Do you know how many federal laws are in force in Russia? Five thousand! And there are even more amendments to them and regulations. It is impossible for any individual entrepreneur to know all our legislation, so today we will talk about the most important laws that are important for business.
Probably, so many laws are necessary. But it’s difficult even for specialists to navigate them. And non-specialists recall the phrase of the ancient Greek historian and writer Tacitus that the closer a state is to its fall, the more numerous its laws.
But, be that as it may, IPs are obliged to know their basic laws in order to simplify their life and not get into trouble.
No. 2 – Article 171 of the Criminal Code on illegal entrepreneurship
If you decide to do business, then you must do so according to the law, that is, you must, firstly, register. Secondly, you should obtain a license if your business is required to have one. Thirdly, you must comply with the conditions of your activity dictated by a license or special permit.
A business without registration and compliance with other conditions, in which you regularly receive income, is illegal and subject to punishment.
First of all, illegal business activities are punishable by fines. The size of the fine depends on the scope of your illegal business. The penalty can range from 2,000 rubles to 500,000 rubles if the state damage is assessed as damage on an especially large scale.
But the fine is not the only expense for illegal business. You will also be required to pay a tax of 13% on your entire income, since according to the law you are an individual and are not entitled to a preferential tax system.
Federal Law 129 on state registration of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs: basic provisions
This federal law was adopted and came into force on August 8, 2001. The Law on State Registration of Legal Entities and Individual Entrepreneurs consists of a preamble, chapters, articles and paragraphs.
It regulates legal relations arising in the public sphere. registration of various types of legal entities. persons, for example, LLC, JSC, etc. Among other things, this regulatory legal act also affects the state registration of individuals acting as individual entrepreneurs.
Federal Law 129 is far from the only legal act that regulates such relations. This also includes the law on limited liability companies, the law on joint stock companies, the civil code of the Russian Federation, etc.
The body that carries out registration is the executive authority of the Russian Federation. In this case, it is the federal tax service. It is she who maintains the relevant register, enters the necessary data, and carries out control and accounting in this area.
Article 5 of Federal Law 129
This article regulates the content of registers. It must contain the following data:
- Name, both full and abbreviated, as well as other details and locations.
- Form of formation, for example, limited liability company, joint stock company, etc.
- Phone number and email.
- An indication of whether this legal entity is newly created or reorganized.
- Information about the persons who are part of the legal entity (shareholders, founders, etc.).
- Constituent acts (charter or agreement) and other data that the founder would prefer to include.
As for individual entrepreneurs, this kind of information is also entered into their register. In addition to the above, you must also indicate the passport details of the individual here.
Article 9 Federal Law 129
The procedure for submitting documents to the registration authority is regulated here. It is indicated that several methods of transfer can be chosen, for example, by mail, by a multifunctional center, or by personal appearance at the registration authority.
In a situation where acts are submitted through the MFC, they are sent to the tax office no later than the next business day. The response is also sent to the multifunctional center, of which the applicant is notified.
Article 11 Federal Law 129
It is stipulated here that the decision on state registration will have legal force only after the corresponding entry has been made in the register. The entry is confirmed by documents provided by the applicant.
The registration authority is also responsible for sending information about the newly created legal entity to all interested government agencies.
Article 12 of Federal Law 129 on state registration of legal entities
Here is a list of documents that need to be submitted when performing registration actions.
This includes:
- Statement.
- Founding document.
- Location data.
- Minutes of the meeting at which the decision to create a legal entity was made.
- Acts on the ownership or lease of the building or structure in which the place of registration of the legal entity will be located.
All acts are provided in original form. If the documents are submitted by a representative, he is also required to provide a notarized power of attorney.
Art. 17 Federal Law 129
This article regulates the procedure for providing documents if it is necessary to make changes to the charter of a business entity.
Since the Unified State Register of Legal Entities contains information about all the constituent documents of the enterprise, any amendment to them must also be reflected in the register. To do this, you must provide a new document to the registration authority and write a statement indicating the reason for making certain changes.
Art. 21 Federal Law 129 on state registration of legal entities
Here the liquidation procedure is explained in more detail and the documentary acts that must be provided in this case are listed.
This includes an application, a decision on liquidation, acts confirming the payment of state duty, the balance sheet of the enterprise, etc.
Liquidation will be considered completed only when the corresponding entry is made in the unified state register.
Art. 22 Federal Law 129
The liquidation process is described here in more detail. For this purpose, a liquidation commission is created. It is she who must notify the Federal Tax Service of the results of this procedure and provide other important information no later than two months before the end of the procedure.
The article states that the register is periodically checked for the presence of defunct legal entities that have not reported the termination of their activities. These are subject to removal from the register with appropriate justification.
Art. 23 Federal Law 129 on state registration
It regulates what requirements a refusal of state registration must meet.
The refusal must be made in writing. No later than three days after the relevant decision is made, the applicant must be notified of the refusal.
Failure may occur when:
- Incorrect documents provided.
- The documents do not comply with legal requirements.
- Violations were not corrected within the allotted time frame, etc.
A refusal on any of the above grounds can be appealed. To do this, you can contact the registration authority itself. You can also file a lawsuit in court to appeal an unlawful act.
No. 3 - 422-FZ on professional income tax or the law on self-employed
Today, for legal business activities, it is not necessary to register an individual entrepreneur or LLC. You can become self-employed. If your business is small, then this registration form is the most profitable and simplest for you.
The law has been in effect for the second year. It showed excellent results, which led to the expansion of its coverage area.
We have written a lot and in detail about the self-employed, but let us remind you that these are people who legally engage in their activities for the purpose of making a profit. They pay a tax of either 4% or 6%. They do not pay mandatory insurance premiums. They do not submit annual declarations and do not maintain KUDiR.
Of course, there are conditions that must be met. You need to know them, and we also wrote about them. For example, your annual income should not exceed 2.4 million rubles. If you earn more, then you cannot be self-employed and you need to register an individual entrepreneur or LLC.
No. 4 - Tax Code on taxation systems
If you are an entrepreneur, then you are required to pay tax on your income. But, according to the Tax Code, you have a choice of how to pay this tax.
Firstly, everyone can pay taxes according to the main system - OSNO. This system is quite complex, however, it has no limitations and is suitable for any business.
Secondly, you can pay taxes under one of 4 preferential tax systems if you meet all the requirements of a particular system and have written a corresponding application to your tax office.
Preferential tax systems include:
-STS “Income” or “Income-expenses”;
-patent;
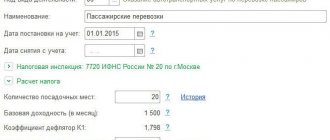
-UTII;
-ESKHN.
Changes in the law
The latest changes and additions to this document in the Russian Federation were related to the possibility of filing an application for registration using the Internet. Among other things, now a representative of a legal entity or an individual entrepreneur can contact a multifunctional center dealing with entrepreneurship issues.
Another innovation is that now, in case of refusal of state registration, a citizen has the right to eliminate the violations committed within three months and re-submit the missing acts once.
Repeated submission of documents is not allowed. In this case, you will have to go through state registration again.
No. 6 - 152-FZ or the law on personal data
Yes, personal data has recently come to the attention of the law, and it protects it. If your company has a website or staff, or a salary project in a bank, then you collect personal data. And since you are doing this, you are the operator of personal data and must notify Rospotrebnadzor. In addition, you must place information on your privacy policy on your website and ask everyone for consent to the processing of their personal data. If there is no such consent, then you are breaking the law.
Let us remind you that personal data is any information about a person: first name, patronymic, last name, address, email, phone number, etc.
Contents of OGRN by numbers
The registration code is formed by 13 characters and contains data that makes it possible to accurately identify the organization.
An example with the contents of the OGRN by numbers is given in the table:
| Decoding | P | D | D | F | F | R | R | X | X | X | X | X | WITH |
| OGRN | 1 | 1 | 9 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 8 | 3 |
The symbols in the code have the following meanings:
- P – sign of assignment of the state registration number of the record. Can take the following values: 1 and 5 (OGRN sign), 2, 6, 7, 8, 9 – sign of another record number.
- DD is the year in which information about a legal entity was entered into the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, indicated by the last two digits (for example, for 2019 – 19).
- FF – code of a subject of the Russian Federation in accordance with the list of subjects established by the Constitution (for Moscow – 77).
- RR – code of the Federal Tax Service body carrying out registration.
- XXXXX is the number in the order of entry in the register, its calculation begins with the value “00001” every year.
- C is a checksum that allows you to check the correctness of the identifier assignment.
Why is OGRN needed?
The identification code issued to a legal entity is used in parallel with other information, so why is OGRN needed and why only legal entities have it. This code must be indicated in the company’s payment details, in information about the company on the official website of the Federal Tax Service, as well as on the government services portal. Also, the identifier must be indicated in any forms in which information about the company is required, and there is a line intended for this. This identifier is used when changing the name of an organization; it can be used to check a company or obtain certain information about its activities.
OGRN is assigned only upon registration of legal entities. Individual entrepreneurs receive a OGRNIP code. Self-employed persons do not need to obtain such an identifier at all.
No. 7 - 55-FZ or the law on online cash registers
This law has been in effect since 2022 and obliges almost all individual entrepreneurs to have certain online cash registers with a fiscal drive. Thanks to such cash registers, the tax office immediately and directly learns about all the cash receipts of your business.
There are few exceptions; they are all specified in the law. The deferment until 2022 applies to individual entrepreneurs without employees who produce something themselves or provide a service.
If you are required to have an online cash register, but work without it, you will be subject to administrative liability, that is, a fine.
No. 8 - 115-FZ law on combating the legalization of illegal income or cashing out
This law applies to banks and entrepreneurs, and often threatens the latter with blocking of the current account. According to the law, the bank monitors the individual entrepreneur and opposes his gray transactions, from which taxes may not be paid, with bribes and fraudulent schemes, as well as with the arms trade. In essence, the bank blocks any actions of the individual entrepreneur that seem suspicious to it. And the entrepreneur himself must prove to the bank that he is not a criminal, but has an honest income, from which he pays all required taxes and payments.
The criteria for suspicious transactions are precisely contained in 115-FZ. The bank itself doesn't come up with anything.
No. 9 - 294-FZ or the law on scheduled and unscheduled inspections
According to the law, individual entrepreneurs can be routinely inspected once every three years. But don’t be too happy, as there are also unscheduled inspections.
You can find out about scheduled inspections in advance by studying the website of the regulatory authority. There, all information on such checks is freely available.
It is impossible to know about unscheduled inspections in advance, since they are usually scheduled after a complaint. Nobody warns you about them. In addition, the inspection body does not understand who exactly the complaint came from: from an offended client or from a dishonest competitor.
A separate category of audits is on-site tax audits. They can happen at any time and without warning.
What can you find out from the OGRN
The main state registration number is a valuable source of information about the company, which can be found out from the OGRN listed below:
- Missing information about the counterparty or partner.
- Information about the director of the organization. Using the OGRN, you can find out the last name, first name, and patronymic of the manager. Thanks to this, it is possible to check whether certain documents, for example, a power of attorney, are actually signed by the current head of the legal entity.
- The presence or absence of problems with government agencies at the head of the organization, whether he is on the list of unreliable persons of the Federal Tax Service.
- The current status of the company - whether it really exists, whether the company is closed. You can also check some information about the current state of affairs of the organization.
- The exact legal address of the organization as indicated in the company's registration entry in the register.
- Compare the information in documents that come from partners with the real data that is indicated about them in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities in order to prevent the possibility of fraud.
- The reliability of the company, the fact that it is or is not on the blacklist of the local authority of the Federal Tax Service.
In general, the OGRN number performs an important function. It is assigned to the company for the entire duration of its existence, without changing when the name or management changes. Thanks to this, you can always check data about any legal entity. Using this identifier, you can track information about the company even after a long time.
No. 10 - 38-FZ or the law on advertising
Any business needs advertising, as it is an effective way to attract not only attention, but also customers. However, you need to know what and how to advertise. The law is tough, has many nuances, violations are punishable by fines of up to 800,000 rubles and suspension of advertising itself. Therefore, any entrepreneur should study this law in his own interests.
For example, you cannot advertise a service if it requires a license and you do not have one. You cannot use a doctor in non-medical advertising. You cannot say that your product or service is approved by the government. In general, there are a lot of these “don’ts”, sometimes you don’t even think about them.