The essence of the audit of financial statements
Financial reporting is a concentrated set of indicators that characterize the work of a specific business entity for a certain period of time.
On its basis, various types of economic and financial analysis are carried out, and management decisions are made. The more reliable the reporting information, the more useful it is for users and the higher the degree of effectiveness of decisions made on its basis. Read about algorithms for using reporting data for analysis in the following materials:
- “Methodology for analyzing the balance sheet of an enterprise”;
- “Features of analysis of consolidated statements”.
To ensure that users of reporting do not have doubts about the quality of the information presented in the reporting, and that its compilers are not tempted to modify this data for their own purposes, an independent assessment of the reliability of financial reporting is required.
This task can be achieved through an audit - a set of special verification activities, as a result of which independent specialists express in the prescribed form an opinion on the degree of reliability of the data presented in the reporting.
The audit makes it possible to:
- the audited entity can see its accounting from the inside through the eyes of professional specialists, receive the necessary recommendations and correct identified distortions, eliminate errors;
- management and owners of the audited entity - evaluate the work of the accounting personnel and the company as a whole and make appropriate organizational conclusions;
- other users of reporting - to receive a qualified professional assessment of the reliability of reporting, on the basis of which effective decisions can be made.
For information about what types of decisions of owners may depend on reporting data, read the article “Decision on payment of dividends to an LLC - sample and order .
Purpose of the financial statements audit
The purpose of the audit of financial statements is deciphered in 2 regulatory legal acts (LLA):
- Law “On Auditing Activities” dated December 30, 2008 No. 307-FZ (clause 3 of Article 1);
- Federal rule (standard) of auditing activities No. 1 “The purpose and basic principles of the audit of financial (accounting) statements”, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of September 23, 2002 No. 696 (clause 2).
It is formulated as follows: expressing an opinion on the reliability of reporting and compliance of the accounting procedure with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
In the process of taking actions to achieve the main purpose of the audit, auditors are required to:
- maintain independence;
- apply professional skepticism;
- follow ethical principles (honesty, objectivity, etc.).
“Procedure for conducting an audit of the balance sheet” will tell you about the main stages of the audit .
Who is subject to mandatory audit
Organizations that meet certain criteria must undergo mandatory audits.
The Federal Law of December 30, 2008 No. 307-FZ “On Auditing Activities” identifies six criteria:
- The organization has the form of a joint stock company.
- The company's securities are admitted to organized trading.
- The company is a credit organization, a credit history bureau, a professional participant in the securities market, an insurance organization, a clearing organization, a mutual insurance company, a trade organizer, a non-state pension or other fund, a joint-stock investment fund, a management company of a joint-stock investment fund, a mutual investment fund or a non-state pension fund.
- The company's revenue for the previous year exceeds 400 million rubles or the balance sheet exceeds 60 million rubles.
- An entity files or publishes consolidated financial statements.
- An organization is required to undergo an audit due to certain laws. For example, developers, state corporations and others.
A mandatory audit is required if the organization meets at least one of the listed criteria.
Independence and professional skepticism in the audit of financial statements
Compliance with the principle of independence is given particular importance in the audit environment. This aspect is covered both in separate articles of a number of regulatory legal acts and documents entirely devoted to issues of auditor independence, for example:
- Art. 8 of Law No. 307-FZ;
- rules for the independence of auditors and audit organizations, approved by the Auditing Council (minutes No. 6 dated September 20, 2012);
- codes of ethics and independence of auditors of the Russian Federation and individual self-regulatory organizations (SROs) of auditors;
- sections of internal auditing standards.
If there is a threat to independence and appropriate precautions to eliminate them cannot be taken (or do not exist), the auditor is required to refuse the engagement (stop performing it).
The auditor is required to:
- be independent of the audited entity during the audit and the period covered by the audited statements;
- reflect your findings on compliance with independence in working documents;
- carry out other actions based on the requirements established by the legal acts.
The concept of “professional skepticism” refers to the category of special audit terms and consists of the following:
- the auditor is obliged to critically evaluate the weight of evidence obtained during the audit;
- Audit evidence that contradicts information obtained from other sources (any documents or management statements) or casts doubt on the reliability of such documents and statements is subject to careful examination;
- When planning audit procedures and preparing conclusions based on audit results, it is important:
- do not ignore suspicious circumstances;
- do not make unjustified generalizations;
- do not use erroneous assumptions when determining the nature, timing and scope of audit procedures (including when assessing audit results).
During the audit process:
- the auditor should not assume that the management of the audited entity is dishonest, but cannot evaluate it as unconditionally honest;
- Management statements (written and oral) are not a substitute for obtaining sufficient appropriate audit evidence.
It is important for the management of the audited entity, as well as specialists who directly provide auditors with the necessary information (preparing and providing documents, drawing up explanations and responses to requests), to correctly understand the content of the terms “independence” and “professional skepticism” - this will allow them to adequately respond to the procedures carried out by the auditor and the clarifications requested by him during the audit of financial statements.
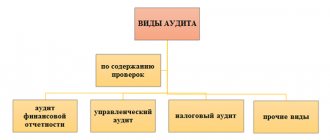
Types of audit
In accordance with current legislation, there are two types of audit control:
- Mandatory audit. Entities that are subject to annual mandatory audit are named in Article 5 of Law No. 307-FZ.
- A random or initiative audit, that is, one that is carried out at the request of the company’s management.
Mandatory audit is carried out once a year. The object of the audit is accounting (financial) statements. Companies are required to submit an audit report to the Federal Tax Service within 10 working days after receiving such a report, but no later than December 31 of the year following the reporting year. Submitting opinions on the 2022 financial statements is required before the end of 2022 (Clause 5 of Article 18 402-FZ dated 12/06/2011).
Let us recall that entities that are subject to annual mandatory audit are specified in Article 5 of Law No. 307-FZ. Here are all the cases of mandatory audit in 2022:
- joint stock companies;
- insurance organizations, mutual insurance societies;
- credit institutions, credit history bureaus;
- clearing companies;
- state and municipal enterprises;
- non-state pension funds and their management companies;
- commodity and stock exchanges;
- professional securities market participants;
- organizers and operators of lotteries (138-FZ dated November 11, 2003);
- self-regulatory organizations (315-FZ dated December 1, 2007);
- institutions of the savings and mortgage system (117-FZ of August 20, 2004).
Legislators have provided a number of additional conditions for companies whose annual reports must undergo a mandatory audit in 2021:
- upon admission of the company's securities to trading;
- when preparing consolidated reporting, except for state and municipal government agencies;
- if the revenue exceeds 800 million rubles per year, except for unitary state enterprises and agricultural cooperatives;
- the total balance sheet asset for mandatory audit at the end of the year exceeded 400 million rubles;
- the obligation is enshrined in separate regulations or local orders of company management.
But the latest news about mandatory audit in 2022 - from 01/01/2021 Federal Law No. 476-FZ dated 12/29/2020 amended the Federal Law “On Auditing Activities”, changing the control requirements for funds and commercial organizations.
A limit has been introduced for funds on the receipt of property and cash for the year immediately preceding the reporting year - over 3 million rubles. For receipts less than this amount, verification of reporting is not required.
For organizations, one of the criteria has changed. Now it is not revenue that is taken into account, but income for the year preceding the reporting year. This indicator is the sum of line 010 and line 020 of sheet 02 of the income tax return.
IMPORTANT!
LLCs must conduct a mandatory audit for 2022, taking into account the new limits:
- income from business activities for the year preceding the reporting year is more than 800 million rubles;
- the amount of assets in the balance sheet at the end of last year was more than 400 million rubles (line 1600 of the balance sheet).
The law contains a clause stating that the exemption from the audit does not apply if, before 01/01/2021, an audit of the financial statements has already begun under an agreement with a specialized organization or an individual auditor. In this case, the new rules apply starting with 2021 reporting. For joint stock companies, limits do not apply, and verification is mandatory under any conditions, as provided for in Article 67.1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
A complete list of those who are required to provide an auditor’s report on the 2022 financial statements is on the official website of the Ministry of Finance.
Additional requirements for the auditor
The audit profession has a special distinctive feature - the auditor is obliged to act in the public interest, and not limit himself solely to meeting the needs of his clients or the audit company.
This “public” responsibility requires the auditor to comply with professional ethics.
In addition to maintaining the principle of independence and applying professional skepticism, the auditor must meet a combination of the following requirements:
- Be honest - act openly and honestly in all professional and business relationships, deal fairly and be truthful;
- ensure objectivity - do not allow bias, conflicts of interest or other persons to influence the objectivity of his professional judgments;
- be professionally competent and perform their duties with due care - constantly maintain knowledge and skills at a level that ensures the provision of qualified professional services (based on the latest developments in practice and legislation), and also act in good faith in the provision of professional services in accordance with professional standards;
- not to violate the requirement of confidentiality - not to use confidential information obtained during the audit to obtain any advantages for him or third parties, and also not to disclose such information;
- ensure professional behavior - comply with the requirements of legal regulations and avoid actions that discredit the auditing profession.
To find out whether accounting specialists must comply with the code of professional ethics, read the article “Job description of the deputy chief accountant” .
The main objectives of the audit of financial statements
To achieve the main goal of the audit described in the first section of our material, it is important to solve the following tasks:
- during an audit, obtain independent and reliable initial information about the financial activities of the audited entity;
- based on the obtained audit evidence, form conclusions about the reliability of the financial statements of the audited entity;
- state in a separate document the identified comments and recommendations for their correction;
- formulate an audit report that corresponds to the actual level of reliability of the audited statements, taking into account regulatory requirements and that is understandable to users;
- other tasks (specified in the contract and audit assignment).
Read about the objectives of other control measures in the material “Financial control: concept, meaning and objectives” .
Property tax reporting
The property tax return for 2022 must be submitted using the new form no later than March 30, 2022 (Orders of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated July 28, 2020 N ED-7-21/ [email protected] and dated December 9, 2020 N KCH-7-21 / [email protected] “On amendments to the appendices to the order of the Federal Tax Service dated August 14, 2019 N SA-7-21 / [email protected] ). Order of the Federal Tax Service dated December 9, 2020 N KCh-7-21/ [email protected] will come into force on March 14, 2022. If you submit a declaration taking into account the latest changes, you should ask the tax office about the possibility of accepting it. In 2022, only real estate assets were subject to property tax. But the declaration for 2022 must include information on the average annual cost of movable property items recorded on the organization’s balance sheet as fixed assets according to accounting rules (paragraph 4, paragraph 1, article 386 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Federal Law dated November 23, 2020 N 374- Federal Law). For this information, the updated declaration provides section 4.
Taxpayers who own only movable property do not have to submit property tax reports (Clause 20, Article 1 of Federal Law No. 63-FZ of April 15, 2019), because Only payers of this tax must submit a declaration on the property tax of organizations (Article 386 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, organizations whose property is exempt from taxation on the basis of benefits are taxpayers, since in fact they have an object of taxation. Therefore, they remain obligated to file a tax return. For example, organizations exempt from paying property tax as a support measure during the spread of coronavirus, in sections 2 and 3 of the declaration show the amount written off as a benefit (clauses 5.3, 7.2 of the Procedure for filling out the declaration, Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated June 10, 2020 N BS-4-21/ [email protected] ).
In addition, tax returns must be submitted by taxpayers whose real estate assets subject to taxation at the average annual value are fully depreciated (clause 1 of Article 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 02/08/2010 N 3-3-05/128). The amount of property tax payable will be zero, information about the value of movable property will be included in the declaration.
The average annual value of movable property related to fixed assets must be indicated for each region, including for separate divisions that have a separate balance sheet. For the future, the legislator is exploring the possibility of making movable property an object of taxation again, but at the same time reducing property tax rates.
Registration of audit results
Registration of the results of an audit of financial statements is a multi-operation procedure, including:
- preparation of a set of working documents for the auditor for the audit and other necessary papers (in accordance with the requirements of federal and internal auditing standards and rules);
- formulating the text of the audit report and written information to the management and owners of the audited entity based on the audit results;
The auditor's working documents are stored in the audit company and are subject to quality control by the SRO and Rosfinnadzor (if the audit was carried out in relation to the reporting of particularly significant business entities).
Providing management and owners with written information containing the auditor’s comments and recommendations is a separate procedure regulated by a special auditing standard, which outlines the requirements for:
- the auditor's identification of the appropriate recipients of such information;
- content of the information;
- timing and form of its presentation.
The auditor's report (AZ) is a final and general document drawn up in accordance with the Federal Auditing Standard (FSAD) 1/2010 “Audit report on accounting (financial) statements and forming an opinion on their reliability” (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 20, 2010 No. 46n), defining the requirements:
- to the form and content of AZ;
- algorithms for signing and presenting conclusions;
- scheme for expressing an opinion on the reliability of accounting (financial) statements.
To find out whether there is interaction between auditors and tax authorities regarding audit data, read the material “Tax authorities will have access to audit data.”
Legal side of the issue
The main document used in drawing up the audit report is standard No. 6 “Audit report on financial (accounting) statements”, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 696 dated September 23, 2002. It contains uniform requirements for the form and content of the audit report.
Federal Standard No. 10 “Events after the reporting date” contains requirements for the auditor’s actions in relation to events that occurred after the date of signing the auditor’s report, but before the date of presentation of financial statements to users.
Data is current as of the end of 2022.
Return to list
Results
An audit is a socially significant and multi-part procedure aimed at confirming by independent specialists the reliability of the financial statements of the audited entity.
The specialists conducting it, as well as the process itself, are subject to certain requirements, the fulfillment of which allows us to consider the audit procedure carried out in compliance with the established rules. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Design features
The following basic requirements apply to the preparation of an audit report of any type.
It must be signed by the head of the auditor or the person authorized by the head who conducted the audit (who led the audit). Signatures must be sealed. Directly attached to the conclusion are financial (accounting) statements indicating the date, signed and certified by the seal of the audited entity. all sheets must be numbered, collected into a single brochure and sealed with the auditor’s seal.
The date of signing of the auditor's report should correspond to the date on which the audit was completed, but not earlier than the date of signing or approval of the financial statements of the audited entity.