Grounds for filing a claim
The basis for payment of the penalty and, accordingly, the right to demand its payment in the form of a claim is enshrined in clause 1 of Art.
330 of the Civil Code (hereinafter referred to as the Civil Code). According to this rule, a party to a transaction has the right to demand payment of a penalty if its counterparty did not fulfill any obligation provided for in the contract, or was fulfilled in violation of the conditions or legal requirements determined by the parties. An important condition enshrined in paragraph 1 of Art. 330 of the Civil Code, is the debtor’s obligation to pay the penalty provided for by contract or law, regardless of whether the other party suffered any losses as a result of the debtor’s improper performance of his duties. This means that the possibility of sending a letter of claim does not depend on the creditor receiving losses under this obligation. This position has been repeatedly confirmed by the highest courts when considering disputes about the legality of the requirement for a penalty of a certain amount and its proportionality to the consequences of a person’s failure to fulfill his duties. For example, this opinion was voiced in the ruling of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 21, 2017 No. 51-KG17-2.
By virtue of paragraph 2 of Art. 330 of the Civil Code, a justified claim can be made only when the improper performance of an obligation by a party to a transaction was a consequence of its guilty actions (or inaction). If the failure to perform occurred due to force majeure circumstances or the actions of the creditor, then the latter has no grounds to demand payment of the penalty. The judiciary is of a similar opinion. An example is the resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated October 21, 1997 No. 4051/97 in case No. 224/8.
How to recover a penalty from a contractor under a work contract? The answer to this question is in the ready-made solution ConsultantPlus. If you don't have access to the system yet, get a trial online access for free.
Penalty, penalty, fine - what exactly to charge?
The Civil Code clearly defines the main points for imposing a penalty. This is a very convenient way to recover costs from the violator, since:
- you are not required to prove that you suffered losses - a penalty can be imposed simply on the fact of violation of contract obligations;
- the parties specify all the details of its issuance in the contract at their discretion (including the amount and procedure for payment);
- in some cases, the need to pay a penalty may be established by law.
The contract may stipulate that penalties must be imposed for various violations of obligations. For example, penalties for late payment under the contract (that is, violations that last over time) and for one-time failure to provide shipping documents. Moreover, you can even make a claim for compensation for losses incurred by you as a result of violation of the terms of the contract.
For example, you ordered furniture for the office that was not produced by the required deadline. You had to order again from another supplier at a higher price. If the contract with the first manufacturer contains the appropriate conditions, then you will be able to compensate for the difference in the price of the furniture.
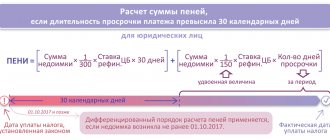
The penalty may be in the form of a fine or penalty. The fine is paid in a fixed amount or as a percentage of a certain amount (for example, 15% of the debt amount) once. Penalties are calculated as a percentage for each day of delay from the amount of the obligation that was not fulfilled (for example, 0.5% of the contract price for days 1–3 of delay, then 0.7% per day).
In rare cases, penalties can also be set at a fixed amount for each day of delay. They are accrued until the violator either fulfills his obligations or compensates for all losses.
Accordingly, we advise you to include a penalty in the form of a penalty in the contract. Then you will be able to recover a much larger amount. You can also use a combination of a fine and a penalty: this is not considered illegal and will not mean that you punish the counterparty twice for one violation.
Contents of a claim for a penalty, sample
It is impossible to find an approved form of a claim with a requirement to pay a penalty for an unfulfilled obligation due to its absence, which is a rational consequence of the principle of freedom of contract enshrined in paragraph 1 of Art. 1 GK. At the same time, you can find samples of this document used in various areas of civil legal relations. For example, a sample claim for improper performance of the duties of a performer or contractor is posted as an official document on the Rospotrebnadzor website.
Claim Sections
Based on the practice of such legal relations and the requirements of § 2 of Chapter 23 of the Civil Code, which regulates issues of penalties, we can identify the following points that a letter of claim with a demand to pay a penalty should contain:
- The name of the counterparty who violated its obligations and its details (address, tax identification number, etc.).
- The name of the creditor (the person demanding payment of the penalty), his details or personal data if he is an individual (address, telephone, etc.).
- Name of the document (claim, letter of claim).
- Indication of the details of the transaction, for failure to fulfill obligations under which the payment of penalties is required.
- List of violated obligations with reference to the relevant clauses of the contract.
- An indication that the creditor has fulfilled its obligations under the transaction (this partially indicates the absence of guilt on the part of the creditor himself).
- Period of delay in fulfilling an obligation.
- Valuation of an unfulfilled obligation in monetary terms.
- The amount of the penalty and its total amount.
- The basis for the penalty claim (clauses of the contract or provisions of the law).
- A requirement to pay a penalty within a certain period of time, indicating that if they are not fulfilled, the person reserves the right to protect his interests in court.
- List of necessary attachments (agreement, payment orders, acts of acceptance and transfer of documents, etc.).
You can download a sample claim for a penalty on our website.
Sample
| ________________________ (Title of the document) |
LLC _________, represented by___________, acting on the basis of_____________, and LLC _________, represented by___________, acting on the basis of_____________, established:
1. Item
1.1. To ensure proper fulfillment of obligations under supply contract No.__ dated _________, the following responsibilities are established:
1.1.1. For violation of the payment terms provided for in clause__ of the Agreement, the Contractor has the right to demand from the Customer payment of a penalty in the amount of _____% of the payment amount for each day of delay.
2. Other conditions
2.1. The document is drawn up in 2 (two) copies, one for each of the parties.
2.4. All disputes regarding this obligation are resolved through negotiations. If the Parties do not reach an agreement during negotiations, the dispute is subject to consideration by the arbitration court of the ______________ region.
3. Addresses, bank details and signatures
Filling example:
Procedure for filing a claim
An important role in obtaining compensation for harm suffered and further collection of penalties in the event of refusal to voluntarily satisfy claims is played not only by the form and content of the claim letter, but also by compliance with the procedure for sending it. Compliance with the order implies sending the demand within the period established by the contract in a manner determined by the parties.
The deadline for filing claims for payment of a penalty is set by the parties at their discretion. If the period has not been determined in advance, then it is necessary, following the meaning of civil law, to send the claim within a reasonable period, which business customs consider to be a two-week or a month period. At the same time, the legislator does not deprive a party to a transaction whose rights have been violated from demanding payment of a penalty in court and within the limitation period. In cases where it is mandatory to comply with the pre-trial claim procedure for resolving a dispute (in the case of legal entities, this is almost always the case), the injured party can submit a corresponding claim at any time before the expiration of this period.
Find out how long it takes to file a claim after filing a claim here.
The optimal way to send a claim, which makes it possible to clearly establish that the debtor has received it, is to send it by registered mail with notification and a list of the attachment. To speed up the exchange of letters between the parties to a transaction, it is often allowed to initially send letters (including claims) by fax or email, followed by sending the original by mail. In this case, the date of receipt is considered to be the date of receipt of the fax or email.
ConsultantPlus experts explained how to prepare and submit a claim for a penalty to an arbitration court. Get trial access to the system and move on to the Ready-made solution.
The size of the penalty matters
You have every right to determine the amount of the penalty in the contract, taking into account its agreement with the other party. However, do not forget that it must be within reasonable limits and correspond to the losses incurred due to violation of contractual obligations. For example, a penalty of 5% of the contract amount per day will be 1800% per year. Of course, your counterparty will not want to pay such amounts. You will have to go to court to get paid.
The court may well reduce its size, but only if several conditions are simultaneously met. Firstly, if the debtor files an application for reduction in court. Secondly, if it is proven that the current amount of the penalty will lead to unjustified benefits.
By law, you can impose a penalty and also demand compensation for losses incurred. You must set sanctions taking into account the rules for their joint application, which are prescribed in the Civil Code.
Results
Thus, a claim for payment of a penalty must comply with the norms of the Civil Code governing the issue of penalties, the terms of the contract determined by the parties independently, as well as the rule of law if the penalty is legal in nature. In addition, it is necessary to comply with the deadlines for sending the claim, as well as the method of sending it, determined by the parties.
Read about tax accounting for penalties under contracts in this article.
Sources: Civil Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
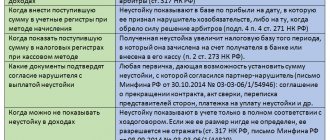
Deadlines for calculating penalties
The Civil Code explains from what day the penalty is calculated under 44-FZ: the next day after the deadline established by the contract is the first day from which the penalty is calculated (Articles 191, 194 of the Civil Code). This rule also applies to cases where the first day of the violation is a holiday or weekend.
If the goods are delivered later than the deadline established by the contract, we make the appropriate notes in the documents that confirm the fact of delivery. We record the shortfall in quantity discrepancies and make a note in other closing documents. If the delivery was not made, we draw up a report on the violation of deadlines.
The day of delivery is the last day that is included in the period of delay (clause 65 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court No. 7 of March 24, 2016). The time that the customer spent on receiving and processing the goods is not added to this period (letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 24-03-07/22888 dated March 24, 2020).
How long to wait for an answer
There is no specific time frame for consideration of a claim by law. Most often, these deadlines are stipulated in the contract or in the claim itself, where you can offer the debtor to fulfill your demands within a certain period (usually 7-14 days from the date of receipt of the letter). The date of receipt can now be tracked using the postal item tracker on the Russian Post website. Please note that the calculated penalty at the time of filing a claim for an unfulfilled main obligation is not final, and when going to court, a fine may be accrued until the actual fulfillment of the obligation. If a response is not received within the established period and the money is not transferred, wait a few more days (depending on how long the postal item takes) and you can send an application to the court - you have complied with the claim procedure for a penalty.