In 2022, the Prosecutor General's Office of Russia put into operation the main information system in the field of control and supervisory activities - the Unified Register of Control (Supervisory) Activities (URKNM).
The resource was created in order to ensure transparency of control activities and digitalize the exchange of information between departments. Now any visit of an inspector to a businessman is possible only after information about this has been entered into the ERKNM.
You can check whether a business is included in the information system by specifying details such as OGRN, Taxpayer Identification Number (INN), month of verification, address, etc.
The number of verification activities planned for 2022 will be the minimum over a 12-year period. Of the 367,000 proposals from controllers, 292,000 were agreed upon by prosecutors.
By comparison, the 2022 plan included 360,000 inspections and the 2020 plan included 384,000 inspections.
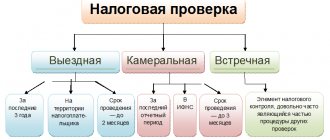
What types of tax inspections for 2022 are provided for by law?
Art.
87 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes 2 types of tax audits: desk and field. Checks of the first type are carried out by Federal Tax Service specialists directly at their workplace. No permits are required. Desk audits must be carried out within 3 months (as a general rule) from the moment the taxpayer submits the declaration (clause 2 of Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). On-site audits are carried out by tax authorities, as a rule, on the territory of the taxpayer, but if the company cannot provide premises, then all procedures are carried out in the Federal Tax Service itself.
The implementation of on-site activities, in turn, requires the head of the tax office to make a separate decision. On-site inspections are appointed based on a comprehensive analysis by specialists of the Federal Tax Service of various indicators of the enterprise’s performance, assessment of tax risks, and the quality of tax and accounting reporting.
The date of the inspection coincides with the moment the head of the local body of the Federal Tax Service signed the decision, which we mentioned above (clause 8 of Article 89 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Legally, the Federal Tax Service is not obliged to warn the taxpayer that department specialists will come with an inspection, but in practice, the territorial structures of the tax inspectorate in many cities first inform organizations and individual entrepreneurs about the decision on the inspection by telephone or by mail.
There are visits from department inspectors without warning. However, such precedents are quite rare. The fact is that the Federal Tax Service itself recommends that its employees give the taxpayer a copy of the decision to conduct an audit. In this case, another copy remains with the department - with o, which is filled out by the relevant entity. If delivery of this document is impossible, it is sent to the taxpayer by mail (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated July 25, 2013 No. AS-4-2/13622).
There is one more nuance - in accordance with the provisions of paragraph 12 of Art. 89 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the taxpayer is obliged to provide access to Federal Tax Service inspectors to documents related to the payment of taxes. Objectively, a company may need time to prepare relevant sources, as well as to organize access to them. In many modern enterprises, the system for obtaining appropriate access is organized quite strictly; in particular, it may be necessary to issue special electronic or biometric passes to certain territories.
Thus, in order to ensure constructive interaction with the payer in terms of gaining access to documents, it can be very useful for the Federal Tax Service to warn him about the visit of inspectors.
ConsultantPlus experts explained in detail what is the difference between a desk tax audit and an on-site tax audit. Get free demo access to K+ and get tips from the experts.
Read about the timing of on-site audits in the article “What is the deadline for conducting an on-site tax audit?” .
Planned and unscheduled events
Inspections of Rosprirodnadzor are regulated by Federal Law No. 294 “On the protection of the rights of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs during the implementation of supervisory activities” dated December 26, 2008. The check is divided into two types.
Planned
Planned activities are carried out no more than once every 3 years. The plan is formed several months before the end of the year. Then it is agreed with the regional prosecutor's office. Information about the inspection plan can be found in the public domain. They are posted on the websites of the Prosecutor's Office and Rosprirodnadzor. Reasons for carrying out inspections:
- State registration of legal entities.
- The results of the last scan expire.
- Start of activities of the legal entity.
The entrepreneur has the opportunity to prepare for the inspection in advance.
Unscheduled
An unscheduled inspection is carried out on specific facts. To implement it, the following grounds are needed:
- Previously, the person was issued an order to correct errors. The period allotted for these corrections has expired.
- There is an order or order from a higher supervisory authority.
- The company received a complaint regarding these offenses: creating a threat to people, the environment, objects of cultural significance, and violating consumer rights.
A complaint can come from any person. An unscheduled inspection involves a narrower set of actions. In particular, the area in which the violation allegedly occurred is checked.
Does the Federal Tax Service have tax audit plans for 2022?
The procedure for conducting on-site tax audits of Federal Tax Service organizations in terms of forming plans is rather superficially regulated at the level of the provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and this gives reason for some taxpayers to doubt - perhaps the department does not plan the relevant activities at all?
There is a version that the main factor in inspections is the interdepartmental interaction of the Federal Tax Service, for example, with the Ministry of Internal Affairs, the prosecutor's office, banks, labor inspectorate (Agreement of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation and Rostrud dated November 25, 2016 No. ММВ-23-2/24@) as well as the involvement of various “unofficial channels " The use of such methods may predetermine the lack of need for planning by the Federal Tax Service - all checks are random in nature and are not based on the department’s adherence to any systemic principles.
However, this point of view is erroneous. The fact that on-site inspections of the Federal Tax Service are nevertheless systematized and included in a separate plan is confirmed by the content of a number of legal acts.
Thus, paragraph 3 of the Federal Tax Service letter No. ShS-21-3/40 dated January 23, 2009 directly states that all on-site inspections are carried out in accordance with approved plans. The document also notes that the mechanism for implementing relevant measures established by the Federal Tax Service does not provide for unscheduled inspections.
How can I find out about an upcoming on-site inspection?
There are situations when tax authorities themselves announce their plans. For example, if the company’s management is able to prepare the necessary documents for audit in a timely manner, then during the tax audit itself there will be no need to waste time collecting them.
The company's counterparties—suppliers (or buyers)—can warn about an impending audit by informing them that, among others, they are being asked for documents regarding transactions with your company.
Information about the inspection may come from the bank - bank employees may report that the inspector is interested in the movement of funds in the accounts of your company, in particular the reasons for the receipt of money in a current and/or foreign currency account and where money is debited from this account.
All this can be a signal for the company, since at the stage of pre-audit analysis, tax authorities examine all the taxpayer’s connections for the presence of tax evasion schemes, imaginary or sham transactions.
Tax audit schedule for 2022
At the same time, the Federal Tax Service is not obliged to formulate public plans for tax audits. Moreover, the department's internal regulations require employees to treat the relevant plans as confidential documents not subject to disclosure. Actually, not even all employees of the Federal Tax Service have access to such information (letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated April 4, 2008 No. ШТ-6-2/255).
The procedure for access of any persons to confidential information is regulated by the provisions of the Order of the Ministry of Taxes of the Russian Federation dated 03.03.2003 No. BG-3-28/96. It provides that the basis for providing information contained in tax audit plans of the Federal Tax Service must be the provisions of federal legislation. In particular, those that give certain persons special powers in terms of gaining access to information in the registers of the Federal Tax Service - for example, law enforcement agencies can receive privileges in this regard.
Some “liberalization” of the rules establishing a ban on disclosing the content of tax audit plans may be applied to the institution of plenipotentiary representation of the President of the Russian Federation. For example, in 2008, employees of the staff of embassies had the right, in a number of cases, to request information from the Federal Tax Service on the total number of inspections and individual entrepreneurs (Federal Tax Service letter No. ШТ-6-2/255).
It may be noted that the provisions of the Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated May 30, 2007 No. MM-3-06/333 approved the conceptual principles of planning tax audits, as well as the criteria for the payer to independently assess the likelihood of an on-site visit by the Federal Tax Service. Despite the age of this legal act, its provisions are also applicable to the analysis of the situation with tax audits of organizations in 2022.
True, this normative act, like other sources of law adopted at the federal level, does not provide any unambiguous guidelines for the timing of relevant inspections. However, it will be useful to study in more detail the key provisions of Order No. MM-3-06/333 in terms of assessing the likelihood of a tax audit by the payer - we will do this a little later.
It is noteworthy that the objects of both on-site and desk tax audits can be any category of taxpayers.
Who exactly will be checked?
The organizations listed in the consolidated inspection plan for 2022 can absolutely expect a visit from government officials in the coming year.
The consolidated plan for inspections of the prosecutor's office is a document developed for each calendar year on the basis of proposals from divisions of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and includes a list of business entities subject to inspection.
The Russian Prosecutor's Office annually publishes the plan for inspections of legal entities (including for 2022) on its official website: plan.genproc.gov.ru.
Who can be included in a scheduled tax audit?
In the provisions of Art. 89 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not specify which persons - legal entities or individuals - can become objects of tax audits of one type or another. Hence the conclusion: absolutely all subjects of tax payment are subject to inspections: citizens, individual entrepreneurs, commercial firms, non-profit organizations, state and municipal structures.
This partly explains the fact that, from a purely technical point of view, it is difficult for the Federal Tax Service to draw up an inspection plan, even if it were required. Based on the provisions of the law, not only legal entities, but also all citizens of the Russian Federation would be included in the corresponding plan. It is extremely unlikely that the Federal Tax Service will have enough human and technical resources to assess the tax history of every Russian, to examine the personal tax profiles of citizens, in particular, for all those risks that are reflected in the provisions of Order No. MM-3-06/333 .
Read more about conducting an on-site tax audit in the article “Procedure for conducting an on-site tax audit (nuances).”
Detailed information on checks
To obtain detailed information about scheduled and unscheduled inspections, you need to click on any of the lines in the “Checks” or go to the “Checks” .
The data presented is grouped (filtered) as follows:
- result of checking
- type , planned or unscheduled
- type , exit, documentary or exit documentary
- year
- inspection body
Inspection analytics
Next, a list of cards appears in front of the user in the context of each check. Each of them contains information such as:
- number assigned by the authorized body
- control body , full name of the authorized body
- purpose of inspection
- period during which the inspection was carried out
- type , planned or unscheduled, documentary or on-site
- result , number of violations with explanation if available
You can get more detailed information about the verification by clicking “Full verification information”.
Card
After this, the card will be supplemented with the following fields:
- order of the body on the basis of which the inspection was carried out by the authorized body
- Full name of the inspector
- Federal State University number , number in the federal register of public services
- fact. date of the event , the actual date or time is indicated
- fact. venue , postal address
- act date
- place of origin, postal address
The Contour.Focus web service provides the ability to search for a specific check by check number. To do this, you need to enter data in a special window, after which the system will display the result.
Search
The user also has an option that allows him to download all the information of interest in the required format: .xlxs, .docs, .pdf . This will allow you to save the information received, prepare reports for your manager and exchange information with colleagues.
Unloading
Information about the results of scheduled and unscheduled inspections can be useful when assessing a potential counterparty, as it allows you to find out the opinion of authorized bodies about the integrity of business. When making an assessment, the user may also benefit from such capabilities of the Kontur.Focus system as financial analysis, extracts of real estate (USRN), notes about the company.
How to assess the likelihood of a company being included in the Federal Tax Service inspection plan for 2022?
What ways can a taxpayer assess the likelihood of meeting with Federal Tax Service inspectors as part of a tax audit? First of all, it is within his power to familiarize himself with the key provisions of Order No. MM-3-06/333.
Despite the fact that the law does not allow payers to have access to tax inspection plans for 2022, a study of the key criteria for assessing the activities of tax payers, which were developed by the Federal Tax Service, can, in principle, provide some guidance on both the timing and likelihood of a visit from tax inspectors.
Thus, the department may pay attention to an organization or individual entrepreneur if:
- the tax burden on the company is below the industry average (clause 1 of order No. MM-3-06/333);
- the company reflects losses in its reporting over several tax periods (clause 2);
- the reporting documents contain too large amounts of deductions for a particular period (clause 3);
- an accelerated dynamics of cost growth was recorded in comparison with the rate of increase in revenue (clause 4);
- the company pays employees a lower salary than the industry average (clause 5);
- the company’s indicators, which give the right to work under special tax regimes, are close to the maximum permissible (clause 6);
- Individual entrepreneurs show in their reporting expenses that are as close as possible to the amount of income (clause 7);
- the company forms an unreasonably long chain of counterparties, consisting of intermediaries and resellers (clause 8);
- the organization does not provide explanations to the Federal Tax Service in response to notifications received about the non-compliance of certain performance indicators with established criteria, and does not transfer the requested documents (clause 9);
- the owners of the company frequently re-register the business in different territorial structures of the Federal Tax Service (clause 10);
- the company has noticeable deviations in profitability from the indicators observed on average in the industry (clause 11);
- According to Federal Tax Service specialists, the company operates with a high tax risk (clause 12).
By what other criteria does the Federal Tax Service select organizations for on-site inspections, find out in the ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
It turns out that the more coincidences on the specified points the Federal Tax Service records in relation to the activities of a particular company, the higher the likelihood of an audit, and the more quickly it can be carried out.
Marking and tax audits of business
Small business tax audits in 2022 may trigger non-compliance with product labeling regulations and requirements. The following may cause special attention from the Federal Tax Service:
- Sales of unmarked goods for which labeling is required. All products that are subject to mandatory labeling must have a DataMatrix digital code on the packaging. The code must be read at the checkout when selling. The production, transportation, sale and storage of unmarked goods can lead to inspections and large fines, and in special cases even criminal liability. All goods without identification marks will be confiscated.
- If the marking codes are difficult to read. This can happen for many reasons, for example, if the code is simply worn out or covered with something. If a product has a labeling code that cannot be read, it must be relabeled.
- If the labeling code data does not match the data in the UPD for the product, such product must be returned to the supplier and cannot be sold.
- If goods with fake labeling codes are sold. In this case, checking is not the worst thing. Criminal liability for up to three years is possible.
Should you trust unofficial data on Federal Tax Service inspection plans?
Numerous “unofficial” indicators are common among experts that determine the likelihood of attracting attention from tax authorities. However, following these in itself may be an additional tax risk, since no one guarantees how close certain theses are to reality. Moreover, some of these points of view, as in the case of the thesis about the absence of plans in the Federal Tax Service, may be formed due to ignorance of the legislation by the persons disseminating this information.
Read more about the content of tax audits of all types, as well as the most notable features of this procedure, in the article “Tax audit - what is it and what is the procedure?” .
Results
The Federal Tax Service's on-site inspection plan is classified information for taxpayers. As a rule, they learn about the upcoming visit of inspectors several days before the start of the inspection. The official list of inspections is published only for companies engaged in government-regulated activities. This list can be found on the official website of the Federal Tax Service.
Sources: Tax Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
How to get information from the new registry
The unified register of control (supervisory) activities is synchronized with the State Services portal. Information about upcoming events and the results after they will be available in your personal account. This information will be official and can be used to appeal decisions, actions (inactions) of supervisory authorities in a pre-trial manner.
There is currently a pilot project for appealing decisions of supervisory authorities. It was signed by the Chairman of the Government of the Russian Federation Mikhail Mishustin back in August 2022. So far, only 19 control agencies for 63 types of control are participating in the experiment.
From July 1, 2022, pre-trial appeals against controllers’ decisions will be introduced for certain types of control determined by the Government of the Russian Federation. However, from January 1, 2023, it is planned to gradually implement it for all types of control that are regulated by the Law on State Control No. 248-FZ of July 31, 2020.