Home/Trade/VAT on goods
A certain list of goods is not subject to VAT - this is a fairly wide list of medical and other goods, the imposition of additional taxes on which is inappropriate. In addition, there are specific types of activities and business support measures that also imply tax exemption or rate minimization. The situation around VAT is recognized by experts as ambiguous, and the tax itself is difficult to calculate and account for, which does not exclude, but rather emphasizes the need for its detailed study.
What is VAT?
VAT (Value Added Tax) is an indirect type of tax that is levied on a wide range of services and goods. It is calculated for the benefit of the country's budget from the surplus value. The final buyer pays tax on the entire purchase price, but the receipt of funds begins earlier, since the calculation occurs at the production stage, being added to the cost of raw materials and creation work, it is paid at all stages.
Attention
Russian legislation assumes a VAT rate of 18%, there is also a preferential rate of 10% and the possibility of a complete exemption from payment.
VAT may resemble sales or turnover tax; it is also added to the cost of goods. But unlike what was mentioned, in a situation where the buyer pays VAT, that is, buys goods whose price includes tax, the seller has the opportunity to deduct from this amount that was paid by the buyer the amount that was paid as the same tax when purchasing goods or raw materials (or using services) from a supplier. That is, the tax in practice turns out to be indirect, and it is the end consumers who pay it. In payment documents, VAT on goods appears as a separate line. This system was not developed by chance, and its use allows you to achieve several goals at once:
- Tax payment is distributed across the stages of production and commerce processes, which eliminates the cascading effect of multiple collections. This eliminates VAT overpayments, which could be very significant.
- The tax is paid by several payers, the responsibility is distributed. Evading VAT on goods using simple methods is impossible; the payment will still go to the budget - if one of the participants in the process evades it, it will still be withdrawn at subsequent stages.
- As part of the current economic situation, it removes national taxes on exports, allowing you to receive an indirect tax.
What goods are not subject to VAT?
There are a number of categories and areas of goods that are not subject to VAT. These are, first of all, areas of social orientation, as well as socially significant goods that should not be provided within the framework of normal market competition due to the fact that this will affect certain segments of the population. Also, this tax is not relevant for a number of business areas, for a sector that requires development and support. By imposing VAT on goods, an import substitution program is being implemented, making it possible to push foreign manufacturers out of the market, providing a place for our own. Moving on to specifics, it is worth listing the following goods that are exempt from payment within the scope of goods and services provided by them:
- Food and related products.
- Food for medical, educational institutions, direct producers.
- Stamps, postcards with stamps, mail envelopes.
- Scrap metal and metal waste, ores, valuable metals and their concentrates.
- Any goods in duty free.
- Diamonds that have not undergone treatment.
- Precious coins that are not accepted for payment.
- Medical products according to the existing list.
- Goods for free assistance.
- Religious goods and literature.
Which goods are not subject to VAT upon import?
Tax must also be paid when importing products into the country for commercial purposes. In this sector there are also categories exempt from payment, and their full list can be seen in Art. 150 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. As an example of goods exempt from payment, one can cite technological equipment and spare parts that are not produced in Russia even within the framework of analogues. The following goods are also completely exempt from VAT when imported:
- Medicines that have no analogues, materials for their production.
- Consumables for scientific purposes that have no domestic analogues.
- Life-saving medical supplies.
- Any cultural values.
- Breeding agricultural animals, embryos.
- Items within the scope of gratuitous assistance.
- Seafood produced by domestic companies.
- Currency, securities - with the exception of collecting purposes.
- Rough diamonds.
- Objects of space activities.
- Printed products for exchange between museums and libraries.
- Goods produced by Russian companies operating abroad.
- Vessels for registration in Russia.
List of goods, works and services exempt from VAT
In the law, the list of services exempt from VAT is dispersed and is contained in paragraphs 2 and 3 of Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In particular, from the general list we can highlight the following basic services that are not taxed:
• medical services provided by medical organizations and institutions, doctors engaged in private medical practice. The list of such services is given in paragraphs. 2 p. 2 art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
• care services for the sick, disabled and elderly, provided by state and municipal social protection institutions;
• keeping children in preschool institutions, conducting classes with minor children in clubs, sections and studios;
• services for the preservation, acquisition and use of archives provided by archival institutions and organizations;
• transportation of passengers by public urban passenger transport (except for taxis, including minibuses), carried out at uniform tariffs with the provision of all travel benefits approved in the prescribed manner.
• funeral services;
• provision of residential premises for use in the housing stock of all forms of ownership;
• depository services (IMF, IBRD, IDA), with the Central Bank of Russia acting as a depository in rubles. In addition, services related to securities provided by specialized organizations on the basis of licenses are not taxed;
• educational services provided by non-profit organizations. The benefit applies to services for the sale of basic and additional educational programs specified in the license;
• services related to social services for minor children, elderly citizens, disabled people, street children;
• services for the preservation of an object of cultural heritage of the peoples of the Russian Federation, included in the unified state register. The list includes historical and cultural monuments;
• services within the framework of arbitration, paid through a non-profit organization, a division of which is this permanent arbitration institution;
• services provided by authorized bodies for which a state fee is charged. Including services for certification of operators for vehicle technical inspection, technical inspection services;
• services of cultural organizations, including theaters, cinemas, concert halls, clubs, zoos, museums, cultural and recreation parks. In particular, rental of audio and video media, making copies of printed materials, exhibits and documents of such organizations, sound recording of theatrical and entertainment events and other similar services. The full list is given in paragraphs. 20 clause 2 art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
• air navigation services for aircraft flights. Such services are exempt from VAT if they are provided by persons who have the appropriate certificate from the Federal Air Transport Agency;
• services of pharmacy organizations for the manufacture of medicines, as well as for the manufacture or repair of spectacle optics, repair of hearing aids and prosthetic and orthopedic products listed in paragraph 1 of this list, services for the provision of prosthetic and orthopedic care;
• organization and conduct of gambling;
• trust management of pension savings;
• sale by foreign entities of the rights to host the FIA Formula 1 World Championship;
• maintenance of sea vessels and mixed (river-sea) navigation vessels provided to foreign persons who are not registered with the tax authorities as taxpayers;
• services of regional operators for the management of municipal solid waste. The benefit is valid if the cost of services corresponds to the maximum unified tariffs, which are approved by authorized regional authorities;
• services related to servicing bank cards;
• insurance, coinsurance and reinsurance services, as well as services for non-state pension provision by non-state pension funds;
• services provided by bar associations, law bureaus, bar chambers of constituent entities of the Russian Federation or the Federal Chamber of Lawyers to their members in connection with their professional work;
• services of sanatorium-resort, health-improving organizations and recreational organizations, recreational and health-improving organizations for children, including children's health camps located on the territory of the Russian Federation, recorded in strict reporting forms;
• services for the provision of airtime provided free of charge in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on elections and referendums;
• utility services provided by management organizations, homeowners' associations, housing construction, housing or other specialized consumer cooperatives;
• production and distribution of social advertising, provided free of charge in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on advertising;
• services of participants in an investment partnership agreement - managing partners in the conduct of common affairs;
• services of a tax agent when selling, leasing state property that is not assigned to state enterprises and institutions, constituting the state treasury of the Russian Federation;
• public catering services through restaurants, cafes, bars, fast food establishments, buffets, cafeterias, canteens, snack bars, culinary departments at the specified facilities and other similar public catering facilities, as well as catering services outside public catering facilities at the location chosen by the customer;
• services provided at no additional charge for the repair and maintenance of goods and household appliances, including medical goods, during the warranty period of their operation, including the cost of spare parts and parts for them.
Please note that the number of tax-exempt services changes frequently. Therefore, it is advisable to regularly check the list for new items that are relevant to the activities of the organization.
How to calculate VAT on a product?
In order to calculate VAT on a product of any amount, there is a simple mathematical formula.
NB × Nst / 100
NB - tax base, total amount, Nst - rate, which can be equal to 18 or 10.
If it is necessary to calculate VAT, including in order to isolate the tax from the total amount, use the following formulas:
C/1.18 × 0.18 (or × 0.10)
C / 1.10—if the tax rate is 10%,
C - total amount including VAT.
When calculating the amount including VAT without first calculating the tax, the following formula is used:
C = NB × 1.18 (or 1.10)
NB - tax base, the total amount excluding tax.
Subject to VAT at the rate of 10%
When importing or selling medical goods, a preferential rate of 10% applies (clause 4, clause 2 and clause 5, article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Codes of medical products that can be imported and sold at a preferential rate of 10% are listed in Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated September 15, 2008 N 688 (as amended on March 20, 2018). Officials also adjust Resolution No. 688 almost every year.
Here are the types of goods taxed at a 10% rate:
- medicines for treatment and clinical research, including pharmaceutical substances, medicinal products manufactured by pharmacies;
- medical products except for the most important and vital medical products from List No. 1042.
Who is exempt from paying VAT?
Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation emphasizes that it is not the organization that is exempt from taxes, but only certain operations. The list of actions falling under the exemption is closed, and if the company’s work is related to the implementation of the listed operations, then it will not have to pay VAT. The list of activities that are exempt from payment includes the sale of medical goods of domestic and imported origin, shares in the capital of a company, and securities. Rights to inventions, industrial designs, databases, know-how, and results of intellectual activity are sold without VAT. Payments within banking transactions are excluded.
IMPORTANT
According to Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, there are certain conditions that will allow you to obtain an exemption - licenses and other supporting documents. In order to implement the exemption, it is necessary to ensure compliance with the conditions under Art. 149 of the Tax Code, however, it is not necessary to send a notification to the tax authorities or issue an exemption.
As specified in paragraph 3 of Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, operations always have the possibility of refusal under clause 5 of Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and such a measure can bring certain benefits, allowing the payer not to keep separate records and apply tax deductions.
Additional Information
To be able to use this approach, you should apply before the first day of the tax period and refuse or suspend the VAT exemption on goods. In order to do this, you must submit an application to the Federal Tax Service. At the same time, you can refuse both in relation to all operations, and for one or several; in this regard, any decisions are open without exception. According to the law, refusal is allowed for a year; shorter periods are not considered.
Results
Types of goods not subject to VAT are indicated in paragraphs. 2 and 3 Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Those of them that are related to medical equipment, medical products, and rehabilitation means for the disabled are specifically spelled out in a special resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation. For these goods, as well as food products produced and consumed in medical and educational institutions, non-taxation of VAT is mandatory. For other goods listed in Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, refusal to apply the benefit is possible. To refuse, you will need to send a special application to the Federal Tax Service.
Sources: Tax Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Calculation example
To understand all the intricacies of calculation, it is worth considering a practical example of calculating VAT on a product. Let’s say that a certain enterprise sells piece building materials, the cost of which per unit of goods is 55 rubles, without including tax in the price. Since we are talking about building materials, tax must be paid, the rate will be 18 percent. It is necessary to calculate VAT and the total cost of the shipment when taking this tax into account.
First, you need to calculate the total cost of the goods without VAT, and if there are 100,000 pieces in the batch. goods for 55 rubles, then it will be 5,500,000 rubles. Next, you need to calculate VAT: 5,500,000 × 18/100 = 990,000 rubles. By adding VAT to the cost of the batch, you can get an amount of 6,490,000 rubles.
For your information
In this case, when filling out the documents, you must indicate that without VAT the product costs 5,500,000 rubles, 18% VAT - 990,000 rubles, with VAT - 6,490,000 rubles. This data will be quite sufficient.
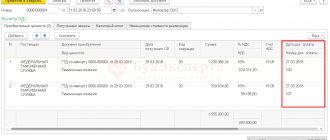
Registration of SF supplier
Input VAT cannot be deducted, even if the 5% rule is observed, since materials were purchased only for transactions not subject to VAT (clause 2 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 2, 2017 N 03-07-11 /63926, dated 10/05/2017 N 03-07-11/65098).
BukhExpert8 advises: regardless of the fact that the invoice is not registered in the Purchase Book, register it in 1C in case in the future the VAT accounting method .
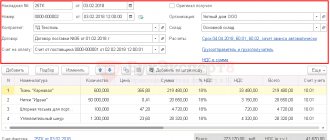
To register an incoming invoice from a supplier, you must indicate its number and date at the bottom of the Receipt document form (act, invoice) and click the Register .
The Invoice document received is automatically filled in with the data from the Receipt document (act, invoice) .
- Operation type code : “Receipt of goods, works, services.”
The document does not generate postings according to BU and NU.
Possible errors in calculations
When calculating VAT on goods, various errors may occur, and the most common of them are the following. Sometimes a reduced interest rate is used in a situation where it is legal to use the main one. In other cases, partial payment that has already been received is not taken into account, or VAT is calculated late. In goods exchange transactions, it happens that VAT is deducted without being transferred to the supplier. Often tax is assessed incorrectly due to incorrect invoices.
Additional Information
Considering the importance of value added tax and serious fines when violations are detected in this regard, it is advisable to pay due attention to the correctness of the calculation, using the labor of exclusively qualified and competent specialists who can confidently cope with such tasks.
Transactions not subject to value added tax
There is one more nuance that must be taken into account when accounting for value added tax. This is that not all transactions carried out by an organization or individual entrepreneur are taxed:
- Transfer of property for investment purposes;
- Seizure and seizure of property;
- Transactions with Russian and foreign currency;
- Government services;
- Transfer of property free of charge;
- Operations for the sale of land plots, etc.
Note: In the case when an organization simultaneously uses two types of transactions in its activities, which are taxed and not taxed, it becomes necessary to keep separate records for each type of transaction. The same situation arises taking into account the input value added tax on purchased products.
VAT accounting entries
Working with VAT on goods becomes the concern of an accountant, one of his most important work tasks. When working with accounting, it should be noted that according to the modern system of accounts for VAT, two points are calculated . This is account 19, which allows you to open an arbitrary number of subaccounts. This column is called VAT on acquired material assets; subaccounts can be opened at any time. The second is account 68 Calculations for taxes and fees, where it is allocated as a subaccount.
Additional Information
It is necessary to reflect and calculate VAT in accordance with all rules when selling all goods that are subject to this tax, reflecting the details using accounting tools.