Car accounting
If the car is intended to be used for official needs for a long time - 12 months or more - then the car is accepted for accounting as an asset (clause 4 of the Accounting Regulations “Accounting for Fixed Assets” PBU 6/01, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n; clause 2 of the Methodological guidelines for accounting of fixed assets, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 13, 2003 No. 91n).
Fixed assets are taken into account at their original cost, which is the sum of the actual costs of their acquisition, excluding VAT and other refundable taxes. When purchasing a car, its cost is equal to the amount paid to the seller in accordance with the contract (clauses 7, 8 of PBU 6/01, clauses 23, 24 of the Methodological Guidelines for Accounting of Fixed Assets). The moment an object is accepted for accounting as part of the operating system is the date the machine is actually ready for use. The fact that an object is ready and accepted for accounting as part of the OS is formalized by drawing up the corresponding primary accounting document (Part 1, 3, Article 9 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”, clause 7 of the Guidelines for Accounting accounting of fixed assets). In the case of a machine, such paper will be an act (invoice) of acceptance and transfer of fixed assets, drawn up for each individual inventory item (clause 38 of the Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets).
Costs for the acquisition of fixed assets are reflected in the debit of account 08 “Investments in non-current assets”, subaccount 08-4 “Purchase of fixed assets”, in correspondence with the credit of account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”.
Read also: “Calculation of transport tax”
The generated initial cost of the object is written off from account 08, subaccount 08-4, to the debit of account 01 “Fixed assets” (Instructions for the use of the Chart of Accounts for accounting financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n) .
Entering vehicle data into the information database
After it has been determined that the car can be accounted for on the organization’s balance sheet as a main vehicle and there are all the primary accounting data for this, it needs to be capitalized and put on the balance sheet. Next, we will look at how non-current assets are accepted in 1C programs.
2.1 Reflection of a car in the 1C: Enterprise Accounting 3.0 program
If there is no section “Fixed assets and intangible assets” among the program sections, then it is necessary to add the ability to reflect transactions on non-current assets. To do this, open the “Administration” section and then select “Functionality”.
In the window that opens, go to the “OS and intangible assets” tab.
Check the boxes next to the corresponding functions and the one we need will appear among the sections.
Since we display the “OS and Intangible Materials” section, in functionality these sections are highlighted in gray and pink with the “full interface” mark, so they can no longer be changed or disabled.
Next, go to the “OS and intangible assets” section.
There are several ways to capitalize fixed assets in the accounting department of an enterprise: when the equipment does not require assembly, the method of calculating depreciation in this case is the one established in the accounting policy (section “Main” - “Accounting Policy”) and when the equipment requires assembly.
It is correct to bring the car in using the first method.
Let’s follow the link “Receipt of fixed assets” and in the window that opens, click the “Create” command located on the command panel. The fixed asset creation document opens.
We enter the document number and date, fill in information about the supplier, create or select an agreement. You also need to choose the method that suits you to reflect depreciation expenses and select an asset accounting group. The down arrow opens a list of OS groups available in this case:
We need to select vehicles. After that, click the “Add” button.
As a result of clicking on the button, a line will appear in the tabular part, from which a list of the last selected elements of the directory will drop out.
Here you need to click on the “Show all” command, or on the button with a green plus, which will allow you to immediately open the window for creating a fixed asset.
Clicking the “Show all” link will open a directory of fixed assets.
In it, you need to click the “Create” button to open the window for creating a new directory element.
In the window that opens, fill in the following information:
— the OS accounting group is selected from the list;
— enter the name of the accepted transport from the primary accounting documents;
- a green “Classification” link opens, where the corresponding OKOF code is selected from the OKOF directory using the down arrow - “Show all”.
Select the grouping name you need and click on the “Transfer OKOF and depreciation group” button. As a result, this data is filled into the card of the element we are filling out.
— after this you can fill in the information for the inventory card from the technical information about the vehicle. Information about the issue date is important; it will be used to determine the tax rate.
Information about the date of acceptance for accounting, location, financially responsible person, as well as accounting and accounting records will be filled in automatically after the “Receipt of fixed assets” operation.
Let's write down the directory element using the "Write" command.
Also, the vehicle registration function is immediately available to us from the card. It is needed in order to automatically calculate advance payments and transport tax for the year based on the data you entered from the vehicle title.
Click on the “Register” link.
Fill in from top to bottom:
— date of registration of the vehicle with the traffic police;
— the vehicle type code is selected from the list using the button next to the input field;
— enter the identification number, make, registration plate, engine power and environmental class from the title.
— the tax rate is selected automatically after entering all the indicators necessary for the calculation above. If, after filling in all the indicators, the line remains red with the words “not defined”, you may need to download the rate classifier from the ITS disk. To do this, you need to go to the reference book that opens by clicking on the tax rate link and click the “download rates” button.
If your car is eligible for multipliers or tax breaks, you will need to enter the appropriate values. In addition, you must provide the tax authority with documents confirming your right to tax benefits so that your calculation of the transport tax coincides with the calculation of the tax authority.
After that, click the “Write and close” command and also write down the item card after finishing editing. This completes its creation. The element we created will appear in the directory; double-clicking on it will transfer it to the tabular part of the window.
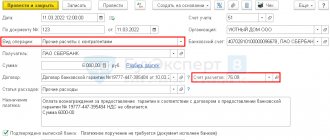
Then enter information about the cost and the amount of VAT. The invoice for fixed assets is set on 01.01, for depreciation on 02.01, for VAT on 19.01. The service life of the vehicle is also from the technical information.
The number and date of the invoice are entered and the “Register” button is used to record the receipt document and invoice. After this, it can be posted and closed, then using the command “DT CT” you can see the postings that were made by the document on the accounting accounts.
According to line 1 of the entries, we see that a truck was entered into the debit on 04/08/2, and the credit of account 60.01 reflected the debt to the supplier in the amount of RUB 408,333.33. The amount of VAT on the car in question is part of the debt to the supplier, therefore it also goes to account 60.01 and is simultaneously recorded on the debit of account 19.01 in the amount of 81,666.67 rubles. Then the non-current asset is written off from account 08.04.2 to the debit of account 01.01, which means the commissioning of the transport, that is, the beginning of its useful life.
After the transport has been accepted onto the balance sheet of the enterprise, you can look at its card, where we will see that information about the date and document of acceptance for accounting, location, MOL and method of reflecting depreciation expenses, as well as data on accounting and accounting records, on depreciation methods and current value were filled in automatically.
Depreciation calculation
The cost of fixed assets is repaid through depreciation (clause 17 of PBU 6/01, clause 49 of the Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets). When using the linear method of calculating depreciation in accounting, the annual amount of deductions is calculated based on its original cost and the depreciation rate, calculated taking into account the useful life of the fixed asset, established by the company when accepting the fixed asset for accounting (clause 18, paragraph 2, clause. 19 PBU 6/01, paragraph “a”, paragraph 54 of the Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets).
Depreciation begins on the 1st day of the month following the month the object was accepted for accounting, and stops on the 1st day of the month following the month of full repayment of the cost of the object, or its write-off from accounting (clause 21 PBU 6/01 , paragraph 61 of the Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets).
Depreciation charges are recognized in accounting as expenses for ordinary activities in the month of their accrual (clauses 5, 8, 16, 18 of the Accounting Regulations “Organizational Expenses” PBU 10/99, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 6, 1999 No. 33n, clause 64 of the Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets).
note
The company's costs associated with the rental of a vehicle used for management needs are classified as expenses for ordinary activities and are recognized monthly in the amounts established by the contract.
Depreciation on a car used for management needs is reflected in the debit of account 26 “General business expenses” (44 “Sales expenses” - for trade organizations) and the credit of account 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets” (clause 25 of PBU 6/01, clause 65 Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets, Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts).
Read also: “Depreciation of a passenger car”
Machine use life
For tax accounting, the purchased car is recognized as depreciable property and is taken into account as part of the fixed assets (clause 1, article 256, clause 1, article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The initial cost of an asset is equal to the price of its acquisition (paragraph 2, paragraph 1, article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). When applying the linear method, the amount of depreciation accrued for one month in relation to an object of depreciable property is determined as the product of its original cost and the depreciation rate determined for this object. The depreciation rate is determined based on the useful life (clause 1, clause 1, article 259, clause 2, article 259.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Read also “Features of depreciation in tax accounting”
The period of use of the machine is determined by the company independently on the date of its commissioning, taking into account the Classification of fixed assets included in depreciation groups, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of January 1, 2002 No. 1 (clause 1 of Article 258 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In accordance with the Classification, passenger cars (except for cars classified as other groups) belong to the third depreciation group (property with a useful life of over 3 years to 5 years inclusive) (clause 1, paragraph 4, clause 3, article 258 of the Tax Code RF)).
Depreciation begins on the 1st day of the month following the month in which the facility was put into operation. The amount of accrued depreciation is recognized monthly as part of expenses associated with production and sales (clause 3, clause 2, article 253, clause 2, article 259, clause 3, article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Differences between leasing and lending
There are several key differences that can help you decide which service to choose.
| Leasing | Credit | |
| Participants in the operation |
|
|
| Ownership | Until the debt is fully repaid, the vehicle is the property of the leasing organization | The vehicle becomes the property of the loan recipient, but there are restrictions on use |
| Application processing time | 1-5 days | 15-60 days |
| Package of documents | Minimum package, since the vehicle remains the property of the lessor, thereby minimizing its own risks | Large package, including confirmation of financial status, income stability, guarantee |
| Additional expenses | Any financial expenses: insurance, state registration, maintenance are offered by lease. company with discounts up to 10%. All expenses can be included in the monthly payment under the contract | All costs are borne by the loan recipient |
| Contract term | From 1 to 5 years | From 1 to 3 years |
| Pledge | Not required | The car itself acts as collateral |
Tax deduction
After registering a car that will be used in activities subject to VAT, the organization can make a tax deduction presented to it by the seller based on the received invoice that meets the requirements established by Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 1, clause 2, article 171 , paragraph 1, 2 clause 1 article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The invoice is recorded in part two of the journal of received and issued invoices and in the purchase ledger.
The amount of VAT presented to the organization upon the acquisition of an asset is reflected in accounting as the debit of account 19 “Value added tax on acquired assets”, subaccount 19-1 “Value added tax on the acquisition of fixed assets”. When accepting VAT for deduction, an entry is made to the debit of account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” and the credit of account 19 (Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts). EXAMPLE.
ACCOUNTING FOR CAR PURCHASE OPERATIONS An organization, under a purchase and sale agreement, purchased a passenger car for management needs.
Its cost was 236,000 rubles, including VAT - 36,000 rubles). Payment to the seller was made by bank transfer in July. The lifespan of the car is 50 months. In accordance with the company's accounting policy, depreciation for the purposes of both accounting and tax accounting is carried out using the straight-line method. For tax purposes, accounting is carried out using the accrual method. In this case, accounting and tax depreciation will be 4,000 rubles. (RUB 200,000 / 60 months). Transactions related to the purchase of a car should be reflected in the following entries: In the month of purchase of the car, Debit 08 Credit 60
- 200,000 rubles - reflects the organization’s investments in the acquisition of an asset;
Debit 19-1 Credit 60
- 36,000 rubles - VAT allocated;
Debit 01 Credit 08
- 200,000 rubles - a passenger car is accepted for accounting as part of the operating system;
Debit 68/VAT Credit 19
- 36,000 rubles - VAT is presented for deduction from the budget;
Debit 60 Credit 51
- 236,000 rubles - funds were transferred to the seller for the car.
Monthly during the established useful life Debit 26(44) Credit 02
- 4000 rubles - reflects the amount of accrued depreciation.
Good to remember
- Individual entrepreneurs can use personal property in business and vice versa. There is no need to submit any documents for this.
- Take into account the costs of purchasing property in the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses” only if you can prove that it is useful for your business.
- Not all property maintenance costs can be taken into account. Communal services in an office apartment are not allowed, gasoline is only for business-related trips, mobile communications are only for business calls.
- You don't have to pay tax on property you use in business. To do this, submit a tax application.
- It is more profitable to sell property as an individual, rather than as an entrepreneur. But the tax office makes sure that they pay the correct taxes and do not try to save where they cannot. If you used the property in business, and the tax office has evidence, you will have to pay tax as an entrepreneur. Even if it's not profitable.
- It is more profitable to sell property that was used in business before the closure of the individual entrepreneur.
The article is current as of 01/25/2022
Car rent
The rented car is accounted for in off-balance sheet account 001 “Leased fixed assets” in the valuation specified in the lease agreement (Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts for accounting financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n). At the end of the contract, the property is written off from the tenant's off-balance sheet account.
The company's costs associated with the rental of a vehicle used for management needs are classified as expenses for ordinary activities and are recognized monthly in the amounts established by the agreement (clauses 5, 6, 6.1, 7, 16 of the Accounting Regulations “Costs of the organization” PBU 10/99, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 6, 1999 No. 33n).
Read also: “Payment for renting a car can be deducted from an employee’s salary”
We pay taxes
As is known, individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs are not recognized as VAT payers, since they are not mentioned in paragraph 1 of Article 143 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. When purchasing a car from a citizen, the entire amount of funds paid to the seller must be taken into account in the cost of the acquired fixed asset.
Buying a car can be profitable for those who do not pay VAT and income tax, but not for organizations on OSNO. The fact is that the latter in this case are deprived of the opportunity to reimburse the value added tax. Therefore, such companies need to calculate everything and, possibly, choose a different option for purchasing a vehicle.
Let's deal with personal income tax. Paragraph 1 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation stipulates that Russian organizations from which or as a result of relations with which the taxpayer received the income specified in paragraph 2 of this article are recognized as agents and are obliged to calculate, withhold from him and pay the amount of tax. However, the Code also contains Article 228, which states that individuals, from the amounts received from the sale of property owned by them, independently calculate personal income tax payable to the appropriate budget in the manner established by Article 225 of the Tax Code. Therefore, in this case, the seller will calculate and pay the tax independently.
Income tax
Rent for the temporary possession and use of a machine used for management needs is taken into account for profit tax purposes as part of other expenses associated with production and sales, on the basis of subparagraph 10 of paragraph 1 of Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
note
The cost of fixed assets is repaid through depreciation. When using the linear depreciation method in accounting, the annual amount of deductions is calculated based on its original cost and depreciation rate.
As a general rule, expenses are recognized subject to their compliance with the requirements established by paragraph 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, i.e. expenses must be documented and justified. Documentary evidence of rental expenses for tax purposes is a concluded agreement containing the procedure for payment of rental payments, documents confirming payment of payments, as well as an act of acceptance and transfer of property. At the same time, monthly preparation of acts of services provided under the lease agreement for these purposes is not required (unless this is provided for in the lease agreement) (see, for example, letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 24, 2014 No. 03-03-06/1/12764, Federal Tax Service Russia in Moscow dated October 17, 2011 No. 16-15 / [email protected] ).
How to take into account purchase costs in the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses”
Under the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses”, business expenses are taken into account when calculating tax. More expenses - less tax. Therefore, I want to take into account the expenses for each purchase. But it's not that simple.
One of the rules for accounting for expenses is that they must be useful for the business. Before you take into account the costs of a purchase in the simplified tax system, think about whether you can prove its benefits. If not, then consumption cannot be taken into account.
When there is a direct connection between the business and the thing you bought, no questions will arise.
Dima opened a company that deals with cargo transportation. He bought a gazelle and took its cost into account in the expenses of the simplified tax system. It's obvious that the purchase benefits the business, so you don't need to make up a story to prove it. There shouldn't be any problems with the tax authorities. The fact that he bought a car for the company does not stop Dima from driving it to the dacha.
If the connection is not obvious, problems may arise. You will have to prove your case to the tax authorities and, possibly, to the court.
Andrey has a law office. Now he travels to the courts by minibus because his car broke down. In transport, he loses a lot of time, which he could spend on one more thing. He decided to buy a new car and is wondering whether its cost can be taken into account in the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses.” He takes a risk: the tax office may decide that the car is not important for his business and charge taxes and fines.
But there will be a chance to prove it right in court. This is what an entrepreneur who was engaged in trade did. He had to try, but he proved in court that he uses the car for business and confirmed this with travel documents.
If your business is related to transportation, take into account the costs of purchasing a car in the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses.” If a car is not necessary for your business, consider whether you are ready to defend your point of view before the tax office.
Take into account in the simplified tax system only the money spent after registering an individual entrepreneur.
The same is true for other purchases that you will use for yourself and for your business. If it is easy to prove their benefit, take into account the expense in the simplified tax system.
Important: purchases over 100 thousand rubles are taken into account in a special manner. Write off the expense in equal parts at the end of each quarter so that it is fully accounted for this year.