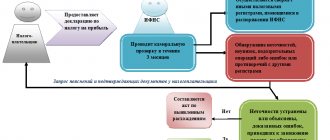
What is a desk tax audit?
A desk audit is a control event that the Federal Tax Service carries out after receiving any declaration and any settlement.
In general, such an audit does not involve tax officials visiting the taxpayer’s location: all activities are carried out within the premises of the inspectorate. Determine the likelihood of an on-site tax audit and receive recommendations on the tax burden
First of all, the received reports are checked to ensure compliance with the deadlines. The Federal Tax Service records that the declaration or calculation was submitted without delay. If the deadline is violated, the payer faces a fine under Article 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Then controllers check the compliance of the reporting with the rules that are prescribed in the order of filling out a particular declaration (calculation). After this, the fulfillment of the control relations is checked.
In addition, within the framework of the “camera chamber”, data from the declaration or calculation is compared with other information that the tax authorities have at their disposal. In particular, information from the received reports is verified with data from other declarations and calculations of the taxpayer himself, as well as with the reports of his counterparties (clause 2.3 of the Federal Tax Service letter dated July 16, 2013 No. AS-4-2/12705). In addition, the information specified in the declaration or calculation is compared with data from information sources to which the Federal Tax Service has access. This is, in particular, information about licenses, bank accounts, data from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, the Unified State Register of Legal Entities and the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs (clause 2.5 of the Federal Tax Service letter dated July 16, 2013 No. AS-4-2/12705).
Receive a fresh extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities or Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs with the signature of the Federal Tax Service Send an application
A desk tax audit is...
A desk audit is a check of the taxpayer’s compliance with tax legislation based on the reports he submitted.
It is mandatory and is carried out in relation to any reporting submitted to the tax authority. The first stage of the desk tax audit 2022 is the registration of the submitted report data in the automated information system of the tax authorities (AIS “Tax”).
At the next stage of the desk tax audit, control ratios are reconciled. In addition, the indicators of the current tax (calculation, reporting) period are analyzed in comparison with similar indicators for the previous period. Also, during a desk audit, the indicators of the submitted declaration (calculation) are reconciled with the indicators in other reporting and, in particular, with reports on other taxes (insurance contributions).
At the same time, during a desk audit, tax service representatives monitor the following points:
- Compliance with the deadlines for submitting a declaration or calculation (clause 1 of article 23, clause 6 of article 80, clause 2 of article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- The presence or absence of contradictions, errors, inconsistencies in reporting (Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Availability of grounds for an in-depth desk audit.
It should be noted that during a desk audit, not only compliance with the reporting deadline is monitored, but also those deadlines that give the tax authorities the right to impose penalties for late submission of the report. If the filing of a declaration (calculation) is delayed for 10 days or more, the tax authorities have the right to suspend transactions on current accounts (clause 3 of Article 76 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The seizure from the taxpayer’s bank accounts will be lifted only the next day after reporting is submitted (Article 76 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Read about the specifics of conducting a desk audit for VAT in the article “Desk tax audit for VAT: deadlines and changes in 2022. ”
Who conducts the desk audit?
As already noted, a desk audit does not require a mandatory visit to the taxpayer. Therefore, almost all control activities are carried out at the location of the tax authority. For this purpose, the inspectorates have created special departments for desk audits, where submitted declarations and calculations are received.
Employees of these departments (tax inspectors), as part of their daily job duties, with the help of special programs, carry out the above control activities.
REFERENCE. The decision of the head or deputy head of the Federal Tax Service to conduct a desk audit is not required. This is directly stated in paragraph 2 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
How long does a desk audit last?
The deadline for conducting a desk audit corresponds to 3 months from the date of submission of reports to the tax service (clause 2 of Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The frequency of the desk audit depends on the submission of reports.
The decision to conduct a desk audit does not depend on the taxpayer.
The procedure for conducting a desk audit is regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
About making a decision based on the results of a desk audit, read the material “A decision on a desk audit can be made before the expiration of a three-month period .
Goals and features of the “camera room”
The main purpose of a desk audit is to ensure that tax obligations are formed correctly in a declaration or calculation. In other words, a desk audit can confirm that the taxpayer has correctly calculated the amount of tax, or refute this. Also, during the audit, data from the reporting will be checked with information about the amounts of taxes already transferred in order to establish the presence of arrears or overpayments.
Within the framework of the “camera chamber”, in addition to checking the control ratios and the accuracy of filling out the declaration, other tax control measures can be carried out. Thus, in cases directly specified in the article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, additional documents can be requested from the taxpayer confirming the data specified in the declaration. For example, this is allowed when discrepancies are identified between the information in the declaration and the information available to the inspectorate (clause 3 of Art. Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Request a tax reconciliation report from the Federal Tax Service via the Internet Request for free
For more details, see: “The Federal Tax Service requires documents: which requests need to be answered and which can be ignored.”
Also, during a desk audit, the Federal Tax Service may conduct so-called counter audits, that is, request documents and information from third parties (Article 93.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). They can be both parties to those contracts that the taxpayer himself entered into, and counterparties of the second, third and subsequent links (resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Ural District dated 02.08.18 No. F09-4001/18). For more details, see: “The Federal Tax Service Inspectorate requested data on the counterparty or transaction: when is it legal, and what will happen if you do not respond to the request.”
In addition, when conducting a “camera chamber”, the Federal Tax Service may call the management of the inspected organization or entrepreneur to the inspectorate to give explanations (subclause 4, clause 1, article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Tax authorities also have the right to conduct interrogations of any other persons, including taxpayer employees, and seizure of documents (Articles and Articles of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In some cases, inspections of premises, territories, documents and objects are permissible (clause 1 of Art. Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
From July 1, 2022, the rule applies: if one of several circumstances listed in paragraph 4.1 of the article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is found in the declaration, the declaration is considered not submitted. Such circumstances include the signature of an unauthorized person, disqualification of the person who signed the declaration, etc. In such circumstances, the “camera chamber” is terminated (see “On what grounds will tax authorities not accept reports submitted after July 1”).
Article 88. Desk tax audit
Article 88. Desk tax audit
[Tax Code] [Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Part 1] [Section V] [Chapter 14]
. A desk tax audit is carried out at the location of the tax authority on the basis of tax returns (calculations) and documents submitted by the taxpayer, as well as other documents on the activities of the taxpayer available to the tax authority. A special declaration submitted in accordance with the Federal Law “On the voluntary declaration by individuals of assets and accounts (deposits) in banks and on amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation”, and (or) documents and (or) information attached to it, and also, the information contained in the specified special declaration and (or) documents cannot form the basis for conducting a desk tax audit.
A desk tax audit of the calculation of the financial result of an investment partnership is carried out by the tax authority at the place of registration of the participant in the investment partnership agreement - the managing partner responsible for maintaining tax records (hereinafter in this article - the managing partner responsible for maintaining tax records).
1.1. When submitting a tax return (calculation) for a tax (reporting) period for which tax monitoring is carried out, a desk tax audit is not carried out, except for the following cases:
- 1) submission of a tax return (calculation) later than July 1 of the year following the period for which tax monitoring is carried out;
- 2) submission of a tax return for value added tax, which states the right to a tax refund, or a tax return for excise taxes, which states the amount of excise duty to be reimbursed;
- 3) submission of an updated tax return (calculation), in which the amount of tax payable to the budget system of the Russian Federation is reduced, or the amount of the resulting loss is increased compared to the previously submitted tax return (calculation);
- 4) early termination of tax monitoring.
. A desk tax audit is carried out by authorized officials of the tax authority in accordance with their official duties without any special decision of the head of the tax authority within three months from the date of submission by the taxpayer of the tax return (calculation) (within six months from the date of submission by a foreign organization consisting of registration with the tax authority in accordance with paragraph 4.6 of Article 83 of this Code, a tax return for value added tax), unless otherwise provided by this paragraph.
If the tax return (calculation) is not submitted by the taxpayer - the controlling person of the organization, recognized as such in accordance with Chapter 3.4 of this Code, or by a foreign organization subject to registration with the tax authority in accordance with paragraph 4.6 of Article 83 of this Code, to the tax authority within the prescribed period, authorized officials of the tax authority have the right to conduct a desk tax audit on the basis of the documents (information) they have about the taxpayer, as well as data about other similar taxpayers within three months (within six months for a foreign organization subject to registration registration with the tax authority in accordance with paragraph 4.6 of Article 83 of this Code) from the date of expiration of the deadline for submitting such a tax return (calculation), established by the legislation on taxes and fees.
If, before the end of the desk tax audit of the documents (information) available to the tax authority, the taxpayer submits a tax return, the desk tax audit is terminated and a new desk tax audit begins based on the submitted tax return. Termination of a desk tax audit means termination of all actions of the tax authority in relation to the documents (information) available to the tax authority. In this case, the documents (information) received by the tax authority as part of a terminated desk tax audit may be used when carrying out tax control measures in relation to the taxpayer.
A desk tax audit based on a tax return for value added tax, documents submitted to the tax authority, as well as other documents on the activities of the taxpayer available to the tax authority is carried out within two months from the date of submission of such a tax return (within six months from the day of submission by a foreign organization registered with the tax authority in accordance with paragraph 4.6 of Article 83 of this Code, a tax return for value added tax).
If, before the end of the desk tax audit of the value added tax tax return, the tax authority has identified signs indicating a possible violation of the legislation on taxes and fees, the head (deputy head) of the tax authority has the right to decide to extend the period for conducting the desk tax audit. The period for a desk tax audit may be extended to three months from the date of submission of the tax return for value added tax (with the exception of a desk tax audit of a tax return for value added tax submitted by a foreign organization registered with the tax authority in accordance with paragraph 4.6 of Article 83 of this Code).
. If a desk tax audit reveals errors in the tax return (calculation) and (or) contradictions between the information contained in the submitted documents, or reveals inconsistencies between the information provided by the taxpayer, the information contained in the documents available to the tax authority, and received by it during the tax control, the taxpayer is informed about this with the requirement to provide the necessary explanations within five days or make appropriate corrections within the prescribed period.
When conducting a desk tax audit on the basis of an updated tax return (calculation), in which the amount of tax payable to the budget system of the Russian Federation is reduced in comparison with a previously submitted tax return (calculation), the tax authority has the right to require the taxpayer to submit within five days necessary explanations justifying changes in the relevant indicators of the tax return (calculation).
When conducting a desk tax audit of a tax return (calculation) in which the amount of loss received in the corresponding reporting (tax) period is stated, the tax authority has the right to require the taxpayer to provide, within five days, the necessary explanations justifying the amount of the loss received.
Taxpayers who are obligated by this Code to submit a tax return for value added tax in electronic form, when conducting a desk tax audit of such a tax return, provide the explanations provided for by this paragraph in electronic form via telecommunication channels through an electronic document management operator in the format established federal executive body authorized for control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees. If the specified explanations are submitted on paper, such explanations are not considered submitted.
3.1. If a foreign organization subject to registration with the tax authority in accordance with paragraph 4.6 of Article 83 of this Code fails to submit a tax return for value added tax within the established period, the tax authority within 30 calendar days from the date of expiration of the established period for its submission sends a notification to such organization the need to submit such a tax return. The form and format of this notification are approved by the federal executive body authorized for control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees.
. A taxpayer who submits to the tax authority explanations regarding identified errors in the tax return (calculation), contradictions between the information contained in the submitted documents, changes in the relevant indicators in the submitted updated tax return (calculation), in which the amount of tax payable to the budget system of the Russian Federation is reduced Federations, as well as the amount of the resulting loss, have the right to additionally submit to the tax authority extracts from tax and (or) accounting registers and (or) other documents confirming the accuracy of the data included in the tax return (calculation).
. The person conducting the desk tax audit is obliged to consider the explanations and documents submitted by the taxpayer. If, after considering the submitted explanations and documents, or in the absence of explanations from the taxpayer, the tax authority establishes the fact of a tax offense or other violation of the legislation on taxes and fees, officials of the tax authority are obliged to draw up an inspection report in the manner prescribed by Article 100 of this Code.
. When conducting a desk tax audit, the tax authority has the right to demand that a taxpayer-organization or a taxpayer-individual entrepreneur provide, within five days, the necessary explanations about the transactions (property) for which tax benefits have been applied, and (or) request documents from these taxpayers in the prescribed manner , confirming their right to such tax benefits.
. When conducting a desk tax audit, the tax authority does not have the right to request additional information and documents from the taxpayer, unless otherwise provided by this article or if the submission of such documents along with the tax return (calculation) is not provided for by this Code.
. When submitting a tax return for value added tax, in which the right to a tax refund is declared, a desk tax audit is carried out taking into account the features provided for in this paragraph, on the basis of tax returns and documents submitted by the taxpayer in accordance with this Code.
The tax authority has the right to request from the taxpayer documents confirming, in accordance with Article 172 of this Code, the legality of applying tax deductions.
8.1. If inconsistencies are identified between information about transactions contained in the tax return for value added tax, or when information about transactions contained in the tax return for value added tax submitted by the taxpayer is identified, information about these transactions contained in the tax return for tax value added submitted to the tax authority by another taxpayer (another person who, in accordance with Chapter 21 of this Code, is charged with the obligation to submit a tax return for value added tax), or in the log of received and issued invoices submitted to the tax office body by a person who, in accordance with Chapter 21 of this Code, is entrusted with the corresponding responsibility, if such contradictions and inconsistencies indicate an underestimation of the amount of value added tax payable to the budget system of the Russian Federation, or an overestimation of the amount of value added tax, declared for reimbursement, the tax authority also has the right to request from the taxpayer invoices, primary and other documents related to these transactions.
8.2. When conducting a desk tax audit of a tax return (calculation) for corporate income tax, personal income tax of a participant in an investment partnership agreement, the tax authority has the right to request from him information about the period of his participation in such an agreement, about his share of profits (expenses, losses) ) investment partnership, as well as use any information about the activities of the investment partnership available to the tax authority.
8.3. When conducting a desk tax audit on the basis of an updated tax return (calculation) submitted after two years from the date established for filing a tax return (calculation) for the relevant tax for the corresponding reporting (tax) period, in which the amount of tax payable in budget system of the Russian Federation, or the amount of the received loss has been increased compared to the previously submitted tax return (calculation), the tax authority has the right to request from the taxpayer primary and other documents confirming changes in information in the relevant indicators of the tax return (calculation), and analytical tax accounting registers, on the basis of which the indicated indicators were formed before and after their changes.
8.4. When conducting a desk tax audit of an excise tax return in which the tax deductions provided for in Article 200 of this Code are claimed in connection with the return by the buyer to the taxpayer of previously sold excisable goods (except for alcohol and (or) excisable alcohol-containing products), the excise tax return submitted in connection with the return by the taxpayer - manufacturer of alcohol and (or) excisable alcohol-containing products of ethyl alcohol to the supplier - manufacturer of ethyl alcohol, an excise tax return reflecting tax deductions of excise tax amounts paid by the taxpayer when importing excisable goods into the territory of the Russian Federation, subsequently used as raw materials for the production of excisable goods, the tax authority has the right to request from the taxpayer primary and other documents confirming the return of excisable goods and the legality of applying the specified tax deductions, with the exception of documents previously submitted to the tax authorities on other grounds.
8.5. When conducting a desk tax audit of a tax return for value added tax, the tax authority has the right to request from a foreign organization registered in accordance with paragraph 4.6 of Article 83 of this Code documents (information) confirming that the place of provision of services specified in paragraph 1 of the article 174.2 of this Code, the territory of the Russian Federation is recognized, as well as other information (information) regarding such services.
8.6. When conducting a desk tax audit of the calculation of insurance premiums, the tax authority has the right to request, in the prescribed manner, from the payer of insurance premiums information and documents confirming the validity of reflecting amounts not subject to insurance premiums and the application of reduced insurance premium rates.
8.7. When conducting a desk tax audit of a tax return for value added tax, in which the tax deductions provided for in paragraph 4.1 of Article 171 of this Code are claimed, the tax authority has the right to request from the taxpayer documents confirming the legality of the application of the specified tax deductions, if inconsistencies are identified in those reflected in the tax return information about such tax deductions to information available to the tax authority.
8.8. When conducting a desk tax audit of a tax return for corporate income tax, in which an investment tax deduction is claimed, provided for in Article 286.1 of this Code, the tax authority has the right to require the taxpayer to provide, within five days, the necessary explanations regarding the application of the investment tax deduction, and (or) to request, in the prescribed manner, from the taxpayer primary and other documents confirming the legality of applying such a tax deduction.
. When conducting a desk tax audit on taxes related to the use of natural resources, tax authorities have the right, in addition to the documents specified in paragraph 1 of this article, to request from the taxpayer other documents that are the basis for the calculation and payment of such taxes.
9.1. If, before the end of the desk tax audit, the taxpayer submits an updated tax return (calculation) in the manner prescribed by Article 81 of this Code, the desk tax audit of the previously submitted declaration (calculation) is terminated and a new desk tax audit begins on the basis of the updated tax return (calculation). . Termination of a desk tax audit means the termination of all actions of the tax authority in relation to a previously submitted tax return (calculation). In this case, the documents (information) received by the tax authority as part of a terminated desk tax audit may be used when carrying out tax control measures in relation to the taxpayer.
. The rules provided for by this article also apply to payers of fees, payers of insurance premiums, tax agents, and other persons who are entrusted with the obligation to submit a tax return (calculation), unless otherwise provided by this Code.
. A desk tax audit of a consolidated group of taxpayers is carried out in the manner established by this article, on the basis of tax returns (calculations) and documents submitted by the responsible member of this group, as well as other documents on the activities of this group available to the tax authority.
When conducting a desk tax audit for a consolidated group of taxpayers, the tax authority has the right to request from the responsible participant in this group copies of documents that must be submitted with the tax return for corporate income tax for the consolidated group of taxpayers in accordance with Chapter 25 of this Code, including those related to activities other members of the audited group.
The necessary explanations and documents for the consolidated group of taxpayers are submitted to the tax authority by the responsible participant in this group.
. When conducting a desk tax audit of a tax return (calculation) submitted by a taxpayer - a participant in a regional investment project, for taxes in the calculation of which tax benefits provided for participants in regional investment projects by this Code and (or) the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation were used, the tax authority has the right request from such taxpayer information and documents confirming the compliance of the regional investment project implementation indicators with the requirements for regional investment projects and (or) their participants established by this Code and (or) the laws of the relevant constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
. A desk tax audit of the calculation of insurance premiums, which declares the costs of paying insurance coverage for compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity, is carried out taking into account the provisions established by Chapter 34 of this Code.
Deadlines for desk checks
As a general rule, a desk audit lasts three months from the date of reporting. VAT returns “by default” must be checked within a shortened period of two months (Clause 2 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In most cases, it is impossible to extend the period of the “camera chamber”. An exception applies to VAT returns. The tax inspectorate may extend the period for auditing such a report from the reduced two to the standard three months if signs of violation of tax legislation are detected (clause 2 of Article 2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Check and submit an electronic VAT return for free
The above inspection periods begin to run from the day the inspection received the declaration or calculation (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated December 22, 2017 No. 03-02-07/1/85955, clause 2.2 of the Federal Tax Service letter dated July 16, 2013 No. AS-4-2/ 12705). The rules for ending the desk audit period are the same as for any other deadlines (Article 6.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This means that the “camera room” must end on the corresponding date after three (two) months. If this day falls on a weekend or holiday, the end date is moved to the next business day. And if there is no corresponding date in the month in which the audit is completed, then the audit must end on the last day of that month.
ATTENTION. The Federal Tax Service cannot suspend the period during a desk audit.
The expiration of the “camera chamber” period means that inspectors must stop all “external” inspection activities. That is, they will not be able to send requests for the submission of documents (to both the taxpayer and third parties), conduct interrogations, inspections, seizures, etc. But “internal” events can continue. The fact is that drawing up an inspection report outside its deadline is not a significant violation of the procedure and does not entail the unconditional cancellation of the decision of the Federal Tax Service (clause 14 of article 101 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 3 of the letter of the Ministry of Finance dated March 23, 2018 No. 03-02-07/ 1/18400).
ATTENTION. If you submit an updated declaration before the end of the chamber meeting, the verification of the primary reports will immediately stop. And the inspection period will begin to run again (clause 9.1 of Art. Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The procedure for holding a camera room
Desk inspection can be divided into two stages: automated control and in-depth inspection. Automated control of reporting occurs virtually without the participation of tax officials. After the data from the declaration (calculation) is loaded into the inspection information system, the computer itself checks the correctness of filling out the reporting lines and verifies the control ratios.
Also, information from declarations is “run” through special databases - the so-called automatic control systems (ACS). The most famous of them is ASK VAT-2, with the help of which a “cross-check” of the data of all VAT returns is carried out and “gaps” in the value added chains are identified. That is, situations are discovered when tax is accepted for deduction, but at the next stage is not transferred to the budget.
ATTENTION . The risk of additional charges during a desk audit for VAT can be reduced if you check received and issued invoices with counterparties in advance.
Carry out automatic reconciliation of invoices with counterparties Connect to the service
If, based on the results of automated control, errors, discrepancies or inconsistencies are found in reporting, this is a reason for an in-depth check. An extended check is also carried out if the declaration states benefits or the amount of VAT to be refunded. In addition, reporting on taxes related to the use of natural resources is subject to a mandatory in-depth audit (clauses 3, 6, 8 and 9 of Art. Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Key features of a desk tax audit
In accordance with Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a desk tax audit is different:
In-depth desk audit
At this stage, control measures are carried out by the tax inspector. He must make sure that the taxpayer did not commit any violations when filling out the declaration and calculating the amount of tax.
To do this, the inspector sends requests for the submission of documents and information both to the taxpayer himself and to other persons (including counterparties of the second and subsequent links). If necessary, it is possible to interrogate witnesses, conduct examinations, seize documents or inspect territories, premises, documents and objects.
Also, as part of an in-depth audit, the inspector may send the taxpayer a message about errors identified in the reporting. It may contain a requirement to provide explanations or to submit an updated tax return (Clause 3 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Receive requirements and send requests to the Federal Tax Service via the Internet
When is an in-depth desk tax audit carried out?
All declarations and reports submitted to the tax authorities undergo an initial desk audit in an automated manner. The desk audit ends at this stage if no violations (contradictions) are identified and there are no grounds for an in-depth check.
If tax authorities have questions regarding submitted reports, they have the right to conduct an in-depth desk audit. The procedure for carrying out an in-depth desk audit depends on its grounds.
An in-depth desk audit can be carried out on formal grounds for an in-depth audit (declared VAT benefits, provision of explanatory documents, etc.). For these reasons, tax inspectors evaluate the submitted documents and carry out specific tax control activities. They may request additional documents from taxpayers or some information from the bank regarding the current account.
When conducting a desk audit of a declaration under the simplified tax system with the object “income,” does the Federal Tax Service have the right to request primary documents confirming the taxpayer’s expenses? The answer to this question is given by 2nd class State Civil Service Advisor E. S. Grigorenko. Study the material for free by getting trial access to ConsultantPlus.
Tax authorities carry out these procedures in order to ensure that there are no errors or distortions in reporting data or to identify violations of tax legislation.
If, during a desk audit, any violations, contradictions, or errors are identified in the declaration (reporting), tax authorities are obliged to notify the taxpayer and require documentary evidence of the data presented or reliable reporting (clause 3 of Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In cases where the basis for an in-depth desk audit are technical errors or obvious discrepancies in financial indicators in the reporting, the inspectors will require explanations or adjustments.
Since 2022, it has become mandatory to submit explanations for VAT in electronic format. Read more about this in the material “Explanations on VAT are accepted only in electronic form.”
Desk audit of VAT refund declaration
As already noted, in relation to VAT returns, including those in which the amount of tax to be refunded is declared, a two-month “delay period” has been established. It can be extended for another month if signs of violations are identified (clause 2 of Art. Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It should also be taken into account that when refunding VAT, an in-depth desk audit is always carried out. This means that in addition to the automated reconciliation of control ratios and verification of the declaration under the ASK VAT-2, inspectors will most likely request from the taxpayer invoices and primary documents on applied deductions (clause 8 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, tax authorities will conduct counter-inspections of counterparties to ensure the reality of the transactions and amounts claimed for reimbursement.
Check the counterparty for the accuracy of information in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities and signs of a shell company
If, as a result, contradictions or discrepancies emerge, then the inspectors may additionally request a sales book, a purchase book, a log of received and issued invoices (clause 8.1 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Federal Tax Service dated August 10, 2015 No. SD-4-15 / [email protected] ). Also, inspectors have the right to inspect, in the presence of witnesses, the territory and premises of the taxpayer to ensure the availability of resources to carry out the operations declared in the declaration (clause 2 of Art., clauses 1 and 3 of Art. Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Since July 2022, the rule has been in force: if the VAT declaration indicators do not correspond to the control ratios, the declaration is considered not submitted. Then the desk audit stops. In the case where the declaration has been updated, the “camera room” of the original version is resumed (see “On what grounds will tax authorities not accept reports submitted after July 1”).
Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Desk tax audit (current version)
1. A desk tax audit is carried out at the location of the tax authority on the basis of tax returns (calculations) or an application specified in paragraph 2 of Article 221.1 of this Code, and documents submitted by the taxpayer, as well as other documents on the activities of the taxpayer available to the tax authority, if otherwise not provided for by this chapter. A special declaration submitted in accordance with the Federal Law “On the voluntary declaration by individuals of assets and accounts (deposits) in banks and on amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation”, and (or) documents and (or) information attached to it, and also, the information contained in the specified special declaration and (or) documents cannot form the basis for conducting a desk tax audit.
A desk tax audit of the calculation of the financial result of an investment partnership is carried out by the tax authority at the place of registration of the participant in the investment partnership agreement - the managing partner responsible for maintaining tax records (hereinafter in this article - the managing partner responsible for maintaining tax records).
1.1. When submitting, during the period of tax monitoring, a tax return (calculation) or an updated tax return (updated calculation) for the tax (reporting) period of the year for which tax monitoring is carried out or carried out, a desk tax audit is not carried out, except in the case of early termination of tax monitoring less than three months from the date of submission of such tax return (calculation). In this case, a desk tax audit is carried out from the day following the day of early termination of tax monitoring.
1.2. If the tax return for personal income tax in relation to income received by the taxpayer from the sale or as a result of a gift of real estate is not submitted to the tax authority within the prescribed period in accordance with subparagraph 2 of paragraph 1 and paragraph 3 of Article 228, paragraph 1 Article 229 of this Code, a desk tax audit is carried out in accordance with this article on the basis of documents (information) available to the tax authorities about such a taxpayer and about the specified income.
If there are circumstances specified in paragraph one of this paragraph, a desk tax audit is carried out within three months from the day following the expiration date for payment of tax on the relevant income.
When conducting a desk tax audit in accordance with paragraph one of this clause, the tax authority has the right to require the taxpayer to provide the necessary explanations within five days.
If, before the completion of a desk tax audit in accordance with paragraph one of this clause, the taxpayer (his representative) submits the tax return specified in paragraph one of this clause, the desk tax audit is terminated and a new desk tax audit begins based on the submitted tax return. In this case, documents (information) received by the tax authority as part of a terminated desk tax audit and other tax control measures in relation to such a taxpayer may be used when conducting a desk tax audit based on the submitted tax return.
2. A desk tax audit is carried out by authorized officials of the tax authority in accordance with their official duties without any special decision of the head of the tax authority within three months from the date of submission by the taxpayer of the tax return (calculation) (within six months from the date of submission by the foreign organization, registered with the tax authority in accordance with paragraph 4.6 of Article 83 of this Code, a tax return for value added tax), unless otherwise provided by this paragraph.
If the tax return (calculation) is not submitted by the taxpayer - the controlling person of the organization, recognized as such in accordance with Chapter 3.4 of this Code, or by a foreign organization subject to registration with the tax authority in accordance with paragraph 4.6 of Article 83 of this Code, the tax authority within the prescribed period, authorized officials of the tax authority have the right to conduct a desk tax audit on the basis of the documents (information) they have about the taxpayer, as well as data about other similar taxpayers within three months (within six months for a foreign organization subject to registration registration with the tax authority in accordance with paragraph 4.6 of Article 83 of this Code) from the date of expiration of the deadline for submitting such a tax return (calculation), established by the legislation on taxes and fees.
If, before the end of the desk tax audit of the documents (information) available to the tax authority, the taxpayer submits a tax return, the desk tax audit is terminated and a new desk tax audit begins based on the submitted tax return. Termination of a desk tax audit means termination of all actions of the tax authority in relation to the documents (information) available to the tax authority. In this case, the documents (information) received by the tax authority as part of a terminated desk tax audit may be used when carrying out tax control measures in relation to the taxpayer.
A desk tax audit based on a tax return for value added tax, documents submitted to the tax authority, as well as other documents on the activities of the taxpayer available to the tax authority is carried out within two months from the date of submission of such a tax return (within six months from the day of submission by a foreign organization registered with the tax authority in accordance with paragraph 4.6 of Article 83 of this Code, a tax return for value added tax).
If, before the end of the desk tax audit of the value added tax tax return, the tax authority has identified signs indicating a possible violation of the legislation on taxes and fees, the head (deputy head) of the tax authority has the right to decide to extend the period for conducting the desk tax audit. The period for a desk tax audit may be extended to three months from the date of submission of the tax return for value added tax (with the exception of a desk tax audit of a tax return for value added tax submitted by a foreign organization registered with the tax authority in accordance with paragraph 4.6 of Article 83 of this Code).
A desk tax audit based on the application specified in paragraph 2 of Article 221.1 of this Code is carried out within 30 calendar days from the date of submission of such an application, unless otherwise established by this Code.
If, before the end of the desk tax audit, on the basis of the application specified in paragraph 2 of Article 221.1 of this Code, the tax authority has established signs indicating a possible violation of the legislation on taxes and fees, the head (deputy head) of the tax authority has the right to decide to extend the deadline conducting a desk tax audit. The period for conducting a desk tax audit may be extended to three months from the date of submission of the application specified in paragraph 2 of Article 221.1 of this Code.
The decision to extend the deadline for conducting a desk tax audit is sent to the taxpayer through the taxpayer’s personal account (if the taxpayer’s access to the taxpayer’s personal account is terminated, by registered mail) within a period not exceeding three days from the date of such decision.
3. If a desk tax audit (except for a desk tax audit based on the application specified in paragraph 2 of Article 221.1 of this Code) reveals errors in the tax return (calculation) and (or) contradictions between the information contained in the submitted documents, or inconsistencies in the information are identified submitted by the taxpayer, the information contained in the documents available to the tax authority, and received by it during tax control, the taxpayer is informed about this with the requirement to provide the necessary explanations within five days or make appropriate corrections within the prescribed period.
When conducting a desk tax audit on the basis of an updated tax return (calculation), in which the amount of tax payable to the budget system of the Russian Federation is reduced in comparison with a previously submitted tax return (calculation), the tax authority has the right to require the taxpayer to submit within five days necessary explanations justifying changes in the relevant indicators of the tax return (calculation).
When conducting a desk tax audit of a tax return (calculation) in which the amount of loss received in the corresponding reporting (tax) period is stated, the tax authority has the right to require the taxpayer to provide, within five days, the necessary explanations justifying the amount of the loss received.
Taxpayers who are obligated by this Code to submit a tax return for value added tax in electronic form, when conducting a desk tax audit of such a tax return, provide the explanations provided for by this paragraph in electronic form via telecommunication channels through an electronic document management operator in the format established federal executive body authorized for control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees. If these explanations are not submitted in the format established by the federal executive body authorized for control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees, or on paper, such explanations are not considered submitted.
3.1. If a foreign organization subject to registration with the tax authority in accordance with paragraph 4.6 of Article 83 of this Code fails to submit a tax return for value added tax within the established period, the tax authority within 30 calendar days from the date of expiration of the established period for its submission sends a notification to such organization the need to submit such a tax return. The form and format of this notification are approved by the federal executive body authorized for control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees.
4. The taxpayer submits to the tax authority explanations regarding identified errors in the tax return (calculation), contradictions between the information contained in the submitted documents, changes in the relevant indicators in the submitted updated tax return (calculation), in which the amount of tax payable to the budget is reduced system of the Russian Federation, as well as the amount of the resulting loss, has the right to additionally submit to the tax authority extracts from tax and (or) accounting registers and (or) other documents confirming the accuracy of the data entered in the tax return (calculation).
5. The person conducting a desk tax audit is obliged to consider the explanations and documents submitted by the taxpayer. If, after considering the submitted explanations and documents, or in the absence of explanations from the taxpayer, the tax authority establishes the fact of committing a tax offense or other violation of the legislation on taxes and fees, officials of the tax authority are obliged to draw up an inspection report in the manner prescribed by Article 100 of this Code.
6. When conducting a desk tax audit, the tax authority has the right to demand that a taxpayer-organization or a taxpayer-individual entrepreneur provide, within five days, the necessary explanations about the transactions (property) for which tax benefits are applied, and (or) request, in the prescribed manner, from these taxpayers documents confirming their right to such tax benefits.
The taxpayer has the right to provide an electronic register of supporting documents as an explanation. The form and procedure for filling out the specified register, as well as the format and procedure for submitting such a register in electronic form, are approved by the federal executive body authorized for control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees.
7. When conducting a desk tax audit, the tax authority does not have the right to request additional information and documents from the taxpayer, unless otherwise provided by this article or if the submission of such documents along with the tax return (calculation) is not provided for by this Code.
8. When submitting a tax return for value added tax, in which the right to a tax refund is declared, a desk tax audit is carried out taking into account the specifics provided for in this paragraph, on the basis of tax returns and documents submitted by the taxpayer in accordance with this Code.
The tax authority has the right to request from the taxpayer documents confirming, in accordance with Article 172 of this Code, the legality of applying tax deductions.
8.1. If inconsistencies are identified between information about transactions contained in the tax return for value added tax, or when information about transactions contained in the tax return for value added tax submitted by the taxpayer is identified, information about these transactions contained in the tax return for tax value added submitted to the tax authority by another taxpayer (another person who, in accordance with Chapter 21 of this Code, is charged with the obligation to submit a tax return for value added tax), or in the journal of received and issued invoices submitted to the tax body by a person who, in accordance with Chapter 21 of this Code, is entrusted with the corresponding responsibility, if such contradictions and inconsistencies indicate an underestimation of the amount of value added tax payable to the budget system of the Russian Federation, or an overestimation of the amount of value added tax, declared for reimbursement, the tax authority also has the right to request from the taxpayer invoices, primary and other documents related to these transactions.
8.2. When conducting a desk tax audit of a tax return (calculation) for corporate income tax, personal income tax of a participant in an investment partnership agreement, the tax authority has the right to request from him information about the period of his participation in such an agreement, about his share of profits (expenses, losses) ) investment partnership, as well as use any information about the activities of the investment partnership available to the tax authority.
8.3. When conducting a desk tax audit on the basis of an updated tax return (calculation) submitted after two years from the date established for filing a tax return (calculation) for the relevant tax for the corresponding reporting (tax) period, in which the amount of tax payable in budget system of the Russian Federation, or the amount of the received loss has been increased compared to the previously submitted tax return (calculation), the tax authority has the right to request from the taxpayer primary and other documents confirming changes in information in the relevant indicators of the tax return (calculation), and analytical tax accounting registers, on the basis of which the indicated indicators were formed before and after their changes.
8.4. When conducting a desk tax audit of an excise tax return in which the tax deductions provided for in Article 200 of this Code are claimed in connection with the return by the buyer to the taxpayer of previously sold excisable goods (except for alcohol and (or) excisable alcohol-containing products), the excise tax return submitted in connection with the return by the taxpayer - manufacturer of alcohol and (or) excisable alcohol-containing products of ethyl alcohol to the supplier - manufacturer of ethyl alcohol, an excise tax return reflecting tax deductions of excise tax amounts paid by the taxpayer when importing excisable goods into the territory of the Russian Federation, subsequently used as raw materials for the production of excisable goods, the tax authority has the right to request from the taxpayer primary and other documents confirming the return of excisable goods and the legality of applying the specified tax deductions, with the exception of documents previously submitted to the tax authorities on other grounds.
8.5. When conducting a desk tax audit of a tax return for value added tax, the tax authority has the right to request from a foreign organization registered in accordance with paragraph 4.6 of Article 83 of this Code documents (information) confirming that the place of provision of services specified in paragraph 1 of the article 174.2 of this Code, the territory of the Russian Federation is recognized, as well as other information (information) regarding such services.
8.6. When conducting a desk tax audit of the calculation of insurance premiums, the tax authority has the right to request, in the prescribed manner, from the payer of insurance premiums information and documents confirming the validity of reflecting amounts not subject to insurance premiums and the application of reduced insurance premium rates.
8.7. When conducting a desk tax audit of a tax return for value added tax, in which the tax deductions provided for in paragraph 4.1 of Article 171 of this Code are claimed, the tax authority has the right to request from the taxpayer documents confirming the legality of the application of the specified tax deductions, if inconsistencies are identified in those reflected in the tax return information about such tax deductions to information available to the tax authority.
8.8. When conducting a desk tax audit of a tax return for corporate income tax, in which an investment tax deduction is claimed, provided for in Article 286.1 of this Code, the tax authority has the right to require the taxpayer to provide, within five days, the necessary explanations regarding the application of the investment tax deduction, and (or) to request, in the prescribed manner, from the taxpayer primary and other documents confirming the legality of applying such a tax deduction.
8.9. When conducting a desk tax audit of a tax return, the obligation to submit which is assigned to the taxpayer in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 80, Chapters 21 and 26.2 of this Code, or a tax return, the obligation to submit which is assigned to the taxpayer in accordance with Chapter 26.1 of this Code (for with the exception of the specified declaration submitted by a taxpayer who does not have the right to exemption from the performance of taxpayer obligations related to the calculation and payment of value added tax, or who does not use this right), the tax authority has the right to request from the taxpayer, unless otherwise provided by this paragraph, invoices - invoices, primary and other documents related to transactions with goods subject to traceability, if inconsistencies are identified:
1) between the information contained in the tax return submitted by the taxpayer in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 80 and Chapters 26.1 and 26.2 of this Code, and the information contained in the report on transactions with goods subject to traceability and (or) documents containing traceability details submitted to the tax authority by the taxpayer carrying out transactions with goods subject to traceability;
2) between information on transactions contained in the tax return for value added tax submitted by the taxpayer and information on these transactions contained in the report on transactions with goods subject to traceability, submitted to the tax authority by another taxpayer carrying out transactions with goods subject to traceability traceability;
3) between information on transactions contained in the report on transactions with goods subject to traceability, submitted by the taxpayer carrying out transactions with goods subject to traceability, and information on these transactions contained in the report on transactions with goods subject to traceability, submitted to the tax authority another taxpayer carrying out transactions with goods subject to traceability.
At the same time, the tax authority does not have the right to request from the taxpayer invoices, primary and other documents related to transactions with goods subject to traceability, if inconsistencies specified in this paragraph are identified, if such documents were previously submitted to the tax authority in cases and in the manner that established by the Government of the Russian Federation.
9. When conducting a desk tax audit on taxes related to the use of natural resources, tax authorities have the right, in addition to the documents specified in paragraph 1 of this article, to request from the taxpayer other documents that are the basis for the calculation and payment of such taxes.
9.1. If, before the end of the desk tax audit, the taxpayer submits an updated tax return (calculation) in the manner prescribed by Article 81 of this Code, the desk tax audit of the previously filed tax return (calculation) is terminated and a new desk tax audit begins on the basis of the updated tax return (calculation). ).
A desk tax audit based on a tax return (calculation), according to which the tax authority, in accordance with paragraph 4.2 of Article 80 of this Code, sent a notice to the taxpayer that the tax return (calculation) was declared unsubmitted, is terminated on the day the specified notice is sent.
If the tax return (calculation) specified in paragraph two of this paragraph has been updated, then the desk tax audit is resumed based on the tax return (calculation) previously submitted to the tax authority by the taxpayer. In this case, the deadline for conducting a desk tax audit on a previously submitted tax return (calculation) does not include the deadline for a desk tax audit terminated in accordance with paragraph two of this clause.
Termination of a desk tax audit means termination of all actions of the tax authority in relation to a previously submitted tax return (calculation). In this case, the documents (information) received by the tax authority as part of a terminated desk tax audit may be used when carrying out tax control measures in relation to the taxpayer.
10. The rules provided for by this article also apply to payers of fees, payers of insurance premiums, tax agents, and other persons who are responsible for submitting a tax return (calculation), unless otherwise provided by this Code.
11. A desk tax audit of a consolidated group of taxpayers is carried out in the manner established by this article, on the basis of tax returns (calculations) and documents submitted by the responsible participant of this group, as well as other documents on the activities of this group available to the tax authority.
When conducting a desk tax audit for a consolidated group of taxpayers, the tax authority has the right to request from the responsible participant in this group copies of documents that must be submitted with the tax return for corporate income tax for the consolidated group of taxpayers in accordance with Chapter 25 of this Code, including those related to activities other members of the audited group.
The necessary explanations and documents for the consolidated group of taxpayers are submitted to the tax authority by the responsible participant in this group.
12. When conducting a desk tax audit of a tax return (calculation) submitted by a taxpayer - a participant in a regional investment project, for taxes in the calculation of which tax benefits provided for participants in regional investment projects by this Code and (or) the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation were used, the tax the body has the right to request from such a taxpayer information and documents confirming the compliance of the indicators for the implementation of a regional investment project with the requirements for regional investment projects and (or) their participants established by this Code and (or) the laws of the relevant constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
13. A desk tax audit of the calculation of insurance premiums, which declares the costs of paying insurance coverage for compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity, is carried out taking into account the provisions established by Chapter 34 of this Code.