Reflection of financial and other current assets in the balance sheet
Some organizations are given the right to prepare simplified reporting.
Such organizations include small businesses, non-profit organizations and participants in the Skolkovo project (Clause 4, Article 6 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ). Read more about simplified reporting and the organizations that use it in this article.
A simplified form of the balance sheet is given in Appendix No. 5 to Order No. 66n of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 2, 2010. It is advisory and can be modified by the organization independently. The asset items of the balance sheet form are grouped as follows:
- tangible non-current assets;
- intangible, financial and other non-current assets;
- stocks;
- cash and cash equivalents;
- financial and other current assets.
Let's look at what ends up on the last line. And this:
- accounts receivable,
- advances issued,
- short-term financial investments (hereinafter referred to as FI),
- other immaterial current assets (unwritten-off shortfalls, amounts of VAT not accepted for deduction, amounts of VAT on advances, amounts of overpaid taxes or other fees that have not yet been offset against other payments, etc.).
Read about the criteria for short-term financial investments in the article “Short-term financial investments are…”.
Note that highly liquid investments, such as demand deposits, are not included in this line; they are classified as cash equivalents. Organizations using simplified accounting and reporting can take into account financial contributions in a general manner, or they can use some relaxations. The nuances of accounting for financial investments will be discussed below.
Accounting for financial investments
This section of accounting is regulated by PBU 19/02 “Accounting for Financial Investments”, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 10, 2002 No. 126n. Financial investments include:
- various securities,
- bonds,
- bills,
- contributions to authorized capital,
- loans issued,
- deposits, etc.
The capitalization of financial assets occurs at the original cost, which includes the sum of all purchase costs: payments directly to the seller under the contract, costs of consulting specialists, fees to intermediaries, etc. In addition to the purchase, financial assets can be received in other ways. The diagram shows other options for estimating the initial cost of the investment fund.
In the future, the PV should be considered for the possibility of revaluation. PBU 19/02 divides PV into two types; depending on the type, the subsequent assessment of PV occurs. Options for subsequent assessment are presented in the diagram.
Let's look at the example of the initial and subsequent reflection of debt securities.
Example
On March 1, Vector LLC purchased 100 bonds at a price of 7,000 rubles. a piece. The nominal value of 1 bond is 10,000 rubles. The maturity of these bonds is 1 year. Interest accrues every month at a rate of 15% per annum. Vector LLC exercises the right to increase the value of bonds to par during the circulation period, which is enshrined in the accounting policy. The accountant made the following entries.
March 1
Dt 58.2 Kt 76 - 700,000 rub. — bonds were capitalized as part of financial investments.
Dt 76 Kt 51 - 700,000 rub. - payment of bonds has been made.
March 31
Dt 76 Kt 91.1 - 12,740 rub. (10,000 × 100 / 365 × 31 × 15%) - interest accrued on bonds for March.
Dt 58.2 Kt 91.1 — 25,479 rub. (10,000 – 7,000) × 100 / 365 × 31) - partially reflects the difference between the original and nominal value relating to March.
The last two entries are made similarly every month. At the end of the circulation period, bonds are listed on the balance sheet at par value. At the maturity date, the accountant made the following entries:
Dt 76 Kt 91.1 - 1,000,000 rub. — shows the income on redeemed bonds.
Dt 91.2 Kt 58.2 — 1,000,000 rub. — repaid bonds are written off.
Dt 51 Kt 76 — 1,000,000 rub. — money received on bonds.
As for those using simplified accounting, clause 19 of PBU 19/02 allows you to take into account any financial assets as those for which the current market value is not determined, that is, not to overestimate them.
Let us also pay some attention to the depreciation of financial assets. The impairment test is performed for financial assets for which the current market value is not calculated. The organization itself develops a methodology for calculating the amount of reduction in the cost of a financial investment. A reserve must be created for this amount, which is accounted for in account 59 and attributed to other expenses. Then the financial assets will be shown in the balance sheet in an amount equal to the book value minus the reserve.
Optimal amount and structure of financial investments
Financial investments include those types of investments that financiers call portfolio: these are investments in the capital of other companies with the acquisition of securities or debt obligations, or this is the placement of money on deposits with interest income.
Financial investments have varying degrees of profitability and risk. Bank deposits and the purchase of government bonds or other government securities are characterized by the lowest degree of risk, but also the lowest level of profitability. Riskier financial investments can bring higher profits.
The purpose of investing in financial instruments is the organization’s desire to diversify the income that the enterprise can receive, to increase profitability not only through its core activities, but also through the efficiency of financial investments.
An optimal portfolio of financial investments may include high-yield and risky assets, but it is still better to form its basis from assets with a lower degree of risk. The enterprise chooses the optimal ratio of these components of the investment portfolio independently, focusing not only on market conditions, but also on the experience of financial managers.
When making financial investments, you must remember that most financial market instruments have a value that constantly changes depending on the market and market conditions. Therefore, the optimal portfolio of financial investments is those investments for which the expected income significantly covers the cost of their acquisition and the risk of loss. Calculating the internal rate of return will help determine the optimal parameters of a financial investment portfolio.
You can learn how to do this from the material “How to calculate the internal rate of return (formula)?”
In addition to calculating internal returns, we recommend calculating the sensitivity of the market and analyzing the distribution of returns by probability level. Since the state of financial investments affects the liquidity and financial stability of the enterprise, it is necessary to form a portfolio of financial investments in such a way as to avoid negative changes in these indicators.
To optimize work with financial investments, the portfolio structure should contain both long-term and short-term investments. In addition, the structure of the financial investment portfolio should be made up of various types of securities.
Amortized cost of a financial asset
Currently, there is a process of convergence of Russian accounting rules with international ones. And some organizations named in paragraph 1 of Art. 2 of the Law “On Consolidated Financial Statements” dated July 27, 2010 No. 208-FZ, for example, banks already prepare consolidated statements in accordance with IFRS.
For financial instruments, international rules are collected in several standards:
- IFRS 9 “Financial Instruments”,
- IAS 39 “Financial instruments: recognition and measurement”,
- IAS 32 “Financial Instruments: Presentation of Information”,
- IFRS 7 Financial Instruments: Disclosures.
Find information on the application of international standards, on the initial and subsequent assessment of financial instruments on our website:
- “IFRS No. 9 Financial instruments - application features”;
- “We apply IFRS No. 39 Financial instruments (nuances)”;
- “We apply IFRS No. 32 Financial instruments (nuances).”
How to organize accounting of financial assets within the framework of IFRS can be found in the article from ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
The concept of amortized cost is applied in the subsequent accounting of a financial asset. The organization must determine how to account for it:
- at amortized cost,
- at fair value.
Amortized cost is calculated using the effective interest method, which discounts the future cash inflows from the financial asset. The calculation of amortized cost is relevant for financial investments that are not quoted on the market, for example loans, debt securities. The Central Bank has developed detailed methodological recommendations for calculating amortized cost dated April 27, 2010 No. 59-T, which can be downloaded on the Central Bank website.
Accounting
For any company, an important factor is the accounting of financial assets, because the rationality of their use depends on this. When solving a problem, several types of prices are taken into account:
- Fair. Investments and equity shares are reported. For example, when purchasing securities, information is reflected in account “58”. When additional income is received, entries are adjusted.
- Nominal. When cash is received, the information is reflected in account “50”.
- Depreciation. Here debt instruments, for example bonds, are taken into account. Such information is entered into account “58”.
In accounting, the above funds are reflected as a balance sheet. According to current rules, they can be listed as current or non-current assets.
Financial assets in budget accounting are...
The Unified Chart of Accounts for budgetary structures, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n, contains a section devoted to financial assets, which includes:
- cash,
- financial investments,
- various types of receivables and advances issued,
- issued loans.
The balance sheet for government agencies is compiled according to the principle of the arrangement of items in the chart of accounts. The composition of financial assets in the balance sheet is similar to this section in the chart of accounts. Let's focus on accounting for FV.
FV is accepted for accounting at its original cost, which is equal to the amount of actual investments. Revaluation of financial assets is carried out on the reporting date or on the date of transactions with them. The value of the investment fund is formed on account 021500000 “Investments in financial assets”. The chart of accounts for budgetary institutions, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 16, 2010 No. 174n, provides for the following procedure for reflecting financial assets.
Accounting for income from financial investments
If we invest our money in something, we always expect to receive income. By purchasing shares of other companies, you can receive dividends by issuing a loan - interest, and so on. Keep records of income from financial investments in account 91. The table contains the main transactions.
| Debit | Credit | Description |
| 76 | 91 | Accrued income from financial investments |
| 50 / 51 / 52 | 76 | Income from financial investments went to the cash desk, to a current or foreign currency account |
For example, Alpha LLC issued a loan to Bravo LLC for a year at 10% per annum in the amount of 200,000 rubles. Alpha's accountant will make the following entries:
Debit Credit Sum Description 58 51 200 000 Transferred the loan from the current account 76 91.1 20 000 Interest was calculated based on the calculation of 10% per annum 51 76 20 000 The debtor transferred interest 51 58 200 000 The debtor returned the loan amount
Results
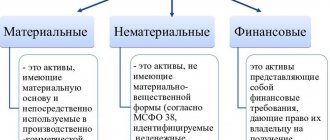
Depending on the scope of application of the concept of financial assets, their composition may vary.
Thus, in the budget chart of accounts, they include both cash and receivables, which corresponds to the composition of financial assets according to IFRS. In a simplified balance sheet, cash is allocated as a separate line. Financial investments are part of financial assets, but should not be identified with them. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Areas of regulation
Law No. 259-FZ regulates:
- issuance, accounting and circulation of digital financial assets (taking into account the provisions of the Law on the Securities Market of April 22, 1996 No. 39-FZ on equity securities);
- features of the activity and responsibility of the operator of the information system in which the release of these assets occurs, and the operator of their exchange;
- circulation of digital currency in Russia.
Also, Law No. 259-FZ contains requirements for the decision to issue digital financial assets. the procedure for maintaining the register of users of the information system and the rules for the exchange of digital financial assets, the procedure for their approval.
The requirements of Law No. 259-FZ do not apply to:
- circulation of non-cash and electronic money;
- issue, accounting and circulation of uncertificated securities.