2021-09-20 6565
Assets, profits and cash flow describe a business, how it is doing and how attractive it is to investors. These terms were discussed in detail in the article “10 financial concepts.” In this material, together with tutor Natalya Ostapyuk, we looked at what is included in financial statements and how information on these parameters is reflected in the company’s three main reports:
- Balance sheet
- Profit and Loss Statement (OPL)
- Cash Flow Statement (CFS)
Where is depreciation shown on the balance sheet?
It is impossible to see the amount of depreciation in the balance sheet, since in this accounting form all assets are reflected at their residual value, that is, minus depreciation. By debit account 01 “OS” the initial cost is fixed, depreciation is accrued on the credit account. 02, in the balance sheet they indicate the difference between the initial cost and accrued depreciation (credit balance of account 02) - the residual value in line 1150. This is the principle of constructing the balance sheet - the user of financial statements should see the real cost reflection of assets as of a certain reporting date.
So, depreciation of fixed assets is taken into account on the account. 02, which according to its characteristics is regulatory, i.e., does not have independent significance. It is used only in conjunction with main account 01, which takes into account the initial cost of depreciable property. The same algorithm is applied to intangible assets, the initial cost of which is fixed on the account. 04 and is regulated by the calculation of depreciation according to account. 05. Thus, it is impossible to see depreciation charges in the balance sheet. Accrued depreciation is not recorded in the balance sheet, since it is not an asset, but transfers the value of the property to production costs, participating in the formation of production costs.
What is profit and loss reporting?
Profit and loss statements show not only the financial performance of the enterprise, but also how certain funds were received and spent. Such a report allows you to analyze the effectiveness of the organization. It is considered on a par with the balance sheet as one of the most important sources for analyzing the economic situation in the company.
In addition, the report can be used for the following purposes:
- Comparative analysis of the current reporting period with the past one to identify positive and negative trends.
- Determination of factors affecting the final financial result of the activity.
- Studying the structure, composition, as well as the dynamics of gross profit, income from various sales, net profit, etc.
- Determining the effectiveness of a particular organization, as well as the level of benefits of investments in this enterprise.
Reporting on profits or losses is prepared in accordance with Form No. 2 established by the Ministry of Finance. Knowledge of this form is mandatory for all accountants and financiers.
Depreciation: fixed or variable costs
Since the amount of accrued depreciation of fixed assets practically does not depend on changes in production volume, it is classified as a fixed cost: no matter what method of calculating depreciation is adopted by the company, the amount of monthly deductions will remain unchanged both with the volume of output, for example, 100 units of product, and with production of 1000 units.
If the economist has no problems with the issue of the constant nature of such costs as depreciation, then attributing them to direct or indirect costs often involves enormous analytical work and the subsequent consolidation of the methodology for determining costs in the company’s accounting policy.
Structure of the income statement
The report structure contains several components:
- Income . This report item consists of any kind of contributions that increase the company's budget, without taking into account the contributions of the owners. One of the most important items in income is revenue. Revenue includes rent, sales, interest and dividends, payments for services, and royalties. Other types of income in their essence differ little from revenue and serve to increase the company’s budget.
- Expenses . Expenses include all operations that reduce the economic benefits of the enterprise by wasting fixed capital in one direction or another. Expenses include various losses, as well as natural costs that arise during the operation of the enterprise.
- Gross profit . It is calculated by deducting the cost of goods sold from sales revenue. From the resulting gross profit, the remaining expenses that are not included in the production costs are subtracted.
The document form looks like this:
Thus, the holistic structure of the report includes income and expenses with all their items, as well as detailed calculations to determine the performance of the enterprise.
How to prepare a profit and loss statement?
Sometimes in business documents, long nomenclature is specifically replaced with this - capacious, short and clear - form No. 2. The following items must be filled in:
- Income statement with expenses for ordinary activities . According to the direct nature of the enterprise's activities, it itself declares which of its income and expenses relate to ordinary activities and which do not. For example, an ordinary type of activity may be considered to be one whose share of income is more than 5% of the total amount of income.
- Other income and expenses . Such income and expenses include operating, non-operating and extraordinary income or expenses. It is important to take into account that non-operating and operating expenses and income are reflected in one account (91), and emergency ones in another (99).
- Determination of financial result . This article reflects directly the calculations that determine the “net” income of the enterprise or loss from sales, depending on the efficiency of work. This calculation is made before taxation, so it does not show completely accurate data. The financial result is indicated under line 050.
- Income tax calculations . Here you must indicate the amount of tax on current profits. It is determined according to tax accounting for the reporting period. In accounting, the indicated amount should be reflected in account 68.
- Calculation of net profit or loss . In this case, the accountant will need to indicate the net profit or loss, taking into account various nuances for the billing period. The form also provides for writing net profit or losses for the past year for comparative analysis.
- Reference Information . As reference information, the Ministry of Finance recommends indicating the amount of the organization’s permanent tax liabilities, as well as the amount of basic and diluted loss (or profit) per share in accordance with the current economic situation.
The procedure for filling out a report can be significantly simplified by relying on the sample filling offered by the Ministry of Finance:
Depreciation: direct or indirect costs
The point is that Ch. 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not provide direct instructions limiting enterprises from classifying any specific costs as direct or indirect. And this becomes the basis for the taxpayer to classify the amounts of accrued depreciation as indirect expenses.
However, during audits, tax authorities often raise the issue of grading these costs, citing the fact that the enterprise’s choice regarding the costs that form the cost of manufactured products must have a strong justification, i.e., in the company’s accounting policy it is necessary to establish a clear mechanism for allocating costs into direct and indirect using economically sound indicators .
Form and general rules for filling out
Reporting is prepared strictly on the OKUD 0710002 form approved by the Ministry of Finance. Free forms are prohibited. The structure of the profit and loss statement involves indicating information about the organization's income and expenses recognized in the accounting records for the reporting and previous years in the form of a table. To fill out the form correctly and accurately, you must have the following documents on hand:
- turnover balance sheet;
- balance sheet for the subaccount “Other income” to account 91 “Other income and expenses” (with breakdown by subaccount);
- balance sheet for the subaccount “Other expenses” to account 91 “Other income and expenses” (with breakdown by subaccount).
Take information for the previous year from the previously submitted Form 2. If there is no data to fill out, put dashes in the appropriate lines. The report is prepared in thousands of rubles.
Depreciation in the income statement
So, if fixed asset depreciation is not shown on the balance sheet, where can you see it? In the form of financial statements - a statement of financial results. True, depreciation amounts can be reflected in it on several lines, depending on the type of activity. For example, if fixed assets are used exclusively in the production process for the main activities, then depreciation will be taken into account in line 2120 “Cost of sales”. For depreciation of assets used in trading activities, line 2210 “Business expenses” is provided.
If the fixed assets are used by the company in auxiliary production that is not related to ordinary types (for example, leasing, provided that this activity is not declared as the main one), then these costs are reflected in other costs on line 2350.
When the fact of using PF for general business purposes is established in the accounting policy, the amount of depreciation may be reflected in line 2220 “Administrative expenses”.
You can find out the exact depreciation amounts from the transcripts attached to the form.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
New name - same content
The new name of the report, which all organizations must annually submit together with the balance sheet to the territorial body of Rosstat and the Federal Tax Service of Russia, is “Report on Financial Results.” It contains information about the organization’s income and expenses for the year, and many “old school” accountants, out of habit, call it by its old name - the profit and loss statement. The current form is given in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated November 25, 2019 No. VD-4-1 / [email protected] (in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 19, 2019 No. 61n).
IMPORTANT!
A new form of income statement is required starting with reporting for 2022. But it is allowed to be used when reporting for 2019.
In addition, there is a profit and loss statement, the form of which is shorter than the usual one. It is filled out by small businesses that have the right to submit simplified reporting.
The annual financial statements, in accordance with Article 14 of the Federal Law on Accounting, include:
- balance sheet;
- statement of financial results (profit and loss statement (form 2));
- applications to them (usually form 3 and others).
The organization submits the entire final set together; Rosstat and the Federal Tax Service do not consider these forms separately.
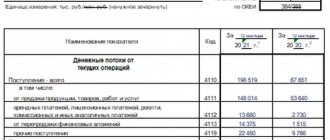
Cash Flow Statement (CDS)
DDS is filled out “for payment” and not “for shipment”. The report should include income and expenses for all accounts and cash. Transfers between accounts are no exception; they help keep track of balances. The DDS is intuitive and questions rarely arise about it.
Often the report is divided into three blocks:
1. Operational activities - payments for main business processes.
2. Investment activity - long-term investments, for example, in fixed assets: transport, premises, equipment.
3. Financial activities - payments for loans and borrowings.
Profit and loss statement according to IFRS
IFRS is an international financial reporting standard. Novice accountants may confuse this type of reporting with accounting reporting standards (for example, Russian PBU). IFRS is a standard that reflects the final stage of accounting work on the report. IFRS uses two options for presenting expenses, according to which expenses are broken down into subclasses. Let's look at these methods in more detail:
Nature of costs
The criterion for the nature of costs involves combining costs in accordance with their nature and excluding further redistribution according to their purpose within the organization. This method is considered the simplest due to the absence of the need to distribute expenses.
According to this method, classification includes:
- revenue;
- Other income;
- changes in the quantity of leftovers of manufactured products or work in progress;
- raw materials and supplies that were used;
- employee expenses;
- depreciation and other expenses;
- general expenses;
- calculation results.
By purpose of costs
A more complex method that involves a significant amount of paperwork. In this case, expenses will need to be divided into subclasses according to their purpose as cost of sales. The distribution is quite subjective, which is one of the very serious disadvantages of the method. However, it provides more useful information than the previous method.
The classification will include:
- revenue;
- cost of sales;
- gross profit with other income;
- costs and expenses, including administrative;
- final net profit.
Russian practice provides for the classification of costs precisely by functional purpose as the most effective for analyzing the activities of an enterprise.