No one is immune from tax debt. Is it possible to write off the resulting debt, if so, how to do it? Let’s look at these and other related issues.
ATTENTION: watch the video about appealing a tax decision and the participation of a lawyer in a tax audit. Subscribe to the YouTube channel to receive free advice on taxes and other issues through comments on videos:
Is it possible to write off tax debt?
On the issue of the possibility of writing off tax debt, Art. 59 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation speaks about the possibility of recognizing arrears and debts on penalties and fines as hopeless for collection and writing them off in the following cases:
- in case of liquidation of a legal entity, exclusion of a legal entity from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities by decision of the tax authorities
- in the event that an individual entrepreneur is declared bankrupt in terms of arrears, debts on penalties and fines that have not been repaid due to the insufficiency of the debtor’s property
- if a citizen is declared bankrupt
- if a citizen has died or been declared dead, the write-off is carried out in the part that exceeds the amount of the inheritance
- if the court has adopted an act according to which the tax office has missed the statute of limitations for debt collection
- in other cases
Tax Debt Relief Act 2022
In 2022, a large-scale amnesty was announced for a number of unpaid tax obligations. Relief from debt burden affected individuals and commercial entities. The Federal Law on writing off tax debts this year, in contrast to previous cases of tax amnesty, involves the repayment of not only fines and accrued penalties, but also the debts themselves.
Write-off of property tax debts payable by individuals is possible for a group of debts generated on the first day of January 2015. Art. The law provides for the recognition as hopeless of arrears for the following types of taxes:
- It is allowed to write off transport tax debts of individuals in 2022 for 2013;
- the norm applies to property tax amounts;
- land tax is written off.
The regulatory authorities will “forgive” the debt and penalties accrued on its amount, prescribed fines that were already recorded before 2015. If a person has debts for which the penalty continued to be calculated and added to the total amount of arrears after January 2015, then the debt will be forgiven in full. Writing off tax debts from individuals in this case will also affect that part of it that falls on penalties for the period of time after January 1, 2015
Application for writing off tax debts - a sample is not needed for this, since individuals will not need it - tax officials will independently carry out the procedure for paying off debts. The debtors themselves will not be notified.
The 2022 transport tax debt must be written off by linking the amounts of arrears to the deadline for payment of the tax liability. That is, debts for 2013 will be forgiven, and obligations accrued for 2014 are subject to repayment, since their payment period falls on the period after 01/01/2015. You can read about how transport tax (debts of individuals) are written off in our article.
Documentation of the procedure is carried out by the Federal Tax Service in any form. The templates developed by the tax authority must contain information identifying the debtor and the amount of the arrears, broken down into the principal debt, penalties and fines. Write-off of tax arrears from 2022 does not take into account the amount of the debt. The main criterion for selecting hopeless arrears is the timing of their occurrence.
How to write off debts to a pension fund?
The pension fund may recognize financial sanctions as hopeless for collection and write them off.
Resolution of the Board of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation dated August 28, 2017 No. 600p approved the procedure for writing off financial sanctions, according to which the write-off is carried out on the basis of a decision made to recognize them as hopeless for collection.
According to Art. 11 Federal Law No. 436 dated December 28, 2017, arrears on insurance contributions to extra-budgetary funds of the Russian Federation for periods that expired before January 1, 2017, attributed to individual entrepreneurs and other persons engaged in private practice are recognized as uncollectible and subject to write-off. The decision is made by the tax office.
What can a taxpayer do?
- the taxpayer has the right to initiate recognition of his tax debts (contributions, penalties, fines, interest) as uncollectible (Definition of the Constitutional Court dated May 26, 2016 N 1150-O);
- since pre-trial procedure for writing off tax debts at the initiative of the taxpayer, you should immediately go to court to recognize debts as bad (Decision of the Supreme Court dated November 2, 2016 N 78-КГ16-43);
- After the decision to recognize the debt as bad comes into force, you can contact the tax authority with an application to write off the debt based on a court decision.
How to write off taxes under the tax amnesty?
The tax authorities write off taxes under the tax amnesty independently.
In some cases, due to a technical error or other reasons, the tax office may not write off the tax, and therefore the individual or individual entrepreneur will be in debt. In such a situation, the taxpayer should submit an application to the tax office, indicating a request to write off the debt.
At the same time, the procedure does not provide for the initiation of a procedure for recognizing a debt as uncollectible at the request of the taxpayer, since the tax office itself decides to write off taxes or not.
How are bad tax debts written off?
So, the concept of “writing off bad tax debts” is multifaceted: this method of debt relief includes their cancellation as a general rule (if the collection period has expired) and tax amnesty. First of all, let's figure out when the debt is canceled under Art. 59 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It should be noted that the tax office may require payment of the debt within 3 years.
This period is provided for both transport tax and payments for real estate (apartments, houses, etc.) and land. It is possible to write off tax provided that the tax authority:
- did not send a request for its payment to the taxpayer;
- did not file a statement of claim in court (if there is a debt, tax authorities have the right to go to court to collect the debt from the taxpayer);
- did not present the writ of execution for execution.
To write off a tax, you do not need to submit any applications to the tax authority, since the debt is written off by the inspectorate itself. But, of course, if there are grounds for writing off the debt, but this does not happen, the taxpayer has the right to submit a corresponding application to the tax office. If a controversial situation arises, it may be necessary to go to court to recognize the debt as bad and, accordingly, for its subsequent write-off.
It is important that tax authorities are given the right through the court to restore the deadline for filing claims against the taxpayer that was missed for good reason. If the term is restored, then it will no longer be possible to write off the debt.
Statement of claim for write-off of tax debt
Taxpayers may file an administrative claim in court to declare tax debts uncollectible. The following information must be indicated in the claim:
- name of the court that will hear the claim
- information about the plaintiff (full name, address, telephone number)
- information about the tax defendant (name, address, TIN)
- title of the document – administrative statement of claim
- the text of the claim must set out the circumstances of the case, why the debt should be considered uncollectible with legal justification
- the pleading part sets out specific requirements that the plaintiff asks the court to satisfy
- the list of attachments indicates the documents attached to the claim
- at the end of the claim there must be a signature of the plaintiff
USEFUL : watch a video with tips on filing a claim, and also order a ready-made version from our lawyer
How to write off debts on penalties
Until 2015, an enterprise’s debt for penalties, interest and fines was considered uncollectible due to the completion of enforcement proceedings if 5 years had passed from the date the debt was formed. In this case, the amount of debt had to be less than the requirements for the debtor approved for initiating proceedings to declare him bankrupt.
Since 2015, writing off a debt, the collection of which is considered impossible due to the bailiff issuing a resolution to complete the enforcement proceedings when returning the writ of execution to the collector on 2 grounds, if more than 5 years have passed since the discovery of the arrears or the debt for fines/penalties, possibly in the next situations:
- If the amount of debt turns out to be no more than the claim against the debtor, approved at the legislative level due to the lack of an amount of money sufficient to compensate for the legal costs of initiating processes related to the bankruptcy case.
- If the court returned the petition to declare the debtor bankrupt or terminated the bankruptcy proceedings due to a lack of funds that would be sufficient to compensate for the legal costs of the procedures necessary to consider the bankruptcy case.
The writ of execution must be returned to the claimant after the initiation of legal proceedings in the following cases:
- If the debtor does not have property that could be recovered to pay off the debt. Or all the measures that the bailiff took within the framework of the law to search for such property were unsuccessful.
- If the location of the debtor could not be established. Or it was not possible to discover the location of his property. No information was found about whether the debtor has valuables and money in storage at the bank, in deposits, or in accounts (this does not mean situations where the law provides for the search for property or the debtor himself).
It is also worth mentioning the documents that are evidence that the debt on penalties, fines and interest is recognized as hopeless for collection. Until 2015, the list consisted of only 2 documents - a certificate from the Federal Tax Service and a resolution of the bailiff. Today the list includes:
- A copy of the resolution on the completion of enforcement proceedings when returning the writ of execution to the claimant from the bailiff.
- Certificate from the Federal Tax Service on the amount of debt and arrears of interest, fines, penalties.
- A court ruling on the return of an application to declare the debtor bankrupt (or to complete the paperwork due to the lack of money to compensate for legal costs associated with the bankruptcy procedure).
How to calculate the statute of limitations for taxes?
To calculate the limitation period, the amount of debt and the deadline for fulfilling the claim are important.
The tax office issues a demand to an individual to pay a tax, fine, or penalty and sets a deadline for fulfilling such a demand. After the expiration of the deadline for fulfilling the requirement, the tax authority goes to court within 6 months if the debt exceeds 3 thousand rubles. If the amount of the debt is equal to or less than 3 thousand rubles, then the debt is collected after 3 years, when the deadline for fulfilling the requirement expires. The period for filing a claim is 6 months.
The limitation periods for debt collection from legal entities are considered the same as for collection from individuals.
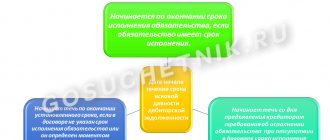
Grounds for recognizing debt to the budget as uncollectible
If an organization has a debt to the tax authorities for which the statute of limitations has expired, then the tax authorities cannot force them to pay these debts to the budget.
However, it can be excluded from the RSB card only if the debt is considered uncollectible. Often, the reason for writing off arrears is either the cessation of activity or the insufficiency of property to pay off debts to the budget, for example, the liquidation of an organization, declaring an entrepreneur or individual bankrupt, the death of a taxpayer, a bailiff issuing a decree to terminate enforcement proceedings due to the impossibility of collecting arrears (sub. 1–4.1 clause 1 article 59 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It is possible to recognize the debt as uncollectible for collection through the court. This is carried out on the basis of a judicial act, from which it follows that the deadline for collecting arrears has expired, and therefore the tax authorities do not have the right to collect debts on taxes and fees. Such a conclusion can be contained in both the operative and motivational parts of a judicial act on tax disputes (clause 9 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 30, 2013 No. 57, order of the Federal Tax Service dated April 2, 2019 No. ММВ-7-8 / [email protected] ). Such acts include:
- a court decision on the merits of the issue, for example, the inspection denies the possibility of collecting debts from the taxpayer for payments to the budget, since the period for their collection has expired (Part 1 of Article 167 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation);
- a court ruling to refuse the tax authority to restore the missed deadline for filing an application for debt collection with the court (subclause 4, clause 1, article 59 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- another judicial act on any tax dispute that contains a conclusion that the inspectorate has lost the right to collect arrears, fines, and penalties from the taxpayer due to the expiration of the period for their collection.
The tax inspectorate is obliged, immediately after the entry into force of one of the above judicial acts, to exclude the entry about the debt from the taxpayer’s personal account (paragraph 4, paragraph 9 of Resolution No. 57 dated July 30, 2013).
A ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus will help you determine whether the statute of limitations for collecting taxes, penalties, and fines has expired. Trial access to the legal system is provided free of charge.
Read about the rules for accounting for written off accounts payable in this article.
Appeal against refusal to write off debt under tax amnesty
If the tax office refuses to write off debt, then there is a possibility that it refuses justifiably. However, the tax office may be wrong and its refusal will be illegal.
The taxpayer may apply to the court to declare the debt uncollectible.
There is judicial practice on claims from taxpayers when they ask to recognize as illegal the inaction of the tax service in not writing off the debt, the obligation of the tax service to write off.
To appeal the write-off refusal, the taxpayer should determine the requirements and file an administrative claim with the district court. Based on the results of the consideration of the claim, the court will make a decision.
ATTENTION : our lawyer on credit matters in Yekaterinburg and issues of writing off debts to microfinance organizations will help you: professionally, on favorable terms and on time. Call today!
How to take advantage of the tax amnesty
A tax amnesty was carried out by the Federal Tax Service. The tax service automatically selected citizens with debt from the database, wrote it off and made the necessary adjustments to the accounting documents. The participation of the taxpayer in it was not required.
Currently, the tax amnesty procedure is completely completed. Whether it will ever be repeated is unknown. There is no point in hoping for this in the foreseeable future. It is better to look for other options for getting rid of debt obligations.