (shares) in them provided for individual housing construction, and land plots or shares (shares) in them on which the acquired residential buildings or share (shares) in them are located, as well as for the repayment of interest on loans received from banks in for the purpose of refinancing (on-lending) loans for new construction or the acquisition on the territory of the Russian Federation of a residential building, apartment, room or share(s) in them, the acquisition of land plots or share(s) in them provided for individual housing construction, and land plots or share(s) in them on which the purchased residential buildings or share(s) in them are located.
Clause 2 of Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
2) The property tax deduction provided for in subparagraph 1 of paragraph 1 of this article is provided taking into account the following features:
1) property tax deduction is provided:
in the amount of income received by the taxpayer in the tax period from the sale of residential houses, apartments, rooms, including privatized residential premises, dachas, garden houses or land plots or share(s) in the said property that were owned by the taxpayer for less than the minimum maximum period of ownership of the real estate property property established in accordance with Article 217.1 of this Code, not exceeding in total 1,000,000 rubles;
in the amount of income received by the taxpayer in the tax period from the sale of other real estate that was owned by the taxpayer for less than the minimum maximum period of ownership of the real estate object established in accordance with Article 217.1 of this Code, not exceeding in total 250,000 rubles;
in the amount of income received by the taxpayer during the tax period from the sale of other property (except for securities) that was owned by the taxpayer for less than three years, not exceeding a total of 250,000 rubles;
2) instead of receiving a property tax deduction in accordance with subparagraph 1 of this paragraph, the taxpayer has the right to reduce the amount of his taxable income by the amount of expenses actually incurred by him and documented in connection with the acquisition of this property.
When selling a share (part thereof) in the authorized capital of a company, when leaving the company's members, when transferring funds (property) to a company participant in the event of liquidation of the company, when reducing the nominal value of a share in the authorized capital of the company, when assigning rights of claim under a participation agreement in shared construction (under an investment agreement for shared construction or under another agreement related to shared construction), the taxpayer has the right to reduce the amount of his taxable income by the amount of expenses actually incurred by him and documented expenses associated with the acquisition of this property (property rights).
The taxpayer's expenses associated with the acquisition of a share in the authorized capital of a company may include the following expenses:
expenses in the amount of cash and (or) the cost of other property made as a contribution to the authorized capital when establishing a company or when increasing its authorized capital;
expenses for acquiring or increasing a share in the authorized capital of the company.
In the absence of documented expenses for the acquisition of a share in the authorized capital of the company, a property tax deduction is provided in the amount of income received by the taxpayer as a result of termination of participation in the company, not exceeding a total of 250,000 rubles for the tax period.
When selling part of a share in the authorized capital of a company owned by a taxpayer, the taxpayer’s expenses for the acquisition of this part of the share in the authorized capital are taken into account in proportion to the decrease in the share of such taxpayer in the authorized capital of the company.
When income is received in the form of payments to a company participant in cash or in kind in connection with a decrease in the authorized capital of the company, the taxpayer’s expenses for acquiring a share in the authorized capital of the company are taken into account in proportion to the decrease in the authorized capital of the company.
If the authorized capital of the company was increased due to the revaluation of assets, when it is reduced, the taxpayer’s expenses for acquiring a share in the authorized capital are taken into account in the amount of payment to the company participant exceeding the amount of the increase in the nominal value of his share as a result of the revaluation of assets;
Clause 2 of Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
2)1) upon the sale of property (property rights) received during the liquidation of a foreign organization (termination (liquidation) of a foreign structure without the formation of a legal entity) by a taxpayer - shareholder (participant, shareholder, founder, controlling person of a foreign organization or a controlling person of a foreign structure without formation legal entity) whose income in the form of such property (property rights) was exempt from taxation in accordance with paragraph 60 of Article 217 of this Code, such a taxpayer has the right to reduce the amount of his taxable income from the sale of such property (property rights) by an amount equal to the value of the property (property rights) according to the accounting data of the liquidated organization on the date of receipt of property (property rights) from such organization, specified in the documents attached to the taxpayer’s application submitted in accordance with paragraph two of paragraph 60 of Article 217 of this Code, but not higher than the market value of such property (property rights), determined taking into account Article 105.3 of this Code;
Clause 2 of Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
2)2) upon the sale of property rights (including shares, shares) acquired from a controlled foreign company, if the income of such a controlled foreign company from the sale of these property rights (including shares, shares) and expenses in the form of price their acquisitions are excluded from the profit (loss) of such a foreign company on the basis of paragraph 10 of Article 309.1 of this Code, the taxpayer recognized as a controlling person of such a controlled foreign company or being a Russian interdependent person of such a controlling person, the amount of expenses actually incurred in the form of the value of property rights (including number of shares, units) is determined based on the lower of the following values:
documented value according to the accounting data of a controlled foreign company on the date of transfer of ownership of the specified property rights (including shares, shares) from the controlled foreign company,
the market value of the specified property rights (including shares, interests) on the date of transfer of ownership from a controlled foreign company, determined taking into account the provisions of Article 105.3 of this Code;
3) when selling property that is in common shared or common joint ownership, the corresponding amount of property tax deduction is distributed among the co-owners of this property in proportion to their share or by agreement between them (in the case of the sale of property that is in common joint ownership);
4) unless otherwise provided by subclause 2.1 or 2.2 of this clause, the provisions of subclause 1 of clause 1 of this article do not apply to income received:
from the sale of real estate and (or) vehicles that were used in business activities;
from the sale of securities;
5) upon the sale of property received by a taxpayer-donor in the event of dissolution of the endowment capital of a non-profit organization, cancellation of a donation, or in another case, if the return of property transferred to replenish the endowment capital of a non-profit organization is provided for by the donation agreement and (or) the Federal Law of December 30, 2006 year N 275-FZ “On the procedure for the formation and use of endowment capital of non-profit organizations”, the expenses of the taxpayer-donor are recognized as documented expenses for the acquisition, storage or maintenance of such property, incurred by the taxpayer-donor on the date of transfer of such property to the non-profit organization - the owner of the endowment capital for replenishment of the target capital of a non-profit organization. The period of ownership of real estate received by a taxpayer-donor in the event of dissolution of the target capital of a non-profit organization, cancellation of a donation, or in another case, if the return of such property transferred to replenish the target capital of a non-profit organization is provided for by the donation agreement and (or) Federal Law dated 30 December 2006 N 275-FZ “On the procedure for the formation and use of endowment capital of non-profit organizations,” is determined taking into account the period of such property being in the ownership of the taxpayer-donor until the date of transfer of such property to replenish the endowment capital of a non-profit organization in the manner established by Federal Law dated 30 December 2006 N 275-FZ “On the procedure for the formation and use of endowment capital of non-profit organizations.”
Clause 3 of Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
3) The property tax deduction provided for in subparagraph 3 of paragraph 1 of this article is provided taking into account the following features:
1) a property tax deduction is provided in the amount of expenses actually incurred by the taxpayer for new construction or the acquisition on the territory of the Russian Federation of one or more items of property specified in subparagraph 3 of paragraph 1 of this article, not exceeding 2,000,000 rubles.
If the taxpayer has exercised the right to receive a property tax deduction in an amount less than its maximum amount established by this subclause, the balance of the property tax deduction until its full use may be taken into account when receiving a property tax deduction in the future for new construction or acquisition on the territory of the Russian Federation residential building, apartment, room or share(s) in them, acquisition of land plots or share(s) in them provided for individual housing construction, and land plots or share(s) in them on which the acquired residential buildings or share are located (shares) in them.
In this case, the maximum amount of a property tax deduction is equal to the amount in force in the tax period in which the taxpayer first acquired the right to receive a property tax deduction, as a result of which a balance was created that is carried forward to subsequent tax periods;
2) when purchasing land plots or a share(s) in them provided for individual housing construction, a property tax deduction is provided after the taxpayer receives a certificate of ownership of a residential building;
3) the actual costs of new construction or the acquisition of a residential building or share(s) in it on the territory of the Russian Federation may include the following costs:
costs for the development of design and estimate documentation;
expenses for the purchase of construction and finishing materials;
expenses for the acquisition of a residential building or share(s) in it, including those not completed construction;
expenses associated with construction work or services (completion of a residential building or share(s) in it that has not been completed) and finishing;
costs of connecting to electricity, water and gas supply and sewerage networks or creating autonomous sources of electricity, water and gas supply and sewerage;
4) the actual costs of purchasing an apartment, room or share(s) in them may include the following costs:
expenses for the acquisition of an apartment, room or share(s) in them or rights to an apartment, room or share(s) in them in a house under construction;
expenses for the purchase of finishing materials;
expenses for work associated with finishing an apartment, room or share(s) in them, as well as expenses for developing design and estimate documentation for finishing work;
5) taking for deduction the costs of completing and finishing an acquired residential building or share(s) in them or finishing an acquired apartment, room or share(s) in them is possible if the agreement on the basis of which such acquisition was made provides for the acquisition unfinished construction of a residential building, apartment, room (rights to an apartment, room) without finishing or share(s) in them;
6) to confirm the right to a property tax deduction, the taxpayer submits to the tax authority:
an agreement on the acquisition of a residential building or a share(s) in it, documents confirming the taxpayer’s ownership of a residential building or a share(s) in it - during the construction or acquisition of a residential building or a share(s) in it;
an agreement on the acquisition of an apartment, room or share (shares) in them and documents confirming the taxpayer’s ownership of the apartment, room or share (shares) in them - when purchasing an apartment, room or share (shares) in them;
an agreement for participation in shared construction and a transfer deed or other document on the transfer of a shared construction object by the developer and its acceptance by a participant in shared construction, signed by the parties - when acquiring rights to a shared construction object (an apartment or a room in a house under construction);
documents confirming the taxpayer's ownership of a land plot or share(s) in it, and documents confirming ownership of a residential building or share(s) in it - when acquiring land plots or share(s) in them provided for individual housing construction, and land plots on which the acquired residential buildings or share(s) in them are located;
child’s birth certificate – when parents purchase a residential house, apartment, room or share(s) in them, land plots or share(s) in them provided for individual housing construction, and land plots or share(s) in them, on in which the acquired residential buildings or share(s) in them are located, into the ownership of their children under the age of 18;
decision of the guardianship and trusteeship body on the establishment of guardianship or trusteeship - when guardians (trustees) acquire a residential building, apartment, room or share (shares) in them, land plots or share (shares) in them provided for individual housing construction, and land plots or shares (shares) in them, on which the acquired residential buildings or share (shares) in them are located, in the ownership of their wards under the age of 18 years;
documents confirming expenses made by the taxpayer (receipts for receipt orders, bank statements on the transfer of funds from the buyer's account to the seller's account, sales and cash receipts, acts on the purchase of materials from individuals indicating the address and passport details of the seller and other documents) ;
7) a property tax deduction is provided to the taxpayer on the basis of documents confirming the emergence of the right to the specified deduction, payment documents drawn up in the prescribed manner and confirming expenses incurred by the taxpayer (receipts for receipt orders, bank statements on the transfer of funds from the buyer’s account to the seller’s account, commodity and cash receipts, acts on the purchase of materials from individuals indicating the address and passport details of the seller and other documents).
Clause 4 of Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
4) The property tax deduction provided for by subparagraph 4 of paragraph 1 of this article is provided in the amount of expenses actually incurred by the taxpayer to pay interest in accordance with the loan (credit) agreement, but not more than 3,000,000 rubles in the presence of documents confirming the right to receive property tax deductions specified in paragraph 3 of this article, a loan (credit) agreement, as well as documents confirming the fact of payment of funds by the taxpayer to repay interest.
Clause 5 of Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
5) Property tax deductions provided for in subparagraphs 3 and 4 of paragraph 1 of this article are not provided in relation to the taxpayer’s expenses for new construction or acquisition on the territory of the Russian Federation of a residential house, apartment, room or share(s) in them, covered by employers’ funds or other persons, maternal (family) capital funds allocated to ensure the implementation of additional measures of state support for families with children, through payments provided from the budgets of the budget system of the Russian Federation, as well as in cases where the purchase and sale transaction of a residential building, apartments, rooms or share(s) in them is committed between individuals who are interdependent in accordance with Article 105.1 of this Code.
Clause 6 of Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
6) The right to receive property tax deductions provided for in subparagraphs 3 and 4 of paragraph 1 of this article are taxpayers who are parents (adoptive parents, foster parents, guardians, trustees) and who carry out new construction or purchase on the territory of the Russian Federation at their own expense of a residential building , apartments, rooms or shares (shares) in them, acquisition of land plots or share (shares) in them provided for individual housing construction, and land plots or share (shares) in them on which the acquired residential buildings or share (shares) are located ) in them, into the ownership of their children under the age of 18 (wards under the age of 18). The amount of property tax deductions in the case specified in this paragraph is determined based on the actual expenses incurred, taking into account the restrictions established by paragraph 3 of this article.
Clause 7 of Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
7) Property tax deductions are provided when the taxpayer submits a tax return to the tax authorities at the end of the tax period, unless otherwise provided by this article.
Clause 8 of Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Property tax deductions provided for in subparagraphs 3 and 4 of paragraph 1 of this article may be provided to the taxpayer before the end of the tax period when he submits a written application to the employer (hereinafter in this paragraph - tax agent), subject to confirmation of the taxpayer's right to property tax deductions by the tax authority in a form approved by the federal executive body authorized for control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees.
The property tax deduction provided for in subparagraph 4 of paragraph 1 of this article can be provided only in relation to one piece of real estate.
The taxpayer has the right to receive property tax deductions from one or more tax agents of his choice. If, having received a property tax deduction from one tax agent, the taxpayer applies for a property tax deduction to another tax agent, the specified property tax deduction is provided in the manner prescribed by paragraph 7 of this article and this paragraph. The tax agent is obliged to provide property tax deductions upon receipt from the taxpayer of confirmation of the right to property tax deductions, issued by the tax authority, indicating the amount of property tax deductions that the taxpayer has the right to receive from each tax agent specified in the confirmation.
The taxpayer’s right to receive property tax deductions from tax agents in accordance with this paragraph must be confirmed by the tax authority within a period not exceeding 30 calendar days from the date of filing the taxpayer’s application and documents confirming the right to receive property tax deductions provided for in subparagraphs 3 and 4 of paragraph 1 of this article.
If, at the end of the tax period, the amount of the taxpayer’s income received from all tax agents was less than the amount of property tax deductions determined in accordance with paragraphs 3 and 4 of this article, the taxpayer has the right to receive property tax deductions in the manner provided for in paragraph 7 of this article.
If, after the taxpayer has submitted in the prescribed manner an application to the tax agent for receipt of property tax deductions provided for in subparagraphs 3 and 4 of paragraph 1 of this article, the tax agent withheld the tax without taking into account property tax deductions, the amount of tax withheld in excess after receipt of the application shall be returned to the taxpayer in the procedure established by Article 231 of this Code.
Clause 9 of Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
9) If during the tax period the property tax deductions provided for in subparagraphs 3 and (or) 4 of paragraph 1 of this article cannot be used in full, their balance may be transferred to subsequent tax periods until they are fully used, unless otherwise provided by this article.
Clause 10 of Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
10) For taxpayers receiving pensions in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, property tax deductions provided for in subparagraphs 3 and 4 of paragraph 1 of this article may be transferred to previous tax periods, but not more than three, immediately preceding the tax period in which the transferred tax period was formed. balance of property tax deductions.
Clause 11 of Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
11) Repeated provision of tax deductions provided for in subparagraphs 3 and 4 of paragraph 1 of this article is not allowed.
How many times to ask
A property deduction for an apartment or other real estate can be issued once. But it happens that the buyer’s actual spending on housing turns out to be less than the specified limits. In the current situation, it is allowed to draw up deductions for property as long as required until the maximum amounts allocated by the state are fully spent. But in our case, there is one serious limitation - the transfer of the balance of the deduction is allowed only to those who bought housing after 2014. If the property was purchased earlier, you will not be able to take advantage of this benefit.
The same applies to reducing the personal income tax base when selling housing. A citizen can deduct from the profit received the amount of expenses he previously incurred, but not more than 1,000,000 rubles. If it is less, it is allowed to carry forward the remainder of the deduction to the future.
If the applicant purchases several properties, he can apply for a deduction for one of them, and transfer the remainder, if any, to another property. Very comfortably!
Types and amount of benefits when selling property
The amount of the refund depends on the amount of funds received, but certain limits are established at the state level. These include:
- if real estate is sold, which includes an apartment, house or plot of land, then a deduction in the amount of 1 million rubles is provided;
- if other valuables are sold, which include cars or garages, then the amount of the benefit will be equal to 250 thousand rubles.
For example, a citizen is selling a one-room apartment that he bought two years ago. The cost of real estate is 1.4 million rubles. When using a deduction, the tax base is reduced by 1 million rubles, so a tax is levied on 400 thousand rubles. You will have to transfer the following amount to the state: 400,000 x 13% = 52 thousand rubles.
Rules for counting when purchasing
How to calculate property deduction? “Entertaining mathematics” must be treated extremely carefully. And then everything will work out.
To find out how much you can get back for buying a home, you need:
All that remains now is to draw a conclusion about how much can be returned. If the amount of the deduction is more than the personal income tax paid, the entire income tax for a particular period is reimbursed, and if it is less, the full amount of the deduction received.
Important: to avoid making mistakes with your calculations, you should use tax calculators. They help, free of charge and quickly, based on the data specified by the user, to calculate what the size of the property tax deduction will be in a particular case.
When is a deduction not allowed when selling objects?
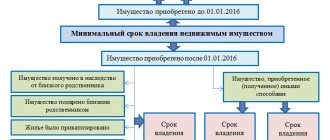
When selling real estate, it becomes necessary to pay personal income tax on the income received. This applies to a situation where the property has been owned by a private individual for less than three or five years. If the ownership period exceeds this period, then there is automatically no need to pay tax.
If you need to sell the apartment as soon as possible, then tax is paid on the income received. To reduce the tax base, a deduction of 1 million rubles is applied. The sale price of the property is reduced by this amount, after which 13% is calculated from the resulting value. The correctly calculated amount is transferred to the budget.
The tax deduction law says that it will not be possible to obtain such a benefit under the following conditions:
- securities are sold;
- property that was used by the citizen to conduct business activities is sold;
- the citizen owned the property for more than three or five years, so there is no need to use the deduction at all, and it cannot be provided based on the taxpayer’s application.
Most often, citizens are faced with the need to obtain a deduction after purchasing real estate. This gives them the opportunity to receive a significant amount of funds from the state, which they then use for any purpose.
About authorized bodies
You can only apply for a deduction in certain places. At the moment, you can submit a corresponding application through:
- Multifunctional Center;
- local tax office.
If necessary, it is possible to send an application to the Federal Tax Service by mail, but this step significantly slows down the process.
You can apply for a deduction at your place of employment. That is, ask for it at work. This is not a very popular technique, but everyone should remember it. During its implementation, personal income tax will not be paid on the person’s earnings in the amount of the deduction.
Important: if a citizen decides to contact the Federal Tax Service directly, it is necessary to take into account the applicant’s place of registration.
What is a simplified tax deduction procedure?
On May 21, 2022, the Federal Law of April 20, 2022 No. 100-FZ “On Amendments to Parts One and Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation” came into force, which introduced a new way to issue a deduction.
It's called hands-off, or proactive, because you don't have to do anything. The tax office itself collects information about your income and expenses and decides whether you are entitled to a deduction. If yes, then a pre-filled application will be sent to your personal account on the Federal Tax Service website. It will need to be signed - probably with an electronic signature, which can be issued there, on the tax office website.
Since the Federal Tax Service has all the data, there is no need to check it for three months, as usual. They promise to get it done in no more than one. It will take up to 15 days to transfer money. That is, the waiting time for funds compared to filing a declaration will be more than halved.
Spouses and deductions
Often real estate is purchased during marriage. What should husbands and wives know before filing a deduction?
If housing was purchased during marriage and with common money, and the second spouse is the owner of the corresponding residential property, both the husband and wife have equal rights to the deduction. However, there is one caveat.
To eliminate problems when registering it, it is necessary to submit an application for the distribution of property deductions between spouses. The husband and wife themselves must think about how they can demand it. It may be more profitable to issue a deduction for one of the spouses or in equal shares.
If housing is purchased with the money of only the husband or wife, and the second spouse is not a co-owner of the property, you should not count on equal rights regarding the deduction. They are simply not provided for by the country's legislation. An application for distribution of property deductions between spouses in this situation is not submitted. Instead, it is enough to fill out a regular application for “compensation” for the purchase of a residential property.
Conditions for receiving benefits
If a citizen, after purchasing real estate, plans to apply for a deduction, then he takes into account the requirements for this process. These include:
- It is important, before contacting the Federal Tax Service or the employer, to obtain an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate, which indicates that the citizen has become the full owner of the property;
- pensioners can count on this benefit from the state only on the condition that they continue to officially work in retirement, so employers pay personal income tax for them;
- Additionally, pensioners can receive a deduction three years before retirement;
- when working people apply to their employer, a deduction is issued from the next month, regardless of the date of application, and when using the Federal Tax Service, you will have to collect the necessary package of documents annually.
Although many people have difficulties preparing documentation, they still prefer to contact the inspectorate for benefits. This is due to the fact that they can count on a large lump sum of funds.
Brief design guide
Claiming a housing deduction is not as difficult as it may seem, but the process requires advance preparation. What is needed to achieve the goal?
In our case, it is recommended to do this:
Further, everything will depend on what decision is made by the tax authorities. If they agreed to provide the opportunity, the citizen will only have to wait for the money to be transferred to the account specified in advance. Property deductions for mortgage interest or cash loan interest are not issued.
You may be interested in: ROC indicator settings: nuances and subtleties
Otherwise, you need to study the reason for the refusal. If it can be corrected, it is recommended to do this within one month - then you will not have to contact the authorized service again for appropriate service.
Medical expenses
The procedure and conditions for providing a deduction related to payment for medical services are identical to the conditions for providing a deduction for education. That is, these must be actual expenses incurred, the amount of which cannot exceed 120,000 rubles for the tax period. The unused balance of the deduction is not carried over to the next year.
Note! The limit on the amount of social deduction applies to the totality of all expenses (with the exception of expenses for the education of children). At the same time, you independently determine which expenses and in what amounts you will take into account to receive a deduction.
Example 4. Ivanova G.V. During the tax period, she paid for hospital treatment in the amount of 65,000 rubles and her own university education in the amount of 70,000 rubles. The total amount of expenses amounted to 135,000 rubles, which exceeded the maximum allowable deduction. Therefore, Ivanova G. indicated training expenses in full in the 3-NDFL declaration, i.e. 70,000 rubles, and medical expenses in the amount of 50,000 rubles.
The exception is expensive treatment, determined by the List and accepted in full amount of actual expenses incurred:
- Surgical treatment of congenital anomalies (developmental defects).
- Surgical treatment of severe forms of circulatory system diseases, including operations using artificial blood circulation machines, laser technologies and coronary angiography.
- Surgical treatment of severe forms of respiratory diseases.
- Surgical treatment of severe forms of diseases and combined pathologies of the eye and its appendages, including the use of endolaser technologies.
- Surgical treatment of severe forms of nervous system diseases, including microneurosurgical and endovasal interventions.
- Surgical treatment of complicated forms of diseases of the digestive system.
- Endoprosthetics and reconstructive operations on joints.
- Transplantation of organs (complex of organs), tissues and bone marrow.
- Replantation, implantation of prostheses, metal structures, pacemakers and electrodes.
- Reconstructive, plastic and reconstructive plastic surgeries.
- Therapeutic treatment of chromosomal disorders and hereditary diseases.
- Therapeutic treatment of malignant neoplasms of the thyroid gland and other endocrine glands, including the use of proton therapy.
- Therapeutic treatment of acute inflammatory polyneuropathies and complications of myasthenia gravis.
- Therapeutic treatment of systemic connective tissue lesions.
- Therapeutic treatment of severe forms of diseases of the circulatory, respiratory and digestive organs in children.
- Combined treatment of pancreatic diseases.
- Combined treatment of malignant neoplasms.
- Combined treatment of hereditary bleeding disorders and aplastic anemia.
- Combined treatment of osteomyelitis.
- Combined treatment of conditions associated with complicated pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period.
- Combined treatment of complicated forms of diabetes mellitus.
- Combined treatment of hereditary diseases.
- Combined treatment of severe forms of diseases and combined pathologies of the eye and its adnexa.
- Complex treatment of burns with a body surface area of 30 percent or more.
- Types of treatment associated with the use of hemo- and peritoneal dialysis.
- Nursing premature babies weighing up to 1.5 kg.
- Treatment of infertility using in vitro fertilization, cultivation and intrauterine embryo insertion.
A prerequisite for providing a deduction for medical expenses is:
- The medical organization has a license to conduct relevant activities;
- Provision by the taxpayer of documents confirming his actual expenses.
Based on numerous clarifications from regulatory authorities, here is a list of documents required to be submitted to the tax authority to receive this deduction:
| Documents submitted to the tax authority to obtain a tax deduction in the form of expenses for medical services (including expensive treatment) | Documents submitted to the tax authority to obtain a tax deduction in the form of expenses for medicines for medical use |
| Declaration in form 3-NDFL | |
| A copy of the contract for the provision of medical services (if concluded) with copies of appendices and additional agreements. | |
| Original payment certificate medical services according to the form, approved by the Order Ministry of Health of Russia N 289, Ministry of Taxes and Taxes of Russia dated July 25, 2001 N BG-3-04/256 | |
| If medical services or medications are paid for by the taxpayer for parents or children, then a copy of a document confirming the degree of relationship (for example, a birth certificate) is submitted. | |
| If medical services or drugs were paid for by the taxpayer for a spouse, then submit a copy of the document confirming the marriage (for example, a marriage certificate). | |
| – | The original prescription in form N 107-1/u with the stamp “For the tax authorities of the Russian Federation, Taxpayer INN |
| – | Copies of documents confirming payment for medicines (for example, cash register receipts). |
For all listed documents, the Tax Authority has the right to request originals. You also decide how to receive a deduction for medical expenses yourself.
Step-by-step algorithm for receiving a deduction
From the employer:
- Prepare supporting documents
- Receive a notification from the tax authority confirming the right to deduct
- Submit an application and notice to the employer confirming the right to deduction
- Receive social benefits from your employer.
At the tax office:
- Fill out a tax return and an application for a refund of the overpaid personal income tax amount
- Submit your tax return and supporting documents to the tax authority
- Wait for the tax authority’s decision and refund
Rules for filling out the declaration
Anyone can file a tax return for deductions for an apartment or house. You can do this manually or using special programs. It is best to use the second method. It will avoid most of the problems associated with filling out the form. The “Legal Taxpayer” program was recognized as the best.
The 3-NDFL declaration for property deduction for 3 years is drawn up in three separate documents.
The form of the document must correspond to the forms used in the year in which the person applies for “compensation”. As a rule, it changes from year to year. This must be monitored carefully.
The prepared certificate must indicate:
- all expenses incurred;
- taxable income;
- data from documents prepared in advance.
As a rule, if a person uses a program to generate tax returns, he will simply need to fill out the fields on the “D1” form, then select the type of deduction and fill out the form that appears again. The finished declaration will be generated automatically.
Important: if problems arise with preparing the 3-NDFL form, you can turn to intermediaries for help. Private companies often help to process deductions, but for an additional fee.
Rules for applying for benefits after the sale of housing
Such a refund is considered easy to obtain, since there is no need to prepare a lot of documents or wait for a decision from the tax office. Therefore, to achieve this, the following steps are performed:
- an application for benefits is drawn up in the form of the Federal Tax Service;
- the 3-NDFL declaration is filled out correctly, where information about the object sold and the amount of funds received is entered;
- documents for the sold object are transferred.
During the preparation of the declaration, the section intended for deduction must be filled out. It indicates the possibility of using a benefit in the amount of 1 million rubles. A calculation is carried out directly in the document, allowing you to determine the optimal amount of tax after using the deduction. You need to transfer the amount calculated in the declaration.
Basic papers
Do you want to file a property deduction? What documents will be required to complete the task?
The list of references to achieve the required goal is different each time. First, let's look at the main documents. Confirmation of the right to a property deduction is carried out using title documents for housing, as well as receipts indicating expenses incurred.
The citizen will need:
- passport;
- application form;
- tax return;
- income certificates;
- contract of sale or mortgage;
- receipts and receipts indicating the applicant's expenses;
- USRN extract.
These are mandatory certificates that you cannot do without. If you have taken out a mortgage, you will additionally need to prepare a loan repayment schedule.
What documents are being prepared?
A list of documents for tax deductions can be obtained directly from Federal Tax Service employees. To apply for the benefit you will need the following documents:
- a correctly completed declaration in form 3-NDFL, and to carry out this process it is advisable to use special programs issued directly by the tax service;
- 2-NDFL certificate for a year of work, which must be taken at the place of work, and if a citizen works in several organizations at once, then several certificates are prepared for him;
- copy of the passport;
- an application for a benefit, drawn up by hand and containing information about the bank account details where, after a positive decision is made, the funds will be transferred;
- purchase and sale agreement or DDU for the purchased object;
- payment documents confirming that the citizen actually transferred all the necessary funds to the seller for the property;
- technical papers for an apartment or house;
- if borrowed funds were used to purchase the property, then you will additionally need a loan agreement and a bank statement;
- If the property was purchased for spouses, then you need to draw up an application for the distribution of the deduction.
A tax deduction certificate indicating the amount of income allows you to determine how much money can be paid to a citizen in one year.
If the property was purchased by spouses, they can draw up a statement on the basis of which the benefit is provided only to the husband or wife. Typically, this decision is made if one family member is unemployed or receives too little salary, and therefore cannot count on a significant amount of return.
For families
How to fill out a property deduction declaration is now clear. What exactly is required to register it?
In addition to the previously specified certificates, family people must attach:
- Marriage certificate;
- marriage agreement;
- birth or adoption certificates of children;
- any certificates indicating that the purchase was made from the personal money of the husband or wife.
Usually all specified documents are provided along with copies. When sending them by mail, you will have to have photocopies certified by a notary. There is no need to send originals. They will only be required when contacting the authorized body in person.