No matter how noble the goals of an entrepreneur, the main essence of any business is to make a profit. Without a good, fairly high income, no business can simply exist. There are many areas in business. But the entire activity of a businessman, to put it very simply, boils down to selling a produced or purchased product (or service) at a favorable price. A favorable price implies a price that exceeds the cost of producing or purchasing a product.
It would seem that the greater the difference between the price of a product and its costs, the greater the profit. And indeed it is. However, if your product is too expensive, no one will simply buy it from you (unless, of course, you are the only organization in the country that produces a vital product). How then to find a middle ground so that the profit from sales is large, but at the same time the price of the product suits buyers? There are special calculation methods for this. And the markup itself depends on many factors. We will discuss these factors and the correct formulas for calculating the markup below.
Understanding the terms
Product markup is a term in business. To talk about it, we need to figure out whether we correctly understand the meaning of this term. The fact is that in business there are two very similar concepts - markup and margin. Non-professionals very often confuse them.
An entrepreneur purchases goods at the purchase price and sells them at the retail price. The difference between these two prices is called added value. And the percentage of added value from the retail price is called margin.
The markup on a product is the ratio of the purchase price to the retail price. Simply put, by what percentage of the cost of a product is the retail price higher than the purchase price.
Why do you need a markup?
It allows you to make a profit and cover all the company’s expenses associated with the sale of products. If you produce a product, then the markup should include the costs of receiving orders, delivery to points of sale, staff wages, and so on. It is also important to add profit to this amount. In order not to work at a loss and have an income, it is necessary, in addition to the cost and markup, to calculate the break-even point and the margin of financial strength.
If a company buys and resells goods, the markup is the difference between the purchase price and the retail price. However, in order to set a competitive price for products, a number of factors should be taken into account. It is important to find a middle ground between the company’s profit and a favorable price for potential customers. Next, you will learn what affects the markup and how to set it correctly.
What does the markup depend on?
The markup is never set solely at the request of the entrepreneur. This indicator is calculated based on many details. The main factors influencing this indicator:
- Characteristics of the product, its demand.
- The market situation is competition and the competitiveness of your product.
- All various expenses and expenses (cost of goods, expenses for its transportation, storage, etc.).
- The amount of tax on the product (usually included in costs).
All this must be taken into account. There are special formulas for calculating the markup. But business is not mathematics, where everything can be calculated by plugging data into a formula. This requires careful analysis and a certain amount of intuition.
Formula for calculating markup
To find out the amount of the markup in monetary terms, it is necessary to subtract its cost from the final cost of the product. This indicator can also be calculated by adding up company expenses such as taxes, intermediary commissions, personnel costs and company profits. However, it is best to rely on the break-even point when looking for markup. This way you will know the minimum premium level. See how to calculate markup percentage.
Please note that the difference between the price of a product and its cost is the gross profit. We wrote more about it in this article.
Determining the markup on a product - step-by-step instructions
Step one - we calculate the cost . The cost of a product is the total amount you spend to produce one item. Some believe that if a company does not produce a product, but purchases it and then sells it at a retail price, then the purchase price is the cost. In fact, this is not true. Don't forget about transportation and similar expenses. If you produce the goods yourself, the cost includes the price of raw materials, wages for workers, minor expenses such as rental costs, electricity, etc. In general, to determine your cost, you need to take one product and calculate how much you spent in total to produce it.
Step two - determine the threshold price. The threshold price is the minimum cost of a product at which you can sell it without incurring a loss. All costs, taxes, etc. must be taken into account here. The sale of goods must fully cover everything. Calculate all your expenses, for example, for a month. Calculate the quantity of goods produced (or purchased), subtract from this the errors for the fact that not all of the goods will be sold, something will spoil during transportation, and the like. Then divide all costs by the approximate quantity of goods - and you will get an approximate threshold price. There is simply no point in selling the product below this price.
Step three – analyze the market situation. Here it is very important to look at the market price and competition. Let's start with the market price. It must be greater than your threshold price. If the market price is lower, then you must have something special that will make the buyer buy your products at higher prices. If you don’t have anything special and your threshold price is higher or equal to the market price, then there is no point in continuing the business. It won't bring you income.
If everything is in order with the ratio of threshold and market prices, we look at the competition. You cannot enter the market by selling the same product as your competitors at the same prices. People simply won't buy your products. You must have an advantage that will make consumers pay attention to you. And to do this, you must know everything about your competitors.
Step four – analysis of the product features. It is necessary to pay attention to general features, such as the elasticity of demand. Demand is said to be elastic if it changes when the price of a product changes. Those. if demand increases greatly when prices drop, it may make sense to enter the market with lower prices than competitors.
It's worth paying attention to whether buyers will be attracted to the additional options you can offer them (if you can). For example, a new feature has recently appeared in shoe stores - selling shoes on credit. New ideas applied to the product will definitely work in your favor and allow you to raise the price higher.
Finally, you need to know exactly who your customers will be. If you are going to produce, for example, luxury watches, naturally, you can set the price for them much higher than for a simple Chinese watch. The target audience depends not only on the type of product, but also, for example, on the location of the store. For example, bags in an expensive area of Moscow will definitely cost more than the same bags in a store on the outskirts of a small provincial town.
What is a trade margin?
Trade margin is a certain amount that is added to the cost of the product. This markup constitutes the company's net income. In essence, this is added value, which is formed by increasing the price. Cost is the total cost of manufacturing products. These are expenses for transportation, raw materials, management, commercial and other expenses. Goods are almost never sold at cost, since in this case the company will only cover its costs, but will not make a profit. The final cost of goods and services includes cost and trade margin. This allows you to cover all expenses and make a profit.
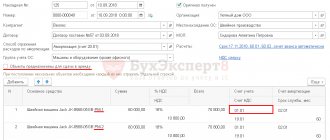
Question: How to reflect in the accounting of a retail trade organization the purchase of goods and their sale if the goods are recorded at the sale price and the organization has established a single trade margin (40%) for all goods? At the beginning of the month, a product whose sales value is 140,000 rubles was not sold. During the month, goods were purchased for 354,000 rubles. (including VAT RUB 59,000). The sales value of goods sold in the current month amounted to 528,150 rubles. (including VAT RUB 88,025). The cost of goods sold according to tax accounting data is 377,250 rubles. In tax accounting, the cost of purchasing goods is determined based on the price paid to the supplier. The cost of purchasing goods unsold at the beginning of the month is 100,000 rubles. View answer
The size of the markup in most cases is not set at the state level. But some products have price limits. If the cost exceeds the established figure, the company will have to pay a fine. This is an indirect limitation on the amount of markup. These restrictions apply to essential products. However, it cannot be said that for all other goods a markup of any size can be established. There is always such a factor as indirect restrictions. This is competition, the level of demand.
There are some peculiarities in retail trade - goods can be accepted for accounting at their sales value. It is equal to their selling price - the purchase price, increased by the trade margin. The markup is taken into account separately
Example
The company is engaged in the production of shoes. The cost of one pair of shoes is 1000 rubles. The company sets the retail price at 1,500 rubles. That is, the markup was 50%. The boots are selling quite well. They are in demand among the target audience (TA), who prefer budget options. The company, satisfied with sales, decides to increase the markup to 100%. That is, the cost of the boots will be 2,000 rubles. In this case, sales will fall, since the company has lost its target audience, but has not found new consumers, since the quality of the product remains the same. That is, indirect restrictions continue to apply. Let's look at the company's profit figures. The company sells 100 shoes per month. The costs for them will be 100,000 rubles. The company will receive revenue in the amount of 150,000 rubles. The profit generated from the markup will be 50,000 rubles.
Mathematical calculation of markup
After all the analyzes carried out, you can set a certain markup. There are two methods here.
The first one is the simplest. You simply add the desired profit to the costs and get the value. This method is as simple as possible, but it has disadvantages. First, it does not take into account changes in the market. And secondly, it does not show to what extent you can reduce the price if, for example, you are having a sale. You will not be able to accurately determine the amount of profit. It will always be less than expected, since there is almost always some part of unsold goods left, and if you have seasonal products, at the end of the season you will have to sell off the remainder at discounts. Plus, various troubles and losses can happen, from which no one is immune.
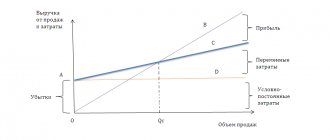
The second way is to determine the markup using the break-even method. This method allows you to set minimum production volumes at which the company will operate without losses. The markup percentage here is calculated using the formula: 1-(volume of planned gross revenue / Variable costs) * 100%. Let's say you expect gross revenue of 30 million. Costs – 10 million. 1-(30 / 10)*100% = 200%. This is the minimum markup for the product. Based on the market situation and the characteristics of the product, you increase this coefficient to the one you need. This method will provide you with 100% profit.
Accounting markup
The accounting entries used will depend on the specific transaction being carried out.
Write-off of markup when selling products
The markup should be written off after the products are sold. The total markup is calculated at the end of the month. Moreover, it is determined based on the average markup for all products. The average markup percentage is determined by this formula:
P = (TNn + TNp – TNv) / (V + OT) x 100%
The formula uses these values:
- P – average % markup.
- ТНн – markup on the balance of products at the beginning of the reporting period.
- ТНп – markup on products received during the reporting period.
- ТНв – markup on products disposed of during the reporting period (for example, goods returned to the supplier).
- B – sales revenue.
- OT – balance of production at the end of the month.
After this, the markup amount is set:
ТНр = В x П / 100%
The specified markup amount will be reversed as follows:
DT90-2 KT42
The posting includes an indication of the transaction amount and the name of the primary documents.
Reducing the markup
Sometimes a company decides to reduce the cost of products. In this case, the markup will also decrease. This is reflected as follows:
DT41 KT42
The operation involves writing off part of the cost of the goods. It should be reflected as follows:
DT91-2 KT41
IMPORTANT! If the amount of the markdown exceeds the amount of the markup, taxable profit is not reduced.
Product returns
The consumer can return the product if it is not of the required quality: defective, expired product. In this case, the company must return the buyer's money. The wiring will be as follows:
DT90-2 KT42
In this case, you will need to reverse the tax accrued from the markup.
Accounting for markups
Once the trade valuation has been determined, it must be recorded in the retail price register. The register is the primary document on the basis of which accounting entries are reflected. It records the retail price of the product. The size of the markup is fixed using this posting:
DT41 KT42
IMPORTANT! The register is formed on the basis of Appendix No. 2 to the recommendations. However, there is no mandatory form of registry. It can be created according to the needs of the company. But in any case, the primary documentation must contain the mandatory details specified in Article 9 of the Accounting Law.
Average markups
Each industry has its own markups on goods that have been established over the years:
- Clothing items – 40%-105%
- Jewelry and souvenirs – 100%-250%
- Auto parts and accessories for cars – 30%-55%
- Household utensils, household supplies – 25%-65%
- Cosmetics – 25%-75%
You can rely on these indicators when calculating your markup. But you don’t need to stay strictly within the limits. It is best to rely on competent market analysis and your own calculations.
Types of markup
There are three main types of markup. Let's take a closer look at each of them.
- Basic markup. The amount that provides income from the sale of one unit of product.
- Additional surcharge. An increase to the base cost of goods due to additional requirements of the buyer.
- Intermediary markup. This is a markup made by a dealer or intermediary to make a profit for his activities.
When setting the price for a product, it is extremely important to take into account all the company’s fixed and variable costs associated with the production and sale of products. To maintain solvency, regularly monitor various financial indicators such as margin of financial safety, gross profit, return on sales, and so on. Only with the help of competent analysis can you expand or reduce production and make other important decisions.
Offering additional services
Most people are willing to overpay when purchasing for additional services, comfort, extended warranty and other bonuses. Therefore, with a well-delivered service, entrepreneurs can safely make a higher markup than their competitors.
The presence of a guarantee is an important criterion when choosing a store
An example is elite shoe repair, which provides a visit to the client, the use of imported consumables, compensation for damaged shoes, a long-term quality guarantee, etc. The markup in such a workshop can be several times higher than that of an ordinary “shoemaker”.
Additional services in retail trade may include deferment, sale of goods on credit, free delivery or installation. But the cost of these bonuses must be taken into account when creating markups on goods. After all, the purpose of providing additional services is to increase profits, and not just to gain customer loyalty.
How to increase your markup
The store’s income directly depends on the size of the trade markup, so any merchant is interested in increasing it. How can you raise the selling price of a product to earn more? The first way is a small gradual increase in price up to 5%. Most often, a small increase in price not only does not repel buyers, but also remains completely invisible to them.
The second option is to reduce costs and purchase prices, that is, look for more profitable suppliers. Low-cost goods can be sold at the same market prices as more expensive ones. It turns out that the TN will be higher for them, but again, unnoticeable for buyers. The third option to increase the markup is similar to the second: cutting costs. Try to reduce the costs of shipping and storing goods.
The fourth option is to encourage staff to sell the highest-margin products. Works in an area where a sales consultant or manager directly interacts with the client and can offer him specific products. Such sales are subject to a higher percentage or premium.
Authority to set trade margins
Supply and demand for goods and services in the Russian Federation are regulated using a market mechanism. The state does not take part in the direct creation of trade margins on goods and services sold. It performs only control functions, as well as functions to establish the maximum amount of markup for certain groups of goods.
Enterprises, organizations, and private entrepreneurs who are engaged in economic and trading activities participate in the formation of the trade markup. Prices for certain popular groups of retail goods are set by them with the highest possible markup, which gives a decent benefit to sellers. These are products that are in constant high demand among customers:
- alcoholic and non-alcoholic drinks;
- packaged sweet and savory foods;
- flowers;
- accessories for holidays.
For some groups of essential goods, the size of the markup is determined by local executive authorities. For example, this is baby food (milk formula), food for schoolchildren and students in educational institutions, medical devices and products, special goods for the regions of the Far North. This is done in order to prevent unlimited increases in prices for this type of product. The territorial bodies of the antimonopoly service have special powers of control.
Market situation and competitor analysis
When setting a markup, you should also take into account the pricing policies of competitors. You should find out the cost of all similar products presented by your opponent. But what price should you set for yourself in the end?
You need to study prices from competitors anonymously, trying to find out all the details of their pricing policy
Under equal trading conditions, it is better not to dump and indicate the cost of goods as a competitor. Especially if there is a high probability that the rival will also reduce the price, because as a result a trade war will break out, which will bring losses to both entrepreneurs.
It is better to win customer loyalty in other ways: service, goodwill, promotions, etc. This way you can attract buyers and make a good profit due to high markups.
The ECAM warehouse accounting program will help you create your own discount card system. It is available even to entrepreneurs with small incomes who are engaged in retail trade and the provision of ]Warehouse accounting program[/anchor] allows you to maintain a customer base, analyze sales and plan purchases, so its purchase will pay for itself in a matter of months.
Customer Focus
Whatever formula for calculating the trade margin you use, the most important thing for you is that the price is focused on the target buyer. This should be an acceptable amount for his wallet. It is important to take into account the type of product, the location of the outlet, the behavior of competitors, etc.
Only by taking into account all of the above will it be possible to formulate an adequate average price for the product. For certain types of goods, a deviation of 25% is permissible, both downward and upward. Only for large, highly competitive retail outlets is it rational to introduce a larger difference from the average price.
Competitors' strategy
An important factor in pricing is competition. Not only the presence of competitors, but also their quantity and quality. Any businessman must pay due attention to studying prices for similar products from other market participants and analyzing their competitiveness.
The most important thing is to decide on a strategy in the competitor market. There are two main ones:
- Low prices and large volumes.
- High prices and small volumes.
Based on this, you need to build your own strategy.
Another important factor: the saturation of the area with offers for similar goods. If there are quite a lot of entrepreneurs in your segment offering, in general, the same products, then it would be wrong to start your activity with a high trading margin. But if you present a product that is unique in its characteristics, then starting with an increased premium will be less risky.