Over the past 4 years, the number of additional VAT charges based on the results of desk audits has increased by more than one and a half times . 8% resulted in charges .
A special role in tightening control over VAT belongs to the ASK VAT-2 system, which is used by the Federal Tax Service to verify submitted declarations. Thanks to it, last year the tax authorities recorded more than 3.2 million breaks in VAT chains worth over 2.6 trillion rubles . At the same time, the average amount of the gap exceeded 800 thousand rubles . A colossal result was achieved in the fight against fly-by-night companies participating in VAT refund schemes - after the introduction of ASK VAT-2, their number decreased by 21 times .
Desk tax audit for VAT: definition and subject
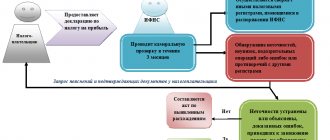
A desk audit of a VAT return is a form of control.
With its help, representatives of the tax service identify discrepancies and errors in the reporting submitted by the payer of the relevant tax (Articles 82, 87 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Such an inspection is carried out on the territory of the tax authority; in general, a visit to the office of the company being inspected is not provided (Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If necessary, documents and explanations are requested via telecommunication channels (TCS). At the same time, as of January 1, 2015, tax officials have the right to inspect the taxpayer’s premises during a desk audit.
A desk tax audit for VAT is a verification of the information provided by the taxpayer in the form of a declaration. The latter is the subject of verification.
The period allotted for carrying out the necessary procedures is 2 months. But in some cases it can be extended to 3 (Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The period of the desk audit for VAT begins to count from the date (day) when the declaration was received by the tax service.
In 2022, a pilot project of the Federal Tax Service was launched, within the framework of which the period of the VAT cameral can be reduced to 1 month. Read more here.
Submitting documents to controllers
In the process of communication between a company and tax authorities as part of an audit, every detail is important. For example, copies of documents provided must be prepared in a special way - otherwise they will simply not be accepted for verification. Let's look at this in more detail.
Let's continue the example: Hellas LLC collected the necessary documents within the prescribed period according to the request sent by the inspectors.
Important! The documents requested as part of the desk audit must be submitted within 10 working days from the date of delivery of the request (Clause 3 of Article 93 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Company employees prepared copies of the requested documents and certified them properly.
Important! Since April 2015, companies may not use a round seal in documents drawn up on paper (Law No. 82-FZ dated 04/06/2015).
Hellas LLC stamped the copies. The company proceeded from the following: the term “certified copies” is not defined in the Tax Code, and therefore whether it is now necessary to put the company’s seal on the copy is not completely clear. On this issue, Ministry of Finance officials refer to GOST R 6.30-2003 (clause 3.26), according to which copies of the document should be stamped. To avoid unnecessary nagging from inspectors, the company decided to play it safe and put the seal on anyway.
Deadline for desk audit for VAT and filing a VAT return
The deadline for filing a VAT return is the 25th day of the month following the tax period that has expired (clause 5 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, the period for a desk audit of the VAT return is 2 months from the date of submission of the tax return (clause 2 of Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and within the framework of the pilot project, 1 month. Previously, this period was 3 months, but was reduced by the Law “On Amendments...” dated August 3, 2018 No. 302-FZ.
How to determine the start and end date of a desk audit? The answer to this question is in ConsultantPlus. If you don't already have access, get a free trial online.
Tax officers are required to complete desk audits after 2 months from the date of submission of the VAT return, while simultaneously meeting the following conditions:
- there are no contradictions in the declaration, and the information contained in it corresponds to information about transactions submitted by other taxpayers (or the unresolved discrepancies do not indicate an understatement of the amount of tax payable to the budget);
- there are no signs of violations of tax legislation leading to an underestimation of the tax payable (or an overestimation of the tax claimed for reimbursement), and there is no information indicating that the taxpayer has received an unjustified tax benefit.
If the taxpayer does not meet the above criteria and the tax authorities identify contradictions, then the period of the desk audit can be extended to 3 months.
The publication will introduce you to the features of a desk audit for reimbursement.
What documents are used to process a VAT refund?
The tax legislation does not regulate the list of documentation required for VAT compensation. The following documents are submitted to the Federal Tax Service at the place of registration by the taxpayer:
- a handwritten request for reimbursement;
- declaration (copy) for the period in which the amount of deductions exceeded the calculated amount of VAT;
- a letter where the taxpayer asks to return the refund amount to a bank account, or to offset the compensated VAT against the existing tax arrears for other reporting periods.
This list of documents is minimal. How the procedure for refunding part of the VAT to the taxpayer is a legal operation that occurs when the tax subject to deduction exceeds the amount calculated for payment. From a theoretical point of view, VAT compensation from the budget should not be accompanied by any difficulties. However, in practice, the largest number of tax disputes are associated with VAT refunds.
VAT declaration form
Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] approved:
- declaration form;
- the procedure for filling it out;
- format for reporting to tax authorities.
You can find out more about the composition of the declaration, download its form and sample from the materials in the section “What is the procedure for filling out a VAT declaration (example, instructions and rules)”.
If a company charges VAT and then claims the tax as a deduction, it will have to provide the relevant data on the invoices that formed the basis for the calculations. For this purpose, the declaration provides sections for reflecting data from the purchase book, sales book, and invoice journal.
Find out who is now required to fill out the invoice journal here.
Currently, tax inspectors have the opportunity to compare the data reflected in the sales book and purchase book of the selling company and the buying company. This makes it possible to identify, during a desk audit of VAT, unscrupulous persons who do not pay taxes to the budget, but claim to receive a VAT deduction.
Responsibility for violating the declaration submission form
Most VAT payers are required to file their returns electronically. If, instead of an electronic declaration, a paper declaration is submitted, the organization will face a fine.
In paragraph 5 of Art. 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that a VAT return submitted on paper is not submitted. As a result, the consequences have become more serious: the fine has increased, and administrative liability is possible.
For more information about liability, see our material “What is the liability for a late declaration?” .
In addition, your organization’s account may be blocked (Clause 3, Article 76 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For more information about suspending account transactions, see our material “Late with your declaration? Get ready to block your account .
Tax collection deadlines
According to paragraph 1 of Article 46 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, if the payer has not timely paid the tax debt, which is determined on the basis of available reporting (can be adjusted based on the results of audits), his obligation is compulsorily fulfilled by foreclosure on his funds in bank accounts.
The statute of limitations for collection is determined by paragraph 3 of Article 46 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, according to which the tax authority has 2 months, which are calculated from the end of the period for fulfilling the requirement to pay taxes, to make a decision on forced collection. After acceptance, it is sent to the taxpayer, as well as to the banks where the debtor has accounts.
Missing the two-month deadline entails the invalidity of the decision and the further impossibility of collecting funds in an administrative manner, which does not deprive the tax inspectorate of the right to go to court to collect the same payments (i.e., already in court). The tax authority, in accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 46 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, has 6 months to go to court, which are also calculated from the date of expiration of the period specified in the requirement to pay taxes. Missing this deadline without the possibility of restoration leads to the impossibility of forced collection.
In the event that there are insufficient funds in the organization’s accounts, the penalty, in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 47 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, is applied to other property of the payer. In this case, a similar administrative or judicial procedure applies - with the only difference that the tax authorities are given 12 months to make a decision, and 2 years to go to court, which are calculated from the end of the period specified in the request for payment of taxes.
Limitation period for collecting taxes from citizens
According to paragraph 2 of Article 48 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, unpaid taxes are collected from citizens only in court. Moreover, in order to go to court, it is necessary that the total amount of debt exceeds 3 thousand rubles. The tax office has 6 months to submit an application.
If the amount of debt is less than 3 thousand rubles, then paragraph 2 of Article 48 defines the following period for foreclosure:
- when the total amount of debt within 3 years reaches more than 3 thousand rubles. the period for going to court is limited to 6 months from the date of accumulation of 3 thousand rubles;
- If within 3 years the amount of debt has not exceeded 3 thousand rubles, then 6 months for going to court will begin to count after 3 years from the date of the first non-payment.
Practitioners need to remember that the tax on real estate and vehicles, due to the requirements of paragraph 2 of Article 52 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, is calculated only for the last 3 tax periods. The tax office does not have the right to calculate tax and send notification of its payment for earlier periods.
Receipt of electronic documents from the tax office must be confirmed
In clause 5.1 of Art. 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that each taxpayer sending an electronic declaration to the tax service is obliged to ensure that the inspection receives from the inspectorate in electronic form via TKS the documents sent by the tax office during the control. What might your tax office require? This means:
- notice of summoning the taxpayer (Article 31 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- requirement to provide explanations (Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)/documents in relation to the submitted reports (Articles 93 and 93.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The list may be supplemented by other documents necessary for conducting a desk audit.
When a notice or demand is received, the taxpayer must send a receipt to the tax office confirming receipt. The legislation allows no more than 6 days for this from the date when the tax authorities requested documentation or clarifications on reporting.
See “Formalized response to the tax office’s demand for VAT – nuances.”
NOTE! Failure to fulfill the obligation to transfer the said receipt will have serious consequences (Article 76 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Thus, the tax service has the right to freeze all transactions on the accounts of the offending company - from banking transactions to money transfers via electronic channels.
Cancellation of such a decision is possible on the basis of Art. 76 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Frozen accounts are unblocked provided that the taxpayer:
- handed over a receipt confirming the receipt of documents that were sent by the tax office;
- provided the documents/explanations originally requested by the tax authority.
Then the cancellation of the order to block the account must occur no later than one day following the earliest of the specified dates.
What mistakes do taxpayers make?
Let's be honest - it's not just tax officials who commit violations. Entrepreneurs themselves sometimes make mistakes too.
The tax authority asks to provide documents for one counterparty as part of a counter audit.
Let us remind you that when refunding VAT, the inspectorate conducts an in-depth desk audit and inspectors can request information and documents from your counterparties about your activities as part of a counter-inspection (Clause 1, Article 93.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Situation: the tax authority requested, during a desk audit of a VAT return, invoices and primary documents for one counterparty. The taxpayer did not provide anything to the tax office, and was brought under clause 1 of Art. 126 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation to liability in the form of a fine. The complaint to the higher tax authority was rejected, and the company went to court.
In this situation, the court refused to satisfy the taxpayer’s stated claim and supported the tax authority.
The court came to the conclusion that the tax authority’s demand was properly drawn up, and the requested documents were directly related to confirming the right to VAT tax deductions for business transactions with a disputed counterparty; their request by the tax authority is legal (Resolution of the Arbitration Court PO No. F06-60320 /2020 dated June 10, 2020 in case No. A12-20791/2019).
The court came to the same conclusion in a similar situation in the Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Eastern Military District No. F01-3770/2019 dated September 13, 2019 in case No. A28-15406/2018 (Decree of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. 301-ES19-23690 refused to transfer the case for revision).
How to find out whether the counterparty looks dubious and whether he is reliable? Use Taxk-Dossier . You will be able to assess the financial situation, learn about the upcoming liquidation, about the mass director and tax arrears from your counterparties. And switch to EDI - this way you can receive the necessary documents from suppliers and buyers much faster.
The taxpayer decided that the desk audit had already ended and did not submit documents.
Situation: The company received a request from the tax authorities to submit documents for one counterparty as part of a counter-inspection; the inspectorate was checking its VAT return. The company refused to send the documents, since it considered that three months had already passed and the period for the desk audit had expired.
The taxpayer lost the case. The fact is that the tax authority decided to carry out additional tax control measures, and therefore the audit deadlines were not violated (Resolution of the Arbitration Court PO No. F06-41631/2018 dated 02/01/2019 in case No. A55-7123/2018).
The requirement to provide documents regarding the counterparty as part of the counter-inspection is legal.
When can tax authorities request documents?
Tax authorities have the right to demand, during a desk audit, that the taxpayer submit invoices, primary and other documents related to the transactions reflected in the submitted declaration (Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The following are cases when this right is subject to exercise:
- If the data provided by two different taxpayers for the same transaction do not correspond to each other.
- If the information specified in the declaration does not correspond to the data from the invoice journal.
- If inconsistencies are identified in the submitted declaration.
IMPORTANT! The intention to request documentation from the taxpayer must be based on compelling reasons. That is, the “irregularities” in the reporting identified by the fiscal service should indicate the taxpayer’s desire to underestimate the amount of tax payable and an attempt to overstate the amount of compensation from the budget.
To learn about what points may influence the occurrence of questions during an audit, read the material “VAT Declaration: The Most Common Errors and How to Correct Them .
Tax authorities accept any explanations regarding VAT only in electronic form. Find out about it here.
What to do if controllers ask for unnecessary documents?
The first question after receiving a request: how to collect documents within the deadlines established by the Tax Code and avoid liability for failure to comply with its norms?
Important! For each tax claim document not submitted or submitted late, a fine of 200 rubles is possible. (clause 1 of article 126 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
There is no need to immediately drop everything and collect the entire requested list. It is important to make sure that all the documents listed in the request relate to the declaration being verified and confirm the information reflected in its lines.
Important! During a desk audit, tax officials can request only those documents that directly relate to the subject of the audit (Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the requested information does not relate to the declaration being verified, controllers do not have the right to demand it (clause 7 of Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It will be difficult for tax authorities to punish a company for failure to submit such documents - judicial practice is mainly on the side of the taxpayer. For example, the FAS Resolution No. A45-2243 dated October 09, 2013 states that the primary documents confirming the right to deduct VAT do not include balance sheets, account analyzes and other accounting registers.
However, sometimes you can find a different judicial position when judges support the right of the tax authority to independently determine the list of requested documents (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated October 4, 2006 No. KA-A40/9438-06). The ambiguity of the situation is explained by the fact that the criteria for selecting documents for verification are not defined in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Having found out that some of the documents were requested incorrectly, it is risky to simply reduce their volume - it is better to send a letter to the tax authorities explaining the reason for the non-submission of certain documents. In the text of the letter, you can make a reference to clause 2.8 of the Federal Tax Service letter dated July 16, 2013 No. AS-4-2/12705, in which the tax authorities themselves indicated that the inspector’s right to request documents during desk audits is limited.
Judicial practice on VAT refunds is very extensive. Get trial access to the Consultant and study the Encyclopedia of Controversial Situations for free.
Desk inspection of VAT: territory - for inspection!
Representatives of the tax service, during a desk audit, have the right to inspect the territory of the organization, the premises it occupies, as well as other property (Article 92 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
See also our material “Inspection: rules for conducting and reporting results” .
That is, a desk audit of VAT is work carried out by fiscal officials not only within the office, but also on the territory of the taxpayer.
When is an inspection allowed? Inspection is possible in the following cases (clause 1 of article 92, clauses 8 and 8.1 of article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- submission of a declaration in which the amount of VAT is claimed for reimbursement;
ConsultantPlus experts explained how a desk audit of a declaration is carried out in the event of a VAT refund. Get trial access to the system and move on to the Ready-made solution.
- identification of contradictions and inconsistencies that give reason to believe that a business entity is trying to underestimate the amount of tax payable or overstate the amount of tax to be reimbursed.
The resolution of the controlling person conducting the inspection is a sufficient basis for inspecting the territories, premises and other property of a legal entity. At the same time, it must have the following characteristics:
- firstly, have motivation;
- secondly, to be approved by the head of the tax authority or his deputy.
A resolution that fully complies with these requirements is the basis for the fiscal service to have access to the territory/premises of the company being inspected. In addition, representatives of the tax service are required to have official identification.
The company reflected the VAT refund in its return: what to expect?
Let's consider an example: Ellada LLC filed a tax return for the 1st quarter of 2022, in which it indicated VAT to be refunded.
Our checklist will help you fill out the declaration for the 1st quarter of 2022, which can be downloaded in the material “Checklist for filling out the VAT return for the 1st quarter of 2021”.
By submitting a declaration with the amount of tax to be refunded, the company was prepared for the fact that tax authorities would pay close attention to its report, so it prepared the necessary documents in advance (invoices, primary documents, purchase and sales books).
However, having received a request from the tax authorities to submit documents, the company was surprised to discover that in addition to the initial statements and invoices, the controllers also requested a number of other documents (accounting policies, analysis of accounts, explanations regarding sources of financing, etc.). We will consider what to do with this request further.
Read about the form in which explanations for filling out the declaration must be submitted to the Federal Tax Service here.
See also “What to answer the inspection’s request for clarifications on the VAT declaration?”
The criteria by which tax authorities check a declaration when refunding VAT are discussed in detail in the ConsultantPlus Ready Solution. Get trial access to the system and start learning the material for free.
Tax monitoring and desk audit of VAT: points of contact
Starting in 2015, some taxpayers may be interested in a new form of tax control - tax monitoring.
To whom tax monitoring is available, see the material “From 01/01/2015, large taxpayers will be able to be “monitored”” .
The subject of tax monitoring is the correctness of tax calculations, as well as compliance with the deadlines for their payment to the budget, in particular this applies to VAT verification (Article 105.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Tax officials do not have the right to conduct desk (by the way, on-site, too) audits within the time period that falls under monitoring.
True, the legislator has provided several exceptions to this rule. For example, if during the period subject to monitoring, representatives of the tax inspectorate reveal that the amount of tax that should go to the budget does not correspond to what the company indicated in its declaration, an audit will be carried out.
Please note that tax monitoring can be carried out exclusively voluntarily. The obligatory basis for it is the decision made upon consideration of the application submitted by the organization initiating its implementation. Moreover, this is not the only thing required. The application must be supplemented with certain documents and a number of data must be provided about the organization.
The order of the Federal Tax Service dated April 21, 2017 No. ММВ-7-15/ [email protected] approved new forms of documents used when conducting tax monitoring. Find out about them by following the link .
We “recapture” every ruble of VAT refund from controllers
If the act describes many violations, there is no need to despair, much less remain inactive. First, it needs to be carefully studied - usually not all identified violations are justified, and the company still has a chance to defend, if not all, then a significant part of the deductions. The main thing is to present your objections in a timely manner, supporting them with appropriate justifications.
Important! 1 month is allotted for written objections to the company’s inspection report (clause 6 of Article 100 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
A sample objection to an office inspection report can be downloaded in this material.
The tax authorities in our example, having considered the company’s arguments, removed some of their comments, and the amount of VAT refund increased significantly. However, now is not the time to relax - not the entire amount that can be defended in a difficult battle with controllers may end up in the company’s account.
This can happen if the company has arrears on VAT or federal taxes (including debts on penalties and fines) - under clause 4 of Art. 176 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax authorities have the right to independently offset the amount of tax to be reimbursed against the repayment of these debts.
Therefore, the taxpayer should check with inspectors in advance so that by the time the refund is transferred, the entire amount is at his disposal.
For information about the form of the reconciliation report, valid in 2022, read the material “Form of the reconciliation report with the tax office.”
Results
A desk audit of the VAT return is carried out by the tax office. If necessary, inspectors may request documents or come to the taxpayer to inspect premises and territories.
The period for a desk audit of a VAT return is generally 2 months. This period can be extended up to 3 months if tax authorities find errors or discrepancies.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected]
- Order of the Federal Tax Service dated April 21, 2017 No. ММВ-7-15/ [email protected]
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Who is at risk
Everyone who has filed a tax refund return is under special control. Some inspectorates even have special departments that check only those who refund the tax.
The larger the amount to be returned, the more thorough the check will be. Especially if the payer has been constantly reimbursing the tax for several years. For large amounts, employees of the regional department of the tax service and even the central office of the Federal Tax Service of Russia can be involved in the audit.
The tax authorities are reluctant to give away budget money. Firstly, due to taxpayer fraud. Before handing over the money, the inspectorate needs to check whether there is an illegal compensation scheme.
Secondly, the tax authorities have a refund plan. When drawing up the budget, the state determines in advance the amount that can be given and distributes it among inspectorates depending on how much each tax office has reimbursed in previous years.
If you do not fit into the return plan, inspectors will look for an opportunity to refuse you or at least delay the inspection so that it moves to the next quarter.
Sometimes payers, tired of endless disputes with the tax authorities, switch to register in another larger region, where the refund limits are higher.