When the management of an enterprise needs to check documentation related to its activities for accuracy and compliance with the requirements specified in the legislation, an independent verification is carried out - an audit. For some companies, this is a mandatory procedure that must be completed annually.
Auditing activities in the Russian Federation are regulated by the Federal Law of December 30, 2008. No. 307 (law “On auditing activities”).
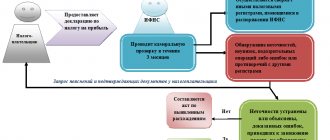
Who should undergo a mandatory audit ?
Goals and objectives of the audit of accounting (financial) statements
The purpose of this audit is to form an audit specialist’s opinion about the reliability of the company’s accounting (financial) statements and, in addition, to find out whether accounting compliance complies with the legislation of our country.
Question: Is the auditor's report part of the financial statements? View answer
The following tasks of accounting audit are distinguished:
- find out whether the reporting and its indicators comply with the law and the company’s accounting policies;
- find out how fully all business transactions are reflected in the documentation;
- check how the company’s internal control systems are organized and functioning;
- check whether the indicators in all forms of financial statements coincide and correspond to real ones.
Question: How to reflect penalties for failure to submit an audit report in the accounting of an organization (joint stock company)? The organization did not conduct a mandatory audit of its annual financial statements within the prescribed period. According to the resolution imposing an administrative fine for failure to submit an audit report, a fine of 5,000 rubles was imposed on the organization. For the purposes of tax accounting of income and expenses, the accrual method is used. View answer
The methods used by specialists when auditing financial statements are similar to the methods of auditing in general. These include:
- actual control (observation, inventory, expert assessments);
- documentary (study of important company papers in form and content);
- computationally analytical (statistical calculations, economic analysis).
How to pass a mandatory audit ?
Which companies must undergo an audit?
An audit of financial statements can be mandatory and proactive. The first can only be external, that is, carried out by independent experts from firms specializing in auditing, or by individual auditors who are not employees of the audited company.
Firms that must be subject to the mandatory audit procedure are named in the Federal Law dated December 30, 2008. No. 307 (law “On auditing activities”). These enterprises include:
- companies with the legal form of JSC;
- companies whose securities are admitted to organized trading;
- firms with a certain type of activity (this includes credit, clearing, insurance, companies participating in the securities market, microfinance, self-regulatory organizations, cooperatives, gambling organizers, etc.);
- companies that have revenue over 400 million rubles or assets over 60 million rubles (for the year preceding the reporting year), etc.
A detailed list can be seen in Art. 5 Federal Law No. 307 “On auditing activities”.
An initiative audit can be carried out in certain cases, such as: bank lending, the need to participate in tenders, the desire of company managers to reduce tax risks, checking the qualifications of the accounting department, preparing a report for a potential investor.
Regulatory rationale
Documentation is carried out based on these standards:
- MSA 230, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 207n dated November 9, 2016.
- FPSAD Rules No. 2.
The second standard is no longer valid at the moment.
What is the general approach to documenting independence in audit and review engagements ?
ISA 230.7 states that documents can be either paper or electronic. This category of papers may include analyses, reviews, verification programs, letters, and electronic correspondence materials. RDs sometimes include excerpts from contracts. However, it must be taken into account that the auditor’s RDs do not replace accounting certificates.
IMPORTANT! Work papers must be combined in a single file.
The procedure for conducting an audit of financial statements
The audit takes place in several stages:
- Traditionally, the first stage is planning and preparing for the inspection. The auditor studies the company's activities, draws up a work plan, and requests the necessary documents. At the same stage, an agreement is concluded between the auditing firm and the audit object.
- Next, the collection of evidence and analysis of data received for verification begins. A list of all requested documents is examined. If necessary, company employees are interviewed, sometimes in writing. Data is grouped and systematized. The auditor makes an opinion on the reliability of the financial statements.
- The head of the audited company is informed of the conclusion - an opinion on the reliability of the financial statements. An auditor's report is drawn up and issued, which is the immediate purpose of the audit. In addition, some companies prepare an audit report, which describes in detail the progress of the audit, all identified deficiencies and other information that may be useful to the management of the audited company to improve the quality of the accounting department.
Varieties
Audit documentation is divided into 2 types:
- Permanent. They include papers that are needed to understand the specifics of the company’s activities. Based on these documents, one can understand the pace of development of the subject. They contain significant issues of interest to auditors.
- Current. They include papers that are needed to carry out ongoing inspections and solve current problems.
Typically, each of these sets is structured in a separate order.
What documents are checked?
During the audit, auditors request a large list of documents, which includes:
- accounting (this includes 2 important papers: a balance sheet and a statement of financial results of the company, but they are accompanied by a lot of other documents - the latter are listed below);
- tax returns;
- primary documents;
- statutory documents;
- permits, licenses and much more.
It is checked whether the papers are filled out correctly, whether they correspond to the approved forms, whether the deadlines for filing (declarations) are met, whether the documents are certified by the signatures of the chief accountant and manager, etc.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! If an audit is carried out on a special assignment, then in such a situation only the documentation that relates to a specific task is checked.
Result
So, at the end of the audit, the company receives a report and an audit opinion. The form in which the information will be provided, as well as its recipients, must be specified in advance in the contract with the audit firm. The report, also known as written information, is a confidential document. Typically it contains the following information:
- methods that the auditor uses during the audit;
- recommendations for changes in accounting policies that may affect the financial statements of the organization;
- proposals for adjusting the company’s reporting;
- other points that the head of the organization needs to pay attention to (this may include errors in internal control, situations of unreasonable actions by management).
The report outlines the identified violations and possible options for correcting them. Typically, this is presented in the form of a pivot table.
ATTENTION! The report must be accompanied by copies of the financial statements for the current year and, most importantly, the auditor’s report.
Auditor's report
This is an official document that contains the opinion of an expert auditor on the reliability of the accounting records of the company being audited. It is this that should be submitted to the statistical authorities along with the financial statements.
The structure and information that must be included in the auditor’s report is described in detail in Art. 6 Federal Law No. 307, mentioned earlier.
Briefly about what the document should contain:
- title “Audit report”;
- information about who the document is addressed to (JSC shareholders, LLC participants, etc.);
- information about the audited entity;
- information about the auditor conducting the audit;
- a list of documents (accounting statements) that were checked by the auditor, indicating the period when they were compiled;
- the auditor's opinion on the reliability of the information specified in the audited documents;
- test results;
- the date on which the conclusion was drawn up.
The conclusion can only be provided to the person with whom the agreement was concluded.
Features of compilation
Each document created in the course of work is drawn up in accordance with the law. In particular, each document must contain the following information:
- The name of the company that conducts the audit.
- Verification period.
- Name of documents.
- Full name of the persons who prepared the document.
- Audit date.
- Names of persons performing the audit.
The RD includes papers on certain areas of the company's activities. They indicate detected deviations and errors, and significant risks. It is recommended to provide references to the provisions of the company's accounting policies that the auditor relied on when identifying errors.
The specialist must ensure the safety of work papers, as well as their confidentiality. The auditor is required to limit physical access to documentation. For example, it can be placed in a safe located in a locked room. You also need to take care of the availability of electronic security and passwords.
Typical errors and violations
Here is a list of common violations that may be detected during an inspection:
- expenses and income are reflected incorrectly;
- the accounting details are filled out incorrectly or incompletely;
- tax amounts are calculated incorrectly;
- indicators of different reporting forms contradict each other;
- the amount of the authorized capital differs from what is stated in the charter;
- arithmetic errors in calculations;
- formal inventory taking, carrying it out with errors, etc.
Responsibility for failure to carry out
The business entities listed earlier must undergo an audit of their financial statements every year, and also send the conclusion to the statistical authorities. Submission of the report must be carried out together with the submission of reports. If you cannot send the document on time, you can submit it within 10 days from the date of issue, but no later than December 31 of the year following the reporting year. This is stated in the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402 (the Law “On Accounting”), namely in its 2nd article.
In addition, within 3 working days from the date of issue of the conclusion, the company is obliged to enter information about the results of the audit into the Unified Federal Register on the facts of the activities of legal entities.
The fact of failure to conduct an audit does not entail punishment. Administrative liability occurs in the cases described below. Punishment is possible only for those organizations that are required to undergo a mandatory audit of their financial statements.
| Initiator of the fine | Cause | Article | Fine |
| Federal Tax Service | During an on-site inspection, it was discovered that an audit report was missing for the required storage period (from 5 years). | Part 1. Art. 15.11 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation | From 5 to 10 thousand rubles for officials. |
| Rosstat | If an audit report has not been provided to this body within the required period. | 19.7 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation | From 300 to 500 rubles for officials and from 3 thousand to 5 thousand rubles for legal entities. |
| Bank of Russia | The audit report was not posted on the JSC website within the required period. | Part 2 art. 15.19 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation | From 30 thousand to 50 thousand rubles or suspension from work for 1-2 years for officials. For legal entities - from 700 thousand to 1 million rubles. |
The amount of the fine may be reduced by court decision if there were any exceptional circumstances that resulted in an administrative offense.
Auditor's Record Keeping Responsibilities
ISA 230 outlines these responsibilities of the examiner:
- Timely recording of discussions of all significant issues with the management staff of the audited companies.
- Documentation of reconciliation activities when reaching the final conclusion.
- The audit file must be generated in a timely manner, after the conclusion is made based on the results of the event.
RD must be systematized. Features of systematization are determined by the specific circumstances and needs of the inspector. The specialist must develop standard forms of papers. The presence of standard forms reduces the time for drawing up documents.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! Once the final audit file has been created, the practitioner cannot remove or remove papers until the retention period is complete. The latter is at least 5 years from the date of the conclusion.