It all started in 2016, when the Federal Tax Service introduced a new form of control - tax monitoring. Until 2022, only large taxpayers could use it. But from July 1, 2021, representatives of medium-sized businesses were also allowed to join the new form of control.
The essence of the tax monitoring system is that inspectors no longer conduct on-site and desk audits. Instead, they gain remote access to the organization's information systems to view accounting and tax reporting. The Federal Tax Service pays special attention to checking non-standard transactions and those associated with risks.
Pros and cons of tax monitoring
What are the benefits of voluntarily revealing your cards to the tax authorities:
- a company that has nothing to hide is more trusted by government agencies and partners;
- During the tax monitoring period, desk and field audits will not be carried out. There are exceptions - inspections can be carried out in the event of a VAT or excise tax refund, a decrease in the amount of tax payable or an increase in the loss compared to the previous declaration, early termination of monitoring, submission of a declaration later than July 1 of the year following the monitored year;
- during the monitoring process, the organization can immediately learn about errors and contradictions found and resolve these issues without penalties;
- If you have doubts about the correctness of the calculation or payment of taxes, you can consult with inspectors and get their motivated opinion. Moreover, if a company does something based on a motivated opinion and this leads to violations, they will no longer be able to fine it for this, if the motivated opinion was not drawn up on the basis of distorted data.
If the organization participating in the monitoring does not submit a declaration on time, the responsibility will be the same as for everyone else.
Disadvantages include constant tax control by the Federal Tax Service, the risk of leakage of confidential information and high requirements for the internal control system in the organization.
Nuances
Tax monitoring is regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The company must submit an application to the Federal Tax Service inspectorate at the place of registration, in response to which the tax authority makes a decision to conduct monitoring.
The decision to conduct tax monitoring is made by the tax authority before November 1 of the year in which the application for tax monitoring is submitted.
Tax authorities analyze the organization’s risks and evaluate the effectiveness of its internal control system. Based on this, the tax authority moves from a complete audit to a joint assessment of tax risks (this is called a risk-based approach).
If contradictions and inconsistencies are identified in the organization’s documents, the tax office sends a message demanding clarification or corrections within five days.
If violations are detected in the calculation or payment of taxes, the tax office within ten days sends a notification to the organization about “the existence of grounds for drawing up a reasoned opinion.” This is the name of the decision of the tax authority on issues of correct calculation (withholding), completeness and timeliness of payment (transfer) of taxes, fees, and insurance premiums.
There are two types of motivated opinion:
- at the request of the organization (if it has questions about compliance with tax laws);
- at the initiative of the tax authority (if a violation of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is established).
If the organization agrees with the reasoned opinion, it notifies the tax authority within a month and attaches documents confirming its implementation.
If the organization does not agree with the reasoned opinion, a mutual agreement procedure is carried out. It consists in the fact that the head of the tax inspectorate or his deputy considers the arguments of both sides and decides who is right.
Based on its results, the Federal Tax Service notifies the organization of a change in the reasoned opinion or leaving it unchanged.
After this, the organization notifies the tax authority within a month of its agreement (disagreement) with the reasoned opinion and attaches documents confirming its implementation.
How to become a monitoring participant
An organization that wants to participate in monitoring and meets its criteria must submit an application to the tax office at its place of registration.
You cannot apply for monitoring only for individual taxes.
The Federal Tax Service of Russia approved the official application form by order No. ММВ-7-15/323 dated 04/21/2017, but it is better to use the form recommended by Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia No. BV-4-23/ [email protected] dated 08/31/2020.
The application deadline is July 1 of the year preceding the monitoring period. The following documents must be attached to the application:
- regulations for information interaction. Form of regulation according to Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated April 21, 2017 No. ММВ-7-15/ [email protected] ;
- information about individuals or legal entities whose share of participation in the organization exceeds 25%;
- the current accounting policy of the organization for tax purposes;
- information about the organization of internal control in the company. It must comply with the requirements established by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated June 16, 2017 No. ММВ-7-15/ [email protected]
The recommended forms of these documents can be found in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia No. BV-4-23 / [email protected] dated 08/31/2020. The entire package of documents must be sent electronically.
Until November 1, the tax inspectorate reviews the materials received and makes a decision within five working days:
- conduct tax monitoring. In this case, organizations will send a notification in the form specified in Appendix No. 5 to Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia No. ММВ-7-15 / [email protected] dated 04/21/2017;
- refuse to conduct monitoring - the organization will receive a notification in the form in Appendix No. 6 to Order No. MMV-7-15 / [email protected]
Refusal may occur due to non-compliance with the criteria, or non-compliance of the internal control system or information interaction with the established requirements.
If the decision is positive, monitoring begins on January 1 of the following year. If the organization does not want to continue monitoring during the second year, it must submit a refusal application to the tax authorities no later than December 1 of the monitored year. If such a statement is not made, monitoring is automatically extended for another two calendar years. That is, if a company applied in 2022 and during 2022 is a participant in monitoring, then in order for there to be no monitoring in 2022, it is necessary to submit an application for refusal before December 1, 2022. If there is no application, monitoring will continue in 2022 and 2023.
Tax monitoring
The process of tax monitoring is regulated by Article 105.29 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Inspectors analyze the organization’s risks and check the effectiveness of the internal control system. This makes it possible to move from a complete audit to assessing tax risks together with the audited organization.
Joint risk assessment
Taxpayers disclose tax financial and economic information and submit information quarterly (Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated May 25, 2021 No. ED-7-23 / [email protected] ):
- about the organization’s risks identified by the ICS, indicating their description and source, probability, possible consequences and group;
- about risks for individual transactions and operations, indicating the type and amount of the transaction, information about the counterparty, and contract details.
In turn, inspectors assess industry risks, analyze control procedures and risks of the organization, and then formulate a monitoring plan and the scope of control activities.
If during monitoring, inspectors find contradictions and inconsistencies in the taxpayer’s documents, they send a request for explanations or corrections. Additionally, to assess risks, the tax authority can attract specialists and experts and conduct inspections.
If the inspectors find facts that indicate that taxes, fees, and insurance premiums were calculated incorrectly, paid incompletely or untimely, they will notify that there are grounds for preparing a reasoned opinion under Art. 105.30 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Within 15 days, the organization has the right to provide explanations or make corrections by notifying the tax authorities. If, taking this into account, the identified violations are not refuted, the inspectors will draw up a reasoned opinion.
Motivated opinion
A reasoned opinion is the position of inspectors on issues of calculation and payment of taxes, fees, and contributions. Also, in a reasoned opinion, tax specialists can assess how much you comply with tax laws when reflecting transactions and their results.
A reasoned opinion can be drawn up:
- at the request of the organization - if you have doubts about the correctness of calculations and payment of taxes, accounting of transactions and other facts;
- at the initiative of the inspection - when violations of the law are detected.
At the request of the organization, the tax office must send a reasoned opinion within a month. The deadline may be extended if inspectors request additional documents or information.
A reasoned opinion, at the initiative of the tax authority, is drawn up during the monitoring period. It is sent to organizations within five working days after preparation. A reasoned opinion is not a basis for a fine. You can react to it in two ways:
- agree with it - within a month after receipt, inform about your consent and confirm compliance with the instructions;
- If you do not agree with it, within a month after receiving it, send your disagreements and go through a mutual agreement procedure with the Federal Tax Service of Russia, as a result of which your opinion may change or remain the same.
If the opinion is not fulfilled by December 1 of the year following the monitoring period, the inspectorate conducts an on-site inspection of the organization, based on the results of which it may impose a fine, additional taxes or bring other types of liability.
Information interaction regulations
The regulations are drawn up in the form approved in Appendix No. 7, and in accordance with the requirements listed in Appendix No. 8 to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated May 11, 2021 N ED-7-23/ [email protected]
It should state:
- method of interaction with the tax authority: through access to the information system, access to the analytical data showcase, via TCS through an electronic document management operator;
- the procedure for disclosing tax reporting indicators;
- data on the internal control system with a description, methods used, control procedures, documentation procedures.
It is important to carefully study this document so that the tax office does not refuse to join the monitoring. In the future, an organization’s violation of regulations may result in early termination of monitoring.
Monitoring period
Monitoring covers one calendar year: from January 1 to December 31. The tax office must complete it by October 1 of the following year.
For example, in a company, tax monitoring will be carried out from January 1 to December 31, 2022. The Federal Tax Service Inspectorate, by October 1, 2023, is obliged to complete an inspection of the activities of this company for 2022 and provide all the necessary documents.
If an organization violates the rules of interaction, does not provide documents or provides false information, monitoring may be terminated early. The Federal Tax Service Inspectorate will notify the organization of this in writing within 10 working days after the circumstances arise, but no later than September 1 of the year following the control year.
Who can apply for monitoring?
Submitting an application to host an event involves a number of restrictions. You can submit an application only if the following conditions are met:
- The total amount of taxes for the year preceding the year of filing the application is equal to 3 billion rubles or more.
- The total amount of income according to reporting for the year preceding the year of filing the application is equal to 3 billion rubles or more.
- The total value of assets as of the last day of the year preceding the year of implementation of the event is no less than 3 billion rubles.
When carrying out an event in order to establish the need for a tax audit, fulfillment of the conditions specified in paragraph 3 of Article 105.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is not necessary. This rule is established by paragraphs 4 and 7 of Article 105.27 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Application Features
The application is submitted to the inspectorate at the company's address no later than July 1. The application must be submitted in advance. For example, if an event is required in 2022, the application must be submitted no later than July 1, 2017. If the company is one of the largest taxpayers, the application must be submitted to the body in which the company is registered as the largest taxpayer. This procedure is established by Article 83 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Applications can be submitted during the event. For example, monitoring is carried out in 2022. Company management aims to schedule the next review for 2022. The application must be submitted by September 1, 2022. The application form for monitoring is established by order of the Federal Tax Service dated April 21, 2022.
The following documents must be submitted along with the application:
- Regulations for interaction of an informational nature.
- Information about companies or individuals participating in the management of the company, if the share of participation is more than 25%.
- Accounting policy in the year of application.
- Local acts establishing the company's control system.
The duration of the event is a year. The verification period begins on January 1 and ends on October 1 of the same year. The deadlines are regulated by Article 105.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Inspection activities of tax authorities during the conduct of NM
During the period of tax monitoring, tax authorities have the right to conduct desk and on-site tax audits only in certain cases:
- Desk tax audits - upon submission:
- tax return (calculation) later than July 1 of the year following the period for which tax monitoring is carried out;
- a VAT tax return in which the right to a tax refund is declared, or an excise tax return in which the amount of excise tax to be refunded is declared;
- an updated tax return (calculation), in which the amount of tax payable to the budget system of the Russian Federation is reduced, or the amount of the resulting loss is increased compared to the previously submitted tax return (calculation);
- early termination of tax monitoring.
- 2. On-site tax audits - when:
- conducting an on-site tax audit by a higher tax authority - in order to monitor the activities of the tax authority that conducted tax monitoring;
- early termination of tax monitoring;
- failure by the taxpayer to comply with the motivated opinion of the tax authority.
If subsequently the organization, as a result of fulfilling the Reasoned Opinion of the tax authority, experiences arrears, the organization will be exempt from the accrual of penalties and fines (paragraph one, clause 8, article 75, paragraph one, subclause 3, clause 1, article 111 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), for with the exception of cases when the Reasoned opinion is based on incomplete or unreliable information provided by the organization (paragraph two, paragraph 8, article 75, paragraph two, subparagraph 3, paragraph 1, article 111 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
From the editor. Previous articles on the control activities of the Federal Tax Service, as well as inspections of other supervisory authorities, can be found on the website https://buh.ru under the tag “encyclopedia of inspections”.
Application for conducting NM
Tax monitoring is carried out according to the organization’s Application. An application for conducting NM can be submitted by an organization that meets the criteria listed above.
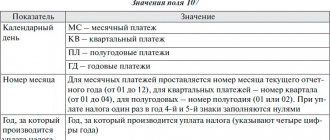
- [email protected] of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 05/07/2015 , hereinafter referred to as Order No. ММВ-7-15/ [email protected] ) is submitted by the organization to the tax authority at its location no later than July 1 of the year preceding the period for which tax monitoring is carried out*.
- Along with the Application the following must be submitted:
- the Information Interaction Regulations developed by the organization (hereinafter referred to as the Regulations);
- information about organizations and individuals who directly and (or) indirectly participate in the organization submitting an application for tax monitoring, and the share of such participation is more than 25 percent;
- the organization's accounting policy for tax purposes, valid at the time of submission of the application.
- An application for tax monitoring may be withdrawn by an organization before the tax authority makes a decision to conduct (refuse to conduct) tax monitoring. To do this, the organization submits a written application (in any form) to the tax authority.
- The regulations for information interaction with the tax authority are developed by the organization in the form and in accordance with the requirements approved by Order No. ММВ-7-15/ [email protected] In the Regulations, the organization reflects the order in which it provides the tax authority with documents (information) that serve as the basis for the calculation ( withholding), payment (transfer) of taxes and fees: in electronic form and (or) by providing access to the organization’s information systems, as well as the procedure for familiarizing the tax authority with the originals of such documents, if necessary.
Note
: * An organization classified as a major taxpayer submits an application for tax monitoring to the tax authority at the place of its registration as a major taxpayer.
A diagram of the procedure for submitting an Application and making a Decision is presented in Figure 2.
Rice. 2. Scheme of the procedure for submitting an Application for tax monitoring and making a Decision
Required documents (information) during tax monitoring
During the implementation of the necessary tax monitoring activities, the authorized body may require additional documents and information.
The current procedure for conducting tax monitoring establishes that the required documents and information must be specified in a written request from the tax authority, which it sends to the taxpayer - a legal entity.
In cases where the audit is carried out on the territory of a legal entity, the tax authority employee transmits to the head of the organization the requirement to submit certain documents in person, against signature.
Documents required by the authorized person may include:
- additional financial reporting data for a certain time period;
- information confirming the legality of the procedure for calculating and paying taxes by the organization;
- information about the employees of the legal body, the staffing table valid during the period in which tax monitoring is carried out;
- other information that can clarify certain nuances and circumstances, highlight the necessary details, confirm the legality of the taxpayer’s actions, etc.
The requested documents and information can be submitted to the tax authority in various ways: personally by the taxpayer or his representative, by mail, or via electronic mail.
Submission of written documents is carried out in the form of certified copies of those papers that needed to be provided.
Sending documents via electronic channel requires mandatory compliance with the established procedure and forms. Otherwise, all data provided by the taxpayer may be rejected due to its non-compliance with applicable standards.
In cases where the taxpayer, for certain reasons, cannot fulfill the requirement of the tax authority to submit certain documents within the specified period, he must notify the relevant official to whom this requirement was sent about this fact. This must be done no later than the next day after the day on which this request was submitted.
The written explanation should indicate the reasons that can actually confirm the fact that the submission of the requested documents and information cannot be carried out within the specified time frame.