Concept and classification of assets
Assets are the property of an enterprise that should bring profit in the future. In other words, these are financial investments that create constant passive income for the asset holder and increase their value over time. Assets are classified:
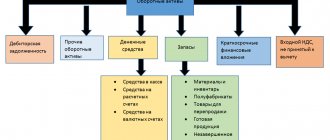
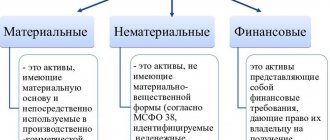
- By form of functioning: material: land, structures, finished products, equipment;
- intangible: licenses, copyrights, patents, trademark;
- financial: cash deposits, accounts, debts from individuals and legal entities.
- current assets are property assets used in the current activities of the organization and involved in daily production costs. This group includes cash (in cash, on current and foreign currency accounts), investments in securities (short-term), inventories (raw materials, supplies, inventory, finished products), accounts receivable (if the maturity date is no more than a year), VAT according to acquired values;
- gross - property assets acquired with both own and borrowed capital;
In addition to the main types, there are “hidden” and “imaginary” assets. “Hidden” assets are not reflected when preparing the balance sheet. These may be organizational expenses when creating an enterprise, costs for acquiring a license, training and certification of personnel, improvement of equipment, underestimated residual value of fixed assets and intangible assets due to the use of various methods of depreciation.
“Imaginary” assets, although reflected on the organization’s balance sheet, are in fact absent. It is impossible to obtain significant financial benefits from owning “imaginary” assets, either in the present or in the future. Usually these are funds that have already been written off for a certain time, but for some reason remain not written off. For example, unwritten-off unusable and damaged materials or expired accounts payable.
According to the classification of IFRS (international financial reporting standards), there is another type of assets - excess. These include funds that are not currently needed for the main activities of the organization, for example, an excess amount of equipment in a construction company.
Table of potential investments
| Assets | Receiving a profit |
| Bank deposits | Money stored in a bank account (ruble or foreign currency) generates passive income thanks to accrued interest on the investment |
| Business | Money can be invested in a business that will generate income over time |
| Stock | When purchasing shares, the owner can expect to receive dividends from business profits. You can make a profit both from annual income and from the sale of shares |
| Bonds | Purchasing long-term bonds will create a stable source of income for many years. Interest on bonds is accrued once or twice a year |
| Real estate | Investing in real estate is considered the most reliable way to generate passive income. Such a purchase guarantees the owner a constant flow of funds from rent. In addition, the price of real estate increases every year |
| Shares and units in mutual funds (mutual investment funds) | This method is usually used by people who want to quickly and easily invest their capital, without thinking about what and where. For profitable and effective use, the money is placed under the management of professionals who charge a certain percentage for their services. |
| Precious Metals and Collectibles | Investing in gold, silver, paintings, rare coins and other items is one of the best and most reliable ways to invest your savings, as their value is constantly growing |
| Machinery, equipment, transport and more | The owner of these things can receive revenue from their operation |
In addition to the usual sources of income, there are non-standard assets. These can be content sites, YouTube channels, promoted Instagram profiles, VKontakte public pages, photo stocks.
Passives and their varieties
Unlike an asset, a liability is the source of the formation of these assets - capital, as well as reserves. Liabilities also include obligations to the budget and creditors, for example a bank or supplier.
Liabilities include:
- taxes;
- mortgage;
- consumer loans;
- borrowed funds (IOUs, checks, bills, letters of credit);
- movable and immovable property (apartment, car, equipment).
An apartment is one of the controversial points when dividing property into assets and liabilities, since it can fall into two categories at once. For example, renting out an apartment implies receiving passive income, and accordingly is classified as an asset. If the owner personally moves into the apartment or lets his relatives there free of charge, in this case the apartment will be in the role of a liability.
In the production sector, a liability reflects the obligations that an organization has undertaken in the course of doing business. Paying off liabilities results in a decrease in assets. This could be the payment of funds, the provision of services, or the replacement of one obligation with another. Obligations are:
- short-term - current liabilities that must be repaid in the next year from the date of drawing up the balance sheet. This includes accounts payable of the organization itself, for example, debts to employees, lessors, suppliers of raw materials and equipment;
- long-term – financial obligations that require partial repayment over a long period of time. These include deferred liabilities for loans and credits received for a period of more than one year.
All liabilities of the organization are classified into the following categories:
- Imaginary liabilities. They are reflected in tax or accounting records on a certain date to calculate the exact value of net assets, and in fact they are repaid. Timely identification of imaginary liabilities will help prevent double payment, that is, it will preserve the company’s working capital without reducing its value.
- Hidden liabilities are obligations that are actually absent, but, nevertheless, are reflected in the structure of credit, tax and off-budget payments. They can arise when drawing up a balance sheet due to untimely write-off of credit and tax debts in accounting.
- Actual - liabilities that actually exist and are reflected in the balance sheet. The maturity of these liabilities is determined by the date of their repayment, specified in the drawn up agreement. When fulfilling obligations on actual liabilities, the organization always loses part of its own assets. This can be finished products, fixed assets or working capital.
Liability structure
Most of the liabilities consist of various obligations of the enterprise: loans, borrowings, debts to employees or counterparties. Obligations are divided into these types:
- Imaginary . These include money that was provided by the owner of the company, debts that have expired. Imaginary obligations can be conditionally called extinguished. They are recorded in accounting and tax accounting. Taking them into account protects the organization from double payments. The cost of turnover will not decrease.
- Hidden . Obligations that appear in official documentation, however, do not actually exist. They appear when repaid debts are not entered in the accounting records on time. Hidden liabilities include deferred tax liabilities, contributions for charity, and coverage of debts of the company's branches.
- Actual . Such obligations actually exist and are correctly reflected in the balance sheet. They include debts to banking and credit institutions, staff, and shareholders.
Obligations are a heterogeneous structure. To understand the position of the company, it is important to analyze the composition of liabilities.
Balance sheet
The balance sheet is the most important form of corporate reporting, characterizing the financial position of an organization for a certain period of time. Balance sheets are submitted to the tax authorities. Banks study such reports to assess the creditworthiness of the organization, and for shareholders they serve as a financial indicator of the work performed by management.
The balance sheet consists of two sections: assets and liabilities. Although these two sections are different, they are still closely related to each other. The slightest changes in one section will affect the other section. Therefore, the total amount of all components of the balance sheet must be the same, that is, in the end, assets and liabilities must always be equal.
The balance sheet is the main source of information for analyzing the production activities of an organization. The planned balance sheet is compiled on the basis of information about all financial flows of the company (including those expressed in foreign currency). It is depicted in the form of a table, where assets are on the left side and liabilities are on the right.
| Balance sheet | |
| Assets | Liabilities |
| Fixed assets and intangible assets (apartments, cars, equipment, computers) | Capital and reserves, earmarked proceeds, treasury shares |
| Inventory | Profit and loss from activities |
| Accounts receivable (cash or inventory that is owed to you) | Short-term obligations to suppliers, budget |
| Cash and short-term investments | Long-term obligations to lenders, banks |
Video on the topic:
Liability Analysis
Liability analysis includes the following measures:
- Estimation of shares of short-term and long-term liabilities.
- Determining the number of liquid assets that can serve as a source of repayment of debts from the liability column.
- Valuation of shares of own and borrowed funds.
The analysis allows you to build a development plan for the enterprise aimed at increasing its own funds. The indicators provide timely monitoring of the company's difficult financial situation.
So, let's remember:
- Liability is a component of the company's balance sheet.
- Reflects the sources of assets.
- Liabilities may include short-term and long-term liabilities, authorized capital, and debts to employees.
- Obligations are divided into many categories: imaginary, hidden, actual. The company's liabilities can and should be analyzed. They reflect the stability of the company, its independence from creditors.
- Based on the obtained indicators, you can draw up a plan that will help improve the well-being of the enterprise.
Personal budget accounting
Assets are a positive cash flow that multiplies capital. Liabilities are negative cash flows that take cash away from equity. In simple and accessible language, an asset is property, a liability is the source of this property. It is necessary to strive to ensure that the income received from assets exceeds the expenses on liabilities. To do this you need:
- Determine the size of your own liabilities, that is, monthly expenses and current needs.
- Distribute expenses. Refuse unnecessary entertainment (restaurants, theaters, clubs) and the purchase of expensive things.
- Determine your own assets with the highest return, that is, everything that brings profit.
- Compare the difference between assets and liabilities. Successful people argue that there should be more assets than liabilities. If they are in equal proportions, the person will balance at the same level.
| Tools | Are an asset | Are a liability |
| Cash | On a bank account | If borrowed from a friend |
| Real estate | For Rent | Used for personal purposes |
| Automobile | Involved in business | Used for personal purposes, incurs expenses or is rented |
| Earth | Rented and generates income | Not used and does not generate income |
| Knowledge | When they bring in income | When they paid for them, but they never brought any income |
Only by correctly distributing assets and liabilities can one achieve material well-being. To put it most simply, assets are everything that generates income, that is, they are positive cash flows that increase capital. Liabilities are everything that money is spent on, negative cash flows, in other words, expenses.
Dotting the E
Develop financial literacy to achieve financial well-being. One of the components of financial wealth is an accurate understanding of what of your property or property is an asset and what is a liability.
As already mentioned, assets are, first of all, all our property and financial instruments that should generate income for us. From this point of view, it is necessary to invest money in tangible and intangible objects.
So which property is classified as an asset and which is not? As was written earlier, the main criterion for such a division will be the fact that income is received into the personal or family budget.
An example of dividing property into categories of assets and liabilities is presented in the table.
| Property | Assets | Passive |
| Own apartment for living | YES | |
| Own apartment for rent | YES | |
| Own garage for car storage | YES | |
| Own garage for rental | YES | |
| Car for own use | YES | |
| Own car for taxi | YES | |
| Land plot | YES |
Yes, you can receive income when selling an apartment, however, it will be a one-time income. And there is no need to talk about permanent income, and even in passive mode. In addition, you will also be left without an apartment after its sale. Where to live? If this is the only apartment, then there may be expenses for renting an apartment. The apartment in which you live is classified as a liability, since it constantly consumes money in the form of utility bills and contributions for major repairs. And someone else has to pay mortgages and insurance.
Whether this sale will bring income to the family budget is still a question. Since the amount of income will depend on the economic situation in the country (if sold during a crisis period, the price will be lower), on the expenses that you incurred for the purchase and maintenance of the apartment. You also need to take into account the period of ownership of the apartment, as it may be necessary to pay taxes.
The same situation applies to the rest of the property you own. Conduct an analysis of your property and think about how to transfer at least part of it from the Liabilities category to the Assets category. Perhaps it would be better to sell or rent something? Start making money from your property.
Industrial use
Modern economists and investors interpret the concepts of asset and liability in two ways. The first interpretation defines traditional economic concepts from the field of accounting. The second is used in connection with the development of the topic of personal capital management. Assets and liabilities are everything that forms a company's balance sheet. Company property in any form is considered an asset; liabilities are debt obligations.
Any intangible and tangible property that an enterprise has, as well as rights to property, are assets of the company. Assets are any property of the enterprise, liabilities are the funds at the expense of which the formation of property is carried out. Liabilities are considered to be the capital of an enterprise:
- joint stock;
- borrowed;
- statutory;
- credit.
The assets of the enterprise are classified according to:
- Form of participation in the production process (current and non-current).
- The nature of the functioning (financial, intangible, material).
- Ownership rights (own, leased).
- Source of formation (net, gross).
- Liquidity.
Assets and liabilities reflect the company's balance sheet, which is prepared for a specific period. Balance sheet equilibrium is considered to be their equality. The first ones are arranged in the balance sheet according to increasing liquidity, and the second ones - according to the urgency of involvement in turnover.
Asset Roadmap
To achieve financial well-being, you need to acquire more assets and fewer liabilities. At the same time, it is necessary to acquire good assets. And in some cases, liabilities, but only good ones.
For example, you can take training in interior design and landscape design. On the one hand, this is a liability, since you need to pay for training. But this is a good liability, because you can use the knowledge gained to organize additional income. You can provide services for planning summer cottages or designing apartments in your free time from your main job. At the same time, you can earn extra money on tuition fees if you pay for it with a cashback card. So with an Alfa Bank card you can get up to 2% cashback.
The concept of assets and liabilities is discussed very well and clearly in Robert Kiyosaki’s book “Rich Dad, Poor Dad.” We recommend reading it.
Look for opportunities to create Assets that generate passive income. This could be dividend shares, commercial real estate, investments in rental funds, and much more.
We tried to explain in simple words the value of assets and the essence of liabilities. Apply the acquired knowledge in your daily life. Take advantage of opportunities that come from good liabilities and avoid bad assets.
Now you know what assets and liabilities are. In simple words, these are the sources of your financial well-being. Achieve financial freedom and be open to new things.
Types of assets
Assets in the modern investment interpretation are all investments that generate constant (passive) income or increase in value over time: investments that generate constant income, profits from your own business, land, real estate, etc. There are many different assets, the most famous and popular of which are:
| Assets | Description |
| Bank deposits | Funds held in bank accounts from which interest accrues |
| Bonds | Income is generated through coupon payments, which are accrued after a certain time (once every 3 months, 6 months or 12 months). Purchasing long-term bonds creates a constant source of income for a long time. |
| Stock | These securities provide the opportunity to receive two types of income. Firstly, purchasing shares is buying part of a business that will rise in price over time, which means that the price of shares will also rise. Secondly, by purchasing shares that involve the payment of dividends, the owner has the right to expect to receive the company's annual profit, which is proportional to the number of shares purchased |
| Real estate | It is considered the most reliable way to generate income. Investing in the purchase of real estate guarantees a constant flow of cash from rental income. And the price of real estate gets higher over time |
| Mutual funds and other investments | This method of generating income is suitable for those who do not want to think independently about where to invest their capital. In this case, finances are transferred to the management of a team of professionals who have experience in this field and know how to effectively use financial instruments. This contributes to more efficient use of money |
| Borrow money | This will be considered an asset if the money is lent for a reason, but out of financial interest. Otherwise, the debt will be a liability |
| Acquisitions with future appreciation | This is everything that constantly increases in price over time:
|
Types of liabilities
The following are considered liabilities:
- mortgage;
- loans;
- credit cards;
- consumer loan taken for the purchase of expensive items, travel, etc.;
- all property (movable and immovable): apartment, car, household appliances, gadgets, etc. Everything that a person owns and uses in everyday life is considered liabilities;
- unprofitable business, since additional funds will be needed to close it;
- money borrowed. Even if money was lent without interest, it is still a liability, since it must be returned.
To better understand what a passive is, we can consider two examples:
- A man bought an expensive car. It appears to be a valuable purchase and could be considered an asset. However, as soon as the car leaves the showroom, it immediately loses about 20% of its price. The owner will have to pay insurance, buy gasoline, pay for repairs, etc. Consequently, in this situation, the car does not make a profit, but requires additional expenses.
- A man took out a mortgage and bought a house. The banker considers the purchased real estate an asset, and in his own way he is right. But the subtlety is that the house is an asset of the bank, but not the borrower. It makes no difference to the banker what the loan is for: to purchase a house, a yacht, or a luxury car. The bank will own this property until the borrower pays off the entire cost with interest. Thus, the acquired property is a liability.
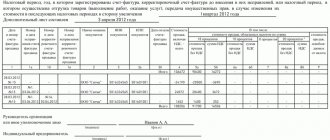
Why are all entries in the balance sheet double?
Yulia: “When we maintain a management balance sheet, we are guided by the principle of double entry. This applies to any financial transaction. Because they are all reflected in two balance sheet items: one of them is increased, and the other is decreased, and invariably by the same amount.
So it turns out: on the balance sheet, assets are always equal to liabilities. And if they are not equal, it means that something was calculated incorrectly.
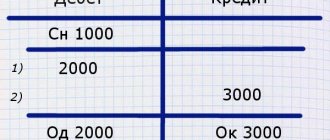
In accounting and balance sheets, four types of transactions can be distinguished:
#1. They increase both the asset and the liability. We bought goods for $10 thousand with an installment plan - the asset includes products worth $10 thousand, the liability includes accounts payable (everything that the business owes to someone) for the same amount.
#2. Reduces both asset and liability. We paid $5 thousand of the debt for the goods - minus $5 thousand in the asset on the “Money” line and minus the same amount in the liability on the “Accounts payable” line.
#3. Increases one asset but decreases another. We bought a machine for $15 thousand - the cost of the equipment increased by this amount, the money became less by the same $15 thousand.
#4. Increases one passive, but decreases another. We paid last month’s salary, for this we used $3 thousand from the overdraft - payables for wages decreased by $3 thousand, but loan obligations increased by the same amount.”
An asset can become a liability and vice versa
For example, people suddenly moved out of an apartment that the owner had rented out. The owner remains the owner of the apartment and bears the burden of expenses: rent, utilities, repairs, taxes, etc. All this makes him poorer, which means the apartment is considered a liability. But when this apartment is rented again, it will again be a source of income. Therefore, we can conclude: a liability makes a person poorer, and an asset makes a person richer.
Take a look at two more examples:
- It was stated above that purchasing a car is considered a liability. If we assume that the owner of the car decided to work as a taxi driver, the car becomes an asset, since it will generate income;
- real estate (houses and apartments) purchased for rental is an investment and therefore generates profit. Even if we take into account the growth of inflation by 15 -20% per year, the value of real estate grows over time, and such investments bring profit to the owner.
Low-income people tend to spend all their income. All funds are spent on food, utilities, taxes, Internet, communications and entertainment. There is barely enough money until the next salary. A person is forced to borrow money, then pays off his debts, and so on all the time. There are no opportunities to acquire assets.
Middle class people have a lot of expenses equal to a lot of money they earn. These people are accustomed to leading a decent lifestyle and acquire many liabilities: a house, a dacha, a car, etc. Often, to make these acquisitions, they take on debt. It turns out that the higher their income, the higher their expenses. The middle class pays a lot to cover their debts: the more they earn, the more they spend.
Rich, wealthy people are distinguished by the fact that they try to get rid of liabilities and acquire assets. If they really want to buy a liability, they first buy an expensive asset. Wealthy people constantly make sure that their assets always exceed their liabilities.
For example, I wanted to buy a new car. First you need to buy real estate and rent it out, and only after that buy a car. It's safe to say that passive income is created with the help of assets.
Maintaining balance
Our world cannot exist without liabilities. People live in houses, drive cars, and enjoy the benefits of life. You need to learn to find a balance, try to ensure that the income received from assets far exceeds expenses. In order for your life to be financially stable, you first need to determine your existing liabilities and monthly expenses, identify unnecessary expenses and decide how to reduce them.
Then evaluate the assets, determine what and how generates income every month. There can be many sources of income. They contribute to the achievement of financial freedom when money works for the person, and not the person for it. Having assets, a person stops working for money. Of course, you can have a country villa as a liability, but this is if the owner is a billionaire and also has factories, oil rigs, a yacht, etc.
It is necessary to take into account that by owning assets you can live in abundance, but for this you need to learn to live within your means. Try not to take out loans, and if you have them, pay them off on time. Credits and loans are monetary bondage, lowering the overall standard of living.
You need to create a step-by-step action plan to increase income and reduce expenses. Buy assets when free funds appear from existing assets. This could be profit from real estate or business, interest from investment activities. A clear understanding of what the actions taken can lead to - a decrease or increase in well-being - is necessary.