Legislation
First of all, you need to decide on the terminology. From the point of view of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, part-time work is working simultaneously under two labor contracts. It can be (Article 60.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- internal - when the parties to the labor relationship are the same employee and employer;
- external - when in his free time from his main job a person works for another employer.
Moreover, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in Art. 60.2 also highlights the concept of combination. Unlike internal part-time work, in this case a new employment contract is not concluded, but in fact, during the working day or shift, for an additional fee, the employee performs duties in another position besides the one he already holds. It is the absence of a separate employment contract that makes the key difference.
As for maternity leave (hereinafter referred to as BiR for brevity), it is provided, in accordance with Article 255 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, on the basis of an application from the female employee herself and on the basis of an issued certificate of incapacity for work (“sick leave”). The duration of the vacation is :
- 70 days before childbirth and the same amount after;
- 84 days before birth if 2 or more children are expected;
- 90 days before giving birth if the woman lives in an area exposed to radiation contamination (Chernobyl accident, releases at Mayak, etc.);
- 86 days after childbirth with complications;
- 110 days after birth, if there was more than one fetus.
A part-time worker has the same rights as any other employee. Therefore, she can also use the B&R leave. However, since it is provided only at the request of the employee with presentation of sick leave, she must submit the appropriate documents for each of her positions. One application can only be submitted for internal part-time or combination work.
Payment for sick leave under BiR is made on the basis of the Federal Law “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity” No. 255-FZ of 2006.
Art. 13 of this law indicates that sick leave is paid :
- At the place of main work.
- For both places of work with external part-time work - if the insurance period (that is, the time when employers made contributions to the Social Insurance Fund for the employee) is more than 2 years for each place.
- At the choice of the employee - if in the previous two years she worked for other employers who made contributions to the Social Insurance Fund for her.
It should be taken into account that sick leave payments under the BiR are made based on average earnings. However, there are exceptions in which payments will be made based on the minimum wage. They concern the following cases:
- when the total experience in this work is less than 6 months;
- when the average daily earnings for the billing period are less than those calculated on the basis of the minimum wage.
Results
The calculation of the B&R benefit for a part-time worker has a number of nuances, the main one of which is where the part-time worker worked for the last 2 years before the year of receiving the “maternity” certificate of incapacity for work. The algorithm for assigning and calculating the B&R benefit depends on the answer to this question.
Read more about calculating the amount of “maternity” payments in the material “How to correctly calculate maternity leave in 2021?”
Sources:
- Law “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity” dated December 29, 2006 N 255-FZ
- Order of the Ministry of Labor dated April 30, 2013 No. 182n
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Who pays for the BiR slip?
As of 2022, there are two options for paying sick leave:
- It is paid for by the employer, to whom the Social Insurance Fund then reimburses the payments made.
- It is paid directly by the FSS. This is practiced in regions where a pilot project for direct payments is already operating.
What exactly does this look like in practice?
Payment to a part-time worker
If the employee has concluded two employment contracts, payment is made as follows :
- The employee submits the package of documents required by regulations to the employer.
- The employer calculates benefits and sends documents to the Social Insurance Fund. Moreover, in the case of internal part-time work, the average earnings and the amount of payments for each employment contract are calculated separately. Documents must be submitted to the Social Insurance Fund no later than 5 days after receiving them from the employee (clause 3 of the Regulations approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 294 of 2011).
- The Social Insurance Fund checks the received documents and makes a decision on the assignment of payments. The period for this is set at 10 days (clause 7 of the said Regulations).
Important! To receive payments for both places of work, the employee must provide documents to each of the employers.
By combination
In the same case, if a woman does not work part-time, but performs additional duties for additional pay within the framework of one employment contract, the procedure for receiving and paying sick leave under the BiR does not differ from the usual.
How to apply correctly?
The basic steps for registering maternity leave are the same as if the expectant mother worked in only one place.
- The woman registers at the antenatal clinic. In the third trimester, if the pregnancy goes well and the employee continues to work all this time, she receives a certificate of temporary incapacity for work. It clearly states the start and end dates of maternity leave.
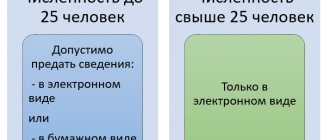
- In the case of a single place of work, the original document is transferred to the employer’s accounting department. If a woman, in addition to her main job, also works as a part-time worker, the doctor issues her several sick leave certificates, separate for each employer - the document states the employee’s position, the name and address of the employer.
- The documents are submitted to the accounting department of each employer.
- In order to correctly calculate maternity benefits, you need information about the earnings of the expectant mother for two years. If a woman has been working in a company for more than two years, the accounting department makes calculations based on internal documents. If the period of work is less than two years, you must provide a certificate of income from your previous place of work.
- If it was not possible to obtain a certificate (the company was liquidated, it was not possible to contact the employer), the value of the minimum wage for this period will be used for calculation for this time.
- At each place where the expectant mother worked before pregnancy, the woman writes a free-form application with a request to issue a vacation with all due monetary payments.
- Within ten days, the employer reviews the application and makes the necessary payments. The only thing accounting pays attention to is that the sick leave certificate is genuine and not filled out with serious errors.
If everything is done correctly, the woman receives a one-time maternity benefit at each place where she is officially registered as an employee. Most often, the money is transferred to the same salary card to which the employee previously received remuneration.
How to apply for a certificate of incapacity for work for both jobs?
In order for a part-time worker to go on sick leave and receive payments under the BiR, she must provide the following package of documents for each place of work :
- An application addressed to the manager with a request to grant leave and pay benefits.
- A certificate from the antenatal clinic about registration for pregnancy.
- Sick leave issued by a gynecologist.
- Salary certificates - if in the previous two years the woman worked in other places. They are necessary to calculate average earnings. Each certificate is issued in accordance with the form approved by order of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation No. 182n of 2013.
From June 2022, sick leave can be issued in the form of ELN - electronic certificates of incapacity for work. However, if the enterprise does not yet use electronic document management, the employer may require that the sick leave be duplicated in the form of a paper document.
The application itself is written in any form, but must contain the following information:
- Full name and position of the head of the enterprise.
- Full name and position of the applicant.
- Please provide leave with dates. Dates are indicated in accordance with the issued sick leave.
- Please provide benefits.
- A way in which it would be convenient for the employee to receive money (cash at the company’s cash desk, on a card, etc.).
- List of attached documents.
- Date and signature of the applicant.
Since sick leave is required for each place of work, a copy will be required for external part-time work. It can be obtained as follows:
- Make a notarized copy and provide it at the additional place of work.
- Obtain two certificates of incapacity for work from the doctor. In this case, the woman must be notified which place of work is the main one and which is a part-time job. A mark will be placed in the corresponding sick leave column (clause 4 of the Procedure for issuing certificates of incapacity for work, approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation No. 624n of 2011).
Procedure for going on maternity leave while working part-time
An employee does not spend much time at a part-time job, and the workload there is usually light. Therefore, a woman has the right to decide for herself whether to go on maternity leave while working at an additional job, or to continue her activities while on sick leave at her main job.
Part-time work during maternity leave is a fairly common phenomenon in our time - a woman goes on maternity leave at her main job, but voluntarily continues to earn additional income.
Let's outline the procedure for going on maternity leave:
- First of all, a woman must register with the antenatal clinic. As a rule, in the third trimester, the doctor issues the expectant mother a temporary disability certificate, which indicates the start and end date of the woman’s maternity leave. The original should be provided to the main place of work, and for additional ones, notarized copies should be made.
- A woman must contact each of her employers with a sick leave certificate or a certified copy thereof.
- To calculate maternity benefits, you will need information about her earnings for the previous two years. Therefore, if a woman has been working in a company for less than 2 years, she will have to provide a salary certificate from her previous employer. If for some period it was not possible to restore the income of a pregnant woman, then the minimum wage value will be taken for calculation.
- At each workplace, a woman going on maternity leave and applying for insurance benefits must write a corresponding application in any form.
- The employer is obliged to review the submitted documents ten days in advance. He has the right to refuse only if the employee has submitted a fake sick leave certificate, or if gross errors are found in it.
How is the maximum benefit amount calculated?
There are upper and lower limits for benefits . The lower one is the calculation based on the current minimum wage. The upper one is determined by the maximum value of the base on which insurance payments were calculated in the Social Insurance Fund.
As for part-time workers, for them the maximum size is taken into account as follows:
- If an employee has worked for the same employers for the last two years, then the B&R benefit is calculated for each place of work separately, without taking into account payments from another employer. In this case, the total amount she will receive may exceed the maximum amount.
- If the period of work at the main place and part-time is less than 2 years, but in the last two years the woman worked, she herself chooses where she will receive benefits. The calculation is made based on salary data from all places of work.
- If during the calculation period of two years a woman worked both for her current employers and for others, she can choose: either to receive payments for one place of work, or for each of the places.
In the last two cases, if the benefit is paid for one place of work, its total amount cannot exceed the established maximum.
Features of assigning benefits to an external part-time worker
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 14, pp. 2–2.2 tbsp. 13 of Law No. 255-FZ, when assigning benefits to an external part-time worker, the following factors are taken into account:
- the presence of a part-time job at the time of maternity leave;
- the presence during the billing period (two previous years) of labor relations with the same or other employers.
Assignment of benefits for each place of work
In accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 13 of Law No. 255-FZ, maternity benefits are assigned for each part-time job under the following conditions:
- if the part-time worker works for several employers at the time of maternity leave;
- if during the billing period the part-time worker was employed by the same employers.
Each employer, when assigning benefits, is guided by the average earnings of a part-time worker at a given place of work. In this case, earnings from another employer are not taken into account (clause 2 of article 13, clause 1 of article 14 of law No. 255-FZ).
Assignment of benefits for one of the last jobs
In accordance with clause 2.1 of Art. 13 of Law No. 255-FZ, the benefit is assigned to one of the last places of work at the choice of a part-time worker, provided:
- if the part-time worker works for several employers at the time of maternity leave;
- if during the billing period the part-time worker was employed by other employers.
In this case, when assigning benefits, the employer takes into account the earnings of the pregnant woman for the billing period from all employers (Clause 1, Article 14 of Law No. 255-FZ). The document confirming earnings is a certificate of the amount of wages for the previous 2 calendar years (approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor dated April 30, 2013 No. 182n).
You can fill out such a certificate here.
Assignment of benefits for each or one of the last jobs
In accordance with clause 2.2 of Art. 13 of Law No. 255-FZ, benefits are assigned at the choice of a part-time worker for each place of work or for one of the last places of work, provided:
- if the part-time worker works for several employers at the time of maternity leave;
- if during the billing period the part-time worker worked simultaneously for the same and other employers.
If the benefit is assigned to one of the last places of work, then in accordance with clause 5.1 of Art. 13 of Law No. 255-FZ, a part-time worker must submit a certificate from his place of employment with another employer, which confirms that the benefit was not issued by another employer.
An example of calculating maternity benefits if an external part-time employee applied with documents (information) to only one employer, from ConsultantPlus Eliseeva M.G. submitted to Romashka LLC, where she has been working externally since January 2022, a sick leave certificate, according to which she is entitled to maternity leave from March 13 to July 30, 2022. At Romashka LLC Eliseeva M.G. works part-time (0.2 rate). The main place of work of Eliseeva M.G. as of March 13, 2022 - Buttercup LLC. Eliseeva M.G. has other places of work. No. She has also been working at Lyutik LLC since January 2022. You can view the entire example in K+, having received free trial access to the system.
How is the B&R benefit calculated?
Calculation of benefits for the BiR is carried out as follows::
- Earnings for the last two years from which funds were deducted to the Social Insurance Fund are summed up.
- The result of the addition is divided by 730 - the number of days in two years. If one of the previous years was a leap year, divide by 731.
- The resulting average daily earnings are multiplied by the number of vacation days (from 140 and above in the case of a complicated pregnancy).
As for payments, the following options are possible:
- In regions already covered by pilot projects for direct payments, the money goes directly to the employee from the Social Insurance Fund.
- In other subjects of the Russian Federation, the following system operates: first the employer pays the money, and then the Social Insurance Fund reimburses him for these funds (more precisely, it does not reimburse him, but reduces the amount of payments by this amount next year, offsetting the expenses incurred).
In the second case, the algorithm of actions is as follows:
- The employee submits an application and accompanying documents to each employer.
- The employer makes the calculations and pays the benefit (usually within the time limits provided for the payment of wages).
- The calculation and justification of the amount paid are submitted to the Social Insurance Fund for verification.
- The FSS checks the information received and, if everything is correct, accepts these funds for credit for the next year.
In cases where a direct payment system is used, the following mechanism applies:
- The employee applies directly to the Social Insurance Fund, having previously notified the employer of her intention to go on leave under the BiR.
- The employer transmits information about average earnings for the billing period to the Social Insurance Fund.
- The FSS verifies the information received and makes payments.
How is sick leave calculated according to BiR for an external part-time worker?
In general, the procedure for calculating benefits for a part-time worker is the same as for main employees. The nuances are related to part-time work for a part-time worker and the option of applying for benefits.
The employee asks to calculate benefits only for this place of work
Average earnings for the Social Insurance Fund are calculated only according to the data available to you. The employee does not need to be required to provide additional certificates from other employers. Data on them can be included in the calculation only if the employee, for some reason, provided it to you herself. For example, in the billing period, your organization was first the main place of work, and then the employee remained part-time. But data from the previous employer was already provided for other calculations.
If your employee does not work full time, then maternity benefits should be calculated as follows:
- The average daily earnings at this place of work are calculated.
- The minimum wage adjusted for actual working hours is calculated as of the start date of leave under the BiR.
Estimated minimum wage = minimum wage / Normal working hours X Duration of the employee’s working hours
- The average daily earnings are calculated from the calculated (adjusted) minimum wage
Average daily earnings from the minimum wage = Estimated minimum wage X 24/730
- The average earnings from the adjusted minimum wage are compared with the actual average earnings of a female employee. The larger of the values is used to calculate the benefit.
- After this, the benefit is calculated in full as usual.
Important! For calculations, the minimum wage must first be indexed to the applicable regional coefficients.
In order for social insurance to make such a calculation, in addition to standard information, they need to provide information that the employee works part-time. In the register, column 41 “Information about part-time work (rate rate)” is intended for this purpose.
An employee asks to calculate benefits for several places of work
In this case, for the average earnings, all available information for all places of work is taken into account (according to the certificates given by the employee).
Please note that comparison of actual average daily earnings in this situation is made only with the maximum value . It does not compare with the minimum wage. Even if the calculations show that the resulting amount is less than the minimum wage, the benefit must still be paid according to the actual average earnings.
The Social Insurance Fund must provide information on all amounts of earnings received by the employee from all employers. In the register, column 42 “Other information” is intended to reflect such information.
Is a woman obliged to notify both employers?
When talking about sick leave payments under BiR, you need to remember the following: going on vacation in this case is a woman’s right, not an obligation. Therefore, if she wants to continue working, she has the right not to report her pregnancy and continue working.
However, the employer’s obligation to provide leave and accrue sick leave payments arises only from the moment the employee decides to exercise her right and provides a certificate of incapacity for work and an application. Until this moment, the management of the enterprise where she works at her main place of work or part-time is not obliged to release her from work, nor make any payments or transfer data to the Social Insurance Fund.
At the same time, there is no obligation to notify both employers about sick leave (in the case of external part-time work) : an employee can go on labor and employment leave at one place of work - but continue to work at another in order to leave later.
When calculating payment terms, you must be guided by Part 2 of Art. 7 Federal Law “On state benefits for citizens with children.” This norm indicates that leave for labor and employment is provided in full and is calculated in total, regardless of how many days of it were actually used before the birth of the child.
In practice, this means that a woman can, if she went on labor and labor leave directly on the day of birth, take paid leave not for 70 days, but for all 140 (or more in case of a complicated pregnancy).
What is part-time work: nuances for maternity leave
Part-time work is a job formalized by an employment agreement, the duties of which are carried out on a regular basis in free time from the main work (Article 282 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, an employment agreement can be concluded both at the main place of work (internal part-time job) and with another employer (external part-time job), and the number of external employers is not limited by law.
Part-time work is not available to everyone. Employees do not have the right to it (Article 282 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- under 18 years of age;
- whose work at the main place is carried out in harmful (dangerous) conditions, if part-time work presupposes the presence of the same working conditions;
- transport managers if, as part-time workers, they are engaged in the same type of activity (Article 329 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The possibility of part-time work is limited (in whole or in part) for civil servants, employees of internal affairs bodies, the investigative committee, the prosecutor's office, the penal system, foreign intelligence, fire service, security and credit organizations, courier communications, heads of legal entities, lawyers, athletes, coaches.
Part-time work is characterized by the following features that are important for maternity leave (Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- it is always carried out on a part-time basis, since the maximum duration of work for a part-time worker is limited to half the normal working time (Article 284), however, for teachers, doctors, pharmacists, and cultural workers, this limit may be exceeded (clause 1 of the Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation of June 30, 2003 No. 41);
- wages for part-time workers are calculated for the time actually worked (although payment for the amount of work performed is also possible), taking into account in this calculation the coefficients in force in the region (Article 285);
- part-time workers have the right to be provided, at the same time as at their main place of work, with not only regular leave (Article 286), but also sick leave pay (including for maternity leave (BiR)), since the income paid to them are subject to insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund.
The fact of paying contributions for disability and maternity insurance automatically makes the provisions of the Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ “On Compulsory Social Insurance...” applicable to part-time workers taking maternity leave.
Difficulties with non-simultaneous registration of leave under B&R in different places of employment
In the event that an employee does not apply for leave under Labor and Employment at the same time for all part-time jobs, certain difficulties may arise.
The main one is the calculation of average earnings for future payments. If benefits are paid only for one place of work, then in this case for the second the woman may not receive anything except the salary for the time actually worked.
In addition, if documents are not submitted to the Social Insurance Fund at the same time, delays in payments are possible . This is due to the fact that the verification period for the fund is 10 days, and therefore payments may take another month.
Finally, if the supply is not made at the same time, difficulties with the work schedule may occur. In particular, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation prohibits the use of pregnant women on weekends or holidays, overtime and in some other cases. If part-time work involves such a regime, the employer may need to transfer the pregnant employee to another position.
Labor law allows a part-time worker to use labor and employment leave both at her main place and part-time. However, when calculating payments, it is necessary to take into account the insurance period, as well as the working hours. In addition, depending on the region, there may be different sick leave payment systems.
Features of external part-time work
The main feature of the work of an external part-time worker is the limitation of its duration.
Based on the standards established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in a second workplace, in addition to the main job, a part-time worker can perform his duties no longer than 4 hours a day. Working part-time for more than this time is permissible only if this day is a day off at the main place.
Let us remind you that the features of planning and recording the working time of a part-time worker should be reflected in a separate employment contract with him.
The remuneration of a part-time worker is calculated depending on the time he works. And, of course, such restrictions on work time and payment affect the calculation of benefits for temporary disability and labor and employment.
Is maternity leave required for up to 1.5 years at a non-main job?
Issues related to parental leave are regulated by Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It states that upon application by the employee, the employer is obliged to provide it. At the same time, there are no special clauses about whether a woman is a permanent employee or a part-time worker. Therefore, the part-time worker has the right to leave.
If a woman has submitted a corresponding application, then the administration of the enterprise is obliged to issue documents for leave. It does not matter whether it is decorated in the main place.
The employer must provide maternity leave to the employee, regardless of whether she receives child benefits.
In addition, a part-time worker has the right to use the rest time provided to him in the same way as a permanent employee. This means that it is not necessary to use all the time until the child reaches three years of age. Vacation can be used in parts, or you can leave it early.
During the absence of an employee working part-time in an organization, his place is retained. If a woman has applied for maternity leave, then the employer cannot fire her (read about dismissal while on maternity leave here). An exception is the liquidation of an organization or the termination of an individual entrepreneur’s activities. In other cases, the employment contract can be terminated only at the request of the employee herself.
An employee may exercise the right to parental leave for up to three years at his own discretion. He is not obliged to register it for all places of work.
With internal alignment
Internal part-time work is performing work in several places, but in the same organization. An employee has the right to use vacation in one place and continue to work in the second. But to calculate the amount of benefits, all accruals are taken into account (that is, for all positions).
The benefit is paid according to the main position. If an employee applies for maternity leave for both places at once, then in the order for a part-time position, the employer makes the clause “Without assigning benefits.” And as a basis, the details of the order for the main position are entered.
For a joint placement, you do not need to provide a certificate stating that the second parent does not receive benefits. But this is done only in cases where payments are not made. This condition is contained in the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 1012n dated December 23, 2009.
With external alignment
If a person works at several enterprises, then in one place he is considered a permanent employee, and in another - an external part-time worker. A person has the right to choose where he will take his vacation independently, including at a non-primary place (Federal Law No. 255-FZ of December 29, 2006, Article 13).
The Social Insurance Fund in letter No. 15-03-09/12-2494P dated September 13, 2013 indicates that in such a situation, the set of documents must include a certificate from another place stating that benefits are not accrued there.
In this case, the amount of the benefit is calculated from earnings in the organization where it will be paid. Income received in another organization in which the employee continues to work is not taken into account. This is exactly how the FSS interprets the provisions of Article 13 of Law No. 255-FZ (see letter dated December 14, 2010 No. 02-03-17/05-13765, tables 11, 12 and 13).
Income from other employers is taken into account only if it is received in the two calendar years preceding the start of parental leave and the employment relationship with them is terminated.
Calculation of payments when paying sick leave to a part-time worker
Correctly calculating the amount of benefits for a period of incapacity for work is a rather difficult task even for an experienced accountant, especially taking into account the regular changes that are made to the legislation. Since 2007, this issue has been regulated by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation “On approval of the Regulations on the specifics of the procedure for calculating benefits...” dated June 15, 2007 No. 375.
According to clause 6 of the regulations approved by him (hereinafter referred to as the Regulations), when calculating benefits, the average daily earnings for the 2 calendar years preceding the occurrence of the insured event are taken into account. Earnings include all payments that were made by the employer for 2 years (but not more than the amount from which insurance premiums were paid for the same period to the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation). The resulting amount is divided by 730 (the number of days for 2 years) - the final figure will be the average daily earnings. Moreover, its size should not exceed the amount that is the result of dividing the base for payment of insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation by the same number (i.e. 730).
Important! When calculating benefits for BiR, the number of days for the calculated 2 years can be equal to 731 if there was a leap year in the calculation period.
If during the previous 2 years the employee had no earnings at all or the amount was less than the minimum wage at the time of illness, his average earnings for these periods, according to clause 11(1) of the Regulations, will be calculated from the same minimum wage. For part-time work, earnings are calculated in proportion to the time actually worked.