Everyone has heard about VAT. Even if you don’t run a business and don’t keep accounting records. The treasured abbreviation can be found in any store receipt. That is, perhaps without knowing it, you always pay value added tax.
For most people, the term “value added tax” will mean nothing. Well, tax and tax, we are used to this. Meanwhile, you need to know. After all, it concerns everyone, whether you are a simple manager in an office, a worker in a factory, or a director of a franchise.
First of all, you need to understand that VAT is imposed on any product and any service that you buy. If the price is higher than cost. And she is always taller. The amount of tax in this case will be calculated based on the difference between the cost of the product and its selling price.
Where does VAT come from?
More than a century ago, in the twenties of the twentieth century, VAT came into the world to replace the sales tax. Before this, the “tax” was taken from all the proceeds that the entrepreneur received. It’s difficult and partly unfair, because actual income was not taken into account. They took it for the bare proceeds, and not for the businessman’s profit.
But VAT was introduced on the territory of the Russian Federation only in 1992. And until recently, it was 18% - a figure to which everyone got used to and paid the tax calmly until 2022 came.
Then the government raised the rate to 20%, and the public began to be outraged. Well, how can you be outraged... political scientists and economists started a debate, criticized the innovation, the other side defended the necessity, declaring that 2% of the weather will not work. And people believed. Well, what is 2%? A trifle. But it’s actually not a small thing at all. Because the tax is taken from everything.
One produces wood and sells it to a kitchen store franchise, which turns it into a product and sells it to the end consumer (and this is the most primitive chain). And the tax accumulates progressively at each price of all participants in this chain. After all, no one wants to pay extra. And prices need to include coverage for this tax.
However, from January 1, 2022, VAT in Russia officially became 20%.
This rate applies, with some exceptions, to most goods and services. But there are other options. Thus, a rate of 10 percent, for example, is levied on medical drugs, which is used by pharmacy franchises, children's products and some food products, which is also actively used by brands and food franchises. But products for export (export) are not subject to this tax at all. There the VAT rate is zero. But perhaps this won't last long. And most still pay 20%
Rates are regulated by Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
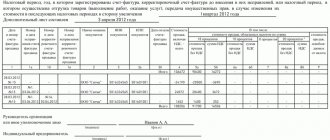
Checking revenue from sales taxed at a rate of 0% (except for the export of non-commodity goods)
This line should include revenue from the sale of goods (work, services), taxable at a rate of 0%, in accordance with Art. 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, except for non-commodity goods.
In the Universal report to check the amount in the line
- subject to VAT at a rate of 0% (except for the export of non-commodity goods)
In the header of the report please indicate:
- Period —the period for compiling the report;
- Accumulation register - type of data source;
- VAT on sales 0% - the report will be generated according to the VAT register on sales 0% ;
- Revolutions — data for creating a report.
Click the Settings in the report header to open the settings panel, click the View – Advanced .
Specify on the Selection :
- 1st line (if accounting is kept for several organizations in the database): Field - Organization ,
- Condition - Equal to ,
- Value - the name of the organization for which you are generating the report,
- The way to display the selection field is asterisk, i.e. show it in the report header.
- Field - State ,
- Field - Type of value ,
On the Fields and Sorting , specify the fields that will be displayed in the columns of the tabular part of the report.
On the Structure , set the set of grouped fields and the order in which the table section headings will be displayed in the report.
Please indicate:
- Organization (if records are kept for several organizations); Detailed entries .
After completing the settings, click the Close and Generate . The program will generate a report according to the form specified by the settings.
Mission accomplished! Using the Universal Report , we deciphered and checked all the lines in the VAT Distribution .
If you are a subscriber to the BukhExpert8 system, then read additional material on the topic:
- How to work with the Universal report
- Uploading and loading Universal report settings
If you haven't subscribed yet:
Activate demo access for free →
or
Subscribe to Rubricator →
After subscribing, you will have access to all materials on 1C Accounting, recordings of supporting broadcasts, and you will be able to ask any questions about 1C.
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Who pays VAT
A scheme may be born in the mind of the average person, suggesting that this tax does not concern him at all. Well, the entrepreneur pays himself, and let him pay. But this is a mistaken opinion. Because in reality, the entire amount of this tax is ultimately paid by the buyer himself. To understand why this happens, let’s look at a simple example and see what stages the emerging value added tax goes through.
- One company orders material from another company to make its product from it. She pays for this material. VAT will be applied to this amount of the cost of the material that the company paid.
- Next, this company produces its product from the purchased material, and then decides what the cost of the finished product will be? So that you yourself don’t end up at a loss, and your clients don’t run away from inflated prices? First of all, take the amount of money that was spent on the production of a unit of a new product. The tax amount is also calculated, but is recorded as a “tax credit”.
- Next, the company needs to decide how much the product will cost the end customer. Here the cost of the goods is added up, excise taxes are calculated, the share that after the sale will go to profit is entered, and VAT is added. That is, it will already be included in the price of the product that the consumer will pay upon purchase.
- When a product is sold in a certain quantity, the company sits down to calculate profits. From the money received, 20 percent of the tax that the buyer has already paid is calculated. And this money is spent on tax obligations to pay VAT.
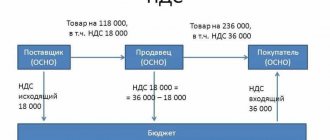
Here is a simple diagram that shows that the price of a product in a store already includes value added tax. And if it were not taken into account, the product would cost less. Even new franchises that want to enter the market with a new product produced personally include VAT in the price of the product, because they pay it when purchasing material for production.
What may be included in revenue?
The indicator under consideration includes:
- the purchase price at which the products were purchased;
- added value that appeared during the sale of goods.
That is, revenue takes into account the full price of products sold.
Sources of revenue are:
- The main activity of the enterprise (for example, the sale of goods and the provision of services).
- Investments (working with securities, selling shares).
- Other financial activities (for example, receiving funds from a company in which the enterprise’s investments were previously directed).
The list of sources depends on the specific company and its type of activity.
How to determine revenue for income tax purposes ?
VAT calculation
To understand the whole process, let's look at an example again.
We opened a clothing store franchise where we sell jeans. To sell something, you must first produce or buy it. In our case, we find a company that sells jeans wholesale. And we spend 100 thousand rubles on the purchase of a consignment of goods, where one pair of jeans costs 10 thousand rubles (the jeans turn out to be expensive, but for an example it will do). That is, we purchased 10 units of goods.
These 100 thousand rubles that were spent on goods already included 20 percent VAT. Since the jeans were sold to us by their supplier, who has already included this tax in the price, because he will have to pay it to the state for selling the product above cost. That is, we paid 20 percent of the tax. If it weren’t for him, the batch would cost not 100 thousand rubles, but 80 thousand rubles.
We calculate this amount as an incoming contribution or deduction. And we will need to have evidence that we paid for the jeans with VAT already included. Therefore, it is important to have one of the supporting documents - this is either an invoice, or a check, or an invoice, where the tax amount is indicated separately. That is why on all such documents we can find a line with VAT.
Further, when we ourselves set the price at which we will sell our jeans at retail, we remove this amount of VAT from the price for the product. And the next VAT, which will be levied on our sale, will be calculated from the amount received. That is, we add up our costs for the goods (this will include not only the cost price, but also our other expenses that we incur during the organization of the sale) without VAT and add 20 percent to this amount.
VAT calculation formulas
Let us first note that the formulas for calculating taxes are not so simple, especially for a person who is not used to dealing with mathematical equations. Therefore, there is more than one calculator that will calculate VAT or the amount excluding VAT for you. You can find them on the Internet, on specialized sites. You don’t need to learn how to use it, everything is extremely simple - there are a couple of fields for entering the amount and that’s it. For those who want to understand the algorithm for calculating the tax percentage, let’s look at the formulas in more detail.
VAT calculation formula
Let’s take the amount we know and denote it by the letter “X”. To understand how much VAT will be, we use a simple formula:
VAT=X*20/100
That is, if our amount of goods is equal to 100 thousand rubles, then the VAT on it will be equal, based on the formula, to 20,000 rubles. This is how much we paid when purchasing goods from a supplier in order to ensure that he paid his value added tax.
Once again, if we want to buy jeans worth 100,000 rubles, we will either pay 120,000 rubles, because we will also need to include VAT (this is done by the supplier), or we will pay 100,000 rubles with VAT already included, and in fact we will buy smaller quantity of goods.
Because in fact the price will be 83,333 rubles. 33 kopecks, and another 16,666 rubles. 67 kopecks is the VAT price for this amount, which is already included in the invoice for us by the supplier. You can open any VAT calculator on the Internet and check the calculation, but for now we’ll move on to the formula that will show us why it turns out to be 120 thousand.
Formula for calculating the amount including VAT
Amount - X. Amount with tax - Xn. Xn = X+X*20/100 Or Xn=X*(1+20/100)=X*1.20
That is, from our amount of 100,000 rubles, the amount including VAT will be equal to 120,000 rubles. We have already described this above, that is, if we want to buy 10 pairs of jeans, then we will actually have to pay 120 thousand, not 100, because the supplier will include VAT in the invoice.
Formula for calculating the amount excluding VAT
Amount including VAT = HN. You need to understand what the amount X will be equal to - the amount excluding VAT. To understand the formula, let’s remember the second formula, which calculated the amount including tax. And we enter the designation of the tax itself - it will be Y. Y, if the VAT is 20 percent = 20/100. Then the formulas will look like this:
Xn = X+Y*X Or Xn = X*(1+Y) From here we get that X = Xn/ (1+Y) = Xn / (1+0.20) = Xn / 1.20
We want to buy goods worth 100,000 rubles, but so that this figure already includes VAT, and at the same time understand how much the true amount we pay for the goods, and not for the tax, will be. We use the calculation:
Amount without VAT (X in this case) = 100,000 rubles (Xn) / 1.20 = 83,333 rubles with kopecks.
That is, if indeed one pair of jeans costs us 10 thousand rubles without VAT, then by paying only 100,000 rubles we will be able to purchase no more than 8 pairs from the supplier (there will be a little money left). Or, if we nevertheless spent 100,000 rubles and bought exactly 10 pairs, and VAT was already taken into account in this amount, then a pair of jeans costs 10,000 rubles with VAT already included in it. And we still paid it for the supplier (who, in turn, also paid VAT for the supplier of the materials from which these jeans are made).
Income from main activities
The company prescribes the main activities in its charter.
If a specific type of activity is not specified in the charter, then it must be checked according to the criterion of materiality. That is, the main type of activity can be considered any work or services if the proceeds from their sale are at least 5% of its total amount. Otherwise, such income is classified as other income.
Income from ordinary activities may also include income from leasing property, participating in the authorized capital of other organizations, granting rights to intellectual property for a fee, etc.
If the main activity of the company is participation in the authorized capitals of other organizations, dividends are included in revenue. They are reflected net of income tax, which is withheld by the tax agent upon payment.
Book of the Year!
Everything you need to submit a report that will satisfy both the director and the tax office. “Annual report edited by V.I. Meshcheryakov” is already on sale. There are several purchasing options: just a book, a package of information publications for accounting, and with a subscription to the press.
Companies whose investment of funds for the purpose of receiving interest is part of ordinary activities, then revenue is all interest on any types of debt obligations: loans, bills and bonds, deposits (clauses 7 and 18 of PBU 9/99). Such companies include, for example, pawn shops.
The amount of revenue is determined based on the price established by the contract, taking into account all discounts: both those that change the price of the product and those that do not affect the price (clauses 6.1, 6.5 of PBU 9/99).
Thus, according to paragraph 6 of PBU 9/99, revenue is the amount of receipts of money, other property or receivables. Regardless of the amount of payment received from customers (full, partial or zero), reflect the revenue in accounting based on the full cost of shipped products, works or services.
Example. How to reflect revenue on line 2110 of the income statement
In the reporting year, Aktiv JSC sold goods worth RUB 1,200,000. The company is not a VAT payer. For the shipped goods, buyers transferred only 800,000 rubles to Aktiva. In the accounting records of “Asset” the following entries were made: DEBIT 62 CREDIT 90-1
– 1,200,000 rubles.
– the debt of buyers for shipped goods is reflected; DEBIT 51 CREDIT 62
– 800,000 rub. – partial payment has been received from buyers. In the financial results report for the reporting year on line 2110, the accountant must reflect revenue in the amount of 1,200 thousand rubles.
For VAT purposes, sales also include the gratuitous transfer of ownership of goods, works and services. For example, distributing samples of goods for advertising, giving holiday gifts to company employees, etc. However, during such operations the company does not receive revenue. Therefore, in such a situation, no entries are made on line 2110 of the report.
Read in the berator “Practical Encyclopedia of an Accountant”
How to determine revenue using the accrual method
Tax credit and tax liability
We looked at the formulas, but how much should we pay to the budget for this tax, you ask. Let's finish off the topic with jeans and resolve this issue, and at the same time we will understand such components of the concepts of value added tax as credit and liability.
We still bought jeans for 120,000 rubles. Of which 20 thousand were paid as VAT for the supplier. We have an invoice from this supplier for our batch of jeans, where it is written in black and white that the price of the goods without VAT is 100,000 rubles, the amount of VAT is 20,000 rubles, and the total cost is 120,000 rubles.
Next, we set aside the VAT figure during calculations and remembered it as a tax credit.
A tax credit is the amount by which at the end of the reporting period it will be possible to make a tax deduction from the tax liability - that is, to reduce the amount of tax we pay to the budget. And what we will have to pay to the budget is a tax obligation.
Let's look further at the jeans.
In reality, we will subtract the VAT we have already paid from the amount of 120,000 rubles to form our price. That is, the amount will be the same 100 thousand rubles.
Let's say, having included all other cost and expense factors, and adding the percentage of the desired profit, we received a price of 200,000 rubles. This is exactly how much our jeans will be sold for in our store to the end consumer. And it is from this amount that our tax liability will be deducted - that is, the tax that we must pay to the budget.
From 200 thousand rubles, according to the formula or calculator, it turns out that VAT is equal to 33,333 rubles. This is our tax liability. But! After all, we also have documents that confirm our tax credit of 20,000 rubles (that is, the fact that we have already paid 20 thousand in the form of value added tax). This means that we can subtract 20 thousand already paid from 33 thousand. In total, we will get 13 thousand rubles, which we will pay after selling all 10 pairs of jeans (let’s say this happened in one reporting period).
From 200 thousand rubles, 13,000 went to the budget from us in the form of tax. But we must not forget that our supplier also paid his 13 thousand into the budget, which he received from us when purchasing the jeans initially.
How is revenue different from profit?
Revenue represents the totality of funds received from activities. This value does not take into account the company's expenses. Profit is the difference between revenue and expenses. Expenses are understood as the costs of supporting the activities of the enterprise. Let's look at all the differences:
- Calculus . The amount of revenue can be zero or positive. Profit can take negative values.
- Compound . To obtain information about revenue, it is enough to know all the income of the enterprise from its activities. To calculate profit, you need to know not only the amount of income, but also the amount of expenses.
- Real expression . Revenue may be potential. For example, the company provides customers with the opportunity to arrange an installment plan. There may not be funds in the company’s account, but there is a guarantee that they will appear. Profit cannot be “virtual”. It is calculated based on actual values.
- Expression . Revenue is a definition that can be interpreted in a single meaning. Profit can be divided into two forms: gross and net. Net profit refers to the amount of income received after paying all taxes.
Profit and revenue differ significantly from each other in a key number of ways.
Example
The company sells phones for 1,000 rubles. We manage to sell 500 phones a month. Revenue is 500,000 rubles. The same company spends certain funds on its activities. They go to pay rent for the premises. Rental payments per month amount to 50,000 rubles. The company also has to pay salaries to its employees. In total, the salary will be 100,000 rubles.
First, you need to add up all the expenses. They will amount to 150,000 rubles. All expenses are deducted from revenue. The profit will be 350,000 rubles.
Types of VAT
- 0%
- 10%
- 20% (replaced the rate of 18%)
As mentioned above, there are a number of goods and services that are not subject to this tax. Therefore, we can talk about the existence of a zero rate. These are exports of goods, products of the space niche, niches of gas and oil transportation and some other types of goods. The list of such positions is regulated by Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
There is also a list of trade names that are subject to a ten percent tax. These are mainly food products - meat, vegetables, dairy products. It also includes children's clothing, children's furniture and more. Again, the list is quite large; it is better to familiarize yourself with it in person in the tax code if this issue interests you.
Well, the rate of 20 percent is the most popular. You can meet her almost everywhere.
Note: since changes in legislation occurred relatively recently (01/01/2019), you can still find outdated data on the Internet, which describes a rate of 18%.
Transactions subject to VAT
- Import of any product
- Any work on the construction of buildings without concluding a contract
- Transfer of services and goods for personal use, the costs of which are not taken into account when calculating tax.
Which processes are not subject to VAT?
- The work of government bodies, which relates to its direct responsibilities.
- The process of purchase and privatization of municipal and state-owned enterprises.
- Investment.
- Sale of land plots.
- Transfer of money to enterprises operating on a non-profit basis.
VAT calculation methods
- Subtraction. In this option, the tax is imposed on the full amount of revenue, and from this amount the VAT payable for the purchase of materials for the product or service is calculated.
- Addition. In this case, VAT is imposed at a fixed rate according to the tax base. It is made up of the added value of each type of product sold.
So, while the second option is difficult to implement, because there are often very many such individual items, the first option is used much more often.
Exemption from payment if sales volumes are less than two million rubles
Firms and individual entrepreneurs whose sales volumes are not high, according to the Code of the Russian Federation, have the right not to pay value added tax. This benefit comes into force if, for three calendar months, the total income from the sale of trade items or the provision of services (not taking into account tax) is less than 2 million rubles (clause 1 of Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Important! If, if there is a tax exemption, during the next three months the total profit (excluding tax) exceeds this amount, then the preferential right is canceled. The tax is restored and payable in the accepted manner, starting from the month where the excess occurred (clause 5 of Article 145 of the Tax Code).
We talked about the rules for displaying income of individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system here.
VAT reporting
It seems that it has become a little clearer what value added tax is, where it comes from, how it is calculated and who pays it. However, you still need to report to the FSN authorities for it. Let's figure out how this is done.
The first thing you need to know is that you need to report quarterly. Moreover, the deadline is until the 25th of the post-reporting month. Otherwise, ugly fines await.
Important! If you send a VAT report by mail, then take into account the filing date - this is the date that will be stamped on the letter.
Example: It took 10 days from the post office where you sent a registered letter with your declaration to the tax office itself. Sent on the 18th, arrived on the 28th. Will it be considered that you submitted the report late? The answer is no. After all, the 18th number will appear on the stamp of the letter.
Tax deductions
In the case of value added tax, deductions are considered to be the amount of tax that is presented for payment by the supplier of the goods. The tax that will go to the budget from you will be reduced by this figure.
But there are some nuances that you need to know and understand. This concerns the conditions for the tax authorities to accept these deductions. Three rules must be followed:
- The product itself, which you purchased for the purpose of subsequent sale, is subject to VAT.
- The company has all supporting documents, including a correctly executed invoice.
- The goods that were purchased went through the accounting procedure.
And only after these conditions are met, the company will be able to accept the entire amount of payments as a deduction at the end of the tax period. Naturally, if all procedures were taxable.
Invoice
This document will reflect several amounts. Firstly, the cost of the goods without VAT. Secondly, the final amount includes VAT.
An invoice is provided for the goods sold to the client. This must be done within 5 days. All documentation is filed and noted in the sales book.
It happens that the audit makes a decision to cross out all calculated deductions and charge unpaid VAT. This can happen if there are errors on the invoice. And it’s not so difficult to allow them, because the invoice is issued by the counterparty, not the taxpayer.
Reflection in the financial results statement:
in form 2 (profit and loss statement - opiu)
In this reporting form, VAT is always indicated as a debit as part of line 2110 Profit. Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 6, 1999 No. 32n established that revenue is the turnover on the credit of account 90-1 Revenue, reduced by the debit turnover on subaccounts 90-3 “VAT”, 90-4 Excise taxes.
On the balance sheet
The tax is reflected in the balance sheet as both an asset and a liability. In the asset it is reflected in two lines at once - 1220 and 1230, in the liability - 1520. Let us consider in more detail the formation of each part.
- Line 1220 of VAT on purchased assets is the amount of tax that the company undertakes to deduct in the future, that is, the balance of account 19 is transferred there. For many companies, by the end of the year 19, the account is reset to zero, and then there is a dash in line 1220.
- Line 1230 is accounts receivable. In other words, this line summarizes everything that buyers or customers did not pay extra (or did not pay) at the time of drawing up the balance sheet, including VAT. This also includes advances for raw materials or supplies to suppliers, which include VAT.
- Line 1520 is the company's accounts payable. That is, this is the sum of all the company’s debts, including VAT. In addition, this line also includes advances received minus VAT.
Thus, VAT is reflected: in lines 1220 and 1230 in the assets of the balance sheet and in line 1520 in the liabilities.
Tax accrued - posting
The VAT entries reflect:
- When selling a product or service.
- Input VAT.
- VAT restoration.
Let's consider each case separately and determine in which case and on which account the tax is determined.
When selling goods, this tax is always taken into account as a credit in accounts such as 68 and 76.
Commercial organizations can reduce the amount of tax payable by deducting input VAT. It is reflected as a debit in accounts 19 and 68. There are a number of cases when the tax accepted for deduction must be restored.
Recovered VAT is reflected only on one account 68 for the loan.
In the declaration
The VAT declaration consists of two parts - the title page and the amount of VAT that is subject to payment to the budget or refund from the budget. To compile this document, 25 days are given from the end of the quarter.
The structure of the declaration is as follows:
- The first section is the final section, in which the accountant writes about the amounts to be paid or reimbursed based on the results of accounting/tax accounting and information from section 3 of the declaration.
- The second section must be completed by tax agents.
- The third section contains the final amount of tax to be paid to the budget or returned from it.
- The next three sections (4,5,6) are filled out only if there was a tax rate of zero percent.
- The seventh section reflects transactions on which VAT is not paid.
- Sections 8 and 9 include counterparties who are included in the tax registers for VAT.
- Sections 10 and 11 are completed only by certain types of business entities.
- Section 12 – designation of taxpayers who do not have to pay this tax.
VAT is reflected in a number of documents of each company. However, goods may be taxed at different rates or not subject to this tax. In order to avoid mistakes and desk audits, it is necessary to take into account all the nuances when paying this tax to the state budget. If the tax inspector still has questions, don’t be afraid, you just need to explain everything in detail, since perhaps your mistake is justified.
Bottom line
Knowing what VAT is is important for anyone. Knowing how to calculate it is important for those who are directly involved in filling out documents and submitting reports to the tax department. Being unaccustomed to doing this using formulas is difficult and tedious. Therefore, to check yourself and your counterparties, there are many electronic resources where you can find a VAT calculator that will calculate it for you in two clicks. The main thing is to remember that attentiveness is an important component in the matter of VAT, and you cannot be late in submitting your reports to the tax office.