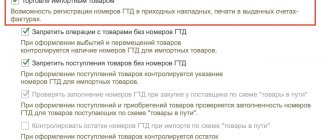
Importing products or receiving services from foreign contractors are mandatory transactions subject to VAT. The status of the Russian taxpayer is not important in this case - these are legal entities operating under the OSN, economic entities exempt from VAT, and “simplified” enterprises applying special tax regimes.
Goods/services received from abroad are subject to VAT if the following conditions are met:
- they will be resold exclusively within Russian territory;
- the foreign counterparty-supplier is not a tax resident and is not registered with the regulatory authorities of the Russian Federation.
VAT is not charged only on certain characteristic groups of commercial products:
- products received under a foreign trade agreement as gratuitous assistance;
- special-tech equipment not created by domestic companies;
- printed publications and cultural rarities for museums, libraries, archives;
- specific modifications of drugs.
VAT rates for the import of goods and services
For taxation of goods or services imported from abroad, standard tax rates are applied - 0%, 10%, 18%. To correctly use the required percentage during customs clearance and VAT calculations, follow the proposed algorithm:
- identify the product code according to the Unified Customs Tariff of the Customs Union ;
- compare the code with the lists of goods taken into account at a 10% rate ;
- in the absence of the required code in the specified lists approved by the Government of the Russian Federation, a rate of 18% .
The specificity of the calculation and payment of “import” VAT is the fact that the required calculations must be made before the item of trade leaves the customs post. Payment of VAT is made directly to the customs authority, as part of the mandatory payments for clearance.
The importer independently determines the tax base, product code and the amount of VAT required to be paid. If a problematic situation arises when customs applies a higher tax rate than the one calculated by the declarant, the importer can appeal to a higher customs authority.
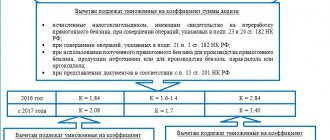
The importer is given 15 days from the date the cargo crossed the Russian border to pay VAT when drawing up a customs declaration. Each day of delay in remitting tax will “cost” the buyer 1/300 of the key rate, multiplied by the full value of the cargo according to the declaration.
VAT on imports from EAEU countries
In case of mutual trade with the former union states, VAT on imported goods or services is calculated according to an elementary scheme, and the payment of the budget fee is made to the treasury account of the territorial tax inspectorate.
The object for VAT taxation in the case of imports from the EAEU powers is determined as the cost of the purchased commodity mass, increased by the amount of excise duty (if necessary). The moment of formation of the tax base is determined by the calendar date when the imported goods are recorded in warehouse accounting. The amount of VAT is determined by simply multiplying the cost of purchased commodity products and the required tax tariff.
At the close of the quarter in which import transactions involving the movement of goods from the EAEU were carried out, the Russian importing company (IP) is obliged to submit a VAT declaration to the fiscal authority. The document must be submitted by the 20th day (inclusive) of the month following the reporting period.
Important: the “import” VAT declaration is submitted in the form of a “paper” document. Electronic reporting is used only by those taxpayers whose staff exceeds 100 people.
Simultaneously with submitting the VAT return, the importer is obliged to pay tax according to the banking parameters of “his” tax department. The payment order applies a separate BCC for VAT when importing from neighboring countries.
Documents for importing goods from Belarus
For imported goods from the EAEU, fill out a declaration on indirect taxes in the form approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated September 27, 2017 No. SA-7-3 / [email protected] It includes VAT and excise taxes. If you are importing excise-free goods, enter data only on the title page and in the first section. Fill out the declaration for the month in which the imported goods are recorded.
Submit the declaration to the tax office at the place of registration before the 20th day following the month the goods were registered, and submit along with it:
- A bank statement confirming payment of VAT, or a copy of the payment order with a bank mark.
- Supply agreement with a Belarusian supplier, intermediary agreement.
- Transport and accompanying documents.
- Invoices or other documents confirming costs.
- Application for import of goods and payment of indirect taxes.
Draw up an application for the import of goods in the form approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated November 19, 2014 No. ММВ-7-6 / [email protected] You must submit an application on paper in 4 copies and one in electronic form to the tax office, and one in electronic form, or only an electronic application certified EP.
Fill out the first section of the application and indicate your data and the supplier’s data, information about the contract and the cost of the imported goods. If you worked through an intermediary, complete the third section as well. The second section will be filled out by the tax authorities and a mark indicating the payment of VAT will be placed there.
Tax inspectors review the application within 10 working days. The tax office will keep one copy for itself, you will take one and send two to the Belarusian supplier so that he can confirm the 0% VAT rate on exports.
VAT on imports from countries outside the EAEU
When importing goods/services into Russian territory from countries outside the Eurasian Union, the importer is required to pay not only mandatory duties, but also VAT at customs. The procedure for calculating and paying taxes is regulated not only by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but also by the Customs Code.
Keep in mind: VAT at customs is paid not at the end of the reporting period, but before the completion of the procedure for releasing the goods from the customs post.
The formula by which the importer calculates the amount of VAT payable is as follows:
VAT = (TSt + VTP + A) x St
where: Tst – the value of the goods indicated in the customs declaration; ICT – the amount of import customs duty; A – excise tax (if necessary); St – VAT rate (%, 10%, 18%).
You need to know: if the imported goods are not subject to customs duties and excise taxes, then the amount of VAT is determined by multiplying the customs value by the desired tax rate.
To avoid conflicts with the customs service due to incorrect calculation of tax, it is advisable for the importer to calculate VAT separately for each group of goods.
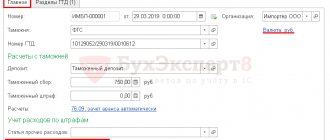
Accounting entries for import transactions
Let's look at the basic accounting entries accompanying the import of goods using an example. Mister LLC purchased 10 refrigerator-freezers with a capacity of 350 liters on February 22, 2022. from a foreign partner at a price of $5,000. Simultaneously with the purchase, Mister LLC received ownership of the goods. The exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation as of February 22, 2019 is 65.54 rubles. We paid for the goods on 03/07/2019 at the rate of 64.50 rubles. Customs duty is 10,000 rubles.
The question arises - how to find out the customs duty rate? To do this, we find the code of the commodity nomenclature of foreign economic activity (HS code), which is suitable for our cargo. This code is 8418102001. For goods falling under this code, the import duty is 12%. Read about how to determine the Commodity Nomenclature for Foreign Economic Activity code in the articles “Handbook of Commodity Nomenclature for Foreign Economic Activity” and “Code of Commodity Nomenclature for Foreign Economic Activity”.
To complicate matters, we add that the customs clearance was handled by a customs broker. His services cost 35,000 rubles.
Keep records of exports and imports using the simplified tax system in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Currency accounting and work instructions, taxes, automatic salary calculation and reporting in one service Get free access for 14 days
As a result, we generate the following postings. Confirm all transactions with documents.
| Dt | CT | Sum | Description |
| 08 | 60 | 5000*65.54 = 327,700 rub. | Imported refrigerators were capitalized |
| 19 | 68 | 5000*65.54*1.12*0.20 = 73,404.8 rubles. (customs duty is included in the price when calculating VAT!) | Import VAT charged at 20% |
| 08 | 76 | 327,700*0.12 = 39,324 rubles. | Customs duty charged |
| 08 | 76 | 10,000 rub. | Customs duty charged |
| 08 | 60 | 35,000 rub. | Accrued costs for customs brokerage services |
| 60 | 52 | 5,000*64.50 = 322,500 rubles. | Payment was transferred to a foreign counterparty for refrigerators on 03/07/2019. |
| 60 | 91 | 5,000*(65.54-64.50) = 5,200 rub. | A positive exchange rate difference is reflected, because in rubles they paid an amount less than it was at the time the contract was concluded |
| 76 | 51 | 10,000+39,324 = 49,324 rubles. | Customs duties and fees have been paid |
| 60 | 51 | 35,000 rub. | Paid brokerage services |
| 68 | 51 | RUB 73,404.8 | Import VAT paid |
| 01 | 08 | 327,700+10,000 + 39,324 + 35,000 = 412,024 rubles. | Refrigerators are accepted for accounting as fixed assets |
| 68 | 19 | RUB 73,404.8 | Import VAT accepted for deduction |
Read more about VAT refunds on import transactions in our article.
VAT on import of services
Receiving services from a foreign counterparty does not require documentation at the customs post. A legal entity or individual acting as a buyer is a tax agent and must withhold the amount of VAT from the supplier and transfer it to the federal budget.
The documentary basis for payment is a contract, in which it is necessary to state the condition that the amount of VAT is included in the total cost of the service provided. If there is no such clause in the contract, then the importer will be required to pay VAT in excess of the contract amount, at his own expense.
If the work and services performed by the foreign partner are subject to Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and are not subject to VAT, the importer is relieved of the duties of a tax agent - he must neither calculate nor transfer tax to the budget. However, he retains the obligation to submit a VAT return with completed section 7 to the tax authority at the place of his registration.
Example of reflecting the VAT amount
In August, Alpha and Omega LLC imported goods from the Republic of Kazakhstan to the Russian Federation for further resale. The cost under the supply agreement is 500,000 rubles. The amount of VAT that Alpha and Omega LLC paid to the Russian budget was:
500,000 rub. * 18% = 90,000 rub.
In the accounting of Alpha and Omega LLC, transactions are reflected in the following entries:
| Operation | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. |
| the cost of the goods is reflected | 41 | 60 | 500000 |
| payment for goods has been made | 60 | 51 | 500000 |
| VAT payable has been calculated | 19 | 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” | 90000 |
| VAT paid | 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” | 51 | 90000 |
Right to tax deduction for VAT
According to the generally established rule, taxpayers who have paid VAT at the customs post have the opportunity to declare a deduction in the declaration for the amount of tax paid. The provision of a deduction is guaranteed if the following criteria are met:
- imported goods will be used on Russian territory in transactions subject to VAT;
- imported products will be resold in the future;
- a tax deduction can be claimed by a Russian company only in the quarter when the goods are registered;
- receipt of imported goods is confirmed by an invoice, contract or customs declaration;
- payment of VAT is certified by primary documents received at customs.
If the importer is a business entity exempt from VAT or operating under a special regime, then the tax deduction is not applied. The VAT paid at customs will be taken into account in the nominal price of the goods upon receipt and subsequent sale.
Information about received imported goods/services is subject to entry into the purchase book indicating the amount of VAT. The prerequisite for registering the fact of purchase is payment of tax and an import statement certified by the tax authority.
Documents to confirm the right to deduct VAT
The initial documents allowing the importer to claim VAT deduction are:
- foreign trade contract with a foreign supplier;
- invoice for payment from the supplier (invoice);
- customs declaration - customs declaration (copy);
- bank statements, certified duplicates of payment orders.
All documents justifying the application for a VAT tax deduction when importing goods should be kept for at least four years.
Tax deduction for prepayment
In most cases, for foreign trade deliveries, prepayment is practiced. When transferring an advance payment for the upcoming receipt of goods, the buyer pays VAT on the advance payment amount.
In order to avoid duplicate taxation, VAT on advances made can be declared as a tax deduction during customs clearance of goods delivery and payment of the final amount of VAT.
Many Russian companies prefer not to deal with customs clearance of imported goods themselves, but delegate this procedure to intermediaries. If VAT at customs was paid by a third party, but at the expense of the importer and on his behalf, then the amount paid can be recorded as a tax deduction.
Documents for customs clearance
List of documents for customs clearance:
- passports of the director and chief accountant;
- constituent documentation, as well as documents on the organization;
- balance sheet of the foreign trade entity for the last reporting period;
- company charter;
- order on the appointment of a chief accountant;
- memorandum of association + amendments;
- decision of the meeting on the appointment of a director;
- tax registration certificate;
- certificates from banks.
For a list of additional documents, see the link.
We recommend watching the video: the procedure for registering customs duties on goods imported from the EAEU countries.