Accounts receivable is a collection of funds that a certain company, firm, other legal entities and individuals receive for providing them with a certain type of service or shipping goods. That is, those persons who owe money to other legal entities or individuals are called debtors. Every legal entity has accounts receivable; without them it is impossible to conduct business. Accounts receivable are also considered an asset of the enterprise and are classified as current assets without a specific period during which they must be repaid.
Important!!! Enterprise assets are the totality of property that belongs to the enterprise. We can say that accounts receivable are also considered property, which after a certain time is transformed into cash.
Types of accounts receivable
Accounts receivable can be classified according to different criteria, for example:
- By timing;
- By type of debt.
Accounts receivable by maturity are further divided into their own categories, namely:
- Short-term receivables are debts that are planned to be repaid in no longer than a year;
- Long-term receivables are debts that will be repaid in more than a year.
Accounts receivable, when they arise, are always documented, and where the time interval for their repayment is indicated. Therefore, based on timely payment or late payment, we can distinguish the type of receivables for debts:
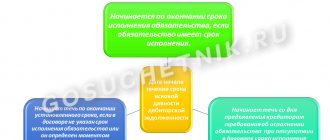
- Normal receivable – making payment for goods or services before the due date;
- Overdue receivable - the payment period is overdue, that is, the buyer received the product or service, but did not pay within the period specified in the contract.
In turn, overdue receivables can be classified into the following types:
- Doubtful - this is considered to be that receivable that may not be returned within the period specified in the contract, and the supplier has uncertainty about its return. But there is still hope that the counterparty will return it, despite the unstable financial condition;
- Impossible is a receivable that is considered practically impossible to recover. For example, in such cases when the debtor is declared bankrupt;
- Unclaimed is a receivable that for some reason was not claimed, for example due to an accountant’s mistake.
Collection of overdue debts
Collection of overdue receivables is possible within the limitation period. The limitation period is the period for protecting the right in a claim of a person whose right has been violated (Article 195 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). That is, this is the time during which an institution can claim receivables in court. The general limitation period is established by Article 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and is three years. For certain types of claims specified, for example, in Articles 725. 797. 966 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, special limitation periods may be established (reduced or longer than the general period).
In accordance with Article 200 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the limitation period begins from the day when the person learned or should have learned about the violation of his right. For obligations with a specific performance period, the limitation period begins upon the expiration of the performance period. If the contract did not provide for a deadline for its execution and did not contain conditions allowing for this period to be established, then the counterparty had to fulfill the obligation within a reasonable time after its occurrence (clause 2 of Article 314 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
If the amount of the overdue debt is not paid within a reasonable time, the debtor is obliged to repay the receivables seven days after the creditor submits a demand for fulfillment of obligations or within the period established for such a case by law. The same conditions apply to the collection of overdue debts, the repayment period of which is determined by the moment of demand.
The limitation period is interrupted in cases where the debtor commits actions indicating recognition of the debt, for example:
- partial payment of debt;
- contacting the creditor with a request to defer payment;
- signing a debt reconciliation act (Article 203 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Article 202 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation also lists the circumstances in which the limitation period may be suspended:
- the filing of a claim was prevented by an extraordinary and unavoidable circumstance under the given conditions (force majeure);
- the defendant was part of the RF Armed Forces, transferred to martial law;
- on the basis of the law, the Government of the Russian Federation established a deferment of fulfillment of obligations (moratorium);
- the operation of the law or other legal act regulating the relevant relations was suspended.
Moreover, the running of the limitation period is suspended if such circumstances arose or continued to exist in the last six months of the limitation period (or simply in the last six months, if the limitation period itself does not exceed this period). As soon as such circumstances disappear, the limitation period resumes. The remainder of the period is extended to six months, and if the limitation period does not exceed six months, to the statute of limitations.
When do accounts receivable arise?
In the process of economic activity, accounts receivable always arise. And so receivables arise in such cases as:
- The enterprise sold a product or provided a service, but did not receive timely payment for this product or service, and thereby incurred a debt;
- Settlement with accountable persons. For example, an employee went on a business trip and was given money. Sometimes it happens that the employee was paid more wages than he should have;
- Advance payment for the purchased product or service received. For example, an enterprise decided to buy products, transferred funds to the current account, but the goods have not yet arrived; delivery will be later than payment. As for the provision of services, here, for example, an enterprise pays a subscription fee for a year for advertising on the Internet and in a newspaper;
- When settling with the budget, paying taxes and fees;
- In other cases, when a receivable arises, a shortage may be identified at the enterprise and the culprit must repay it, and the amount of the debt will be considered a receivable.
Grounds for writing off remote control
The legislation stipulates the following cases in which remote control may be considered hopeless:
- upon the occurrence of an event beyond the control of the parties, which makes the fulfillment of the obligation unrealistic (Article 416 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- in accordance with the decision of the state body, confirmed by the act (Article 417 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- upon the death of the debtor (Article 418 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- upon liquidation of a counterparty (Article 419 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- when the limitation period has passed (Chapter 12 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Events beyond the control of the parties can be emergencies, disasters, military actions, and natural disasters.
An act of a government body, in accordance with which debt can be written off, is, for example, a court decision that the debt cannot be collected. If an organization sues its debtor and the court orders him to repay the debt, then the writ of execution issued in court is forwarded to the bailiffs. From this moment, collection is carried out in accordance with the Law “On Enforcement Proceedings” dated October 2, 2007 No. 229-FZ. If the bailiff service, having carried out all the required actions, has made a decision that it is impossible to collect the debt, a corresponding decree is issued to terminate enforcement proceedings. The reason specified in the decision may be:
- liquidation of the organization;
- impossibility of determining the actual location of the counterparty;
- lack of property and funds from the debtor.
The death of the debtor is the reason for recognizing the debt as bad if the obligation can be repaid only with his participation or is directly related to his person.
The BU can obtain data on the liquidation of a legal entity from an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. Such information is available on the website of the Federal Tax Service or in person. There you can also check the reliability of the counterparty before making any transactions with him: find out the status of the organization, check whether the counterparty’s registered address is not a mass one, whether it submits reports to the tax authorities, etc.
According to general rules, the limitation period is 3 years, but in some cases, in accordance with the law, it may be different. The beginning of the limitation period under the contract is the first day of delay in fulfilling the obligation. If the debtor carries out any actions indicating recognition of the debt, then the limitation period begins to count anew from the day such actions were committed. So, the debtor can sign a reconciliation report, issue a letter of guarantee, transfer some part of the debt, etc.
The debt is considered unrealistic for collection based on the decision of the special commission on the receipt and disposal of assets (clause 339 of the instructions to the unified chart of accounts, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n). The composition of the commission is established by order of the head of the institution. A special provision may also be created to regulate the activities of the commission.
When there is a need to issue an order to write off accounts receivable
The debts of debtors after the expiration of the statute of limitations on a formalized lawsuit and for a number of other reasons can be considered uncollectible. To remove such failed income from the balance sheet, it is necessary to issue an order to write off receivables. The sample order is drawn up according to the internal rules of document flow.
The write-off of accounts receivable must be justified. Justifications include:
- The deadline for collecting the debt through the court has expired;
- The debtor company has been liquidated;
- Impossibility of debt collection by the Bailiff Service;
- Forgiving a debt to a debtor.
If, as a result of the inventory, a debt is identified, the collection of which from the counterparty on the above grounds is impossible, an order is issued to write it off.
Writing off bad debts
Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation defines a bad debt of a debtor. Above we gave a description - the counterparty is bankrupt, therefore, the loan is considered impossible to return and is designated as hopeless.
Such debt is written off under the following circumstances:
- The debtor has been liquidated. The property is not sufficient to repay all debt amounts.
- Bankruptcy of the defaulter.
- Cases in which the statute of limitations has expired. The statute of limitations is considered to have expired when 3 or more years have passed since the last repayment of the debt.
Only overdue debts will be written off.
The procedure for drawing up an order to write off receivables
An order to write off expired accounts receivable does not have a special form that must be used without fail. Therefore, enterprises either use a company letterhead or develop their own order form.
Let's consider in the form of a table how to correctly fill out an order to write off receivables:
| Name | Content |
| Order cap | Full name of the enterprise; Last name, first name and patronymic of the manager; Date and number of the order to write off receivables. |
| Text part | The name of the debtor's enterprise or last name, first name, patronymic if it is an individual is written down; The amount of accounts receivable, which, based on the results of the inventory, is considered unrealistic to be collected; Documents that are the basis for debt write-off; How will the write-off be carried out? If a reserve for doubtful debts has been formed, then the write-off must be made from the reserve. If the company does not have such a fund, then the amount of debt should be included in other expenses. |
What is the purpose of creating a document?
The main reason for writing off a short circuit will be the expiration of the shelf life. But it is not the only one. These may be objective reasons that prevent the debtor from fulfilling his obligations in full. Similar situations arise if:
- The creditor is officially liquidated (then the write-off is carried out after the person is removed from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities).
- If the debtor is declared bankrupt.
- Write-off is carried out if the creditor releases the debtor from payments (for example, if the amount of money was provided to the organization by one of its founders).
- In the event of unforeseen circumstances for which neither party can be held responsible.
- In cases where the authorized state body draws up an act according to which the fulfillment of obligations by the debtor becomes impossible.
- Upon the death of the person who provided the loan.
The above circumstances are defined by law as the basis for writing off short circuits.
LLC "Caramel"
(name of company)
| Document Number | Date of preparation | |
| ORDER | 26 | 31.03.2022 |
on writing off accounts receivable
Based on the inventory report dated June 31, 2022 No. 5
I ORDER:
- Recognize as uncollectible due to documentary evidence of the liquidation of the counterparty and write off the receivables of Cosmos LLC in the amount of RUB 400,000. in accounting due to the previously formed reserve for doubtful debts, in tax accounting - due to non-operating expenses.
- The chief accountant Prikhodko I.M. should take into account the written-off debt on an off-balance sheet account, and reflect the write-off operation in accounting and reporting for the 2nd quarter of 2022.
| Head of the organization | CEO | Novikov | Novikov V.V. |
| (job title) | (personal signature) | (full name) |
Accounting for write-offs
A special feature of accounting for write-off of receivables in the accounting system is the reflection of the written off receivables behind the balance sheet, in account 04 “Debt of insolvent debtors”. Off-balance sheet accounts for accounting systems work the same way as for others, that is, receipts are reflected only by debit, and disposals - only by credit, without correspondence.
A posting to account 04 is made when the commission for writing off the debt is made accordingly. Amounts in account 04 are reflected for as long as the debt collection procedure may begin again or the insolvent debtor may have the means to repay the debt. The chart of accounts for organizations other than credit and government (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n), for example, provides a five-year period for monitoring the possibility of returning the debt.
The bailiff service may again begin collection actions, for example, if the plaintiff re-transferred to them a writ of execution issued by the court, which was already before the bailiffs, but for some reason the enforcement proceedings were completed. In the event of the resumption of the procedure for collecting or returning the debt by an insolvent debtor, the debt is written off from account 04 and reflected on the corresponding balance sheet accounts.
The final write-off of debt from an off-balance sheet account must be approved by the commission on the basis of legally established reasons: death of the debtor, liquidation of the organization, etc.
Analytics for account 04 is carried out in the context of the types of income/expenses for which the debt was taken into account, and the debtors, indicating all their data necessary to repay the debt. Below are the main transactions for reflecting the write-off of receivables. More typical entries can be found in the instructions for the chart of accounts for accounting of budgetary institutions, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 16, 2010 No. 174n.