Last modified: January 2022
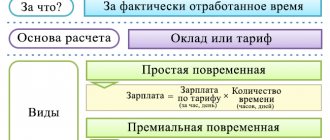
Each company has its own rules for calculating wages, but they are often associated with a salary or rate, supplemented by various additional payments at the discretion of the employer. A tariff rate is a remuneration fixed in internal documents, paid for fulfilling set labor standards of varying degrees of complexity according to a person’s qualifications, calculated per unit of time.
The use of tariff rates presupposes equal conditions for receiving remuneration by different employees engaged in the same work. According to the rules of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the indicator must be fixed in the contract as one of the mandatory conditions of labor relations.
What is the tariff system of remuneration. Differences from the tariff-free system
The tariff system includes a number of provisions, norms, rules and regulations that make up a unified method of calculation, as well as the calculation of employee wages. The form of remuneration under consideration differs significantly from the non-tariff form.
The tariff system takes into account the complexity of the work, its intensity, working conditions, qualifications of certain categories of personnel; only if the specified components are available and analyzed, the employee will be paid a salary.
The non-tariff system has fundamental differences: the wages of all employees of the enterprise depend on the results of the work of the entire enterprise and on the amount of money allocated by the employer to pay for the labor process.
A fundamentally important element of the non-tariff system is the coefficient that takes into account the individual contribution of each employee to the overall final result. The tariff-free system is distinguished by the fact that the salary of each member of the work team is part of the general wage fund.
The tariff system of remuneration includes the main elements:
- tariff schedules;
- tariff directories;
- tariff rates.
Do you need help from a labor lawyer?
We will analyze your prospects for free!
+7
What is the wage rate
The tariff rate is a documented amount of remuneration for achieving a labor standard or other degree of difficulty per unit of time. The basic principle of applying tariff rates is to pay the same remuneration for the same amount of work.
The tariff rate is necessarily fixed in the employment contract, which is signed with employees. The employee will not receive less than the amount specified in the contract, provided that all job functions are performed.
According to Art. 143 of the Labor Code, the tariff system of remuneration involves a certain differentiation of rates depending on the categories assigned to employees. The wage differentiation consists of:
- From tariff rates (the amount that is paid to employees for fulfilling labor standards, depending on their qualifications and the complexity of the tasks performed).
- From tariff schedules (a system consisting of tariff rates and including the ratio of the complexity of the work performed and the level of his salary).
- From the coefficients.
- From salaries.
To determine the tariff rate, you need to multiply the rate for the first category by the increasing tariff coefficient.
The tariff rate as a unit for calculating earnings performs several important functions: it makes payment and labor content commensurate, denotes a minimum depending on quantitative and qualitative characteristics, stimulates work in given conditions (during processing, hazardous work, etc.), adequately calculates wages .
The time period for which the tariff rate is determined can be any: hour, day or month. Hourly rates are usually set if the company has a shift work schedule or if the company employs hourly employees.
The hourly tariff rate is used in the process of calculating pay on weekends, night shifts, in excess of standards, in dangerous, harmful and difficult conditions.
The hourly rate can be determined in several ways : by dividing the monthly rate by the number of working hours according to the calendar. In the second method, the hourly rate is calculated by dividing the salary by the average monthly number of hours during the calendar year. The exact calculation algorithm used by the employer must be recorded in a local regulatory act (for example, in a collective agreement).
For work at night (from 22 to 6), the employee is paid a salary of no less than 20% more than the standard tariff rate. Work on weekends and holidays is paid at double rate.
Day rates apply if work is completed during the day. At the same time, the number of working hours in a day is the same, but differs from the norm under the Labor Code. That is, it is advisable to use daily rates if the number of working days differs from the standard 5 days.
Monthly rates are valid subject to the process of standardization of working hours : if workers have firm, fixed days off and a stable schedule. In this case, the time sheet must be closed regardless of the number of hours actually worked: after working out the monthly quota, the employee earns a salary.
Unified tariff and qualification reference books
These reference books are necessary to regulate the work of representatives of the main working professions, management positions, employees and specialists within the enterprise. Using the provisions of a single directory, you can determine the suitability of an employee for the position held.
The document contains requirements for personnel categories, descriptions for each type of activity, a listing of the employee’s skills and knowledge, and a list of professions related to each type of work.
The unified directory of positions for managers, employees, and specialists contains requirements for the qualifications, knowledge and education of these categories of workers and explains their main job responsibilities.
Using the provisions of the directory, various types of professional activities are compared according to the complexity of their components. In addition, categories and qualifications are determined. This process is generalized into the concept of “tariffication”.
Tariffing procedure
Tariffication occurs by comparing the work performed at the enterprise with the list and examples of work contained in a single directory. For pricing purposes, an enterprise can develop and introduce internal lists of work, and use them along with the main ones.
Depending on the rank, the salary of an employee of an enterprise varies. To transfer an employee from rank to rank, in accordance with the internal regulations of the organization, a qualification commission is formed and convened, and its chairman is elected.
The employee, in the presence of members of the commission, passes a qualification exam, which includes testing theoretical knowledge and, in some cases, practical skills. If the exam is passed successfully, the employee receives a certain rank or moves from one to another, which is recorded in his work book. To rate the salaries of managers, as well as employees and specialists, a single directory of the specified positions is used.
Similarities
Despite all the differences between these systems, they have a lot in common. As it turned out earlier, a salary can only be received after working out the pay period, and the tariff rate involves the payment of earnings for a certain unit of time, an hour or a week a day. But if an employee has not worked in full for a month, for example, was on vacation or on sick leave, then his salary is paid only for the time actually worked.
Let's look at how to calculate the hourly rate from your salary. Everything is quite simple, to do this you need to divide a fixed amount by the number of days or hours worked . For example, if it is 25,000 rubles per month, then you can calculate how much he earns per day if there are 22 working days of 8 hours each in a calendar month. Thus, his tariff rate per day will be 25000/22, equal to 1136.36 rubles per day or 142 rubles per hour.
Please note that in the system of calculating wages from salary, the employer clearly pays the employee only for the time he has worked, that is, payment is taken from the salary for the period that he is absent from the workplace.
Thus, the employer alone establishes the system of remuneration for employees of his enterprise: salary and tariff rate. What is the difference? Significant differences are that the tariff rate is applied in most cases to representatives of a profession in the field of production or service; the salary is more often applied to employees in the field of economics or other intellectual activity.
Tariff rates
The tariff rate is understood as a payment to an employee measured in monetary terms, taking into account his qualifications, nature and standards of work performed. Calculation of tariffs occurs both for time-based and piecework wages.
The tariff rate is a guarantee that the employee will receive money for work, provided that it is performed in good faith. Additional payments, bonuses, compensations are not included in the concept of “tariff rate”. Consequently, the tariff rate is the minimum wage for an employee, to which, in the process of wage formation and calculations, other components of wages are added.
What is salary
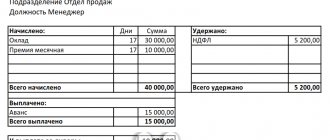
Before you understand the difference between a tariff rate and a salary, you need to review these two concepts in detail. In fact, salary is a fixed amount of an employee’s earnings, which is accrued for the performance of his official duties . In simple words, it is paid in full only if two important conditions are met: that the employee fulfills his job duties and remains at the workplace in accordance with his work schedule.
Wages and salary are two different concepts, for the reason that a fixed sum of money is just part of an employee’s earnings; in addition to it, he can receive various allowances, for example, bonuses and other payments. The definition of salary means a fixed amount that an employee is guaranteed to receive based on the results of the month worked, provided that he stayed at work in accordance with his work schedule.
Tariff schedule and tariff category
The tariff schedule represents the ratio of tariff rates in accordance with the category. Designed in the form of a table for entering data. For different categories of work, tariff scales with different numbers of categories are provided.
Enterprises, as a rule, use a six-digit grid, where the first digit is the lowest and the sixth is the highest.
An enterprise, in accordance with its internal situation, can change the tariff scale towards increasing or decreasing its range. The instrument in question is used not only in relation to blue-collar professions. The tariff schedule is typical for calculating wages of public sector workers.
The tariff category shows the level of qualifications and skills of the employee and characterizes the complexity of the work he performs. The composition and size of an employee’s salary largely depends on the tariff category.
NTC in the employment contract
The size of the hourly wage rate can be fixed in the employment contract (Part 2 of Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Since the wage agreement paragraph is mandatory, it would be appropriate to specify not only the tariff rate that the employee will receive hourly, but also additional incentive and compensation payments - additional payments and allowances.
Important!
You cannot refer in the text of the contract to the Regulations on remuneration or staffing schedule for the enterprise. This is a gross violation of the Labor Code.
Before signing an employment contract, every potential employee should carefully study it. Everything related to changes in wages, including salary increases, must necessarily occur by mutual agreement. This fact must be recorded in an additional agreement to the employment contract. The document must contain a phrase that precisely establishes the size of the hourly tariff rate. For example: “The employee has an hourly wage rate of 200 rubles per hour.”
The use of tariff systems for time-based and piecework wages
The main types of payroll calculation include:
- time payment;
- piece-work payment.
When calculating wages, the employer takes into account the following elements:
- grade of work;
- its characteristics;
- the standard time allotted for its implementation;
- tariff rate.
Calculation of piecework payment is made on the basis of the provisions of the unified tariff and qualification reference books. The most important component of work with piecework payment is production. One of the main disadvantages of piecework payment is the high probability that, in an effort to produce more products, the employee will not pay due attention to the quality of the finished product.
When calculating time wages, the amount of money an employee receives monthly depends on his rank. Also, when calculating time-based wages, the amount of time worked plays a significant role, which fundamentally distinguishes this form of payment from piecework.
Time-based payment requires mandatory staff pricing and clear timekeeping of the time spent by the employee on work. Today, most enterprises produce time-based wages, recognizing it as a more convenient type of payment for the parties to labor relations than piecework wages.
What is the difference
So, we have looked at what salary and rate are, what the difference will be discussed further. The two payroll systems have several differences. The main one is that according to the salary system, wages are accrued to the employee for the pay period, that is, a month or a year, depending on the specifics of the work and the position he occupies. A tariff rate is a payment for a certain period of time; it is mainly applied during a shift work schedule.
Another difference is that the salary is accrued for the employee’s performance of his work duties, and the tariff rate is the amount of time worked. In addition, both of these systems are used depending on the specifics of the work, for example, in some positions the employee’s income level will directly depend on the work performed and volume. Although in this case, wages have a piece-rate wage system, in relation to which both a salary and a tariff rate can be applied, that is, a fixed payment amount for the billing period plus a percentage of the amount of work performed.
Procedure for establishing tariff systems
Russian labor law in its provisions determines the procedure for establishing tariff systems. Regardless of the legal form of the organization and the type of its activity, the tariff payment system is established by local regulations, provisions of collective agreements, and agreements.
Also, when establishing tariff systems, the data of the unified tariff and qualification reference book are fundamentally taken into account, taking into account all the requirements of the labor legislation of the Russian Federation and other regulations mandatory for execution on the territory of the Russian Federation. The employer, when introducing tariff systems to the enterprise, must respect the rights of the employee and create decent working conditions.