How is analytical accounting carried out?
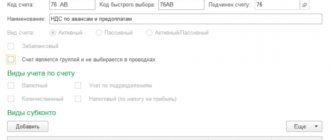
Analytical accounting is accounting that is maintained in analytical accounting accounts that group detailed information about property, liabilities and business transactions within each synthetic account (paragraph 4 of Article 2 of the Federal Law of November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ, no longer in force).
Interesting materials:
Who is Joshua in the Bible? Who is a contract soldier in the army? Who is a contractor? Who is Crash? Who is a production foreman? Who is a young specialist in Belarus? Who is a young specialist in education? Who is a waiter runner? Who is a passive investor? Who is a rooster according to concepts?
Table with explanation of charts of accounts with subaccounts
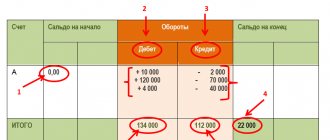
The accounting table for 2019 and 2021 is as follows:
List of accounts
| Number | Account name | Brief Explanation |
| 01 | Fixed assets | Displays general information about property, buildings that are operated or rented by the company. Subaccount: by type of fixed assets (active, inventory). |
| 02 | Depreciation of fixed assets | The cost of depreciation of intangible and tangible fixed assets that have accumulated during their use. |
| 03 | Profitable investments in material assets | This category highlights a company's investments in the rental of material assets for the purpose of generating income. For example, renting premises for a store, equipment for the production of goods, etc. Subaccount - “Disposal of material assets”. |
| 04 | Intangible assets | Intangible asset expenses include income or expenses for patents, commercial research, idea development, scientific work, and design projects. They cannot be measured in real terms, but they have their own material value. Subaccounting is carried out by type of assets and by expenses for various works. |
| 05 | Amortization of intangible assets | Loss of value of intangible assets that has accumulated during their use. Reflected in the loan. |
| 07 | Equipment for installation | Information about equipment that needs installation or configuration. For example, computer networks, equipment for production or laboratories, etc. |
| 08 | Investments in non-current assets | Reflection of assets that will subsequently be reflected as fixed assets. This broad category includes animals, land, and various works. |
| 09 | Deferred tax assets | This account contains taxes that the organization must pay. |
| 10 | Materials | Information about all materials that are used to operate a company or produce a product. For example, a company sells painted teapots and purchased unpainted goods for production. They should be included in this account. Subaccounts:
Materials refer to active accounts. The cost of raw materials or fuel before purchase is calculated according to the planned cost, which is calculated using average purchase prices. Next, take the actual price. |
| 11 | Animals being raised and fattened | As you can guess from the name, this account provides information about those animals that are not yet suitable for sale. As a rule, such cows, rabbits or birds are in feeding or fattening. |
| 14 | Reserves for reduction in the value of material assets | This section is intended to reflect the decrease in the amounts of material assets. As a rule, this happens if prices for feed, raw materials, fuel or finished products fall. |
| 15 | Procurement and acquisition of material assets | This account includes the purchase price of inventories that came from contractors, debtors or other sources. |
| 16 | Deviation in the cost of material assets | The difference between accounting prices and the actual cost of materials or inventories. Can be classified as either a debit or a credit. |
| 19 | Value added tax on purchased assets | Subaccounts:
|
| 20 | Primary production | Reflects the work or services that were used to fulfill the purpose of the institution. For example, if the goal was milk production, then this account reflects the output of agricultural products. |
| 21 | Semi-finished products of our own production | Semi-finished products that were produced by the company. |
| 23 | Auxiliary production | Additional costs that have an auxiliary function for production. |
| 25 | General production expenses | Those needs that are related to the main process only indirectly. |
| 26 | General running costs | Filling out this column is associated with general business expenses. |
| 28 | Defects in production | A collection of defective products. |
| 29 | Service industries and farms | Works and services that will be additional. This category includes expenses for food for employees, housing and communal services, organization of summer camps for children of employees, etc. |
| 40 | Release of products (works, services) | The actual cost of goods or work for a certain period. If for some reason the figure differs from the planned one, then this is also indicated in the accounting. |
| 41 | Goods | If an organization purchases goods for sale, they are indicated in this invoice. Subaccounts:
|
| 42 | Trade margin | If the company resells goods, then this section indicates their markup. |
| 43 | Finished products | Availability and movement of finished products. |
| 44 | Selling expenses | For example, packaging, delivery or fees to intermediaries. |
| 45 | Goods shipped | This category reflects those products that have already been shipped from the warehouse, but have not yet been paid for, that is, the revenue did not arrive immediately. |
| 46 | Completed stages of unfinished work | This account is usually used by organizations that perform long-term work: for example, construction companies. |
| 50 | Cash register | Subaccounts:
|
| 51 | Current accounts | |
| 52 | Currency accounts | |
| 55 | Special bank accounts | The position of funds held in letters of credit, check books or deposit accounts is indicated. |
| 57 | Transfers on the way | Funds deposited but not yet credited to the account. |
| 58 | Financial investments | Investments in securities, bonds or loans. |
| 59 | Provisions for impairment of investments in securities | Information about investing in securities. |
| 60 | Settlements with suppliers and contractors | Information on settlements with suppliers and contractors. |
| 62 | Settlements with buyers and customers | Calculations and reserves for relevant categories. |
| 63 | Provisions for doubtful debts | |
| 66 | Calculations for short-term loans and borrowings | Subaccounts according to the classification of loans and borrowings. |
| 67 | Calculations for long-term loans and borrowings | |
| 68 | Calculations for taxes and fees | Subaccounts by types of taxes and fees. |
| 69 | Calculations for social insurance and security | Subaccounts:
|
| 70 | Payments to personnel regarding wages | Information about payments to personnel. |
| 71 | Calculations with accountable persons | Payments to accountable persons. |
| 73 | Settlements with personnel for other operations | Subaccounts:
|
| 75 | Settlements with founders | Subaccounts:
|
| 76 | Settlements with various debtors and creditors | Information on payments to debtors and creditors that were not assigned to accounts 70 to 75. Subaccounts:
|
| 77 | Deferred tax liabilities | Information about the presence of deferred tax liabilities. |
| 79 | On-farm settlements | This category contains information about settlements with separate organizations. Subaccounts:
|
| 80 | Authorized capital | The state of the authorized capital is reflected. |
| 81 | Own shares (shares) | Information about purchased shares. |
| 82 | Reserve capital | State and movement of reserve capital. |
| 83 | Extra capital | State and movement of additional capital. |
| 84 | Retained earnings (uncovered loss) | Availability and movement of amounts of retained earnings. |
| 86 | Special-purpose financing | Availability and movement of funds that are needed to carry out various targeted activities. |
| 90 | Sales | A report on income and expenses that are related to the main activities of the organization. Subaccounts:
|
| 91 | Other income and expenses | Subaccounts:
|
| 94 | Shortages and losses from damage to valuables | The amount of shortages and damage to valuables. Upcoming expenses. Subaccounts: by type of reserves. |
| 96 | Reserves for future expenses | Data on expenses in the current reporting period. |
| 97 | Future expenses | Data on budget expenditures for future reporting periods. |
| 98 | revenue of the future periods | Estimated income for future periods. Subaccounts:
|
| 99 | Profit and loss | The final financial result of the organization's activities. |
Google Analytics counter to track visitor behavior
Next, we will look at how to generate the code for the Google Analytics version 4 statistics counter. GA4 is improved statistics, a lot of new functionality has been added to it:
- User scrolling the page
- Outbound clicks – registration of clicks on external links from the site
- Search the site - view search results
- Interactions with videos – start, viewing to the end are recorded (for now only for YouTube videos)
- Downloading files – registering a file download on the website
Let's see how to get the counter code
Google Analytics pixel for installation on the site. To do this, you need to create a “Data Flow” in your account.
Create Counter - New GA4 Data Stream
In the Administrator panel of the “Resource” – “Data Streams” section (see the figure above in paragraph 5), select where we will use this code
, in this case – “Web”. The “Data flow setup” window opens in which you need to specify the data of our site:
- Website URL matching your resource (be careful and indicate correctly)
- Stream name
You can refuse to track videos or download files (click the Settings gear) if they are not on your site or leave them as default.
Click the “Create stream” button and now we see the generated stream result:
- there is a stream url
- stream name
- Google Analytics Tracking ID (Data Flow ID)
- instructions for adding a tag
Click on “Global tag”, here is the pixel - the code for the google analytics counter, it must be copied and installed on the site.
Google ID will be needed in webmaster tools, in SEO plugins, for example, Yoast, All in One SEO, Rank Math, etc.
In essence, installing the code is a confirmation of your ownership rights to receive information on this site.
How to add a Google Analytics tag to your website and where to install the counter is indicated in the GA instructions - they recommend installing in
, which covers all pages of the site and this recommendation is suitable for WordPress and other CMS. You can put the code in the footer, header, or create a separate web stream to track some individual pages or blocks.
Now, when we go to the administrative area, Resource → Data Streams, we see our counter.
Connect a Google Analytics counter to your website. 1000 rub.
+7(951) 689-22-35 More contacts
Getting started - signing up for Google Analytics
If this is your first counter in GA, you will need to create a new account. Go to the service page https://analytics.google.com/analytics/web/ in your Google account. (Of course, you must have a Google account and a mailbox; if you don’t have them, you need to create one).
A welcome page opens, where we select “Create an account” and proceed to the next step.
If you have an account, then after logging into it, select Administrator in the side menu. A panel will open in which you can create a New Account or New Resource - go to point 5
Information about the site and account during registration.
Here you need to fill in information about your resource.
- “Account name” is a mandatory item; you must enter a name that you will see in the statistics and that will be understandable if we have several counters.
Enter the Account Name and click the “Next” button. If you wish, you can uncheck all the accesses offered by Google (technical support and for Google specialists), I uncheck them. - The next step of GA4 is Configuring the resource. You must specify:
- Name of your resource
Specify “Time Zone” for ease of viewing time-related statistics
- Specify the currency – for the convenience of calculating conversions
- Information about the company. Fill out information about your field of activity and your goals (I can’t advise anything else
In “Advanced Settings” you can connect the old version of Google Analytics, which is now called Universal Analytics. By default it is disabled. If you don’t need it, then just click “Next” and move on to the next step.