What are the grounds for calculating penalties?
A penalty is not a measure of tax liability, but a payment of a compensatory nature.
The compensatory nature of the penalty follows from the basis that serves for its calculation: late payment of taxes, fees, and insurance premiums (clauses 1 and 7 of Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). For each tax payment, there are payment deadlines that are specified in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Accordingly, if payment was not made within the specified period, then there is a basis for charging a penalty. The penalty is calculated starting from the day that immediately follows the day set as the deadline for paying the tax, and ends with the repayment of the tax debt (clause 4 of Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Important! The number of days of delay is determined differently for insurance contributions to the Federal Tax Service and contributions for injuries, and also depends on the date the debt arose. A ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus will help you calculate them correctly. Trial access to the system can be obtained for free.
“How to correctly calculate tax penalties (nuances)?” will help you understand the nuances of calculating tax .
Subjects of the Russian Federation have the right to establish the possibility of calculating penalties for the property tax of individuals, calculated from the cadastral value (clause 4.1 of Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Article 75. Penalty
Article 75. Penalty
[Tax Code] [Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Part 1] [Section IV.] [Chapter 11.]
. A penalty is the amount of money established by this article that a taxpayer must pay in the event of payment of due amounts of taxes, including taxes paid in connection with the movement of goods across the customs border of the Customs Union, later than the deadlines established by the legislation on taxes and fees.
. The amount of the corresponding penalties is paid in addition to the amounts of tax due and regardless of the application of other measures to ensure the fulfillment of the obligation to pay tax, as well as measures of liability for violation of legislation on taxes and fees.
. The penalty is accrued, unless otherwise provided by this article and Chapters 25 and 26.1 of this Code, for each calendar day of delay in fulfilling the obligation to pay tax, starting from the day of tax payment following the tax payment established by the legislation on taxes and fees until the day of fulfillment of the obligation to pay it, inclusive. The amount of penalties accrued on arrears cannot exceed the amount of this arrears.
Penalties are not charged on the amount of arrears that the taxpayer (a member of a consolidated group of taxpayers against whom, in accordance with Article 46 of this Code, measures were taken to force the collection of taxes) could not repay due to the fact that, by decision of the tax authority, the taxpayer’s property was seized or by a court decision, interim measures were taken in the form of suspension of transactions on the accounts of the taxpayer (a member of a consolidated group of taxpayers against whom, in accordance with Article 46 of this Code, measures were taken to force the collection of taxes) in the bank, seizure of funds or property of the taxpayer (participant of a consolidated group of taxpayers). In this case, penalties are not accrued for the entire period of validity of these circumstances. Filing an application for a deferment (installment plan) or an investment tax credit does not suspend the accrual of penalties on the amount of tax payable.
. The penalty for each calendar day of delay in fulfilling the obligation to pay tax is determined as a percentage of the unpaid tax amount.
The interest rate of the penalty is assumed to be equal to:
- for individuals, including individual entrepreneurs, one three hundredth of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in force at that time;
- for organizations:
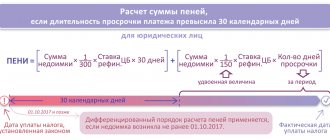
- for delay in fulfilling the obligation to pay tax for a period of up to 30 calendar days (inclusive) - one three hundredth of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in force at that time;
- for delay in fulfilling the obligation to pay tax for a period of more than 30 calendar days - one three hundredth of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, valid for the period up to 30 calendar days (inclusive) of such delay, and one hundred and fiftieth of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, valid for the period starting from 31st calendar day of such delay.
4.1. The legislative (representative) body of state power of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, in whose territory the procedure for determining the tax base for the property tax of individuals based on the cadastral value of taxable objects is applied, has the right to adopt a law establishing that penalties are charged on the amount of arrears for the property tax of individuals :
- 1) for the tax period 2015 - starting from May 1, 2017;
- 2) for the tax period 2016 - starting from July 1, 2018;
- 3) for the tax period 2022 - starting from July 1, 2019.
. Penalties are paid simultaneously with the payment of tax amounts or after payment of such amounts in full.
. Penalties may be collected forcibly from the taxpayer’s funds (precious metals) in bank accounts, as well as from other property of the taxpayer in the manner prescribed by Articles 46 - 48 of this Code.
Forced collection of penalties from organizations and individual entrepreneurs is carried out in the manner prescribed by Articles of this Code, and from individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs - in the manner prescribed by Article 48 of this Code.
Forced collection of penalties from organizations and individual entrepreneurs in the cases provided for in subparagraphs 1 - 3 of paragraph 2 of Article 45 of this Code is carried out in court.
. The rules provided for in this article also apply to fees, insurance premiums and apply to fee payers, insurance premium payers, tax agents and a consolidated group of taxpayers.
. Penalties are not accrued on the amount of arrears that a taxpayer (fee payer, insurance premium payer, tax agent) incurred as a result of his compliance with written explanations on the procedure for calculating, paying taxes (fees, insurance contributions) or on other issues of application of legislation on taxes and fees , given to him or an indefinite circle of persons by a financial, tax or other authorized government body (an authorized official of this body) within its competence (these circumstances are established in the presence of a corresponding document of this body, in the meaning and content related to tax (reporting, settlement) periods for which arrears arose, regardless of the date of publication of such a document), and (or) as a result of the taxpayer (fee payer, insurance premium payer, tax agent) fulfilling the motivated opinion of the tax authority sent to him during tax monitoring.
The provision provided for in this paragraph does not apply if the specified written explanations or the reasoned opinion of the tax authority are based on incomplete or unreliable information provided by the taxpayer (payer of the fee, tax agent).
How is the penalty amount calculated?
Each day of delay in payment of tax obligations will cost 1/300 or 1/150 of the refinancing interest rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation (clause 4 of Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Based on 1/300 of the refinancing rate, penalties are calculated:
- organizations for taxes and contributions for compulsory health insurance, compulsory health insurance and VNIM for the first 30 calendar days of delay;
- for taxes and contributions from the organization for the entire period of delay, if the arrears arose before October 1, 2022;
- on contributions for injuries;
- for taxes and contributions from individual entrepreneurs.
Based on 1/150 of the refinancing rate, penalties are calculated for organizations on taxes and contributions for health insurance, compulsory health insurance and VNIM for the 31st calendar day of delay and beyond (for debt incurred starting from 10/01/2017).
Important! An example of calculating penalties from ConsultantPlus An example of calculating penalties for taxes and insurance premiums The organization paid a tax (insurance premium) in the amount of 25,000 rubles. later than the due date. The delay in payment of tax (insurance contribution) was 26 calendar days. Let’s assume that during this period the refinancing rate was 9% for the first 10 days and 10.5% for the next 16 days (conditionally). Penalties for late payment of tax (insurance premium) are... For the full example, see K+. Trial access is free.
Overdue contributions for injuries
The fact that the policyholder pays penalties when transferring the specified contributions at a later date than those established by law is stated in Article 22.1 of the Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ.
Penalties are accrued for each calendar day of delay in “accidental” contributions, starting from the day following the established day for payment of these contributions, and up to and including the day of their payment or collection.
Penalties are not accrued if the policyholder confirms that he could not repay the arrears due to the suspension of transactions on his bank accounts or the seizure of his property. Also, penalties are not accrued during the period of validity of the granted deferment or installment plan for the repayment of amounts owed on insurance premiums and other payments.
Penalties are determined as a percentage of the arrears, which recognizes the amount of insurance premiums not paid on time.
The interest rate of penalties is set at 1/300 of the Bank of Russia rate in effect at the time the arrears occurred. If the specified rate changes, the amount of penalties based on the new refinancing rate is determined from the day following the day of its change.
Penalties are paid simultaneously with the payment of insurance premiums, and if the policyholder has insufficient funds, after paying insurance premiums in full. Arrears and penalties may be collected by the FSS of Russia forcibly at the expense of funds and other property of the policyholder.
The bank did not execute the payment order on time - is the penalty legal?
Quite often, late tax payments arise precisely through the fault of banking institutions, and not through the fault of tax payers. This is expressed in the untimely execution of the payment order by the bank, which was issued to it by the account owner.
Example. On August 25, Creden LLC sent a payment order in the amount of 65,788 rubles. to pay VAT for July via the Internet banking system. There were no errors when forming the order; the company also had enough money in its account to execute the order. But for some reason, the bank executed the order only on August 26, and therefore Kreden LLC was charged a penalty for 1 day of delay in the amount of 23 rubles. 03 kop.
In this situation, the penalty was charged incorrectly, since in accordance with the requirements of paragraph 2 of Art. 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, LLC “Kreden” fulfilled its obligation to timely pay tax obligations: the payment request was sent, there was enough money, the payment was not rejected by the bank and was transferred to it within the time period that is regulated for accepting orders. In this situation, it is advisable to contact the fiscal authority for recalculation, and if there is a refusal, then a complaint should be sent.
To what extent can a penalty be used?
A penalty (fine and penalty) can be defined in the contract in the amounts that the parties agree to and if the Law does not limit such amounts. The law, by the way, does not limit them, although too high fines may be considered unlawful.
If the penalty payable is clearly disproportionate to the consequences of the violation of the obligation, the court has the right to reduce the penalty.
Art. 333 Civil Code of the Russian Federation
In this case, the penalty will have to be reduced only through the court, since it will not be “automatically” reduced, but it will be calculated without delay or delay. So, when setting the amount of fines and penalties in the contract, you should proceed from the estimated losses, and not get confused about making the penalty a way to earn money. By the way, it is prohibited to charge penalties on fines and penalties on penalties.
Can you be held vicariously liable?
Take the 10-question quiz to find out about your situation. Based on the test results, you will find out what risk group you are in (critical, high, low), and in accordance with it you will receive recommendations on measures to protect against subsidiary liability
No. 1 How long has the counterparty been in debt to you?
No. 2 Is the existing debt confirmed by documents (agreements, acts, etc.)?
No. 3 Have you contacted the Debtor with a demand to repay the debt?
No. 4 Have you sent an official written complaint to the Debtor?
No. 5 Did the Debtor provide security for the fulfillment of obligations?
No. 6 Have you filed a claim with the Debtor in court?
No. 7 The procedure for collecting debt from a counterparty on your part is carried out by:
No. 8 Have enforcement proceedings been initiated against the counterparty at your request?
No. 9 Has bankruptcy proceedings been initiated against your Debtor?
No. 10 Does the Debtor currently operate, including through affiliated companies?
No. 11 Do you know the controlling persons of the Debtor, the ultimate owners of the business, as well as the property status of these persons?
Leave your email to receive the video “32 Debt Collection Strategies” and a detailed plan on how to deal with the debtor to get your money back.
Is a penalty charged if the arrears arose as a result of written explanations from the tax office?
In paragraph 8 of Art. 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that for arrears that arose on the basis of explanations (necessarily written) from tax, financial departments or other authorized government agencies, no penalty is charged. The list of departments that are empowered to provide clarifications in the field of financial or tax legislation is determined by Art. 34.2 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 111 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, such clarifications can be addressed either directly to the taxpayer himself or to an indefinite number of persons. In the second case, we mean explanations that are freely available in the media, various reference and legal systems, magazines, and on the official websites of departments. You just need to be careful in their use, since they often provide for a specific situation that you mistakenly apply to yourself. If you are not completely sure of the identity of the situation, then it is better to send an independent request and receive an answer addressed to you.
Is a penalty charged to tax agents?
In paragraph 7 of Art. 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that a penalty can also be charged to tax agents. Very often this rule applies to personal income tax agents when the tax was not withheld by them and, accordingly, was not paid. But if the failure to pay personal income tax and the agent’s failure to withhold it does not result in collection of the tax itself, then this rule does not apply to penalties. In accordance with the provisions of Art. 46 and Art. 47 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, penalties from the agent may be withheld from the funds or property available to him.
Let's consider a similar situation.
Example. Paro LLC paid Isakov I.R. rent for the use of a passenger car, but did not withhold personal income tax from this payment. Isakov I.R. paid personal income tax on his own, but the fiscal authority imposed a penalty on Paro LLC because the tax was paid late.
Read more about the responsibility of a tax agent for personal income tax in the article “Tax agent for personal income tax: who is, responsibilities and BCC.”.
Results
Failure to timely fulfill tax payment obligations results in the accrual of compensation payments (penalties) by the fiscal authority.
However, their accrual is not always legal, and it should be understood that in some situations you can defend your rights and return the penalties withheld by the tax authorities. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.