When is it permissible to transfer an employee without his consent to another position?
The concept and rules of translation are enshrined in Articles 72 – 73 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In particular, Art. 72.1 and 72.2. determine whether the employer can transfer an employee to another job without his consent to do so. According to general rules, the employee’s opinion is necessarily taken into account. But there are cases when transfer to another job without the employee’s consent is permitted by law (Article 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If there is any doubt that the situation falls into the category listed in the article, it is recommended to conclude an agreement between the parties, because if the audit does not reveal extraordinary circumstances, the organization’s actions will be considered unlawful. At the same time, deliberate failure to perform work when changing a job function, carried out in compliance with the law, is recognized as a violation of labor discipline (Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. 2 of March 17, 2004, as amended on November 24, 2015). An employee has the right to refuse only if labor safety standards are not met and the new job poses a danger to his life and health. At the same time, they are obliged to offer him another (Article 220 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
“Medical” and “judicial” translations
If an employee has a medical report that contraindicates him from working in his current position, then the employer is obliged to transfer him to another job that doctors allow (Article 73 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The employee may not agree to a new “harmless” job. Then you will have to part with the employer on the basis of paragraph 8 of Article 77 of the Tax Code.
If, according to a medical report, a transfer is required for a period of up to four months, the employee will retain his position in any case. Even if he refuses the transfer, the employer is obliged to keep his job. The employee will not go to work and will not receive a salary, but will be able to return without hindrance.
In addition to “medical” translations, there are also “judicial” translations. We are talking about disqualification in court, that is, a ban on holding certain positions. In this case, the employer can transfer the employee to another position that is not prohibited. If the employee does not agree, then he has only one option - dismissal, since he has no right to remain in his position.
Temporarily
In Art. 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation lists the cases in which it is possible to temporarily transfer an employee to another job without his consent:
- upon the occurrence of dangerous circumstances that threaten the lives of the population (in case of industrial accidents, man-made disasters, natural disasters, etc.);
- if a dangerous situation caused downtime or a threat of property damage;
- if during a dangerous situation it is necessary to replace an absent employee.
At the initiative of the employer, the employee is transferred in connection with the prevention or elimination of the consequences of the above circumstances for a period of no more than one month in the same organization. The annual number of such movements is not limited.
When downtime or replacing an absent employee, it is important to consider qualifications. The Code regulates whether an employee can be transferred to another place of work without the consent of an employee to a position of lower qualifications. Consent will not be required only if he is temporarily transferred to a position of the same or higher qualifications. In other cases, a written agreement is required. For example, it is impossible to forcibly transfer a site manager to workers, but vice versa is allowed.
When you can’t and when you can refuse a transfer
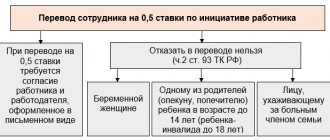
There are situations in which the employer does not have the right to refuse to transfer an employee to another position: this is the employee’s pregnancy and the presence of young children, the presence of medical indications, etc. But, for example, a transfer due to staff reduction or to another location at the initiative of the organization is possible only with the personal written consent of the employee.
The employee himself can, at any time and for any reason, refuse a transfer initiated by the employer, and also demand that he be provided with another, more suitable position, with working conditions that suit him.
Constantly
Art. 72.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows the transfer of an employee at the initiative of the employer permanently due to production needs, if the terms of the employment contract do not change: to another workplace, to another structural unit in the same locality (but only if it is not specified in the contract). If the job function does not change, and the employee still does not agree, then if there are no other vacancies, the previous employment contract is terminated. Under other circumstances, a permanent transfer of an employee in any form, including to another locality (another locality) together with the employer, requires a mandatory agreement with the employee.
Translation and relocation - what's the difference?
Let's start with terminology. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 72.1) refers to a change of workplace without dismissal as a transfer. The position, the nature of the work performed, and the terms of the contract under which the citizen was hired do not change. Example: a retail outlet manager is transferred to a similar retail outlet owned by the same company without leaving the area. Labor payments also remained at the same level.
The employee’s consent to the move is not required, no new entries are made in the work book, and the contract is not adjusted by an additional agreement. All we need is an order for organization.
When transferring, on the contrary, by default the consent of the citizen is required (Article 72.1-1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The profession, position, and sometimes qualifications may change. Such a personnel procedure involves changes to contractual terms, therefore, an additional agreement is required. If an employee leaves for a unit in a different location, he is considered to be transferred and not displaced, although he remains working in the same company. The permanent transfer is recorded in the work book.
Note! A transfer, just like moving a citizen to a workplace forbidden to him by doctors, is not permissible under any circumstances.
Translations are divided into:
- temporary and permanent;
- with or without the consent of the employee;
- at the initiative of staff or administration.
To another employer
To transfer an employee to another employer, it is necessary to carry out the procedure for terminating the employment contract under clause 5 of Art. 77 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This is permitted only with written agreement of the parties.
If a new job is contraindicated for medical reasons, appointment to this position is prohibited (Article 72.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
ConsultantPlus experts discussed how to arrange the transfer of a temporary employee to a permanent place of work upon dismissal of the main employee. Use these instructions for free.
General algorithm for processing a translation
Any transfer involves a temporary or permanent change in the essential terms of the employment contract (Article 72.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- job responsibilities;
- department;
- employer's location.
Such events are carried out only by agreement between the employee and the employer. Since any change in essential conditions is made by agreement between the participants in the labor relationship, a transfer to another position must be formalized by an additional agreement to the employment contract.
At the same time, there are cases when the employer can carry out temporary transfers for a period of up to 1 month unilaterally without the consent of the worker. For example, in the event of an emergency.
The procedure for transferring an employee to another position is given in the diagram below.
Thus, depending on the nature and conditions of the changes being made, documents for transfer to another position may have a different composition.
What documents should I submit?
General step-by-step instructions for transferring an employee to another position without his consent boil down to the following steps.
Step 1: Notification (optional in emergency situations).
Step 2. Drawing up and signing an additional agreement to the employment contract (indicating dates).
Step 3. Issuance of a transfer order (in the T-5 form or another accepted by the organization).
Step 4. Making an entry in the work book (if a temporary entry is not made).
Step 5. Making an entry in your personal T-2 card.
The order and changes in the employee’s personal card must be familiarized with signature.
Basic rules for placing an order
Today, the law says that an order to transfer an employee from one position to another can be issued in a free form. However, many enterprises and organizations, in the old fashioned way, prefer to use the previously approved and widespread T-5 form. This is understandable: the form contains all the necessary data, including information about the employer and subordinate, information about the former and new place of work, reasons for the transfer, etc.
The order can be filled out either by hand or on a computer, but it is printed out in a single copy and, after writing, is given first to the manager for signature, and then for review to the employee for whom it was drawn up. His autograph on the document will indicate that he agrees with the transfer to a certain position with the designation of a specific tariff rate and other conditions.
After registration, the order must be registered in the internal document register, and then transferred for storage to the personnel department.
Lost in translation
The given definitions, at first glance, make it possible to unambiguously determine what translation is and how to reflect it in the documentation. In practice, however, difficulties may arise. Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation determines the content of the contract with an employee. Among the unchangeable conditions is the place of work. If he is transferred from point of sale "A" to point of sale "B" without a change of employer, can it be considered under certain circumstances that his place of work has changed and there has actually been a transfer (not a transfer)? Experts express the following opinion:
- the employment contract must always indicate the place of work;
- if the place of work is a unit located in a different area, it must be named in the contract;
- if the structural unit was indicated in the document, its change means a transfer for the employee; if not, a transfer.
Often, a transition from one structural unit to another is formalized by displacement: without the consent of the citizen, since no changes in his labor functions are expected. Having started to work in a new place, a citizen discovers that in practice he is doing different work with an increased load, requiring different, increased qualifications. He may demand to change contractual terms, increase wages, and reflect higher qualifications in personal personnel documentation. The easiest way to resolve a conflict situation is internally by preparing a package of documents for transfer for this employee.
Transfer to a branch located in another area
If an employee is initially accepted into a branch of an organization located in another locality, the place of work and the name of the branch must be indicated in the employment contract. For example: “The employee’s place of work is the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Secondary Vocational Education “Volzhsky Technical School of Railway Transport” (FGBOU SPO “Volzhsky Technical School of Railway Transport” - a branch of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education “Volgograd State Transport University” (FGBOU VO VGUPS ), located in the city of Volzhsky, Volgograd region).
When an employee is offered to move to a branch located in another area, as well as when transferred from one branch to another located in another area, a transfer must be completed.
note
It is also necessary to carry out a translation when, in violation of Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a branch located in another locality is not indicated in the employment contract.
The transfer of an employee to a branch located in another area should not be confused with a transfer carried out in connection with the employer’s move to another area when the organization itself moves. In this case, employees may refuse to move with the employer and are then subject to dismissal under clause 9, part 1, art. 77 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. If an employee refuses to move to the area where the branch is located, dismissal is not provided.
But the employer will have to reimburse employees for expenses associated with moving to work in another area, as in the case of a transfer together with the employer (Articles 165, 169 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Expenses covered:
- for the relocation of the employee, members of his family and transportation of property (except for cases when the employer provides him with means of transportation);
- for settling into a new place of residence.