Features of accounting for import transactions
Keep records of exports and imports using the simplified tax system in the Kontur.Accounting web service.
Currency accounting and work instructions, taxes, automatic payroll calculation and reporting in one service Get free access for 14 days Firstly , import transactions are carried out in foreign currency. For accounting purposes, it is important to correctly convert it into rubles. Conversion occurs at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, which changes daily, so exchange rate differences arise.
The difference can be positive or negative. A positive one is formed if you received income from a change in the exchange rate, a negative one - vice versa.
Secondly , taxation and customs duties. In addition to taxes in accounting, carry out operations to pay customs duties and fees, which are included in the cost of the purchased goods (clause 6 of PBU 5/01).
Thirdly , the formation of the cost of goods. In accordance with clause 6 of PBU 5/01, in addition to customs duties, fees and taxes, the cost of imported goods includes:
- directly the amount under the contract;
- amounts to third parties for consultations and services (for example, customs brokerage services);
- delivery costs;
- intermediary remuneration;
- and other costs.
You also encounter other operations on the domestic market - settle payments with a counterparty, pay value added tax, capitalize goods, refund VAT.
VAT and tax accounting for profits in foreign trade
The largest number of additional actions in terms of taxation will be necessary for the most complex tax, which in the Russian Federation is VAT. Special attention will be required here:
- export, which requires the organization of separate accounting of all operations on it, compliance with deadlines for collecting a package of necessary documents, identifying unconfirmed and late confirmed shipments, monitoring the completeness of payment for supplies by the counterparty, filling out additional sections of the declaration, regularly preparing large packages of documents for control by the Federal Tax Service;
- imports from countries outside the Customs Union;
ConsultantPlus experts spoke about the nuances of calculating VAT on imports from countries outside the EAEU. To properly organize accounting and determine the amount of VAT, get trial access to the system and go to the Ready-made solution. It's free.
- imports from the countries of the Customs Union, in which it is necessary to comply with fairly limited deadlines for submitting tax documents to the Federal Tax Service, paying it in conjunction with payment - submitting for deduction, drawing up an additional declaration;
- the obligation to pay tax when paying for a number of services (clause 1 of Article 148 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) provided outside the territory of the Russian Federation, and filling out a special section of the declaration for it;
- the presence of features of taxation of goods that arise in certain situations both during their export and import (Article 151 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
What you need to follow when organizing separate accounting for exports - read the material “How separate accounting for VAT is maintained (principles and methods)” .
With regard to income tax, one should not lose sight of the fact that export shipments are taken into account in income at the moment of transfer of ownership (risks) to the goods, i.e. practically at the time of shipment, and the right to deduct VAT on such shipment can be confirmed completely another tax period. That is, the tax bases for profit and VAT when exporting for the same period do not always coincide, and it is impossible for profit to take into account shipments for export in connection with the fact of confirming the right to deduct VAT.
Accounting entries for import transactions
Let's look at the basic accounting entries accompanying the import of goods using an example. Mister LLC purchased 10 refrigerator-freezers with a capacity of 350 liters on February 22, 2022. from a foreign partner at a price of $5,000. Simultaneously with the purchase, Mister LLC received ownership of the goods. The exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation as of February 22, 2019 is 65.54 rubles. We paid for the goods on 03/07/2019 at the rate of 64.50 rubles. Customs duty is 10,000 rubles.
The question arises - how to find out the customs duty rate? To do this, we find the code of the commodity nomenclature of foreign economic activity (HS code), which is suitable for our cargo. This code is 8418102001. For goods falling under this code, the import duty is 12%. Read about how to determine the Commodity Nomenclature for Foreign Economic Activity code in the articles “Handbook of Commodity Nomenclature for Foreign Economic Activity” and “Code of Commodity Nomenclature for Foreign Economic Activity”.
To complicate matters, we add that the customs clearance was handled by a customs broker. His services cost 35,000 rubles.
Keep records of exports and imports using the simplified tax system in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Currency accounting and work instructions, taxes, automatic salary calculation and reporting in one service Get free access for 14 days
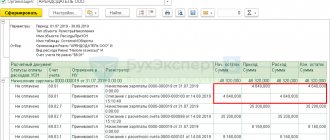
As a result, we generate the following postings. Confirm all transactions with documents.
| Dt | CT | Sum | Description |
| 08 | 60 | 5000*65.54 = 327,700 rub. | Imported refrigerators were capitalized |
| 19 | 68 | 5000*65.54*1.12*0.20 = 73,404.8 rubles. (customs duty is included in the price when calculating VAT!) | Import VAT charged at 20% |
| 08 | 76 | 327,700*0.12 = 39,324 rubles. | Customs duty charged |
| 08 | 76 | 10,000 rub. | Customs duty charged |
| 08 | 60 | 35,000 rub. | Accrued costs for customs brokerage services |
| 60 | 52 | 5,000*64.50 = 322,500 rubles. | Payment was transferred to a foreign counterparty for refrigerators on 03/07/2019. |
| 60 | 91 | 5,000*(65.54-64.50) = 5,200 rub. | A positive exchange rate difference is reflected, because in rubles they paid an amount less than it was at the time the contract was concluded |
| 76 | 51 | 10,000+39,324 = 49,324 rubles. | Customs duties and fees have been paid |
| 60 | 51 | 35,000 rub. | Paid brokerage services |
| 68 | 51 | RUB 73,404.8 | Import VAT paid |
| 01 | 08 | 327,700+10,000 + 39,324 + 35,000 = 412,024 rubles. | Refrigerators are accepted for accounting as fixed assets |
| 68 | 19 | RUB 73,404.8 | Import VAT accepted for deduction |
Read more about VAT refunds on import transactions in our article.
Purchase of imported goods in 1C:KA 2.4
The example was prepared on the demo base of the company 1C release 2.4.12.102
The ability to account for imported goods is determined by the functional option Master data and administration – Setting up Master data and sections – Accounting for VAT and foreign trade activities – Registration and control of customs declaration numbers – Trade in imported goods.
Figure 1 — Configuring customs declaration registration
Purchasing for import without filing a customs declaration
If the supply of imported goods does not require declaration, then it is formalized as a regular supply with the document Purchase of goods and services with the transaction type Purchase from a supplier or Acceptance for commission, indicating the customs declaration numbers and countries of origin in the tabular part of the document. For example, the supplier delivered imported goods that have already passed customs clearance. All expenses associated with the delivery of such cargo are recorded as additional expenses, which can be distributed among the cost of goods, line of business, other expenses, etc.
Import purchase with customs declaration
The possibility of registering the supply of imported goods with a customs declaration is determined by the functional option Master data and administration – Setting up master data and sections – VAT and foreign trade accounting – Import – Import purchases.
Figure 2 — Setting up trade in imported goods
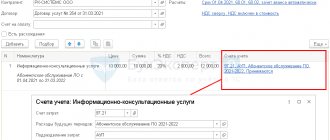
Suppose an organization purchases from an import supplier. To do this, the agreement with the importing supplier must indicate the type of operation Import
.
Figure 3 — Import agreement with supplier
All other parameters of the agreement are filled out in the same way as for the regular supply of goods. Mutual settlements with the supplier-importer can be carried out in the context of contracts or without contracts. A separate contract is drawn up with the supplier-importer for the purchase of imported goods with the established type of relationship: Import.
Figure 4 — Import agreement with supplier
To supply imported goods, use the document Purchase of goods and services with the established type of operation Import. The document is drawn up in the same way as a regular receipt document.
Figure 5 - Purchase of goods and services
It is worth noting that until the customs declaration is completed, imported goods cannot be sold. These goods will be available for sale only after a customs declaration has been registered for them. After completing the customs declaration, the goods will be assigned a CCD number (country of origin) and will become available for sale.
Registration of customs declaration
You can complete a customs declaration from the Customs declarations for imports for clearance workspace (section Purchasing – Customs declaration for clearance).
Figure 6 — Customs declarations for imports for clearance
And you can also create it based on the Purchase of goods and services document.
Figure 7 - Customs declarations for imports based on
When you execute the Create Declaration command, a Customs Declaration document will be created, which will contain a list of goods that have not passed customs clearance, as well as information about the delivery document.
It should be noted that if the Separate import purchases by receipts flag is checked, then when posting a document, the correctness of filling out information on delivery documents will be monitored.
When preparing a customs declaration for import, customs declaration numbers are generated without adding a section number and product number.
Figure 8 — Filling out the customs declaration number
On the Customs Declaration Sections tab, data is filled in; if you need to supplement the Customs Declaration number with the product line number or section number, then for this opportunity, on the Civil Customs Declaration Sections tab in the tabular part of the Declaration Goods, the Serial No. field is provided. By default, the field is not filled in and is not required.
Figure 9 - Filling out the Serial No.
The values entered in the Serial No. field are saved in the CCD Numbers directory in the Product Serial Number attribute. You should also fill out all the information on the rate and duty amount and distribute it to the goods.
In the customs declaration, it is necessary to additionally fill in information about customs duties and fines, enter data on the customs value, duty and VAT of each section, distribute goods into sections, enter the cost of each product and distribute the total customs value among sections.
Figure 10 - Filling out calculations
Next is the document Customs declaration for import
can be carried out in two statuses:
At customs clearance
and
Released from customs
:
- The status at customs clearance
is preliminary.
When making a customs declaration in this status, information about the planned payment (to customs or broker) is recorded in the payment calendar. The planned payment date, type of payment, current account or cash register are filled in on the Additional
; - The status Released from customs
is established after the final processing of the customs declaration. When posting a document, an actual debt arises to customs (broker). The status of goods specified in the customs declaration changes from preliminary to the status of goods available for sale.
When posting a document in the status Released from customs
The cost of the goods specified in the declaration is automatically adjusted taking into account the calculated customs duty and the amount of VAT. No additional cost calculation is required. And also the goods arrive at the warehouse and are ready for sales.
Common Mistakes
Keep records of exports and imports using the simplified tax system in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Currency accounting and work instructions, taxes, automatic salary calculation and reporting in one service Get free access for 14 days
Control over foreign economic activity by the state is stronger than over internal activities. Therefore, avoid mistakes when maintaining accounting records of import transactions. Check the following points:
- currency conversion - often accountants use the exchange rate on an incorrect date;
- translations of documents - import documents must be in two languages: Russian and the partner’s language, sometimes the partner sends documents only in his own language, then you need to prepare a translation;
- correspondence of accounts - an error typical for internal and external activities; it is eradicated with increasing experience of the accountant.
Import documentation
Keep records of exports and imports using the simplified tax system in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Currency accounting and work instructions, taxes, automatic salary calculation and reporting in one service Get free access for 14 days
To generate accounting entries, successfully pass customs authorities and receive a VAT refund, prepare the following documents:
- foreign trade contract with a foreign counterparty;
- invoice from the seller - invoice or invoice;
- transport documents;
- documents confirming cargo insurance;
- customs declaration for goods - after passing customs you will be given it with the stamp of the authority;
- receipts and payment orders confirming the fact of payment of duties, fees and taxes;
- technical documentation;
- acts of acceptance and transfer;
- licenses and certificates as required.
You can familiarize yourself with documents on foreign economic activity in the article “Documents for foreign economic activity.”
Accounting for import of services
Today, a fairly common situation is when an organization purchases goods, works and services from a foreign supplier.
With the acquisition of imported goods, the situation is more clear. When importing goods, the organization pays VAT at customs. The procedure for calculating and paying VAT is regulated by Chapter 29 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the Instruction on the Procedure for the Application of Value Added Tax by the customs authorities of the Russian Federation in relation to goods imported into the territory of the Russian Federation, approved by Order of the State Customs Committee of Russia dated 02/07/2001 No. 131.
Some difficulties usually arise when importing works and services.
Imported works and services are those works and services performed by foreign organizations. Moreover, unlike the import of goods, such work and services do not require customs clearance.
In order to understand whether the work (services) received are subject to value added tax, it is necessary to determine the place of sale of these works and services in accordance with Art. 148 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Guided by the provisions of this article of the Tax Code, the place of implementation of works and services is determined depending on the type of these works and services:
- at the place of activity of the performer,
- at the location of the property,
- at the place of provision of work, services,
- at the location of the buyer,
- at the location of the point of departure or destination.
If the place of sale of purchased works and services is recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation, then these works and services are subject to VAT, otherwise they are not.
Next, you need to find out whether this foreign organization is registered for tax purposes in the Russian Federation.
If not, then the Russian organization that purchases such work (services) acts as a tax agent and is obliged to calculate and withhold the amount of value added tax from the amount to be transferred to the foreign supplier (clause 1 of Article 24 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The responsibilities of tax agents are defined in clause 3 of Article 24 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The main responsibility of a tax agent is to correctly and timely calculate, withhold from taxpayer funds and transfer the amount of taxes to the budget.
According to clause 4 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, payment of VAT calculated by tax agents is made simultaneously with the transfer of funds to the supplier.
Federal Law No. 173-FZ of December 10, 2003 “On Currency Regulation and Currency Control” imposes on currency control agents, which are authorized banks reporting to the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, control over currency transactions, including the performance of duties as a tax agent when transferring funds to a foreign entity - the supplier of such works and services. Clause 4 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation directly indicates that the bank will not accept a payment order to pay for the services of a supplier without simultaneously submitting to the bank a payment order to pay VAT to the budget.
At the same time, it must be remembered that the organization must transfer VAT as a tax agent, i.e. in the payment order you must indicate the payer status “02 – tax agent”.
Guided by Articles 171, 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the amount of value added tax withheld and transferred to the budget by tax agents can be deducted subject to the following conditions:
- the tax agent is a VAT payer (clause 3 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
- works and services are purchased for production activities subject to VAT (clause 3 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
- the amount of VAT is withheld from the foreign supplier of works and services and transferred to the budget,
- purchased works and services are accepted for accounting (clause 1 of article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
It will be possible to accept VAT for deduction in the same tax period in which the actual transfer of tax to the budget was made (paragraph 2, paragraph 4, article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated July 15, 2009 No. 03-07-08/151, dated April 7 .2008 No. 03-07-08/84)
From 01.01.2009, in accordance with clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when calculating VAT, tax agents are required to draw up and register an invoice in the manner established by clauses 5, 6 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The invoice is drawn up in 2 copies, signed by the head and chief accountant of the organization acting as a tax agent.
The first copy of the invoice is registered in the sales book, the second - in the purchase book in order to accept VAT for deduction only after the right to a tax deduction arises, i.e. after paying VAT to the budget. (Rules for maintaining logs of received and issued invoices, purchase books and sales books when calculating value added tax, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 2, 2009 No. 914).
When purchasing imported works or services, you will simultaneously reflect in the Value Added Tax Declaration for the corresponding tax period:
- the amount of value added tax that you calculated and paid as a tax agent simultaneously with payment for the work, services received,
- the deduction amount reflected in section 3 on line 220.
You can find additional information on the topic in the Foreign Economic Activity section.
Author of the article
Ksenia Efimova
Head of the foreign trade department, extensive experience as a logistician, conducting foreign economic activities of the company.
Articles written
100
about the author
Free consultation by phone:
Moscow and region (call is free)
Saint Petersburg
Attention! Due to recent changes in legislation, the legal information in this article may be out of date!
Our specialist will advise you free of charge.