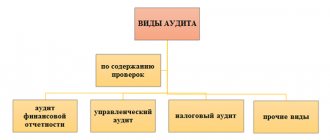
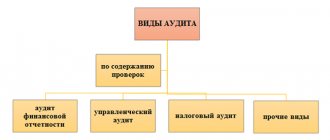
Purposes of financial statements audit
The purpose of the audit is to express an opinion on the reliability of reporting and the correctness of accounting in accordance with the law. Based on the results of the audit, specialists draw up an audit report.
To achieve the stated goal, the following tasks must be completed during the audit:
- collect reliable initial information about the financial activities of the audited entity;
- based on the collected audit evidence, draw conclusions about the reliability of the financial statements;
- record comments and recommendations for their correction in a separate document.
Report easily and without errors. A convenient service for preparing and submitting reports via the Internet. We are giving access to Extern for 14 days!
Internal audit at the enterprise: goals, objectives and types
Internal audit is an activity to monitor the facts of economic life that arise in the process of operation of an enterprise.
The organization of such activities is obligated by clause 1 of Art. 19 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ. However, the owners or managers of the enterprise are also interested in the audit, since the information obtained as a result of control activities allows them to take timely steps to increase business efficiency. The purpose of introducing internal audit is effective systematic monitoring of all circumstances significant to the organization’s activities in order to promptly influence these circumstances. At the same time, the enterprise itself has the right to detail their list, depending on its scale. Legal entities subject to mandatory audit will have to give a special place in this list to control over accounting and the formation of accounting records (Clause 2, Article 19 of Law No. 402-FZ).
Internal audit tasks:
- tracking issues that affect the results of the enterprise;
- identification of errors, shortcomings, abuses;
- warning of possible risks.
Organized internal control makes it possible to quickly identify factors that negatively affect the activities of the enterprise, the quality of its products and financial and economic indicators, and quickly select the optimal measures to correct the situation.
Among the types of internal audit there are those related to control:
- organizational aspects (work of the administration, departments or even specific employees, provision of departments with property);
- compliance in the main activities with the requirements of current legislation or certain regulations;
- accounting and reporting.
The last type is mandatory for every enterprise, since it is it that ensures the fulfillment of the reliability requirement for accounting reporting (Clause 1, Article 13 of Law No. 402-FZ). Other types of control are established at the discretion of the owner/manager of the enterprise.
Audit of financial statements
The audit can be mandatory or proactive.
Organizations undergo mandatory audits in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Companies conduct proactive audits based on their needs. The head of the organization enters into an agreement with the audit firm, and within the agreed time frame, the auditors conduct a proactive audit. In this case, you can check all accounting areas, or you can select individual objects.
During the proactive audit you can:
- Check the accuracy of financial and accounting statements. This will help identify weaknesses and errors in the documentation and correct accounting in a timely manner. It's safer to find and fix errors before the tax inspector arrives. In addition, with an audit report in hand, it is easier to attract investors.
- Check the knowledge and qualifications of the company's accounting service. If necessary, send employees to improve their skills and schedule training seminars.
- Analyze tax risks and reduce them to a minimum.
Audit is also divided into internal and external. An internal audit is most often carried out by an organization's in-house auditors. External audits are carried out by independent audit organizations with the aim of objectively assessing the state of accounting and reporting.
A high-quality audit will help you really evaluate the work of the enterprise’s accounting service and see problems in document flow and accounting in general.
Can an audit be voluntary?
Yes, of course, an audit can be voluntary, that is, initiated by the owner in certain interests.
For example, when there is a change of manager, chief accountant or doubts about the correctness and reliability of accounting.
Often, owners order an audit to check the work of the accounting department in order to assess possible risks.
invites you to a free webinar on how primary management can save a company from claims: more details here.
Who is subject to mandatory audit
Organizations that meet certain criteria must undergo mandatory audits.
The Federal Law of December 30, 2008 No. 307-FZ “On Auditing Activities” identifies six criteria:
- The organization has the form of a joint stock company.
- The company's securities are admitted to organized trading.
- The company is a credit organization, a credit history bureau, a professional participant in the securities market, an insurance organization, a clearing organization, a mutual insurance company, a trade organizer, a non-state pension or other fund, a joint-stock investment fund, a management company of a joint-stock investment fund, a mutual investment fund or a non-state pension fund.
- The company's revenue for the previous year exceeds 400 million rubles or the balance sheet exceeds 60 million rubles.
- An entity files or publishes consolidated financial statements.
- An organization is required to undergo an audit due to certain laws. For example, developers, state corporations and others.
A mandatory audit is required if the organization meets at least one of the listed criteria.
How to become an internal audit specialist
Every day the demand for specialists who are able to carry out internal control of an enterprise is growing. But the requirements for them are also increasing. They must have knowledge in the financial sector, understand internal control and corporate governance, know national and international internal audit standards, and also understand the specifics of the activity that needs to be analyzed.
Online training comes to the rescue of always-busy financial professionals. Online courses allow you to study without interrupting your main activity, at home or at work in convenient, comfortable, familiar conditions. The quality of distance learning is not inferior to, and often exceeds, its face-to-face counterparts, due to the involvement of highly qualified teachers, a modular course system, online tests and much more.
The procedure for conducting an audit of financial statements
There are no fixed deadlines for conducting an audit. Some organizations prefer to conduct an audit in several stages, while others invite auditors after the end of the reporting year.
Not all auditors have the right to conduct statutory audits. The Ministry of Finance publishes on its website a list of organizations and individual auditors that are allowed to conduct statutory audits. A number of companies are prohibited from engaging individual auditors in audits: credit and insurance organizations, non-state pension funds, etc. (Article 5 of the Federal Law of December 30, 2008 No. 307-FZ).
The procedure for conducting an audit depends on various factors. In general, the following stages of working with an audit company can be distinguished:
- Analysis of tasks and determination of audit costs.
- Approval of inspection deadlines.
- Formation of a group of auditors.
- Audit of accounting and financial statements.
- Drawing up a report and recommendations.
- Drawing up an audit report.
- Consulting the customer, explaining the recommendations provided.
Before signing a contract, auditors carefully study the client. Independent auditors look at the technical equipment and automation of accounting at the enterprise, evaluate the specifics of the activity and the qualifications of staff accountants, analyze the financial condition, check for the presence of obligations and litigation.
Next, the audit company develops an audit plan and schedule with dates. Specialists are selected for each stage of work.
The check begins. To obtain evidence, auditors perform special procedures: recount, inspection, oral questioning of employees, confirmation, inspection, study of documents.
Having collected and analyzed evidence, the specialist prepares an audit report and conclusion. The audit report will be positive if no negative facts are found. If errors and inaccuracies are found, a modified conclusion is issued. In some cases, the auditor may issue a refusal to express an opinion.
The audit report is submitted to the tax office. The company can submit the conclusion together with the reporting or separately. The deadline for submitting an audit report to the Federal Tax Service is December 31 of the year following the reporting year. In this case, the approved conclusion must be submitted within ten days from the date of its signing.
Until 2022, it was necessary to submit reports and audit reports to the statistical authorities. This obligation has now been cancelled.
Report easily and without errors. A convenient service for preparing and submitting reports via the Internet. We are giving access to Extern for 14 days!
Who conducts the audit?
The audit is carried out by independent audit companies whose employees are auditors.
Not every person with an economic education has the right to conduct an audit. To carry out such activities, he must pass an exam to obtain a special certificate and be a member of the SRO.
Auditors are required to have a high level of competence and knowledge of accounting and tax legislation in various fields and industries. Ethics, independence and confidentiality play an important role in the performance of professional duties.
What documents are subject to verification?
When auditing financial statements, specialists study not only annual financial statements, but also various registers, contracts, accounts, personnel and other related documents.
In particular, auditors may request:
- primary documentation to verify the formalization and legality of the transaction;
- inventory sheets;
- documents on created reserves;
- contracts;
- constituent documents;
- bank statements;
- financial statements and declarations;
- balance sheets, analysis and account cards;
- personnel orders;
- expense reports;
- staffing table, etc.
Auditors check not only documents, but also various calculations. For example, payroll calculation, calculation of taxes and penalties, calculation of exchange rate differences and material benefits, etc.
The audit company assesses the financial risks of the audited entity. Analyzes overpayments and debt to counterparties and the budget. Based on the assessment results, auditors make recommendations to eliminate errors and minimize risks.
Who should be entrusted with conducting an audit of the financial and economic activities of the enterprise?
To conduct an audit of the financial and economic activities of an enterprise, you can use your own resources or use the paid services of specialized companies and experts.
Who can you trust to audit the financial condition and activities of the company as a whole? There is no single recipe. The decision is influenced by various factors: legal requirements for conducting a statutory audit, the intentions of the management or owners of the company, the availability of funds to pay for the services of independent experts, etc.
If a mandatory audit cannot be avoided, the choice is narrowed. This type of audit is carried out exclusively by auditors who have qualification certificates and are members of a professional self-regulatory organization. When a mandatory audit is not required, but the need for an audit is high and there are financial resources for this, you can use the services of a consulting firm specializing in the analysis and assessment of the financial and economic activities of enterprises. If the company has its own qualified financial and economic personnel and/or management does not want to disclose its activities to third-party analysts, you can conduct an audit on your own.
Next, we’ll figure out how to conduct a financial audit of a company on your own.
Typical errors and violations
Some possible violations depend on the specifics of the activity of the person being inspected. Common and common mistakes, regardless of the field of work, include:
- incorrect calculations of tax payments;
- discrepancies in reporting indicators;
- lack of permitting documentation (licenses, certificates, declarations and other permits);
- inventory and arithmetic errors;
- non-compliance with control ratios in reporting or contradictions in different reports (for example, sales revenue for no apparent reason is different in VAT and profit declarations);
- incorrect filling of details;
- arithmetic errors;
- incorrect calculation of income and expenses;
- collapsed reflection of receivables and payables. The debt must be formed in the context of contracts for each counterparty so that it is possible to separate receivables and payables;
- the authorized capital on the balance sheet does not coincide with the capital stated in the company’s charter;
- the authorized capital is not paid or not fully paid;
- there are no primary documents;
- the required reserves have not been accrued;
- the cash register limit is violated, etc.
Violations of fixed assets:
- real inventories are not carried out, as a result, the actual balances of property and debt do not coincide with those reflected in the accounting;
- deadlines for registering fixed assets are not met;
- there is no analytical accounting;
- expenses for modernization or inventory were taken into account incorrectly;
- the document flow of various operations is disrupted.
Tax violations:
- The lease agreement does not indicate the cost of the leased object. As a result, difficulties arise with the calculation of property taxes;
- unreasonable understatement of taxes;
- VAT is accepted for deduction without supporting documents;
- penalties and tax penalties are not reflected;
- incorrect reflection in the accounting (financial) statements of receivables and payables for settlements with the Federal Tax Service. The organization is obliged to reflect in its reporting settlements with the budget in amounts agreed upon with the Federal Tax Service. Before drawing up a balance sheet, you need to reconcile with the tax office and eliminate discrepancies;
- legal expenses, penalties, fines are not reflected (untimely reflected). The taxpayer must reflect the penalties and fines received and paid in court in non-operating income or expenses on the date the court decision comes into force. Often, information about legal proceedings reaches the accounting department with a delay. Late reporting of income leads to an understatement of the tax base and, as a consequence, income tax.
Report easily and without errors. A convenient service for preparing and submitting reports via the Internet. We are giving access to Extern for 14 days!
Result of mandatory audit
As a result of the study, the director of the enterprise or the responsible person by proxy receives an audit report, which must contain the following data:
- Information about the audit company or individual entrepreneur, full name of the auditor, INN, OGRN.
- Name, INN, OGRN of the business.
- A list of financial statements together with the dates of their preparation, which were studied by the auditor.
- The auditor's opinion on the reliability of the statements.
- Circumstances that may affect the reliability of the reporting.
If the auditor identifies violations, he is obliged to report them to the head of the enterprise and receive in response an agreement on the timing of eliminating the problems.
If the auditor has suspicions that the enterprise is carrying out illegal schemes, he is obliged to contact the tax service, while the Federal Tax Service may require the auditor to provide data obtained during the audit period.