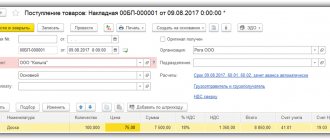
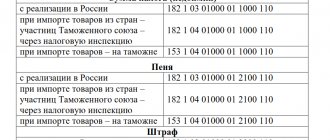
Documents that confirm the zero VAT rate for exports
Along with the VAT return, the following documents are submitted to the tax office at the place of registration:
- original or copy of a foreign trade contract;
- original or copy of the customs declaration with marks from the Russian customs authority (instead of copies of declarations, you can submit registers of customs declarations with registration numbers of declarations);
- copies of transport, shipping and (or) other documents with marks from customs authorities that confirm the export of goods (or registers of these documents according to the TCS).
When is it necessary to separate input VAT?
The need to distribute incoming added tax arises for those persons who simultaneously carry out transactions that are accompanied by the accrual of tax and are exempt from this burden. If the company does not carry out transactions exempt from VAT, then it is not required to distribute the input tax. Regardless of the rate used in the transaction, the input tax is applied to reduce the VAT payable. Read also the article: → “How to take into account input VAT under the simplified tax system. Examples."
Separate accounting is necessary if the company calculates VAT at one of the existing rates and, at the same time, performs the following operations:
- Exempt from the added load under Article 149. Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- Taxable under UTII;
- Sold in a territory other than the territory of the Russian Federation;
- Sale for export.
If at least one of the four specified transactions is performed, then the organization must ensure the distribution of input tax, that is, the allocation of its part attributable to taxable and exempt transactions. If the organization does not provide separate accounting at the proper level, then the input tax on those values, services, and works that are simultaneously used in all transactions performed will not be refundable.
To calculate the share of input VAT sent for deduction, you need to use the following formula:
- VAT deductible = VAT for the period * (cost of taxable sales in this period / total cost of all sales in this period).
To calculate the share of input VAT to be taken into account in the price of inventory, services, and work, you need to use the following formula:
- VAT to be included in the cost = Total amount of VAT for the period * (cost of non-taxable sales for the period / total cost of all sales for this period).
Documents confirming 0% VAT when exporting to the EAEU countries
The member states of the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) are Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Armenia and Kyrgyzstan.
The following documents must be attached to the VAT return:
- an agreement under which a buyer from an EAEU country imports goods;
- an application for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes with a mark from the tax authority of the EAEU member state into whose territory the goods are supplied, regarding the payment of indirect taxes;
- transport (shipping) and (or) other documents that confirm the movement of goods from the territory of one EAEU member state to the territory of another EAEU member state.
Document:
Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 03-07-08/6326 dated 02/03/2020
Other documents (bank statements, invoices) do not need to be attached to the declaration. However, it makes sense to save them in case the tax office asks you to confirm the information specified in the declaration.
Results
The need to maintain separate VAT accounting for exports is determined by the rules for accepting input tax for deduction.
The principles and methods of maintaining separate accounting must be developed independently and consolidated in the accounting policies. It is also recommended to indicate in your accounting policy what documents you will use to confirm the maintenance of separate VAT accounting. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Is VAT always zero when exporting?
From 2022, zero VAT on exports is not an obligation, but a right of the taxpayer (clause 7 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Other applicable VAT rates (10% or 20%) may be applied subject to the following conditions:
- the tax rate chosen by the payer must be applied to all export transactions as a whole;
- an application must be submitted to the tax authority at the place of registration no later than the 1st day of the quarter from which the taxpayer plans to apply the regular tax rate;
- the selected VAT rates must be applied for at least a year;
- You cannot change tax rates depending on who the buyer is.
Note! Exports to the EAEU countries are subject to 0% VAT in any case. The provisions of the Treaty on the EAEU do not provide for a waiver of the zero VAT rate. And the norms of the Treaty on the EAEU take precedence over the norms of the Tax Code.
The question is, why refuse the preferential rate?
One of the reasons is this: confirming the zero VAT rate for exports requires collecting a large number of documents, that is, labor and time costs.
It happens that suppliers do not want to confirm the zero rate and highlight the regular tax in invoices.
Do I need to submit documents confirming separate accounting?
The Tax Code (Articles 165, 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) does not contain requirements to submit to tax inspectors, along with the declaration, documents confirming the maintenance of separate accounting, so taxpayers are not required to do this. Judicial practice has also developed in favor of taxpayers: such, for example, is the decision of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District in resolution No. KA-A41/7691-10 dated July 20, 2010 in case No. A41-20286/07. Also, taxpayers do not have to submit these documents during a desk audit (Articles 88, 93 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, the very requirement of tax officials to provide documents - evidence of maintaining separate records is unlawful (resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated October 7, 2008 No. KA-A40/8592-08 in case No. A40-9998/08-151-31, dated September 11. 2008 No. KA-A40/6520-08 in case No. A40-51243/07-112-285).
Tax base for VAT on exports
The tax base should be determined exclusively in Russian rubles. If the contract is concluded in a foreign currency, then it is necessary to convert it at the official ruble exchange rate according to the Central Bank of Russia on the date of shipment of the goods.
But the moment of determining the tax base for an export transaction depends on when the package of documents is collected. If documents and confirmations are prepared within 180 days from the moment the goods are determined to be subject to the customs export procedure, then the tax base is determined by the last day of the reporting quarter in which the documents were collected. If documents and confirmations were collected after 180 days, then the tax base is determined at the time of shipment.
Document:
Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 03-07-08/29314 dated 04/13/2020
Separate accounting of VAT on received assets
A company acquiring non-current assets for use in taxable and non-taxable transactions must divide the input VAT on the capitalized asset. If it is known in advance in what proportion the fixed asset will be used in various operations, then the division of VAT must be made taking into account this proportion. What to do if it is not known exactly how the OS object will be used in the areas of activity?
In such a situation, one must proceed from the cost of shipped taxable valuables, services, and work in the month of receipt of the fixed asset in the total cost of sales for a given month. This simplified procedure can be applied if the OS was received in the 1st or 2nd month of the quarter.
Change in “Distribution of VAT on indirect expenses”
176 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and paragraphs. 2, paragraph 1, Article 32 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - the tax authorities are charged with verifying the validity of the amount of tax claimed for reimbursement. Thus, during the audit, control is carried out on the amount of tax deductions that the legislator excluded from the total amount of tax deductions by establishing a special procedure for compensation. At the same time, the tax authority may refuse to refund VAT presented by suppliers of goods (work, services) used to carry out transactions taxed at a rate of 0 percent, not agreeing with the method of maintaining separate accounting used by the organization, which is confirmed by arbitration practice. However, if the applied procedure is enshrined in the order on the accounting policy of the organization, the courts support the side of the taxpayer (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated August 27, 2003 in case No. F09-2469/03-AK, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated July 1, 2004 in case No. KA-A40/5352-04, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the East Siberian District dated January 24, 2005 in case No. A33-9843/04-S3-F02-5775/04-S1, letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 19, 2004 No. 03-04 -08/51 “On accounting for input VAT when selling products for export”, dated March 14, 2005 No. 03-04-08/48).
Recalculation of revenue in foreign currency for VAT taxation at the rate of “0%”
When selling goods (work, services) subject to VAT at a rate of 0%, settlements for which are made in foreign currency, the tax base is calculated in rubles at the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of shipment (transfer) of goods (performance of work, provision of services). This follows from paragraph 3 of Article 153 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended by Federal Law dated July 19, 2011 No. 245-FZ. The Federal Tax Service of Russia, in a letter dated October 18, 2011 No. ED-4−3/ [email protected] , agreed upon with the Ministry of Finance of Russia, explained when taxpayers should begin to apply this rule.
If goods (work, services) were shipped (performed, provided) starting from October 1, 2011, then revenue in foreign currency to determine the tax base is recalculated on the date of shipment (transfer).
Date: 2015-09-24; view: 338; Copyright infringement
| Did you like the page? Like for friends: |
Home — Articles
Rules and exceptions
As a general rule, VAT amounts presented upon the acquisition (import) of goods (work, services), including fixed assets and intangible assets, are accepted for deduction. However, there are exceptions. So, in accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, VAT amounts are taken into account in the cost of goods (work, services) in the following cases:
- when using goods (works, services) in transactions that are not subject to taxation (exempt from taxation) in accordance with Art. 149 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- when using goods (works, services) in operations, the place of sale of which is not the territory of the Russian Federation (Articles 147, 148 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- in cases of acquisition of goods (work, services) by persons who are not VAT payers or are exempt from its payment in accordance with Art. 145 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- when using goods (work, services) in transactions that are not subject to taxation on the basis of clause 2 of Art. 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In addition, the transactions listed in clause 3 of Art. are not subject to VAT (not recognized as sales). 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 1, clause 2, article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Taxpayers should also pay attention to: Art. 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows the taxpayer, in the event of receiving payment, partial payment on account of upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), the duration of the production cycle of which exceeds six months (according to the List determined by the Government of the Russian Federation), to accept the moment of determining the tax base as the day of shipment (transfer) of the specified goods (performance of work, provision of services). This right can be applied only if separate records are kept of transactions performed and tax amounts for purchased goods (works, services), including fixed assets, intangible assets, property rights used as part of a long production cycle and other operations.
Let us remind you that according to clause 5 of Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, transactions that are not subject to taxation are divided into transactions:
— exempt from VAT without fail (clauses 1, 2 of Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
— benefits which the taxpayer can refuse (clause 3 of Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Please note: clause 4 of Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation obliges taxpayers to keep separate records of transactions subject to VAT and exempt from taxation. In addition, taxpayers transferred to pay a single tax on imputed income for certain types of activities must also maintain separate accounting (paragraph 6, clause 4, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the procedure for separate accounting should be reflected in the company's accounting policy.
Desk inspection
Having received a VAT return and documents confirming exports, the tax inspectorate can conduct a desk audit of them, as well as counter-checks of the organization’s suppliers, make requests to the customs authorities, etc. (Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the declaration reflects the amount of VAT to be reimbursed from the budget, the tax inspectorate will conduct a desk audit without fail (paragraph 2, paragraph 1, article 176 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Based on the results of the desk audit, the tax inspectorate may make one of the following decisions:
- refund the amount of input VAT on goods (work, services) used for the export operation;
- refuse VAT refund.
The tax inspectorate is obliged to notify the organization in writing of its decision within five days from the date of its adoption (clause 9 of article 176 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the inspectorate decides to refund the tax, then the amount to be refunded is first used to pay off the arrears, pay penalties and sanctions on federal taxes. The inspectorate conducts this assessment independently. This is stated in paragraph 4 of Article 176 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Based on the organization’s application, the inspection must return the remaining amount of the input tax to the current account or offset against upcoming payments for VAT or other federal taxes (clause 6 of Article 176 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).