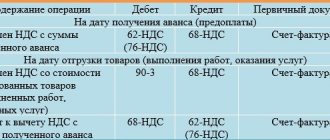
General rules for deducting VAT on fixed assets
The amount of VAT paid by an enterprise when purchasing fixed assets or equipment for use in production activities is legally allowed to be fully deducted. It is possible to deduct VAT on fixed assets by observing the provisions set out in paragraph 2 of Art. 171 Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1, art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It is allowed to deduct VAT on fixed assets if:
- The objects were acquired for use in the activities of the enterprise subject to VAT.
- Objects are registered as fixed assets, for which there is documentary evidence, for example, acceptance certificates (OS-1).
- The VAT amount is confirmed by an invoice issued accordingly.
For some reasons for refusal to deduct VAT, see our material “What is the procedure for applying (accepting) tax deductions for VAT: conditions?”
Is it possible to deduct VAT on fixed assets that have not been put into operation? The answer to this question, as well as some of the nuances of filing a VAT deduction, were explained by ConsultantPlus experts. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
Postings for commissioning of fixed assets in 1C 8.2
According to accounting
When commissioning fixed assets, VAT accounting entries are not created:
For tax accounting
The following entries were created in the VAT accumulation register:
- Entry by type of movement Expense in the VAT register for fixed assets, intangible assets , type of value of fixed assets . The tax is written off from the register, because the conditions for accepting “input” VAT for deduction are met:
- in the VAT register for acquired assets with the movement type Expense , type of asset value. VAT is written off from the register at the time of commissioning:
Moment of deduction of VAT on fixed assets
The peculiarity of accepting a VAT deduction on fixed assets lies in the correct determination of the moment of this operation. One of the conditions for presenting tax for deduction, according to paragraph 1 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, is to register an object as a fixed asset. But the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not have clear characteristics on the basis of which an object can be accepted for accounting as a fixed asset. Therefore, the question of the moment of deduction is not clear-cut.
Thus, initially the regulatory authorities insisted that when purchasing fixed assets, VAT deduction is possible only after the property is reflected in account 01 “Fixed assets” (see, for example, letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 02.12.2015 No. 03-07-11/6141, dated 24.01 .2013 No. 03-07-11/19). Later, the position of the Ministry of Finance changed - see “Deduction for fixed assets on account 08 is not a problem.” Now officials consider it possible to accept VAT for deduction within 3 years after entry into account 08 (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 04/11/2017 No. 03-07-11/21548).
Judicial practice proceeds from the fact that the account into which fixed assets are accepted for accounting does not matter. The thing is that in accounting, acquired property goes through several stages of being reflected in accounting before becoming a fixed asset. Transactions for the purchase of property are initially reflected in account 08 “Investments in non-current assets”. The transfer of an object to 01 account is carried out only after its initial value has been fully formed. Therefore, if the taxpayer decides to receive a deduction for fixed assets placed on account 08, then there is a possibility of a dispute with the tax authorities. However, there is a good chance of defending your point of view in court.
For more information about the arguments, see our material “What is the procedure for deducting VAT when purchasing fixed assets?”
Which account to choose: account 01 or account 08?
According to accounting rules, the initial cost of fixed assets (intangible assets) acquired by a company, as a rule, is first formed on account 08 “Investments in non-current assets”. And only after the object is put into operation, this amount is transferred to account 01 “Fixed assets” (04 “Intangible assets”).
Financiers and tax authorities insist that VAT paid on the purchase of a fixed asset that does not require installation should be deducted only after it has been put into operation, that is, reflected on account 01 (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 24, 2013 No. 03-07- 11/19, dated August 16, 2012 No. 03-07-11/303, dated August 2, 2010 No. 03-07-11/330, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated April 5, 2005 No. 03-1-03/530 / [email protected] ).
Thus, in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 24, 2013 No. 03-07-11/19 it is stated that “... the amounts of value added tax presented by sellers when purchasing fixed assets are subject to deduction after they are registered as fixed assets.”
Some courts agree that the right to deduct VAT for a company arises only after the commissioning of facilities (resolutions of the FAS Moscow District dated February 22, 2012 No. A40-56010/11-91-242 and FAS Volga District dated September 30, 2010 No. A12-24919/2009).
However, the Tax Code does not say in which account the fixed asset should be registered: 01 “Fixed assets” or 08 “Investments in non-current assets”.
This was confirmed by the Supreme Arbitration Court of Russia.
The judges of the Supreme Arbitration Court stated that in order to deduct VAT, it does not matter on which account the fixed asset is reflected - 01 or 08. And the deduction of VAT on an acquired fixed asset when reflected in account 08 is legal (Determination of the Supreme Arbitration Court of Russia dated March 3, 2009 No. VAS-1795 /09).
Guided by the conclusions of senior arbitrators, the majority of federal courts do not support the position of the controllers (resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated January 27, 2012 No. A56-10457/2011, FAS Moscow District dated September 15, 2011 No. A40-113023/09-126- 735, Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated August 24, 2011 No. F09-5226/11).
This means that companies, citing the aforementioned court decisions, can claim a VAT deduction before reflecting the fixed asset on account 01. However, such a position will most likely have to be defended in court.
EXAMPLE In September, Passiv LLC bought a woodworking machine for RUB 70,800. (including VAT – 10,800 rubles). The machine was capitalized in September, and put into operation and paid for in October. DEBIT 08 CREDIT 60 - 60,000 rubles. (RUB 70,800 − RUB 10,800) – reflects the costs of purchasing the machine (excluding VAT); DEBIT 19 CREDIT 60 – 10,800 RUB. – the amount of VAT presented by the supplier is taken into account; DEBIT 68 subaccount “Calculations for VAT” CREDIT 19 – 10,800 rubles. – VAT is accepted for deduction; in October DEBIT 01 CREDIT 08 – 60,000 rubles. – the woodworking machine is put into operation.
But in letter dated July 16, 2012 No. 03-07-11/185, the Russian Ministry of Finance made a completely opposite conclusion, but with regard to VAT deductions on real estate. Amounts of VAT claimed on real estate objects that are acquired for the purpose of their further reconstruction and use in activities subject to VAT are accepted for deduction at the time they are registered on account 08.
The fact is that financiers came to this conclusion based on the provisions of paragraph 6 of Article 171 of the Tax Code, which sets out the procedure for applying deductions for goods purchased for construction and installation work. In this letter, the Ministry of Finance considers a property purchased for the purpose of reconstruction not as an item of fixed assets, but as a product purchased for construction and installation work.
The Federal Tax Service also changed its point of view on this issue. In a letter dated March 20, 2015 No. GD-4-3 / [email protected], tax authorities allowed deduction of VAT until the completion of capital construction of the facility as soon as the contractor presented invoices, certificates of work performed in form No. KS-2 and reflection of the stages of work performed on account 08. The controllers argued their position as follows.
In order to accept VAT as a deduction, an organization must fulfill certain conditions provided for in paragraph 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code. She fulfilled them.
And since all these conditions have been met by the organization, it has the right to deduct VAT on construction and installation work after recording them in account 08 “Investments in non-current assets” on the basis of properly executed invoices and primary documents.
VAT deduction on fixed assets requiring installation
For objects that require installation to bring them into working condition, the law allows for deduction of tax paid to third-party organizations performing work on the assembly or installation of objects, as well as suppliers of equipment and materials used in installation work. This is clearly stated in paragraph 6 of Art. 171 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Assets requiring installation and assembly are initially recorded in accounting account 07 “Equipment for installation” with further debiting to account 08 as the equipment is transferred for installation. Capitalization to account 01 occurs only after the assembled objects are completely ready for use. In this case, it is allowed to deduct “input” VAT already at the time the object is reflected on account 07 (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 29, 2010 No. 03-07-08/20).
VAT deduction on fixed assets subject to state registration
Fixed assets subject to state registration deserve special attention: buildings, structures and other real estate. As noted above, one of the conditions for obtaining a VAT deduction on fixed assets is the registration of these objects and documentary confirmation of this fact, as stated in paragraph 1 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Confirmation of the registration of such objects is a signed acceptance certificate. VAT deduction can be claimed during the period of signing the relevant act and without waiting for state registration.
When there is no right to deduct VAT on fixed assets
Amounts of “input” VAT are not deductible, but are included in the cost of fixed assets if such objects are acquired for operations (clause 2 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- not recognized as sales in accordance with clause 2 of Art. 146 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- carried out outside the territory of the Russian Federation;
- exempt or not subject to VAT;
- carried out by persons who are exempt or who are not tax payers.
When simultaneously carrying out both taxable operations and those exempt from the calculation and payment of tax, the enterprise deducts VAT on fixed assets in proportion to the use of acquired objects in these operations in accordance with clause 4 of Art. 170 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The specified proportion is determined based on the cost of shipped goods (work, services performed), property rights, transactions for the sale of which are subject to taxation (exempt from taxation), in the total cost of goods (work, services), property rights shipped during the tax period.
In this case, the taxpayer is obliged to keep separate records of tax amounts on acquired fixed assets used to carry out both taxable and non-taxable (tax-exempt) transactions.
If the taxpayer does not have separate accounting, the amount of tax on acquired fixed assets is not deductible.
The taxpayer has the right not to apply these rules in those tax periods in which the share of total costs for the production of VAT-free goods (works, services), property rights does not exceed 5 percent of the total total costs of production. In this case, all amounts of “input” tax are subject to deduction.
See also our material “When is separate accounting of “input” VAT not carried out?”
Distribution of input VAT by operating system in “1C: Accounting 8” (rev. 3.0)
Let's consider an example of how the 1C:Accounting 8 version 3.0 program reflects operations on the distribution of input VAT among fixed assets intended for taxable and non-VAT-taxable transactions.
Please note that in accordance with Federal Law No. 303-FZ dated 08/03/2018, VAT tax rates changed from 01/01/2019: from 18% to 20%; from 18/118 to 20/120 and from 15.25% to 16.67%.
Example
| The organization TF-Mega LLC carries out operations both subject to VAT and exempt from taxation in accordance with Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as well as operations the place of implementation of which is not recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation. In addition, TF-Mega LLC sells goods from the warehouse to individuals and is a UTII payer for this type of activity. The organization TF-Mega LLC acquired:
In addition, in July 2022, the organization TF-Mega LLC:
The sequence of operations is given in Table 1. |
Setting up accounting policies, accounting parameters and directories
Due to the fact that the organization maintains separate accounting of the submitted VAT amounts when carrying out operations for the sale of goods (work, services), both subject to VAT and exempt from taxation, as well as operations the place of sale of which is not recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation, it is necessary to make the appropriate settings of accounting policies and accounting parameters.
On the VAT tab of the Accounting policy
(section
Main
- subsection
Settings
-
Taxes and reports
) you should set the flag
Separate accounting of incoming VAT
and
Separate accounting of VAT by accounting methods
.
In the accounting settings settings (section Administration - subsection Program settings - Accounting settings), by clicking on the hyperlink Setting up a chart of accounts, in the line Accounting for VAT amounts on purchased assets, set the value By counterparties, invoices received and accounting methods. To do this, you need to click on the appropriate hyperlink and check the box for the value By accounting methods.
Purchase of MFP
Receipt of a fixed asset (MFP) into an organization (operations 2.1 “Accounting for incoming MFP”; 2.2 “Accounting for input VAT”; 2.3 “Acceptance of MFP for accounting as a fixed asset”) is registered in the program by the document Receipt (act, invoice) with the type of operation Basic funds (section Purchases - subsection Purchases) or the document Receipt of fixed assets (section Fixed assets and intangible assets - subsection Receipt of fixed assets), fig. 1.
Rice. 1. Arrival of MFP
Since TF-Mega LLC carries out both taxable and non-taxable transactions, and the purchased MFP is used in the company’s office, i.e. in all ongoing operations, then in the VAT accounting method
Distributed
is indicated .
After posting the document, the following accounting entries are entered into the accounting register:
Debit 08.04.2 Credit 60.01 - for the cost of the purchased MFP;
Debit 01.01 Credit 08.04.2 - for the cost of the fixed asset accepted for accounting;
Debit 19.01 Credit 60.01 - for the amount of input VAT.
Since the amount of input VAT is subject to distribution, two entries are simultaneously entered into the VAT register submitted: one with the type of movement Receipt and the event Submitted VAT by the Supplier, the second with the type of movement Expense and the event VAT subject to distribution. At the same time, an entry is made in the Separate VAT accounting register for the amount of tax written off in the VAT
.
Register entry Separate accounting
is produced for the further distribution of the amount of input VAT, as well as for the use of data on the acquired fixed asset.
To register a received invoice (operation 2.4 “Registration of a received invoice”), you must enter the Invoice No.
and from the document
Receipt (act, invoice)
(Fig. 1), enter the number and date of the incoming invoice, respectively, and click the
Register
.
Invoice received
will be automatically created (Fig. 2), and a hyperlink to the created invoice will appear in the form of the basis document.
Rice. 2. Invoice received at the MFP
Document fields Invoice received
will be filled in automatically based on information from the document
Receipt (act, invoice)
. Besides:
- in the Received
the date of registration of the document
Receipt (act, invoice)
, which, if necessary, should be replaced with the date of actual receipt of the invoice. If an agreement has been concluded with the seller on the exchange of invoices in electronic form, then the field will indicate the date of sending the electronic invoice file by the electronic document management (EDF) operator, indicated in its confirmation; - in the line Base documents there will be a hyperlink to the corresponding receipt document;
- Operation type code
field the value 01 will be reflected, which corresponds to the acquisition of goods (work, services), property rights in accordance with the Appendix to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] ; - The Receipt Method switch will be set to On paper
if there is no valid agreement with the seller to exchange invoices in electronic form.
If there is an agreement, then the switch will be in the position Electronically
.
Since the organization maintains separate accounting, in the Invoice document received
there is no line with the value
Reflect VAT deduction in the purchase book by date of receipt
, i.e. there is no possibility of a simplified application for input VAT deduction.
As a result of posting the document Invoice received, a registration entry is made in the Register of Invoices. Despite the fact that since 01/01/2015, taxpayers who are not intermediaries (forwarders, developers) do not keep a log of received and issued invoices, and in the document Invoice received in the Amount line it is indicated that the amounts to be recorded in the log book ( “of which by commission”) are equal to zero, the Invoice Journal register entries are used to store the necessary information about the received invoice.
Purchasing a car
Registration of a vehicle receipt operation (operations 3.1 “Accounting for an incoming vehicle”, 3.2 “Accounting for input VAT”) in the program is carried out using the document Receipt (act, invoice) with the operation type Equipment (section Purchases - subsection Purchases) or Receipt of equipment (section OS and Intangible assets - subsection Receipt of fixed assets), Fig. 3.
Rice. 3. Car arrival
Since TF-Mega LLC carries out both taxable and non-taxable transactions, and the purchased car is intended for use in all activities of the organization, then in the VAT accounting method
Distributed
is indicated .
After posting the document, the following accounting entries are entered into the accounting register:
Debit 08.04.1 Credit 60.01 - for the cost of the purchased car;
Debit 19.01 Credit 60.01 - for the amount of input VAT.
Also, if the amount of input VAT is subject to distribution, then two entries are simultaneously entered into the VAT register presented: one with the type of movement Receipt
and the event
Submitted VAT by the Supplier
, the second - with the type of movement
Expense
and the event
VAT is subject to distribution
.
At the same time, an entry is made in the Separate VAT accounting register for the amount of tax written off in the VAT
.
The Separate accounting register entry is made for the further distribution of the amount of input VAT, as well as for the use of data on the purchased asset.
To register a received invoice (operation 3.3 “Registration of a received invoice”), you must enter the Invoice No.
and from the document
Receipt (act, invoice)
(Fig. 3), enter the number and date of the incoming invoice, respectively, and click the
Register
.
Invoice received
will be automatically created (Fig. 4), and a hyperlink to the created invoice will appear in the form of the basis document.
Rice. 4. Invoice received for the car
Document fields Invoice received
will be filled in automatically based on information from the document
Receipt (act, invoice)
.
Besides:
- in the Received
the date of registration of the document
Receipt (act, invoice)
, which, if necessary, should be replaced with the date of actual receipt of the invoice. If an agreement has been concluded with the seller on the exchange of invoices in electronic form, then the date of sending the electronic invoice file by the EDF operator, indicated in its confirmation, will be entered in the field; - in the line Base documents there will be a hyperlink to the corresponding receipt document;
- Operation type code
field the value 01 will be reflected, which corresponds to the acquisition of goods (work, services), property rights in accordance with the Appendix to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] ; - Receipt Method
switch will be set to
On paper
if there is no valid agreement with the seller to exchange invoices in electronic form.
If there is an agreement, then the switch will be in the position Electronically
.
Since the organization maintains separate accounting, in the Invoice document received
there is no line with the value
Reflect VAT deduction in the purchase book by date of receipt
, i.e. there is no possibility of a simplified application for input VAT deduction.
As a result of posting the document Invoice received
a registration entry is made in the Invoice Journal register to store the necessary information about the received invoice.
VAT distribution
According to paragraph 4 of paragraph 4 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the amounts of VAT claimed on goods (work, services), property rights acquired both for taxable transactions and for transactions exempt from taxation are taken for deduction or taken into account in their value in that proportion , in which they are used for the production and (or) sale of goods (work, services), property rights, transactions for the sale of which are subject to taxation (exempt from taxation) - for goods (work, services), including fixed assets and intangible assets, property rights used to carry out both taxable and non-taxable (tax-exempt) transactions, in the manner established by the accounting policy adopted by the taxpayer for tax purposes, and taking into account the features established by paragraph 4.1 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In accordance with paragraph 4.1 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the proportion for the distribution of the amount of claimed VAT is determined based on the cost of goods shipped (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights, transactions for the sale of which are subject to taxation (exempt from taxation), in the total cost of goods shipped (work performed, services provided), transferred property rights for the tax period.
At the same time, for fixed assets and intangible assets purchased in the first and second months of the quarter, the taxpayer has the right to determine such a proportion based on shipment data for the corresponding month.
Despite the presence in paragraph 4 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation indicating the establishment of a proportion between the cost of shipped taxable VAT and non-taxable (exempt from taxation) transactions, when forming the proportion, the amount of revenue from non-taxable transactions will also include revenue from sales transactions that are not subject to VAT. due to the fact that the territory of the Russian Federation is not recognized as the place of their sale in accordance with Article 148 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 03/06/2008 No. 03-1-03/761, Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated 07/05/2011 No. 1407/11).
From 07/01/2019, for the purpose of applying paragraphs 4 and 4.1 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, operations for the sale of work (services), the place of implementation of which, in accordance with Article 148 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, is not recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation (except for operations provided for in Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), relate to transactions subject to taxation (clause “b”, paragraph 3, article 1 of Law No. 63-FZ).
Automatic distribution of the amount of input VAT (operations 4.1 “Distribution of VAT on MFIs by accounting methods”; 4.2 “Distribution of VAT on a car by accounting methods”; 4.3 “Accounting for VAT on a car in the cost of a non-current asset”; 4.4 “Accounting for VAT on MFIs in the cost of a non-current asset” asset"; 4.5 "Accounting for VAT on MFIs in the cost of fixed assets") is carried out by the regulatory document Distribution of VAT
(section
Operations
- subsection
Period closure
).
The distribution of the presented VAT amount is carried out according to those fixed assets, upon acquisition of which the value Distributed is specified in the VAT accounting method (MFP and car)
.
According to established arbitration practice and clarifications of the Federal Tax Service of Russia and the Ministry of Finance of Russia, when purchasing fixed assets, the buyer has the right to claim a tax deduction of the presented amount of VAT in full within 3 years from the date of acceptance of the fixed assets for registration, including in account 08 “Investments in non-current assets "(Clause 1, 1.1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 09/04/2018 No. 03-07-11/63070, dated 12/19/2017 No. 03-07-11/84699, dated 04/11/2017 No. 03-07 -11/21548).
Consequently, input VAT on all acquired fixed assets, both accepted for accounting on account 01 (MFP) and accepted for accounting on account 08 (car), is subject to distribution in the month of acquisition.
Since fixed assets were purchased in July 2022 and the proportion of VAT distribution will be formed based on shipment data for the corresponding month, then in the VAT Distribution
the date must be set to 07/31/2019.
To calculate the proportion of VAT distribution, you must execute the Fill
.
After executing this command on the Sales Revenue tab, the following will be automatically calculated:
- the amount of revenue (the cost of shipped goods (work, services, property rights)) from activities subject to VAT (including the amount of revenue from the sale of non-commodity goods for export and the amount of revenue from the sale of services, the place of sale of which is not recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation according to Article 148 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, i.e. services not on the territory of the Russian Federation);
- the amount of revenue from activities not subject to VAT (not UTII);
- the amount of revenue from activities not subject to VAT (UTII);
- the amount of revenue from sales subject to VAT at a rate of 0% (except for the export of non-commodity goods).
Thus, the proportion indicators for the distribution of VAT for July 2022 will be:
- revenue from taxable activities (cost of shipped goods, works, services, property rights) for July 2022 excluding VAT - RUB 672,600.00. (RUB 600,000.00 (sale of goods subject to VAT at a rate of 20%, excluding VAT) + RUB 72,600.00 (provision of advertising services to a foreign person));
- revenue from activities not subject to VAT (not UTII) - RUB 19,200.00. (transfer of goods for advertising purposes);
- revenue from activities not subject to VAT (UTII) - RUB 350,000.00.
In addition, it should be noted that when carrying out activities taxed in accordance with different regimes (general tax regime and UTII), and distributing costs between these types of activities, the share of VAT included in the cost of purchased goods (works, services) is taken into account accordingly. . To do this, in the Article fields to include VAT in the costs of activities
should be indicated (Fig. 5):
- in the field not subject to VAT (not UTII) - the value Write-off of VAT on expenses (For activities with the main taxation system);
- in the non-taxable VAT (UTII) field - the value Write off VAT on expenses
(
For certain types of activities with a special taxation procedure
).
Rice. 5. Calculation of the proportion for the distribution of VAT
Automatic distribution of the input VAT amount will be reflected on the Distribution
document
Distribution of VAT
.
According to the calculated proportion:
- the share of VAT accepted for tax deduction will be 64.56134% (RUB 672,600.00 / (RUB 672,600.00 + RUB 19,200.00 + RUB 350,000.00) x 100%), which according to MFP it corresponds to 22,928.96 rubles. (RUB 35,515.00 x 64.56134%);
- the share of VAT included in the cost of acquisitions will be 35.43866% ((RUB 19,200.00 + RUB 350,000.00) / (RUB 672,600.00 + RUB 19,200.00 + 350,000.00 rub.) x 100%), which according to MFP corresponds to 12,586.04 rubles. (RUB 35,515.00 x 35.43866%).
The amount of input VAT to be included in the cost of acquisitions will be additionally distributed between types of activities (general taxation system and UTII).
Since the car was accepted for accounting (on account 08) also in July 2022, the distribution of VAT on it should be made in the same way as the distribution of input VAT for MFIs.
| 1C:ITS For more details, see the explanations of O.S. Duminskaya, Advisor to the State Civil Service of the Russian Federation, 2nd class of the Value Added Tax Department of the Department of Taxation of Legal Entities of the Federal Tax Service of Russia, in the section “Consultations on Legislation” and in the article “Distribution of Input VAT on Fixed Assets”. |
If the transaction for purchasing a car was not automatically reflected on the Distribution tab of the VAT Distribution document, then you need to click on the Add button to enter information in the tabular section by filling out the following columns: Invoice, Total, Type of value, VAT account, % VAT, Batch, Cost account , Subconto.
To distribute the reflected amount of VAT (to fill out the columns: Accepted for deduction, Taken into account in the cost, Taken into account in the cost (UTII)), you must click on the Distribute button (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6. Distribution of input VAT by MFP and vehicle
According to the calculated proportion for the car:
- the share of VAT accepted for deduction will be RUB 127,831.45. (RUB 198,000.00 x 64.56134%);
- the share of VAT included in the cost of acquisitions will be RUB 70,168.55. (RUB 198,000.00 x 35.43866%).
After posting the VAT Distribution document, the following entries will be made in the accounting register:
- the amounts of input VAT on the purchased MFP and car will be transferred from the credit of account 19.01 with the third sub-account. Distributed to the debit of account 19.01 with the third sub-account. Accepted for deduction
and
taken into account in the cost
in accordance with the calculated proportion; - the amount of input VAT to be included in the cost of the car will be written off from the credit of account 19.01 with the third sub-account Included in the cost in the debit of account 08.04.1;
- the amount of input VAT to be included in the cost of the MFP will be written off from the credit of account 19.01 with the third sub-account. Taken into account in the cost
in the debit of account 08.04.2 with a subsequent write-off to the debit of account 01.01.
Receipt will be entered into the VAT register presented
with the event, VAT is distributed to the amount of VAT presented by the supplier and subject to deduction after distribution.
VAT-exempt transactions
register will record the amount of VAT that is not accepted for tax deduction and relates to activities with the main tax system.
in the Separate VAT accounting
:
- with the type of movement Expense
- for the VAT amounts presented by the supplier and subject to inclusion in the cost of acquisitions after distribution; - with the type of movement Receipt
- for the VAT amounts presented by the supplier on acquired fixed assets, taken into account at the time of distribution as part of non-current assets (on account 08).
Results
So, if a fixed asset is acquired for an activity subject to VAT, and there is an invoice with allocated VAT, the deduction is made as follows:
- For fixed assets that do not require installation and assembly work, the deduction is carried out during the period when the object is registered as a fixed asset. It may well be declared during the period of registration under account 08. In case of a dispute, you can defend your position in court.
- For fixed assets that require installation, VAT can be deducted already in the period when the object is reflected on account 07.
- For fixed assets that require state registration, the deduction can be claimed already during the period of signing the property acceptance certificate, without waiting for state registration.
Sources: Tax Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Acquisition of a non-current asset
Costs for the purchase of a car, which will subsequently be accepted for accounting as a fixed asset, are accounted for in account 08.04 “Purchase of fixed assets” (Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 N 94n).
In 1C there are two options for registering the acquisition and accounting of fixed assets:
Standard option , which uses documents:
- capitalization of fixed assets - document Receipt (act, invoice) type of operation Equipment ;
- commissioning of OS - document Acceptance for accounting of OS ;
Simplified version , which uses a single document:
- capitalization and commissioning of fixed assets - document Receipt (act, invoice) type of transaction Fixed assets .
Learn more about Options for registering an OS in 1C, as well as the capabilities and limitations of each method
In our example, the initial cost of the OS will include the cost of the fee for registering a car with the traffic police, so we will use the standard option for accepting the OS for accounting.
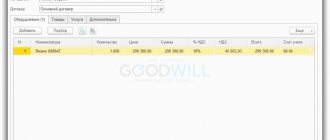
Let's create a document Receipt (act, invoice) operation type Equipment in the section Fixed assets and intangible assets - Receipt of fixed assets - Receipt of equipment. Data about the purchased vehicle is indicated on the Equipment .
The tabular section indicates:
- Nomenclature - the vehicle being purchased from the Nomenclature directory with the Nomenclature Type Equipment (fixed asset objects) .
- The accounting account is filled in automatically in the document depending on the settings in the Item Accounting .
For the item type Equipment (fixed asset objects), the default account is set to 08.04.1 “Purchase of components of fixed assets,” but it can be changed manually in the document. PDF
Find out more about setting up item accounting accounts
In the document Receipt (act, invoice) type of operation Equipment , it is impossible to indicate account 08.04.2 “Purchase of fixed assets”, since it is used to accept fixed assets for accounting in a simplified way.
Postings according to the document
The document generates transactions:
- Dt 08.04.1 Kt 60.01 - acceptance of non-current assets for accounting;
- Dt 19.01 Kt 60.01 - acceptance of VAT for accounting;
- Dt 60.01 Kt 60.02 - offset of advance payment.